当前位置:网站首页>Mysql database index
Mysql database index
2022-07-06 12:41:00 【wake__ up】
1. The concept of index
Database index
The concept of index
● An index is a sorted list , In this list are stored the value of the index and the physical address of the row containing the data of this value ( Be similar to C The linked list of language points to the memory address of data record through pointer ).
● After using the index, it can not be used 1 Trace the whole table to locate the data of a row , Instead, we first find the corresponding physical address of the row data through the index table, and then access the corresponding data , Therefore, it can speed up the query speed of the database .
● An index is like a catalogue of a book , You can quickly find the required content according to the page number in the table of contents .
● Index is a way to sort the values of one or more columns in a table .
● The purpose of indexing is to speed up the search or sorting of records in a table .
2. The function of index
● After setting the appropriate index , The database uses a variety of fast positioning technologies , Can greatly speed up the query speed , This is the main reason to create indexes .
● When the table is large or the query involves multiple tables , Using indexes can improve query speed thousands of times .
● It can reduce the cost of the database I0 cost , And the index can also reduce the sorting cost of the database .
● By creating a unique index , It can ensure the uniqueness of each row of data in the data table .
● You can speed up the connection between tables .
● When using grouping and sorting , Can greatly reduce the grouping and sorting time .
● Indexing can significantly improve performance when searching and recovering data in a database
Side effects of indexing :
● Index takes up extra disk space .
about MyISAM In terms of engines , Index files and data files are separate , The address where the index file is used to hold the data record .
and InnoDB The table data file of the engine itself is the index file .
● It takes more time to insert and modify data , Because the index has to change with it .
3. The principle of index creation is based on
Although index can improve the speed of database query , But it's not always appropriate to create an index . Because the index itself consumes system resources , With an index , The database will perform index query first , Then navigate to the specific data row , If the index is not used properly , On the contrary, it will increase the burden of the database .
● Primary Key 、 Foreign key must have index . Because the primary key is unique , The foreign key is associated with the primary key of the primary table , You can quickly locate when querying .
● Number of records exceeds 300 The table of rows should have an index . If there is no index , Every query needs to traverse the table , Will seriously affect the performance of the database .
● A table that is often connected to other tables , Index should be established on the connection field .
● Fields with poor uniqueness are not suitable for indexing .
● Fields that are updated too frequently are not suitable for creating indexes .
● It often appears in where Fields in clause , In particular, the fields of large tables , It should be indexed .
● On a regular basis GROUP BY、ORDER BY Index the fields of ;
● Indexes should be built on fields with high selectivity .
● Indexes should be built on small fields , For large text fields or even extra long fields , Don't index .
4. Classification and creation of index
create table member (id int (10) , name varchar (10) , cardid int (18) , phone int (11) , address varchar (50) , remark text) ;
(1) General index : The most basic index type , There's no such thing as uniqueness .
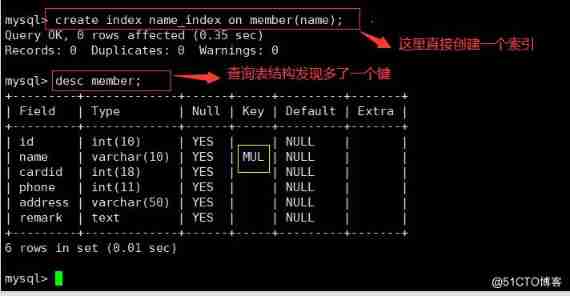
● Create index directly
CREATE INDEX Index name ON Table name ( Column name [ (length)]);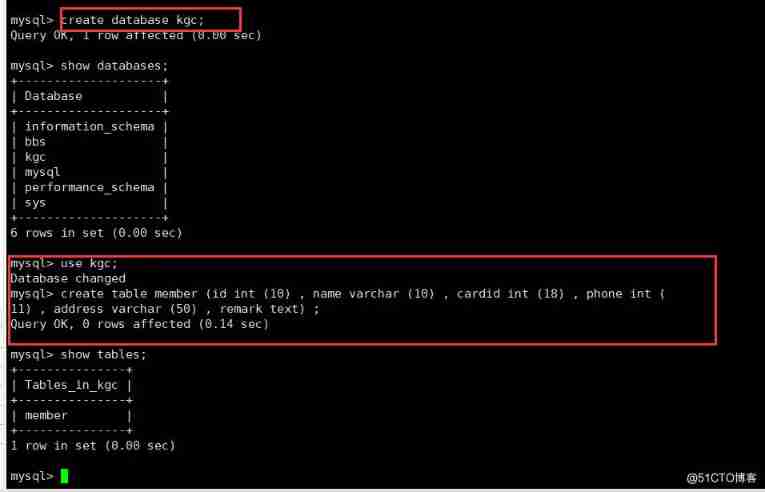
( Name (length)): length Optional. , The same below . If you ignore length Value , Then use the value of the entire column as the index . If specified , Use the front of the column length Characters to create the index , This helps to reduce the size of the index file . Without losing accuracy , The shorter the length, the better .
The index name is suggested to be “ _index" ending .
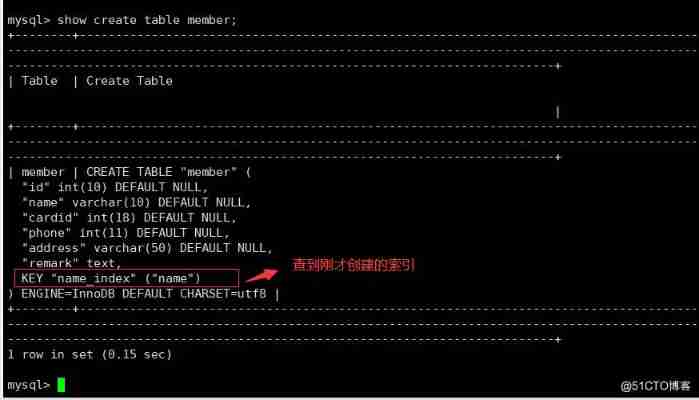
create index name_ index on member (name) ;
● Modify tables to create
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD INDEX Index name ( Name );
● Specify index when creating table
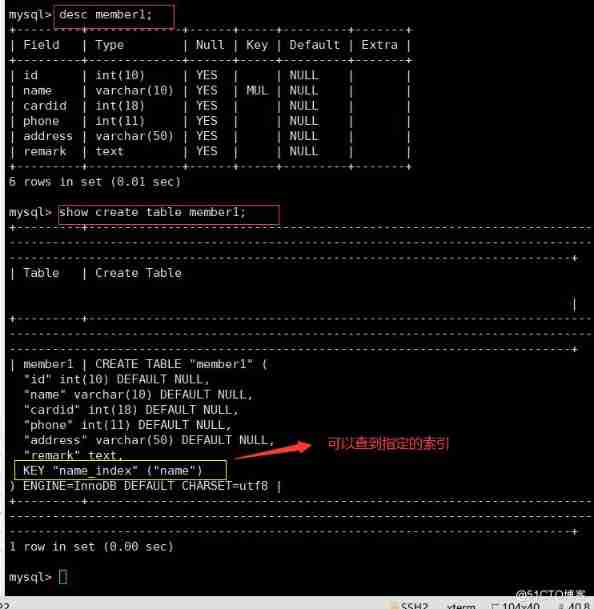
CREATE TABLE Table name ( Field 1 data type , Field 2 data type [,…], INDEX Index name ( Name ));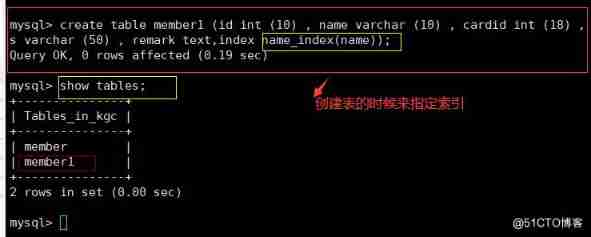
(2) unique index : Similar to a normal index , But the difference is that each value of a unique index column is unique . Null values are allowed for unique indexes ( Note that it's different from the primary key ). If it's a composite index , The combination of column values must be unique . Adding a unique key automatically creates a unique index .
● Create a unique index directly :
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX Index name ON Table name ( Name );
create unique index cardid_ index on member (cardid) ;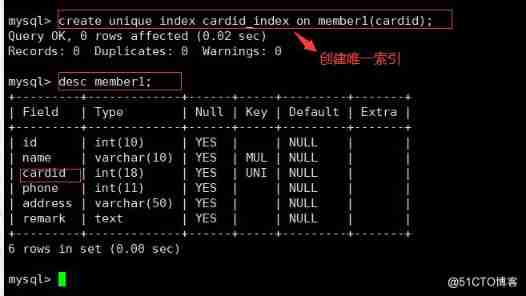
● Modify tables to create
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD UNIQUE Index name ( Name );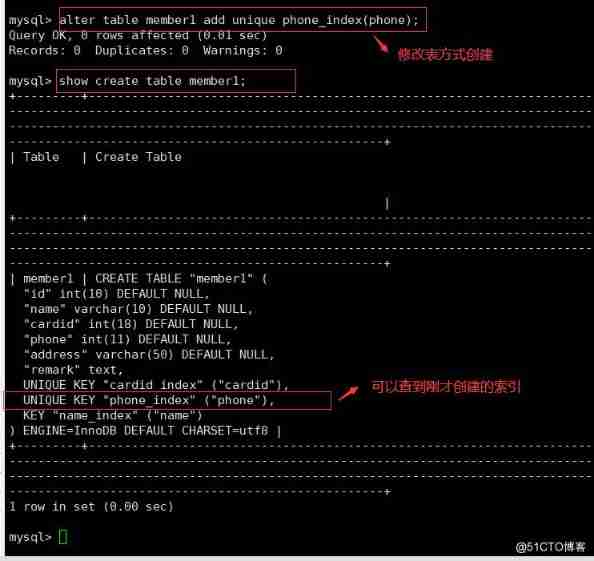
● When creating a table, specify
CREATE TABLE Table name ( Field 1 data type , Field 2 data type [,…], UNIQUE Index name ( Name ));
(3) primary key : Is a special unique index , Must be specified as “PRIMARY KEY”. A table can only have one primary key , No null values are allowed .
Adding a primary key will automatically create a primary key index .
● When creating a table, specify
CREATE TABLE Table name ([…], PRIMARY KEY ( Name ));
● Modify tables to create
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD PRIMARY KEY ( Name ) ;
alter table member add primary key (id) ;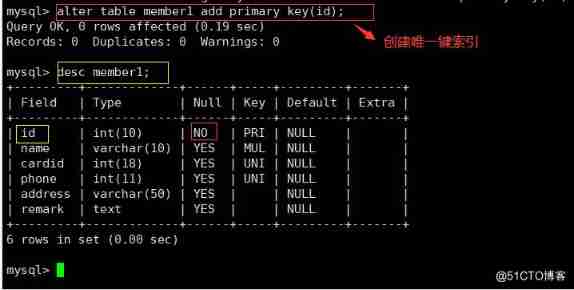
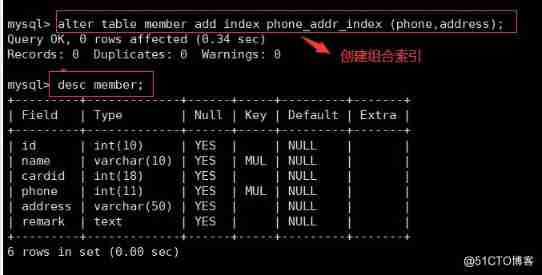
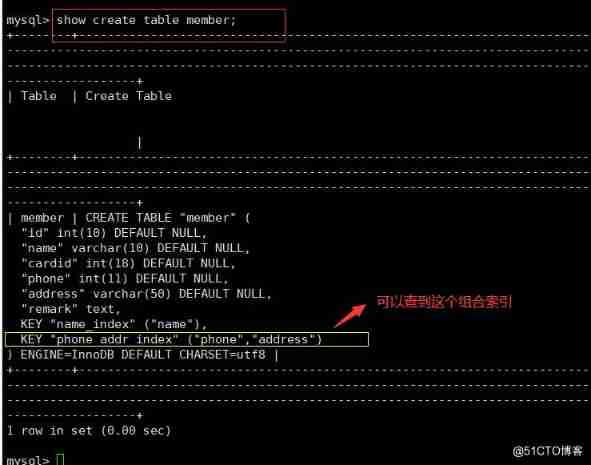
(4) Composite index ( Single column index and multi column index ) : It can be an index created on a single column , It can also be indexes created on multiple columns . We need to meet the leftmost principle , because select Of the statement where The conditions are executed from left to right in turn , So it's using select Statement query where The order of the fields used by the condition must be the same as the sort in the composite index , Otherwise the index will not take effect .
CREATE TABLE Table name ( Name 1 data type , Name 2 data type , Name 3 data type , INDEX Index name ( Name 1, Name 2, Name 3));
select * from Table name where Name 1=‘…’ AND Name 2=‘…’ AND Name 3=’ …';
(5) Full-text index (FULLTEXT) : It is suitable for fuzzy query , Can be used to retrieve text information in an article . stay MySQL5.6 Version before FULLTEXT The index can only be used for MyISAM engine , stay 5.6 After the version innodb The engine also supports FULLTEXT Indexes . Full text indexing can be done in CHAR、 VARCHAR perhaps TEXT Create on column of type . Only one full-text index per table is allowed .
● Create index directly
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX Index name ON Table name ( Name );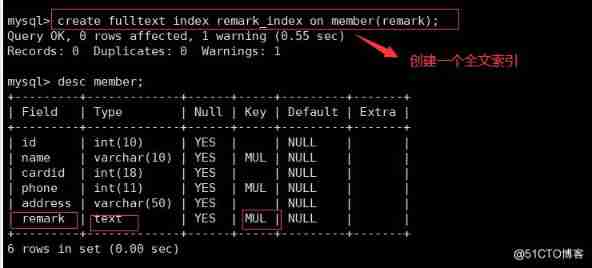
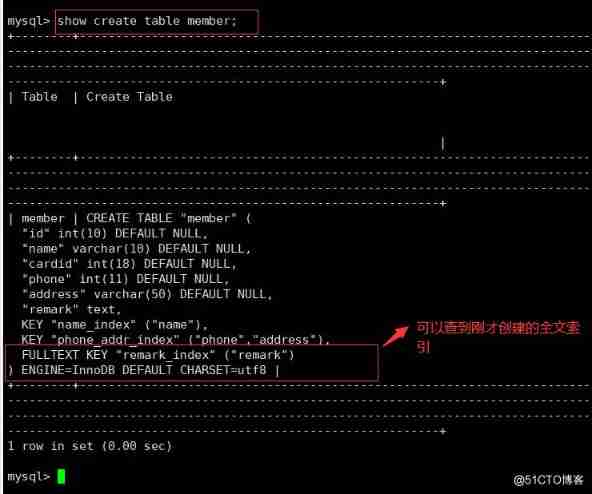
● Modify tables to create
ALTER TABLE Table name ADD FULLTEXT Index name ( Name );
alter table member add fulltext remark_ index (remark) ;
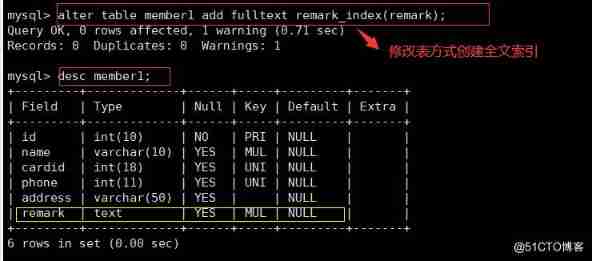
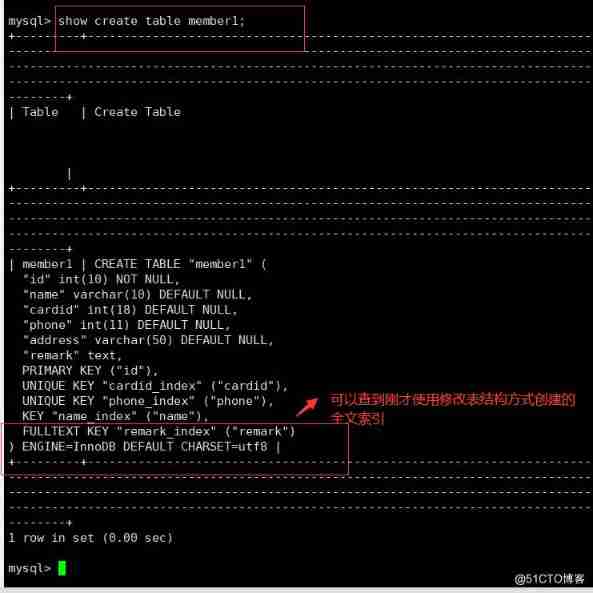
● Specify index when creating table
CREATE TABLE Table name ( Field 1 data type [,…], FULLTEXT Index name ( Name ));
# The data type can be CHAR、VARCHAR perhaps TEXT
● Use full text index queries
SELECT * FROM Table name WHERE MATCH( Column name ) AGAINST(‘ Query content ’) ;
insert into member values (1, zhangsan, 123123, 123123, ‘nanjing’, ‘this is member!’) ;
insert into member values(2, ‘lisi’ , 456456, 456456, ‘beijing’, ‘this is vip!’) ;
insert into member values (3, ‘wangwu’, 789789, 78979, ’ shanghai’, ‘this is vip member!’) ;
select * from member where match (remark) against(‘vip’) ;
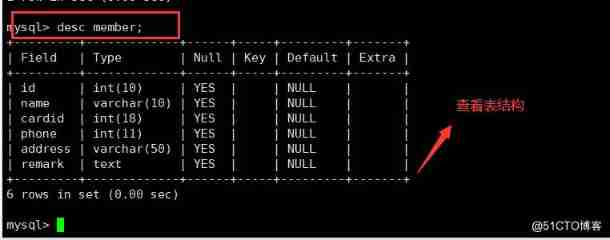
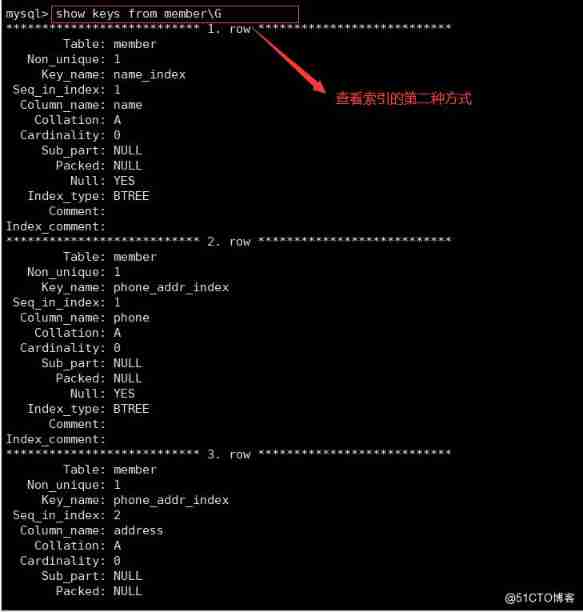
5. Look at the index
show index from Table name ;
show keys from Table name ;
The meaning of each field is as follows :
Table: The name of the table .
Non unique: If the index can't include repetition , Then for 0; If possible , Then for 1.
Key_ name: Name of index .
Seq_ in_ index: Column ordinal in index , from 1 Start .
Column_ name: Column name .
Collation: How columns are stored in indexes . stay MySQL in , Valuable ’A’ ( Ascending ) or NULL ( No classification ).
Cardinality: An estimate of the number of unique values in an index .
Sub_ part: If the column is only partially indexed , Is the number of characters indexed . If the entire column is indexed , Then for NULL.
Packed: Indicates how keywords are compressed . If it's not compressed , Then for NULL.
Null: If the column contains NULL, It contains YES. without , The column contains NO.
Index type: Used indexing methods ( BTREE,FULLTEXT, HASH, RTREE) .
Comment: remarks .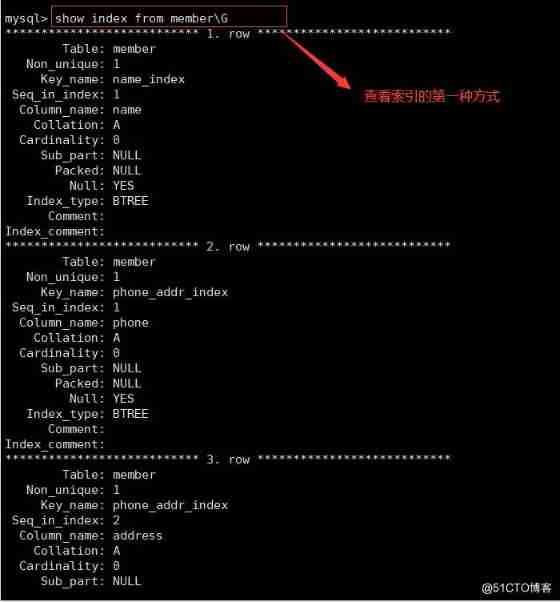
6. Delete index
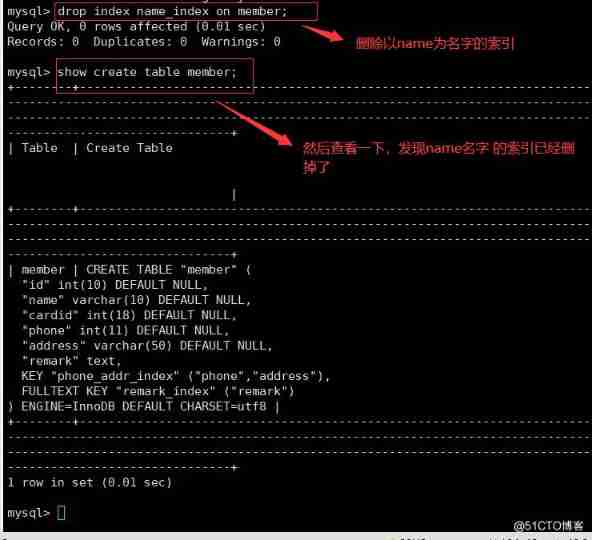
● Delete index directly
DROP INDEX Index name ON Table name ;
● Modify the table to delete the index
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP INDEX Index name ;
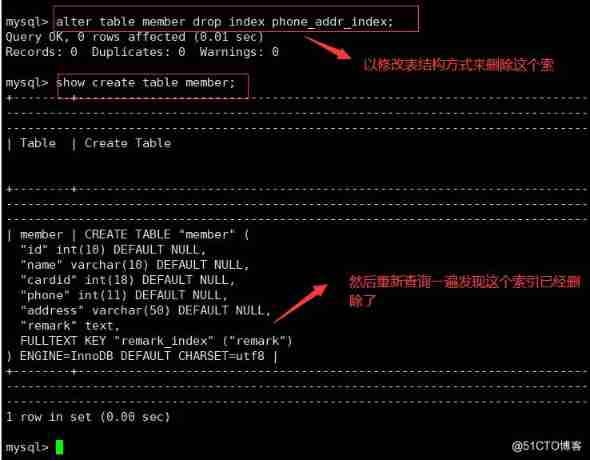
● Delete primary key index
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP PRIMARY KEY;
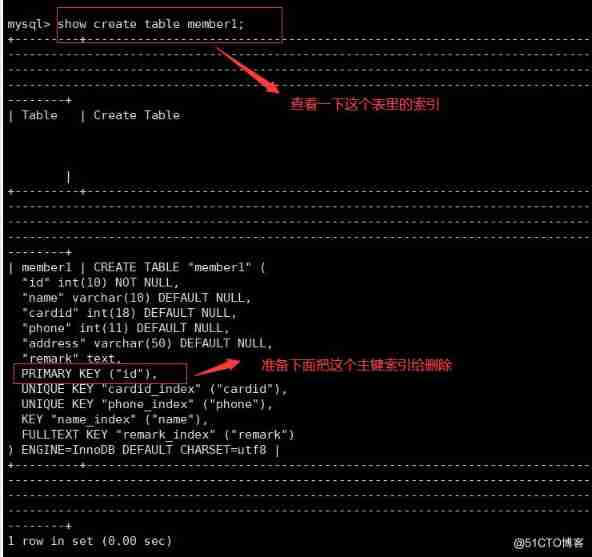
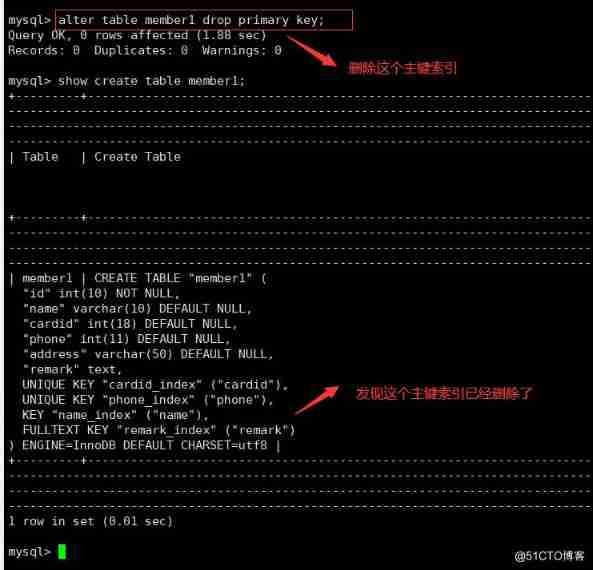
Case study : For example, a membership card system for a shopping mall . This system has a membership table , There are the following fields :
Membership number INT
Membership name VARCHAR(10)
Membership ID number INT (18)
Membership telephone INT(11)
Member Address VARCHAR (50)
Member notes TEXT
create table member (id int (10) , name varchar (10),cardid varchar (10) , phone int (11) , address varchar (50) , remark text) ;
alter table member add primary key (id) ;
create index name_ index on member (name) ;
create unique index cardid index on member (cardid) ;
alter table member add fulltext remark_ index (remark) ;
Then the member number , A primary key , Use PRIMARY KEY
Membership name , If you want to index , So it's normal INDEX
Membership ID number , If you want to index , Then you can choose UNIQUE ( Unique , No repetition )
Member notes , If you need to index , You can choose FULLTEXT, Full text search .
however FULLTEXT When searching for a long article , The best effect . Used for shorter text , If it's just a line or two , ordinary INDEX It's fine too .
边栏推荐
- Basic operations of databases and tables ----- creating data tables
- Expected value (EV)
- Esp8266 uses Arduino to connect Alibaba cloud Internet of things
- FairyGUI人物状态弹窗
- Teach you to release a DeNO module hand in hand
- 2021.11.10 compilation examination
- Working principle of genius telephone watch Z3
- Unity3D,阿里云服务器,平台配置
- [leetcode19]删除链表中倒数第n个结点
- [offer78] merge multiple ordered linked lists
猜你喜欢
Compilation principle: preprocessing of source program and design and implementation of lexical analysis program (including code)
基于Redis的分布式ID生成器

Symbolic representation of functions in deep learning papers
Unity场景跳转及退出
Pat 1097 duplication on a linked list (25 points)
Page performance optimization of video scene
MySQL占用内存过大解决方案
Design and implementation of general interface open platform - (39) simple and crude implementation of API services
ESP8266连接onenet(旧版MQTT方式)
Programming homework: educational administration management system (C language)
随机推荐
JUC forkjoin and completable future
Redis cache update strategy, cache penetration, avalanche, breakdown problems
Expected value (EV)
Office提示您的许可证不是正版弹框解决
Single chip Bluetooth wireless burning
关于Gateway中使用@Controller的问题
(四)R语言的数据可视化——矩阵图、柱状图、饼图、散点图与线性回归、带状图
ES6 grammar summary -- Part 2 (advanced part es6~es11)
SVN更新后不出现红色感叹号
(三)R语言的生物信息学入门——Function, data.frame, 简单DNA读取与分析
数据库课程设计:高校教务管理系统(含代码)
FairyGUI复选框与进度条的组合使用
[Leetcode15]三数之和
Arduino gets the length of the array
Guided package method in idea
JS数组常用方法的分类、理解和运用
Unity3d makes the registration login interface and realizes the scene jump
[Offer29] 排序的循环链表
[Clickhouse kernel principle graphic explanation] about the collaborative work of partitioning, indexing, marking and compressed data
There is no red exclamation mark after SVN update