当前位置:网站首页>Redis cache update strategy, cache penetration, avalanche, breakdown problems
Redis cache update strategy, cache penetration, avalanche, breakdown problems
2022-07-06 12:12:00 【A pole】
Catalog
Preface
This article is learned by me from dark horse programmer B Stop video tutorial (https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cr4y1671t) Notes made in the process of , Mainly records Redis Some ideas about caching , No code involved .
Redis cache
effect
- Reduce back-end load
- Improve reading and writing efficiency , Reduce response time
cost
- Data consistency costs
- Code maintenance costs
- O & M costs
Cache update strategy
Memory obsolescence
Automatically eliminate when the content is insufficient
Default on
You don't have to maintain it yourself
Poor consistency
Low maintenance cost
Time out culling
add to TTL Automatically delete when due
General consistency
Low maintenance cost
Active update
Write business logic , When modifying the database , Update cache
Good consistency
Maintenance costs are high
Select according to business scenario :
Low consistency requirements : Use Redis Built in memory elimination mechanism .
High consistency requirements : Active update , And enable timeout culling ,
Read operations
Cache hits return directly
If not, query the database , And write to the cache
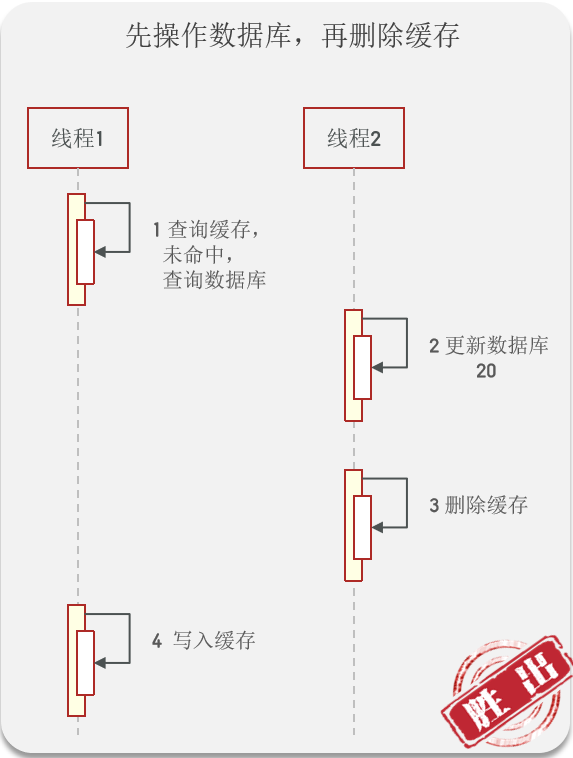
Write operations
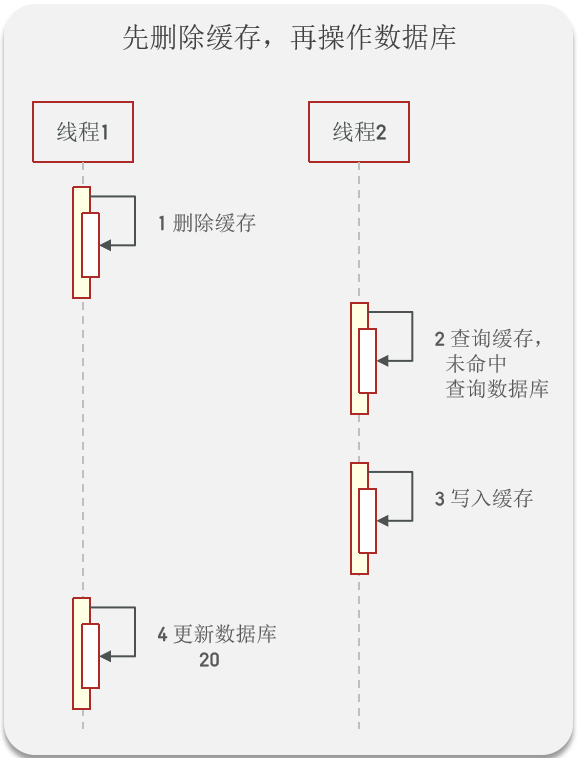
Write the database first , Then delete the cache
To ensure the atomicity of database and cache operations ( Monomer applications can use @Transactional Open transaction )
Cache penetration
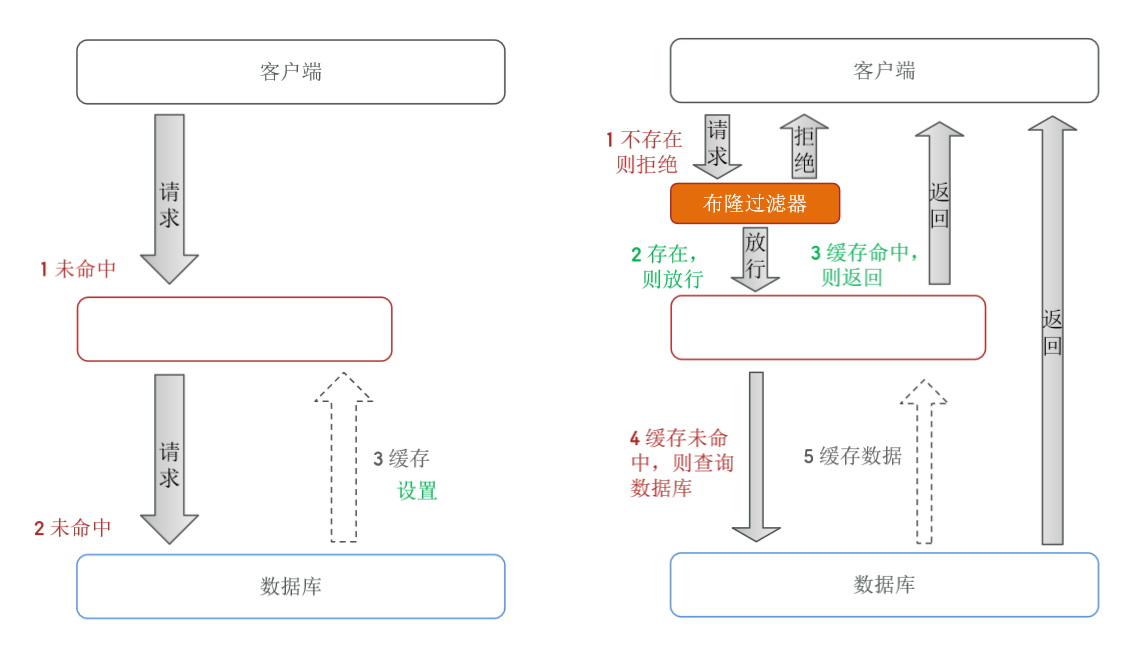
Cache penetration means that the data requested by the client does not exist in the cache or in the database , This cache will never take effect , These requests will all go to the database .
There are two common solutions :
- Caching empty objects
- advantage : Implement a simple , Convenient maintenance
- shortcoming : Extra memory consumption 、 May cause short-term inconsistencies
- Bloon filtration ( be based on bitmap Realization )
- advantage : Less memory , There is no excess key
- shortcoming : The implementation is complex 、 There is a possibility of misjudgment
( On the left is the schematic diagram of caching empty objects , On the right is the schematic diagram of bulon filtration )
Cache avalanche
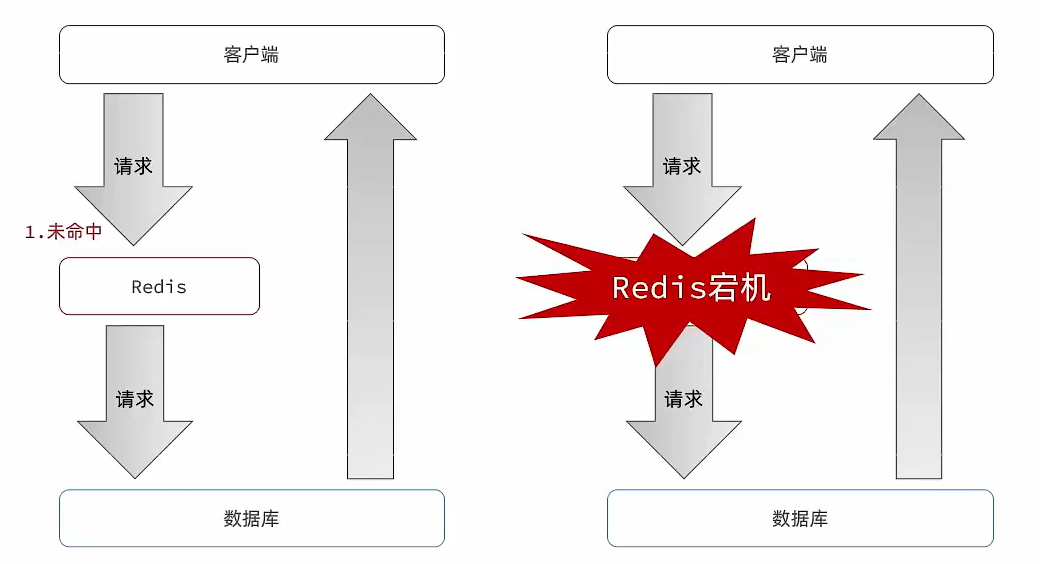
Cache avalanche refers to a large number of caches at the same time key Simultaneous failure or Redis The service outage , Cause a large number of requests to reach the database , It brings a lot of pressure .
( On the left is a large number of cache invalidation diagram , The right side is redis Downtime diagram )
Solution :
- To different Key Of TTL add to Random value
- utilize Redis colony Improve service availability
- Add Degraded current limiting Strategy
- Add to business Multi level cache ( Browser cache 、Nginx cache 、Redis cache 、JVM Local cache 、 Databases, etc )
Cache breakdown
Cache breakdown is also called hot spot Key problem , It is a highly concurrent access and complex cache reconstruction business key All of a sudden it failed , Countless requests for access will have a huge impact on the database in an instant .
There are two common solutions :
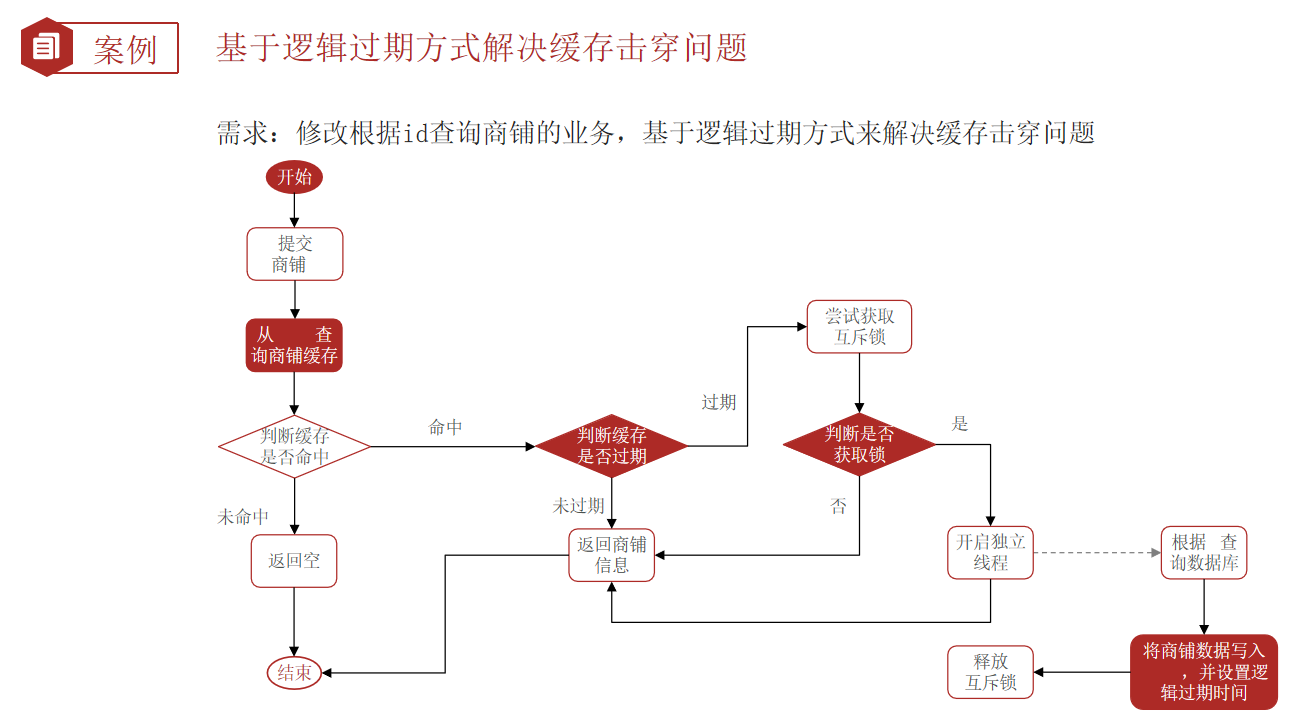
Logical expiration
Not set up TTL, Instead, add a expire Field , When the field time reaches , Update data .
- advantage
- Threads do not need to wait , Good performance
- shortcoming
- There is no guarantee of consistency
- There is additional memory consumption
- The implementation is complex
- advantage
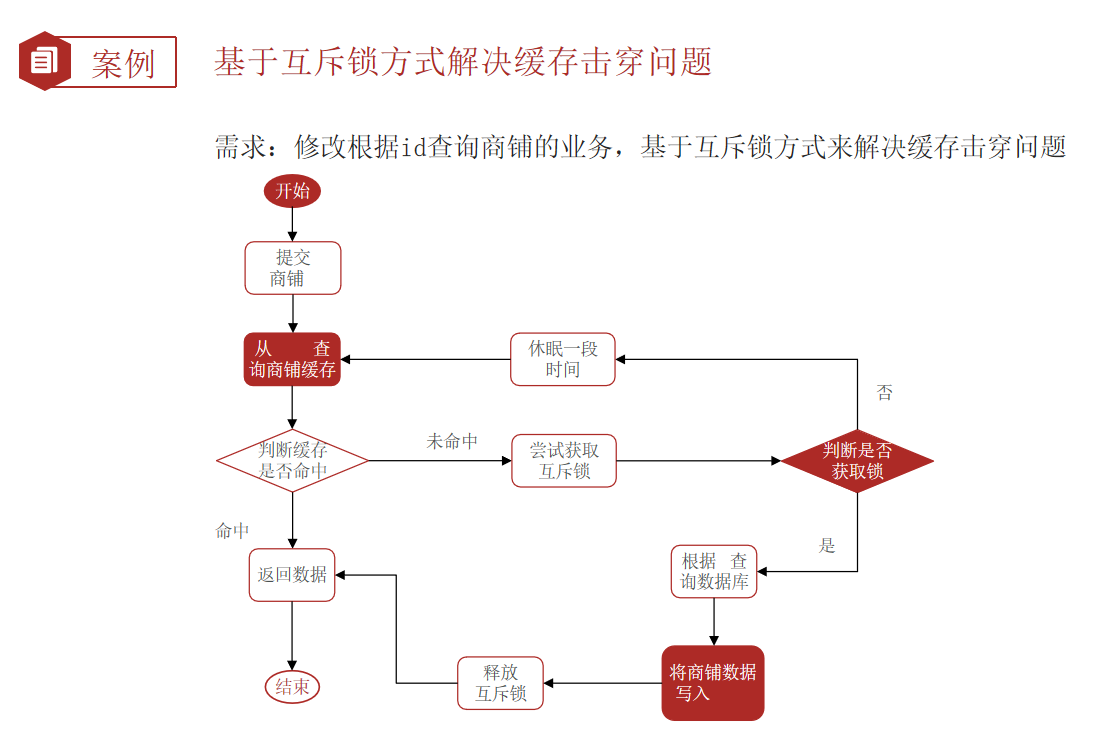
The mutex
- advantage
- No additional memory consumption
- Guarantee consistency
- Implement a simple
- shortcoming
- Thread needs to wait , Performance is affected
- There may be a deadlock risk
( On the left is the schematic diagram of mutual exclusion , Schematic diagram of logical expiration of the right side wall )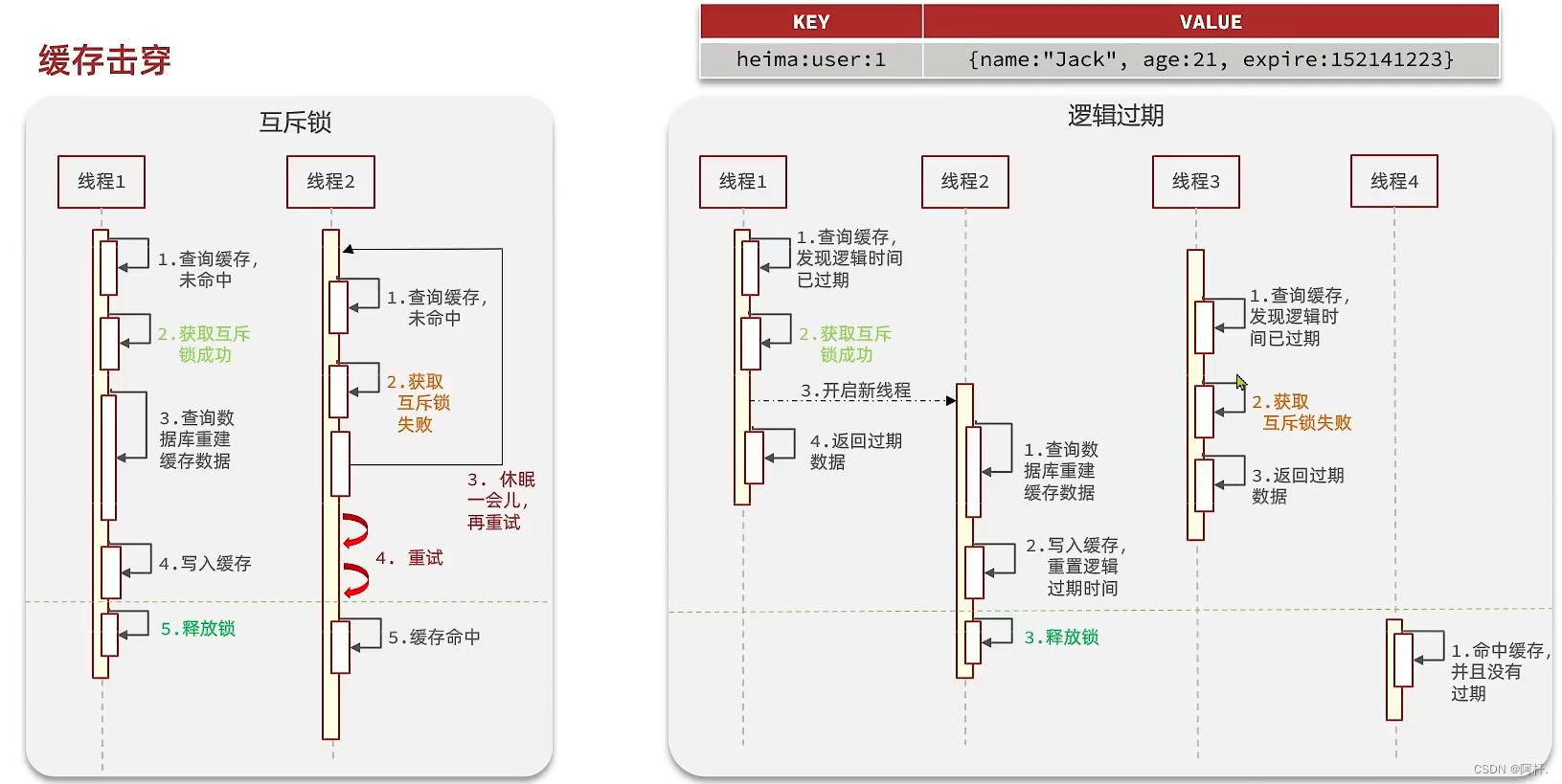
- advantage
Solve the cache breakdown problem based on mutual exclusion
Solve the cache breakdown problem based on logical expiration
Postscript
u1s1, This tutorial is really good , And it's 2022 New version of video , It is highly recommended that you have a look .
边栏推荐
- OSPF message details - LSA overview
- Priority inversion and deadlock
- STM32 how to locate the code segment that causes hard fault
- Kaggle competition two Sigma connect: rental listing inquiries
- JS正则表达式基础知识学习
- Bubble sort [C language]
- Comparison of solutions of Qualcomm & MTK & Kirin mobile platform USB3.0
- uCOS-III 的特点、任务状态、启动
- RT-Thread 线程的时间片轮询调度
- Correspondence between STM32 model and contex M
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Reading notes of difficult career creation
RuntimeError: cuDNN error: CUDNN_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED
Machine learning -- linear regression (sklearn)
AMBA、AHB、APB、AXI的理解
List and set
Kaggle competition two Sigma connect: rental listing inquiries
高通&MTK&麒麟 手機平臺USB3.0方案對比
冒泡排序【C语言】
VIM command line notes
vim命令行笔记
E-commerce data analysis -- salary prediction (linear regression)
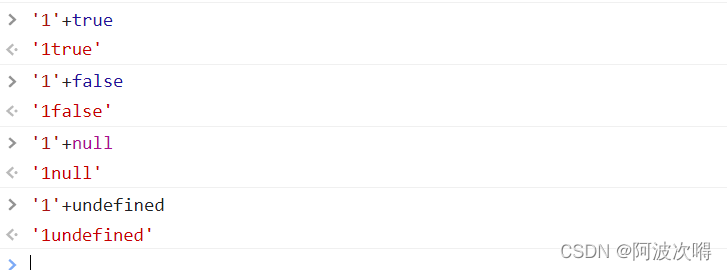
JS variable types and common type conversions
ES6 grammar summary -- Part I (basic)
ARM PC=PC+8 最便于理解的阐述
Machine learning -- decision tree (sklearn)
There are three iPhone se 2022 models in the Eurasian Economic Commission database
ESP8266使用arduino连接阿里云物联网
Amba, ahb, APB, Axi Understanding
Basic operations of databases and tables ----- classification of data
基于Redis的分布式锁 以及 超详细的改进思路