当前位置:网站首页>R语言【逻辑控制】【数学运算】
R语言【逻辑控制】【数学运算】
2022-07-06 23:56:00 【桜キャンドル淵】
目录
一、逻辑运算符
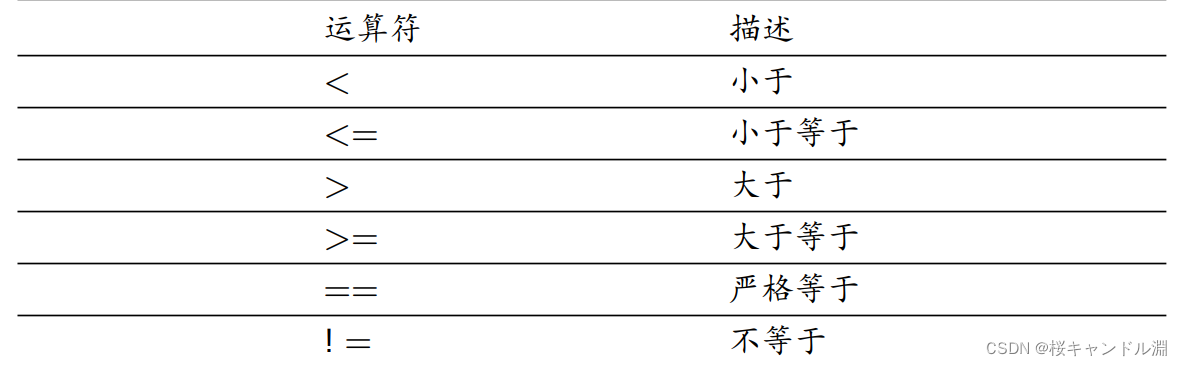
x <- c(3,0,-2,-5,7,2,-1)
y <- c(2,4,-1,0,5,1,-4)
x <= y
compare.xy <- (x<=y)
compare.xy 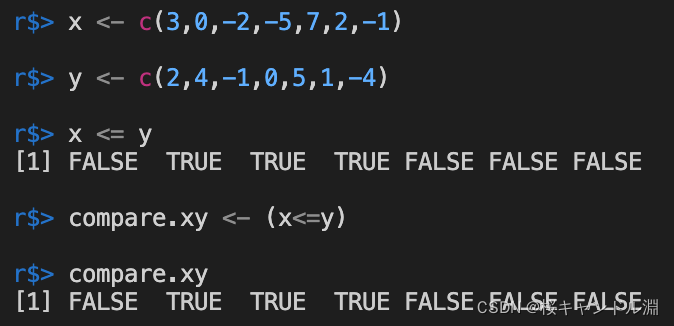
字符串按照字符顺序进行比较
a <- c("ann","gretchen","maria","ruth","wendy")
b <- c("bruce","ed","robert","seth","thomas")
a <= b
a >= b
二、布尔运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
| !x | 非x |
| x|y | x或y |
| x&y | x和y |
| isTRUE(x) | 判断x是否为true |
我们从下面的测试代码中可以看出如果对应位置的元素满足布尔运算符的判断就返回TRUE,如果不是的话就返回FALSE
x <- c(3,0,-2,-5,7,2,-1)
y <- c(2,4,-1,0,5,1,-4)
(x-y > -2)&(x-y < 2)
x[(x-y> -2)&(x-y < 2)]
(x-y >= -2)|(x-y <= 2)
x[(x-y>-2)&(x-y<2)]
(x-y > -2)
!(x-y > -2)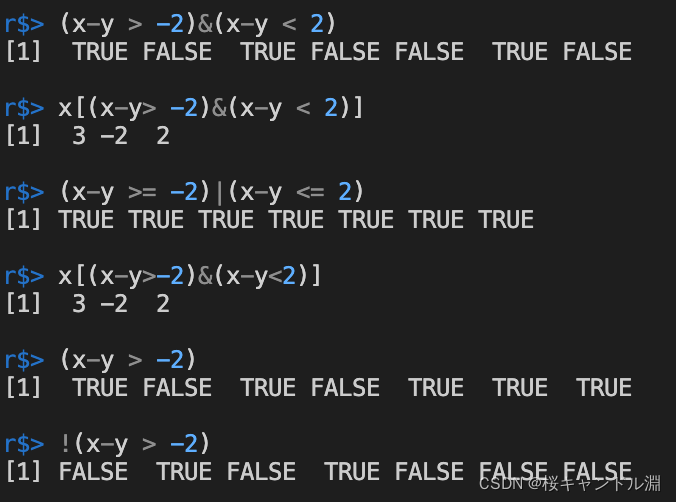
索引及其相关内容
x <- c(3,7,5,-2,0,-8)
x[3]
x[1:3]
x[c(2,4,5)]
x[1+3]
i =4
x[i]
x[-2]
x[-c(2,4,5)]
y <- c(2,7,-5,4,-1,6)
(x+y)[1:3]
z <- c("jan","feb","mar","apr","may","jun")
monthly.numbers <- data.frame(x,y,z)
monthly.numbers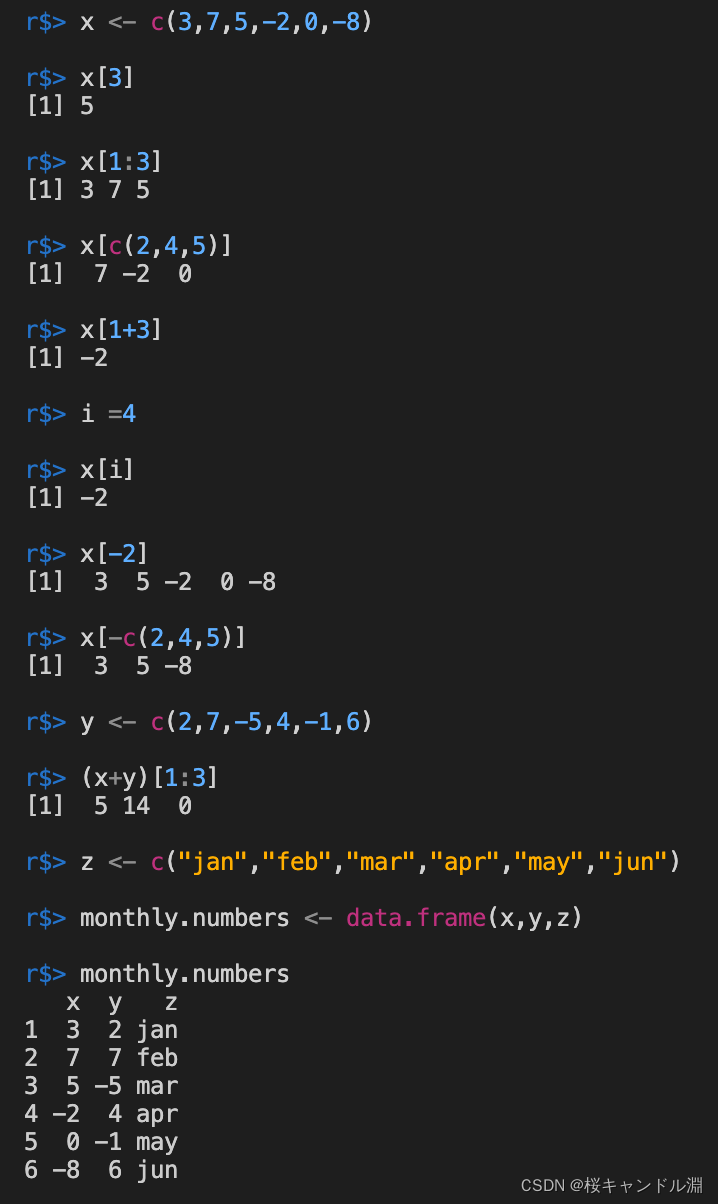
三、数学运算符
3+4 # 7
3-4 # -1
3*4 # 12
3/4 # 0.75
3^4 # 81
16**(1/4) # 2
13%%4 # 1
13%/%4 # 3
x <- c(-1,0,1)
exp(x)
y <- c(1,2,3,4)
sqrt(y) 
二次函数
xlow <- -1
xup <- 2
x <- xlow + (xup-xlow)*(0:100)/100
y <- x^2-x-1
plot(x,y,type="l")
y2 <- numeric(length(x))
#画点,分别以x,y2中对应位置的参数组成坐标点,绘制的直线类型为l,直线为虚线
#lty的参数同样也可以输入1,2,3等参数来绘制不同样式的标注线
points(x,y2,type="l",lty="dashed")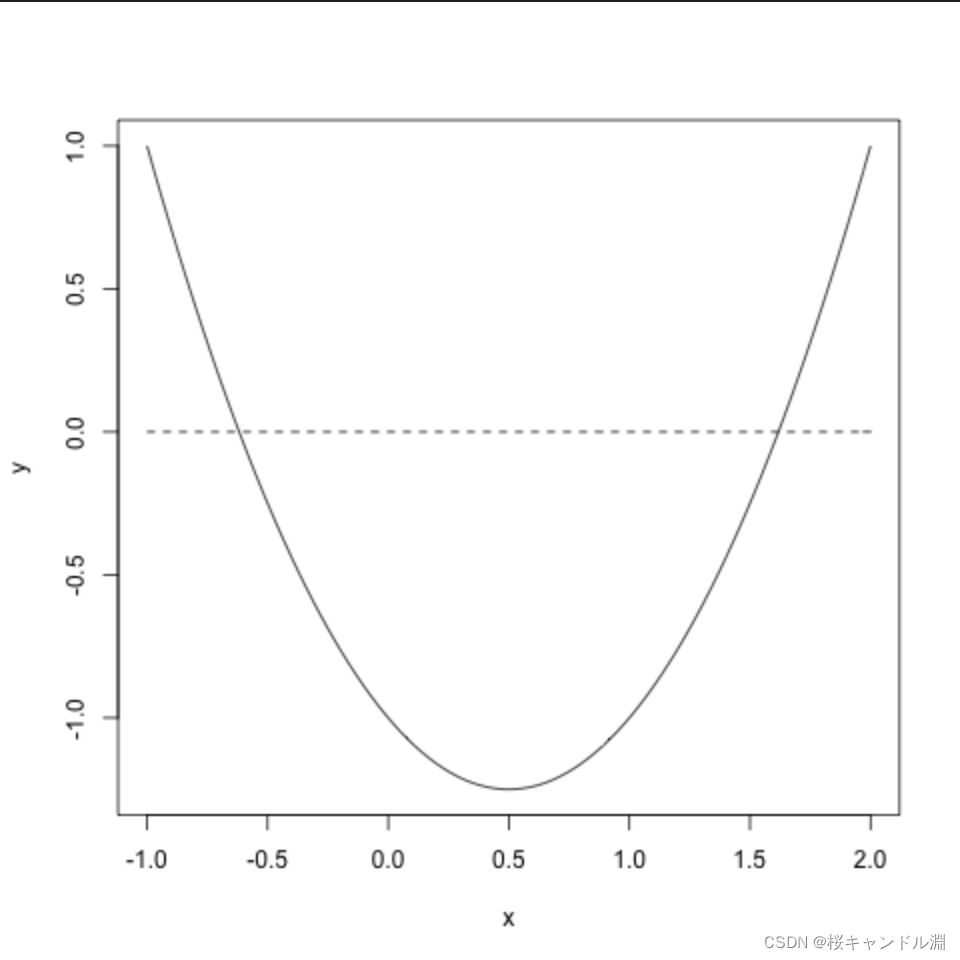
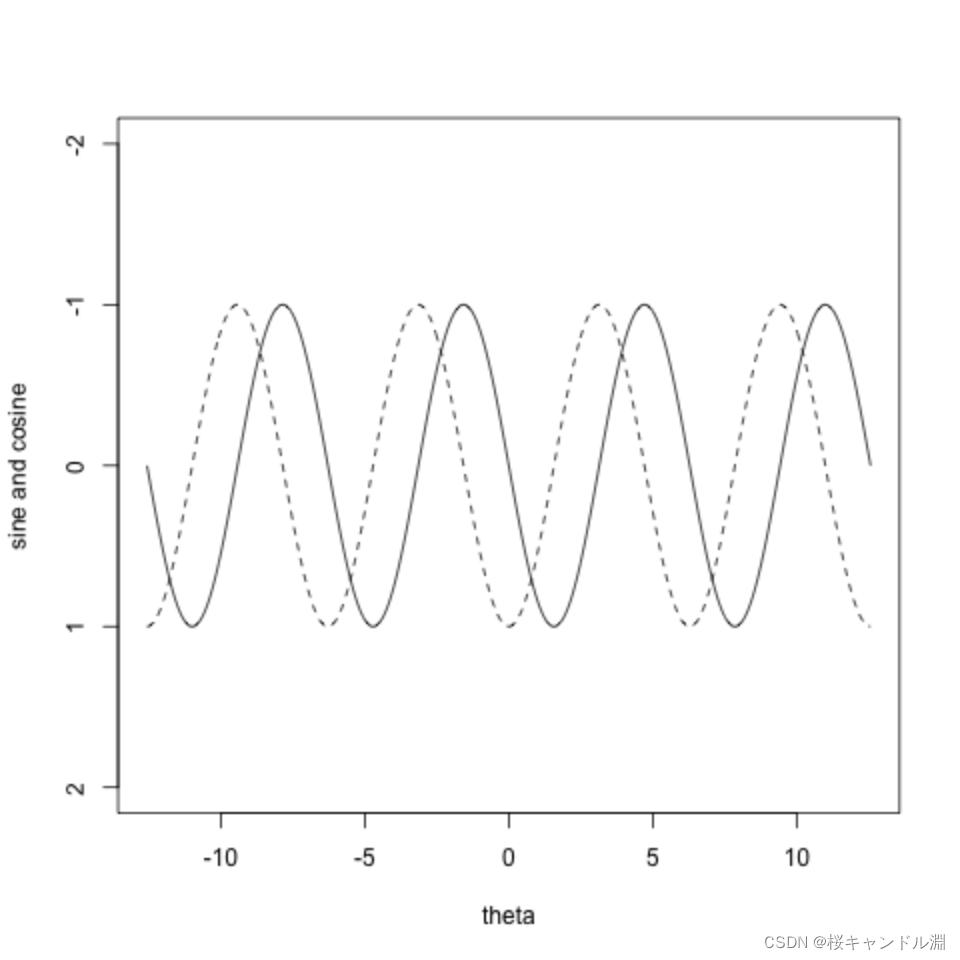
三角函数
#设置上下限
th.low <- -4*pi
th.up <- 4*pi
theta <- th.low + (th.up-th.low)*(0:1000)/1000
y1 <- sin(theta)
y2 <- cos(theta)
plot(theta,y1,type="l",lty=1,ylim=c(2,-2),xlab="theta",
ylab="sine and cosine")
points(theta,y2,type="l",lty=2)
极坐标
#设置角度为0-360度
theta <- 2*pi*(0:100)/100
r <- 1
x <- r*cos(theta)
y <- r*sin(theta)
#设置我们的画布大小长宽都为4英寸。
par(pin=c(4,4))
plot(x,y,type="l",lty=1)
以e为底的指数函数
使用exp函数能够设置以e为底数的指数函数。
x <- 2
y <- exp(x)
z <- exp(0:10)
y
z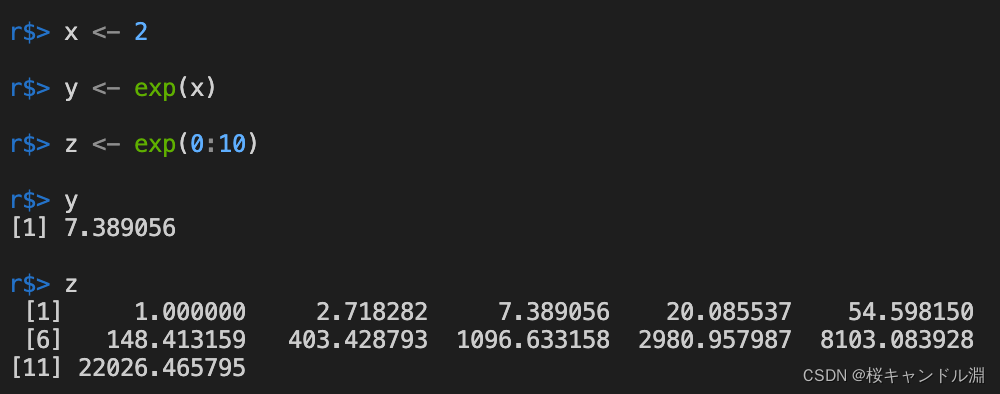
对数函数
y = loga x, R的表示方式log(x,a)
y = ln x, R的表示方式log(x)
y = lg x, R的表示方式log10(x)
y = log2 x, R的表示方式log2(x)
如果直接log(X)默认是以e为底,也就是ln(X)
w <- 0
log(w)
w <- 1:10
log(w)
w <- 10000
log10(w)
w <- 16
log2(w)
log(9,3)
log(64,8)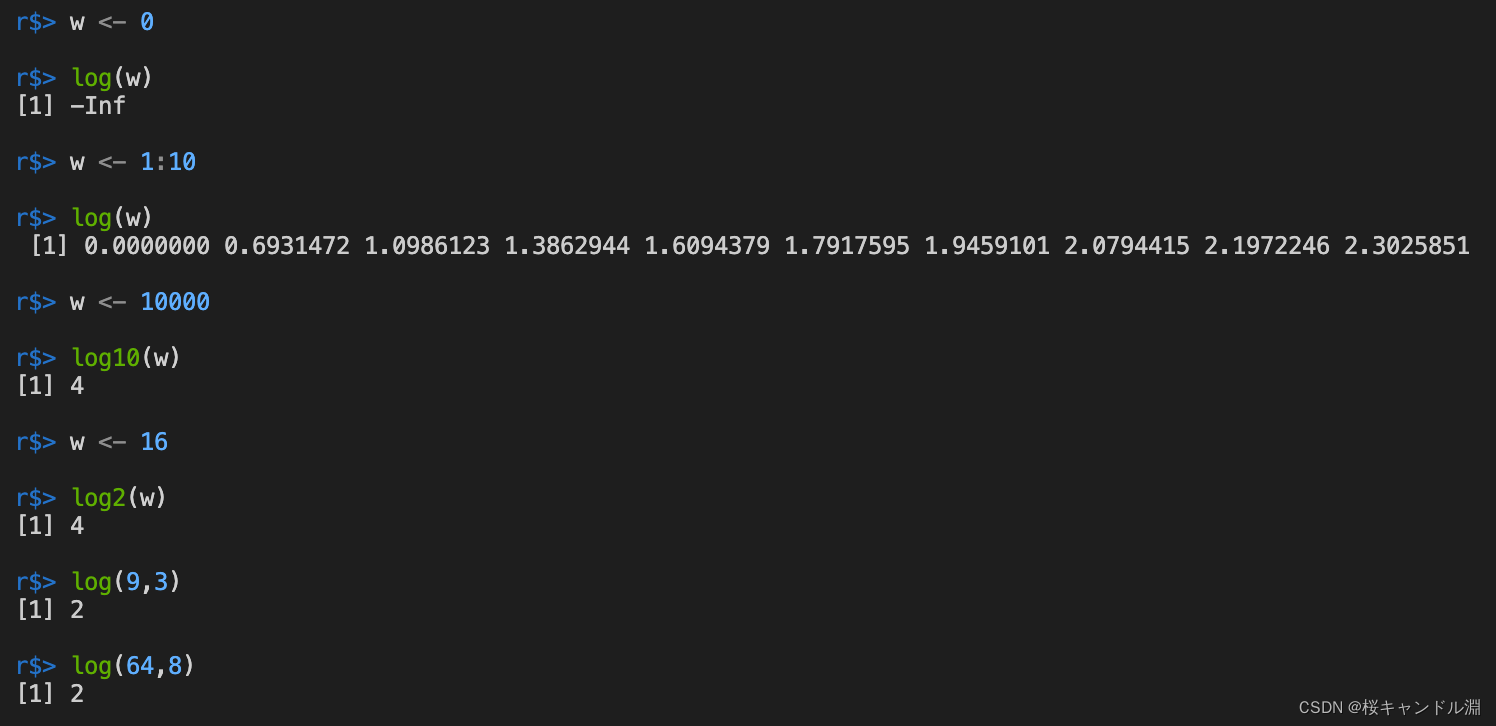
四、矩阵相关运算
1.向量的内积
使用%*%或者crossprod都可以生成向量的内积的结果。
x <- 1:5
x
y <- 2*1:5
y
x %*% y
crossprod(x,y)
2.向量的外积
使用%o%或者tcrossprod或者outer都能够得到向量的外积,外积就是相同位置的元素相乘
x %o% y
tcrossprod(x,y)
outer(x,y)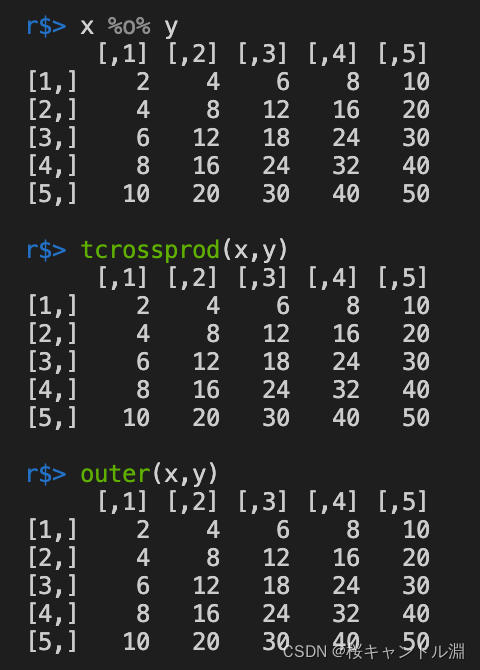
3.矩阵的转置
使用转置命令t(x)可以实现我们矩阵的转置
x <- matrix(1:12,nrow=3)
x
y = matrix(1:12,ncol=3)
y
z = matrix(1:12,ncol=3, byrow=T)
z
X = t(x)
X
Y <- t(t(y))
Y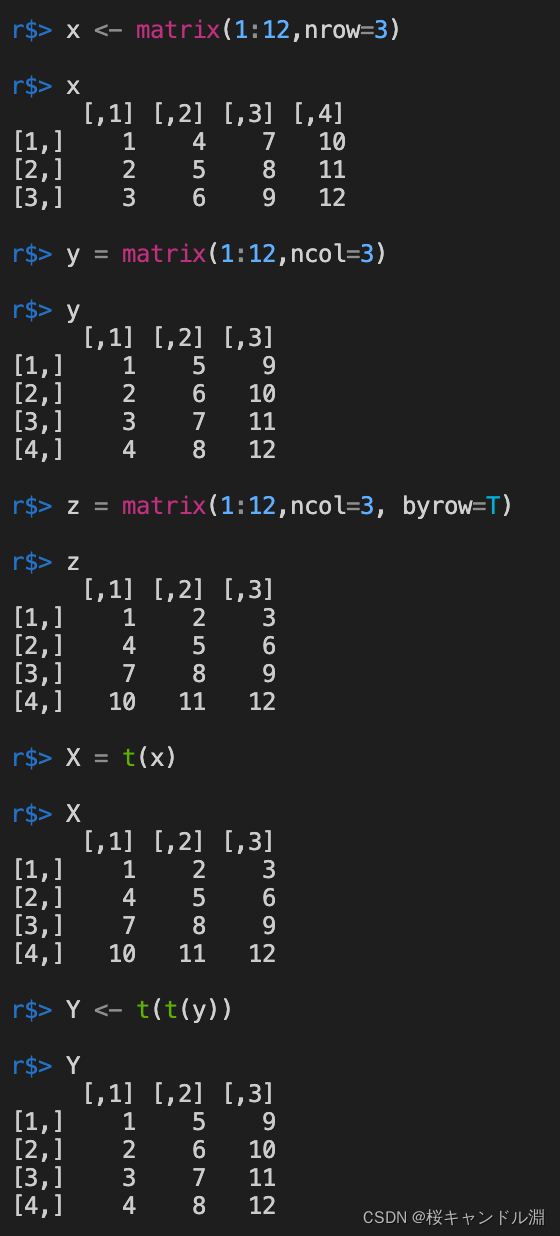
4.矩阵的加减法
x+t(z)
x-t(z)
x + 1
y <- 1:12
x + y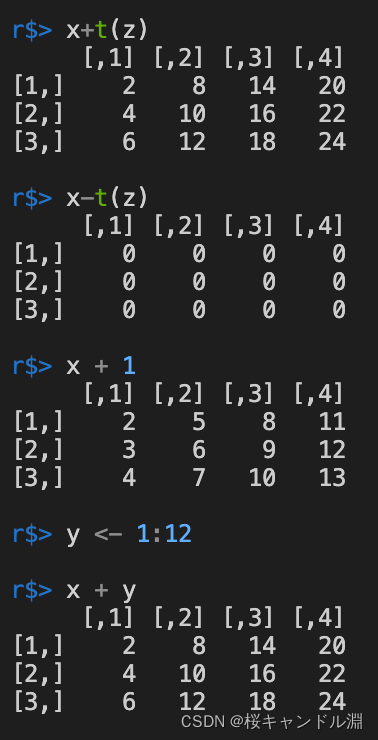
5.矩阵的数乘
矩阵的数乘会对矩阵中的每一个元素进行数乘
a <- 3
M <- a*x
M
6.矩阵乘法
使用%*%或者crossprod都可以实现矩阵的乘法
A = matrix(1:12,ncol=3)
B = matrix(1:18, nrow=3)
A
B
C = A%*%B
C
D = matrix(1:12, nrow=4, byrow=T)
D
t(A) %*% D 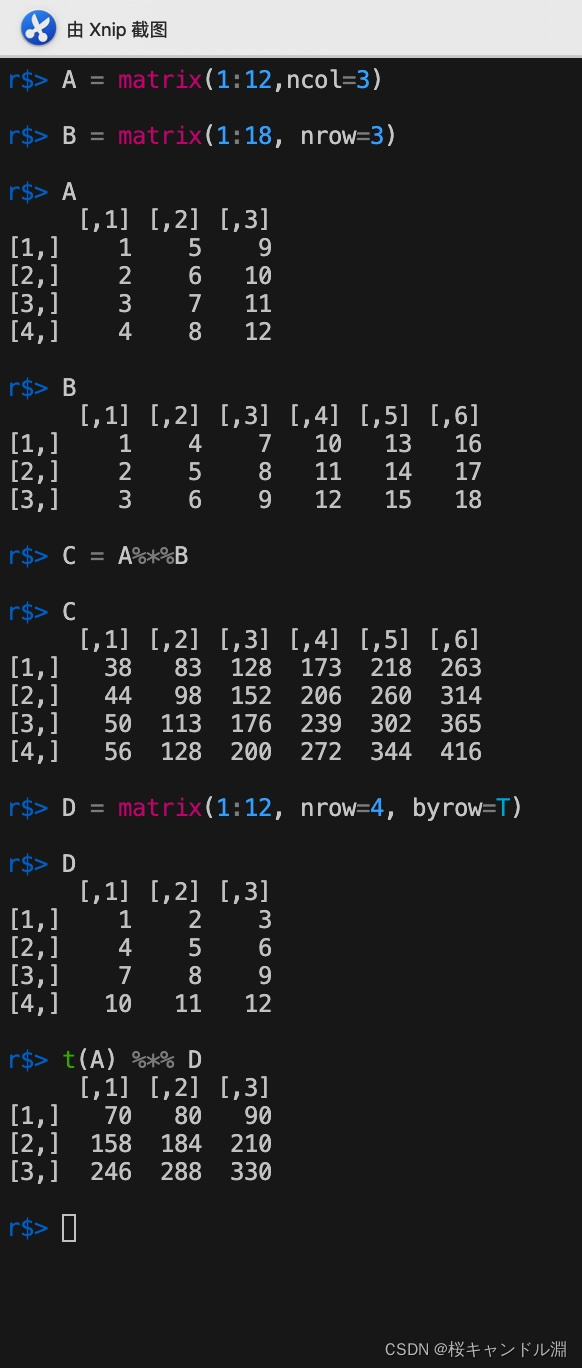
使用了crossprod之后,我们不需用转置,也能够实现我们A与D矩阵的乘法。相比之下crossprod的效率更高,也就是说crossprod会将第一个参数的矩阵转置然后乘以第二个参数的矩阵。
crossprod(A,D)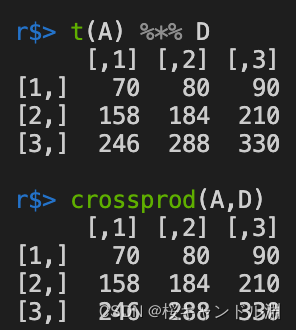
7.与矩阵对角元素有关的运算
使用diag函数能获取到当前矩阵对角线上的元素,并且将其拼接成一个向量。
如果diag的参数是一个向量的话,它就会帮我们生成一个对角阵。
A = matrix(1:16,nrow=4)
A
diag(A)
diag(diag(A)) 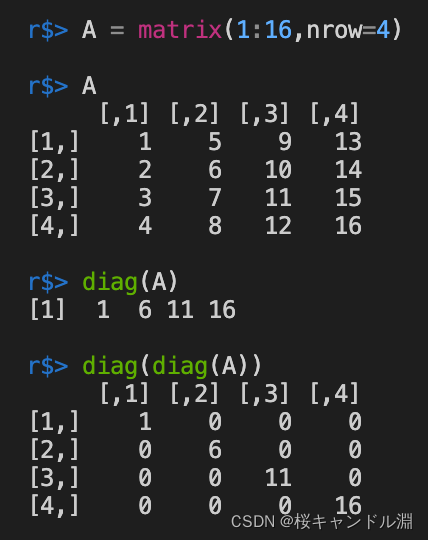
生成一个n维的单位矩阵
diag(n)
n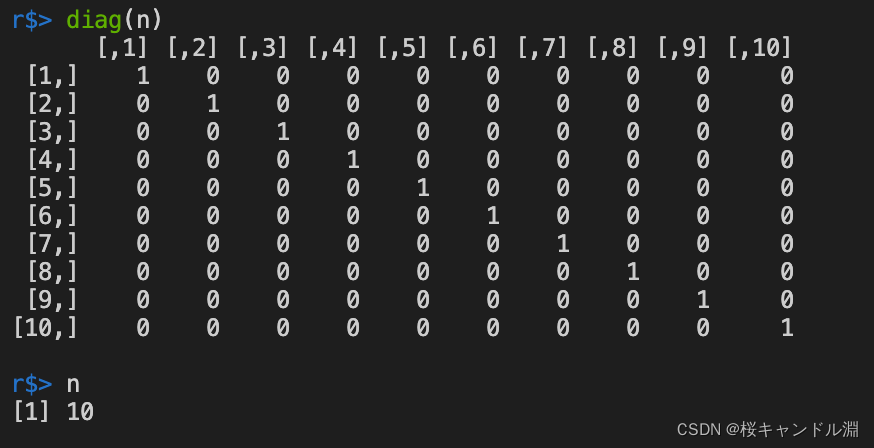
当diag的参数是向量的时候,它会返回一个以该向量作为主对角元素的矩阵。
x<-c(1,2,3,4,5)
diag(x) 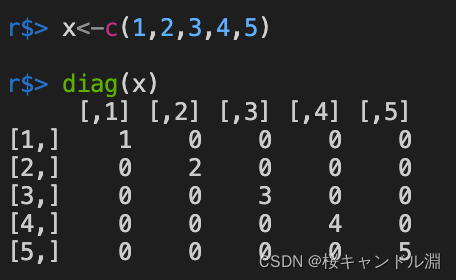
8.矩阵求逆
使用solve函数能够求出我们当前矩阵的逆矩阵
AX=b,X=solve(A,b)
A = matrix(c(1,2,3,4,7,5,2,1,3,1,3,2,3,2,3,2),ncol=4)
A
solve(A)
b <- c(1,2,3,4)
#计算方程组AX=b的解
solve(A,b)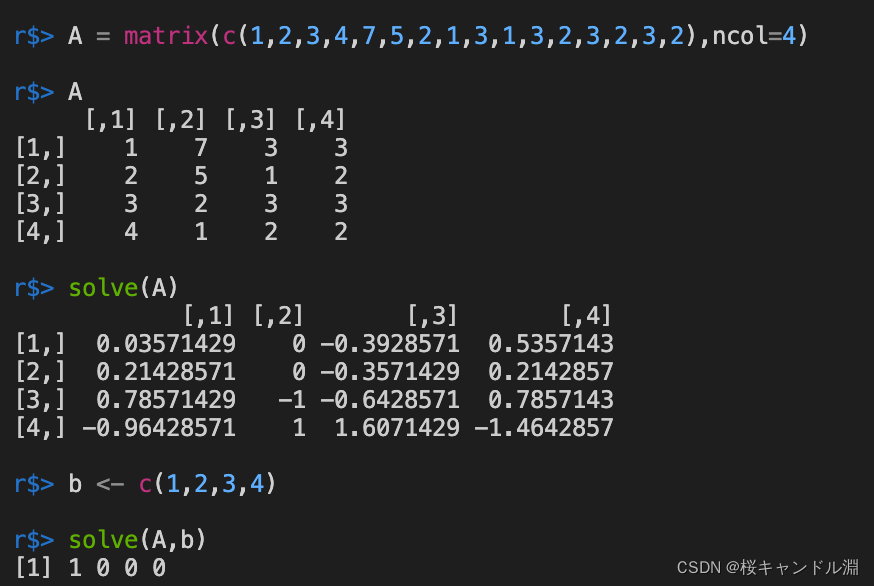
9.矩阵的特征值与特征向量
使用eigen方法能够求出我们当前矩阵的特征值与与之对应的特征向量
values表示的是特征值
vectors表示的是对应的特征向量
A = diag(4)+1
A
A.eigen = eigen(A,symmetric=T)
A.eigen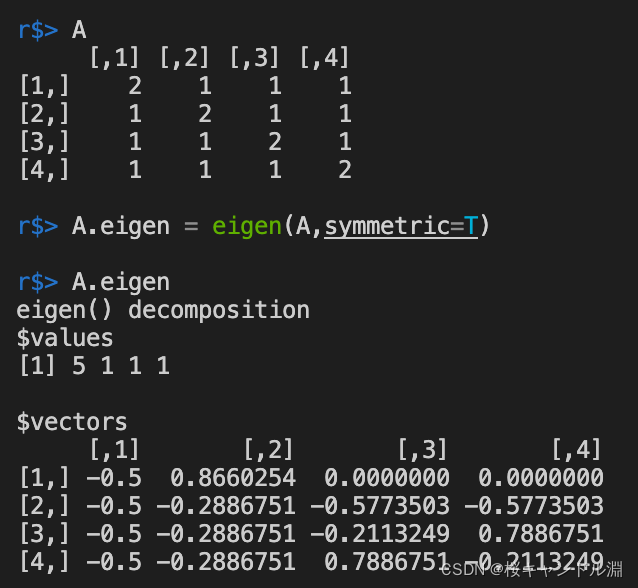
10.矩阵的Choleskey分解
使用我们的chol方法,能够实现我们当前矩阵的分解。
也就是说求将A分解成P'P的P的矩阵
A = diag(4)+1
A
P <- chol(A)
P

11.计算行列式
使用det函数能够对我们的当前矩阵计算行列式。
det(A)
12.提取矩阵的维数
dim(A)计算矩阵A的行数和列数
ncol(A)返回矩阵A的列数
nrow(A)返回矩阵A的行数
dim(A)
ncol(A)
nrow(A)
A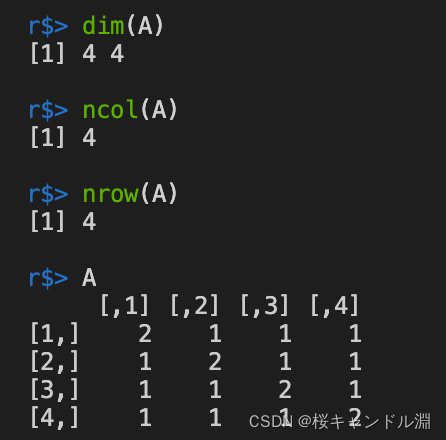
13.矩阵的行和、列和、行平均与列平均
A=matrix(1:16,ncol=4)
A
#行和
rowSums(A)
#行平均
rowMeans(A)
#列和
colSums(A)
#列平均
colMeans(A)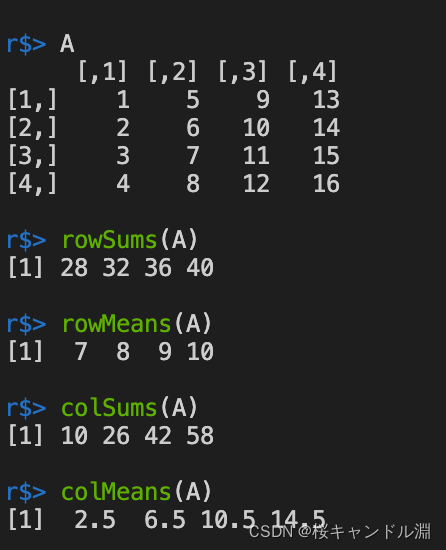
五、积分运算
integrate()
第一个参数为我们的计算积分的式子,第二个参数为我们的下限,第三个参数为我们的上限。下面代码中的Inf表示无穷
integrand <- function(x) {1/((x+1)*sqrt(x))}
integrate(integrand, lower=0, upper=Inf)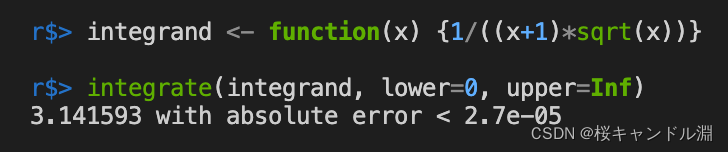
六、负数运算
生成复数向量。
complex(length.out,real=numeric(0),imaginary=numeric(0))
x <- 1+2i
y <- complex(1,1,1)
#取实部
Re(y)
#取虚部
Im(y)
#求模长
Mod(y)
#求共轭复数
Conj(y)
#判断是否是复数
is.complex(y)
#生成复数向量组
complex(re=1:4,im=2:3)
#对-2开平方根是行不通的
sqrt(-2)
#对-2+0i开平方根是行的通的,因为此时为复数运算
sqrt(-2+0i)
#如果要直接对-2求平方根的话,也可以直接将-2转换为复数形式再开平方根。
sqrt(as.complex(-2)) 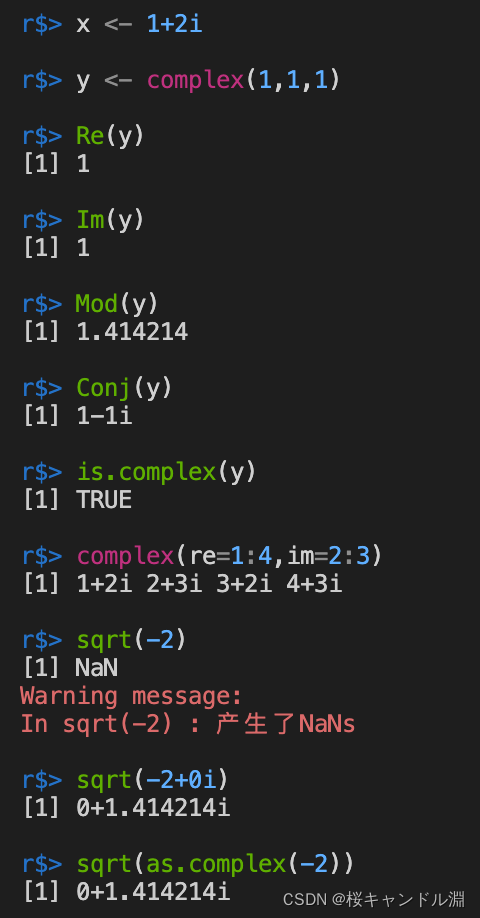
七、数学函数
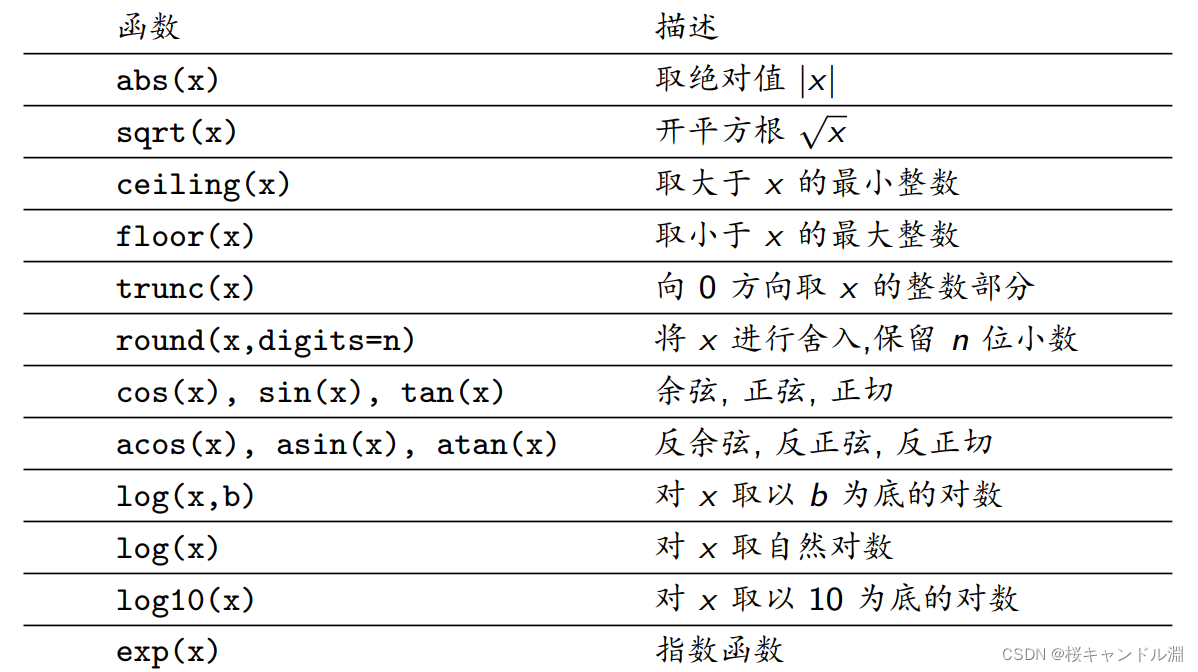
abs(-4.21) # 4.21
sqrt(16) # 4
ceiling(3.78) # 4
floor(3.78) # 3
floor(-3.78) # -4
trunc(-3.78) # -3
trunc(3.78) # 3
round(3.1415926, digits=4) # 3.1415
log(10,2) # 3.321928
log(10) # 2.302585
log10(10) # 1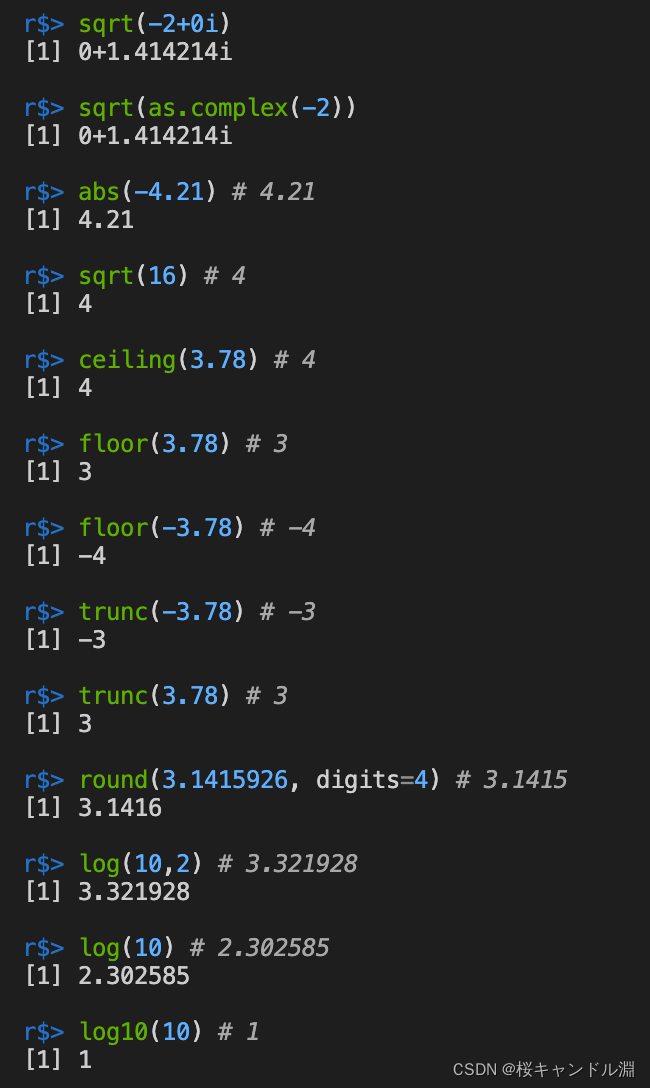
八、其他实用函数

x<- c(1,2,3,4)
length(x)
rep(x,2)
rep(1,10)
seq(1,2,by=0.2) 
将函数应用于数据框和矩阵
b <- c(1.23, 4.271, 9.2727)
#向0方向取整
trunc(b)
#runif(n, min, max)函数,这个函数生成均匀分布的值,n为个数,min和max分别是最小值和最大值,默认参数为0和1。
d <- matrix(runif(12),nrow=3)
#对其中的每一个元素取对数
log(d)
边栏推荐
- 【Shell】清理nohup.out文件
- 集群、分布式、微服務的區別和介紹
- DOM-节点对象+时间节点 综合案例
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
- The year of the tiger is coming. Come and make a wish. I heard that the wish will come true
- [binary tree] binary tree path finding
- 《4》 Form
- The 2022 China low / no code Market Research and model selection evaluation report was released
- Batch size setting skills
- JVM(二十) -- 性能监控与调优(一) -- 概述
猜你喜欢
JVM (19) -- bytecode and class loading (4) -- talk about class loader again
论文阅读【Open-book Video Captioning with Retrieve-Copy-Generate Network】

CentOS 7.9 installing Oracle 21C Adventures

【js组件】date日期显示。

Egr-20uscm ground fault relay
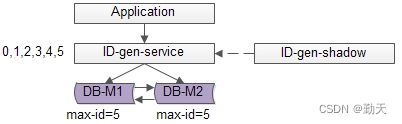
Distributed global ID generation scheme
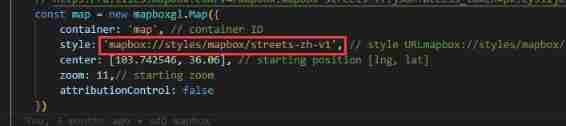
Mapbox Chinese map address
![Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]](/img/db/feb719e2715c7b9c669957995e1d83.png)
Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]
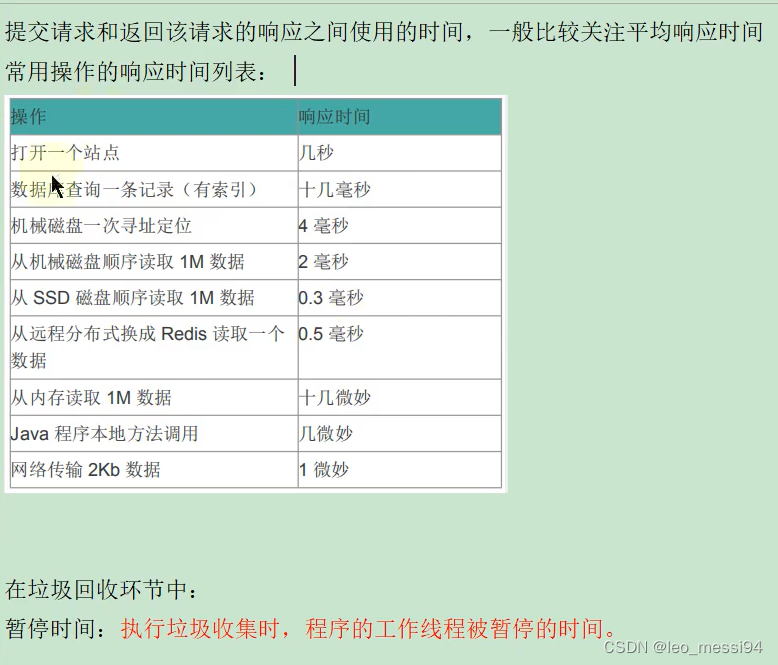
JVM (XX) -- performance monitoring and tuning (I) -- Overview
架构设计的五个核心要素
随机推荐
"Multimodal" concept
消息队列:如何确保消息不会丢失
sql查询:将下一行减去上一行,并做相应的计算
什么是依赖注入(DI)
Two person game based on bevy game engine and FPGA
分布式事务解决方案之2PC
照片选择器CollectionView
JSP setting header information export to excel
Design, configuration and points for attention of network specified source multicast (SSM) simulation using OPNET
MySQL数据库学习(7) -- pymysql简单介绍
基于NCF的多模块协同实例
“多模态”概念
《5》 Table
Mybaits之多表查询(联合查询、嵌套查询)
Most commonly used high number formula
App clear data source code tracking
Tablayout modification of customized tab title does not take effect
Initial experience of annotation
Paper reading [semantic tag enlarged xlnv model for video captioning]
The year of the tiger is coming. Come and make a wish. I heard that the wish will come true