当前位置:网站首页>If you don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
If you don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
2022-07-07 05:57:00 【New horizon of procedure】
summary
In the system architecture , Caching is one of the easiest ways to provide system performance , Students with a little development experience will inevitably deal with caching , At least I have practiced .
If used properly , Caching can reduce response time 、 Reduce database load and save cost . But if the cache is not used properly , There may be some inexplicable problems .
In different scenarios , The caching strategy used also varies . If in your impression and experience , Caching is just a simple query 、 update operation , Then this article is really worth learning .
ad locum , Explain systematically for everyone 4 Three cache modes and their usage scenarios 、 Process and advantages and disadvantages .
Selection of caching strategy
In essence , Caching strategy depends on data and data access patterns . let me put it another way , How data is written and read .
for example :
- Does the system write more and read less ?( for example , Time based logging )
- Whether the data is written only once and read many times ?( for example , User profile )
- Is the returned data always unique ?( for example , Search for )
Choosing the right caching strategy is the key to improving performance .
There are five common cache strategies :
Cache-Aside Pattern: Bypass caching mode
Read Through Cache Pattern: Read penetration mode
Write Through Cache Pattern: Write through mode
Write Behind Pattern: Also called Write Back, Asynchronous cache write mode
The above cache strategy is divided based on the data reading and writing process , Under some caching strategies, the application only interacts with the cache , Under some caching strategies, applications interact with caches and databases at the same time . Because this is an important dimension of strategy division , Therefore, you need to pay special attention to the following process learning .
Cache Aside
Cache Aside Is the most common caching mode , Applications can talk directly to caches and databases .Cache Aside It can be used for read and write operations .
Read operations Flow chart of :
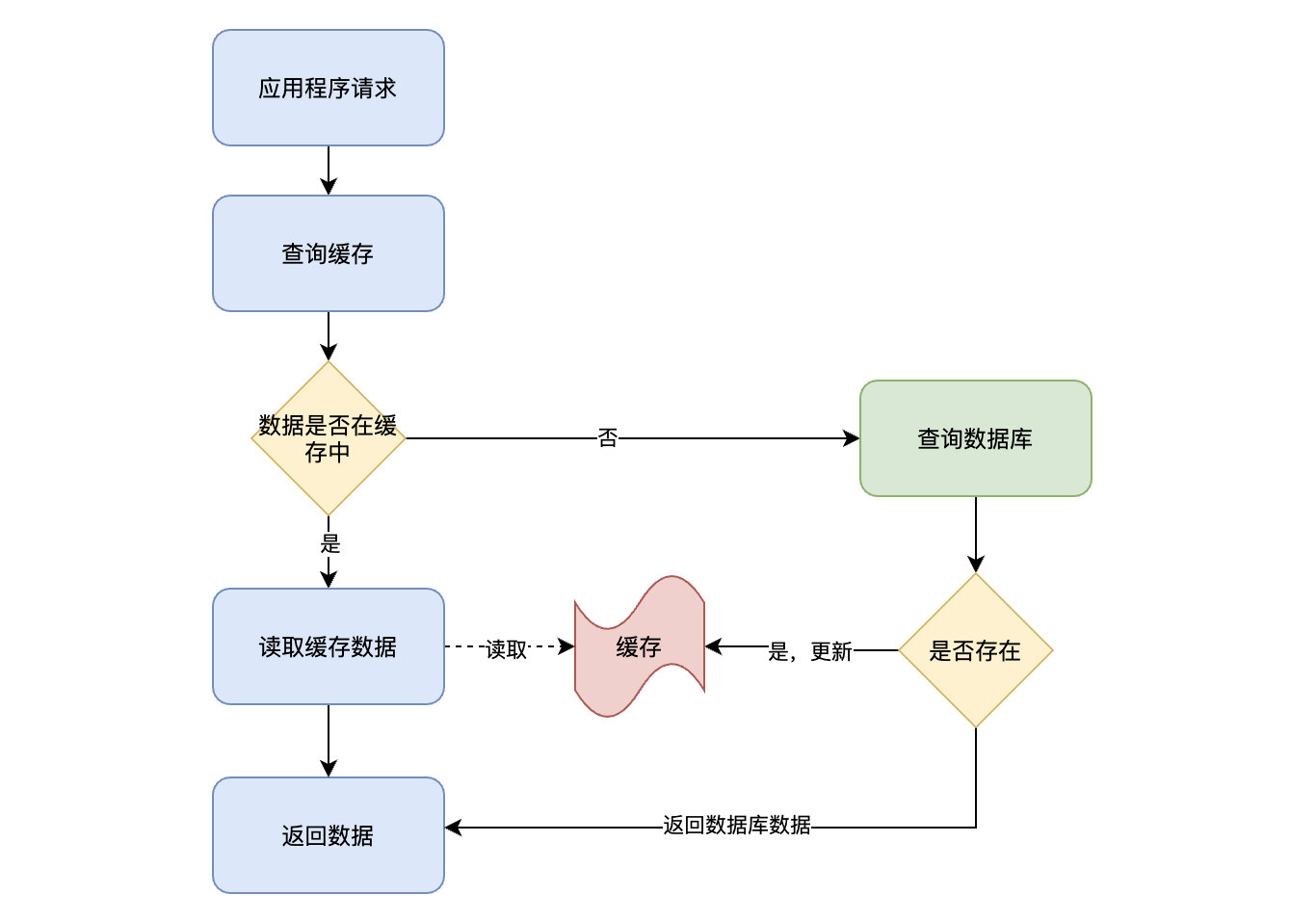
The process of reading operation :
- The application receives a data query ( read ) request ;
- Whether the data that the application needs to query is in the cache :
- If there is (Cache hit), Query the data from the cache , Go straight back to ;
- If it doesn't exist (Cache miss), Then retrieve data from the database , And stored in the cache , Return result data ;
Here we need to pay attention to an operation boundary , That is, the database and cache operations are directly operated by the application .
Write operations Flow chart of :
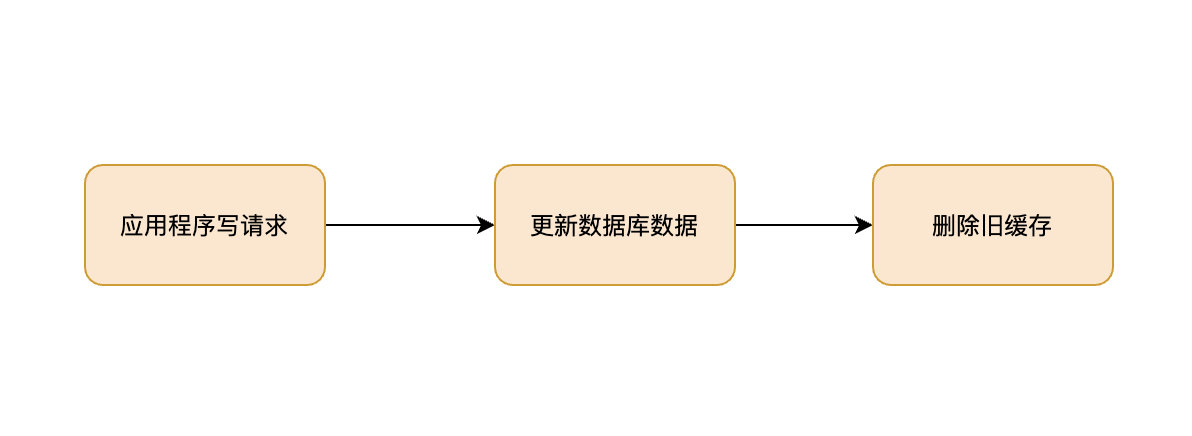
The write operation here , Including the creation of 、 Update and delete . When writing operations ,Cache Aside The pattern is to update the database first ( increase 、 Delete 、 Change ), Then delete the cache directly .
Cache Aside Patterns can be said to apply to most scenarios , Usually in order to deal with different types of data , There are also two strategies to load the cache :
- Load cache when using : When you need to use cached data , Query from the database , After the first query , Subsequent requests get data from the cache ;
- Preload cache : Preload the cache information through the program at or after the project starts , such as ” National Information 、 Currency information 、 User information , News “ Wait for data that is not often changed .
Cache Aside It is suitable for reading more and writing less , For example, user information 、 News reports, etc , Once written to the cache , Almost no modification . The disadvantage of this mode is that the cache and database double write may be inconsistent .
Cache Aside It is also a standard model , image Facebook This mode is adopted .
Read Through
Read-Through and Cache-Aside Very similar , The difference is that the program doesn't need to focus on where to read data ( Cache or database ), It only needs to read data from the cache . Where the data in the cache comes from is determined by the cache .
Cache Aside The caller is responsible for loading the data into the cache , and Read Through The cache service itself will be used to load , So it is transparent to the application side .Read-Through Its advantage is to make the program code more concise .
This involves the application operation boundary problem we mentioned above , Look directly at the flow chart :
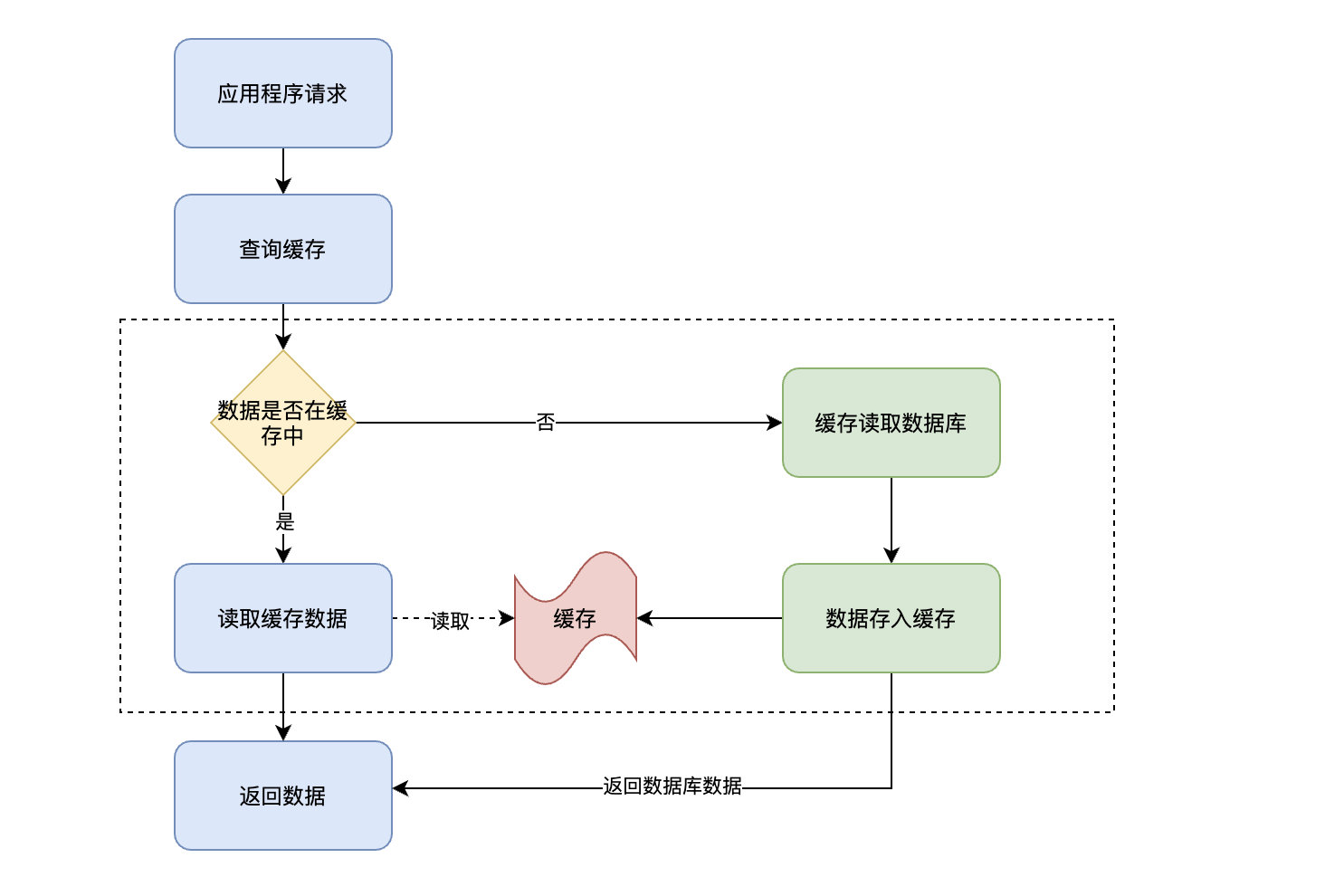
In the above flow chart , Focus on the operations in the dotted box , This part of the operation is no longer handled by the application , Instead, the cache handles it itself . in other words , When an application queries a piece of data from the cache , If the data does not exist, the cache will load the data , Finally, the cache returns the data results to the application .
Write Through
stay Cache Aside in , The application needs to maintain two data stores : A cache , A database . This is for applications , It's a little cumbersome .
Write-Through In mode , All writes are cached , Every time you write data to the cache , The cache will persist the data to the corresponding database , And these two operations are completed in one transaction . therefore , Only if you succeed in writing twice can you finally succeed . The downside is write latency , The benefit is data consistency .
It can be understood as , Applications think that the back end is a single storage , And storage itself maintains its own Cache.
Because the program only interacts with the cache , Coding will become simpler and cleaner , This becomes especially obvious when the same logic needs to be reused in multiple places .
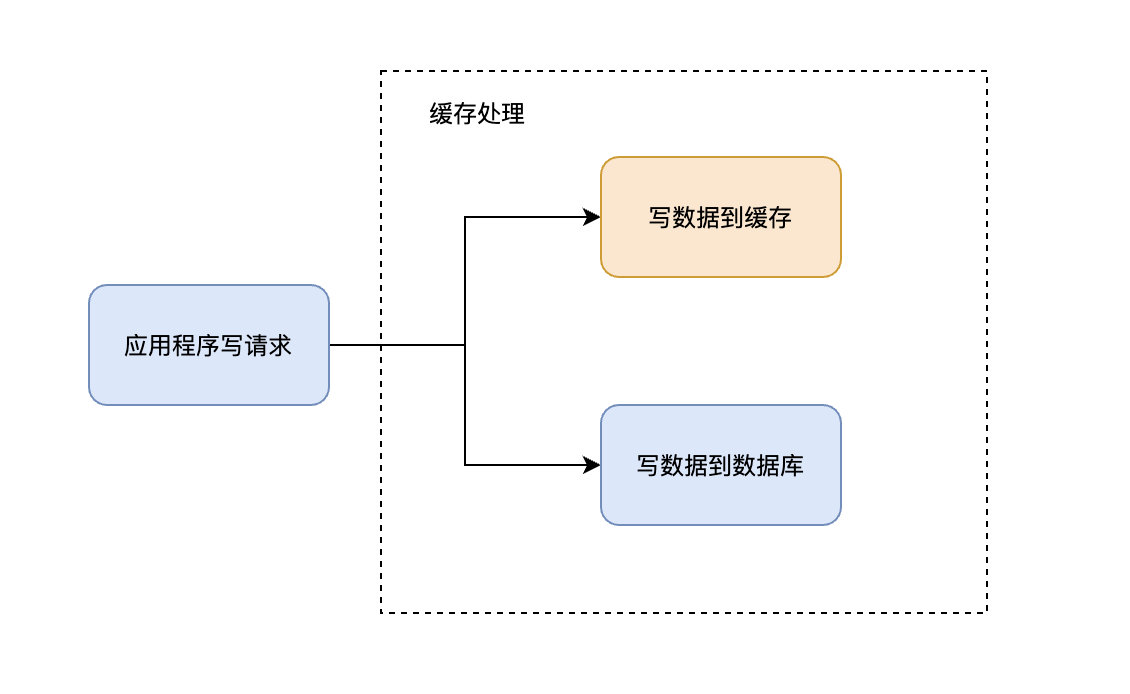
When using Write-Through when , Generally, it is used together Read-Through To use .Write-Through The potential use scenario for is the banking system .
Write-Through Applicable cases are :
- You need to read the same data frequently
- Can't stand data loss ( relative Write-Behind for ) Inconsistent with the data
In the use of Write-Through Special attention should be paid to the effectiveness management of cache , Otherwise, a large amount of cache will occupy memory resources . Even valid cache data is cleared by invalid cache data .
Write-Behind
Write-Behind and Write-Through stay ” The program only interacts with the cache and can only write data through the cache “ This aspect is very similar . The difference is Write-Through The data will be written into the database immediately , and Write-Behind After a while ( Or triggered by other ways ) Write the data together into the database , This asynchronous write operation is Write-Behind The biggest feature .
Database write operations can be done in different ways , One way is to collect all write operations and at a certain point in time ( For example, when the database load is low ) Batch write . Another way is to merge several write operations into a small batch operation , Then the cache collects write operations and writes them in batches .
Asynchronous write operations greatly reduce the request latency and reduce the burden on the database . At the same time, it also magnifies the inconsistency of data . For example, someone directly queries data from the database at this time , But the updated data has not been written to the database , At this time, the queried data is not the latest data .
Summary
Different caching modes have different considerations and characteristics , According to the different scenarios of application requirements , You need to choose the appropriate cache mode flexibly . In the process of practice, it is often a combination of multiple modes .
About bloggers :《SpringBoot Technology insider 》 Technical book author , Love to study technology , Write technical dry goods articles .
official account :「 New perspective of procedure 」, The official account of bloggers , Welcome to your attention ~
Technical communication : Please contact blogger wechat :zhuan2quan

边栏推荐
- Message queue: how to handle repeated messages?
- What EDA companies are there in China?
- STM32 key state machine 2 - state simplification and long press function addition
- 苹果cms V10模板/MXone Pro自适应影视电影网站模板
- 如果不知道这4种缓存模式,敢说懂缓存吗?
- 解决pod install报错:ffi is an incompatible architecture
- JVM命令之 jinfo:实时查看和修改JVM配置参数
- Message queue: how to deal with message backlog?
- 【Shell】清理nohup.out文件
- Data storage 3
猜你喜欢
bat 批示处理详解
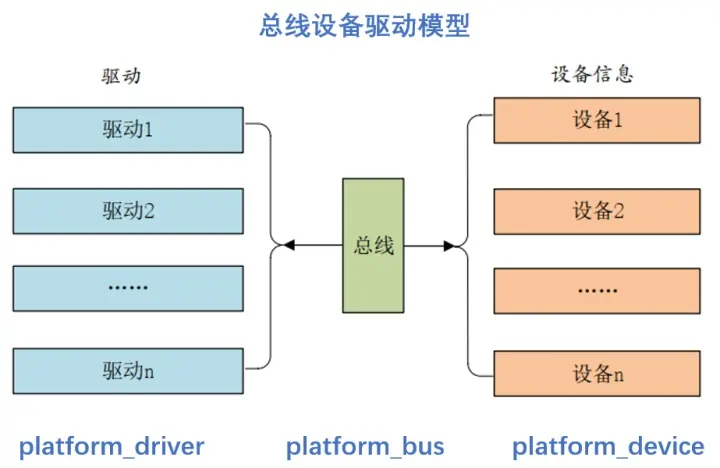
Detailed explanation of platform device driver architecture in driver development
《HarmonyOS实战—入门到开发,浅析原子化服务》
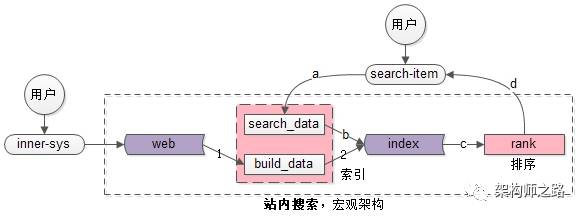
每秒10W次分词搜索,产品经理又提了一个需求!!!(收藏)
【FPGA教程案例14】基于vivado核的FIR滤波器设计与实现
![[cloud native] what is the microservice architecture?](/img/84/a0ec68646083f3539aa39ad9d98749.png)
[cloud native] what is the microservice architecture?
2pc of distributed transaction solution
OpenSergo 即将发布 v1alpha1,丰富全链路异构架构的服务治理能力
Mac version PHP installed Xdebug environment (M1 version)
Message queuing: how to ensure that messages are not lost
随机推荐
【SQL实战】一条SQL统计全国各地疫情分布情况
EMMC打印cqhci: timeout for tag 10提示分析与解决
【FPGA教程案例14】基于vivado核的FIR滤波器设计与实现
[shell] clean up nohup Out file
Digital IC interview summary (interview experience sharing of large manufacturers)
Hcip eighth operation
话说SQLyog欺骗了我!
Go语学习笔记 - gorm使用 - 原生sql、命名参数、Rows、ToSQL | Web框架Gin(九)
毕业之后才知道的——知网查重原理以及降重举例
VScode进行代码补全
[InstallShield] Introduction
win配置pm2开机自启node项目
STM32 key state machine 2 - state simplification and long press function addition
Reptile exercises (III)
目标检测中的BBox 回归损失函数-L2,smooth L1,IoU,GIoU,DIoU,CIoU,Focal-EIoU,Alpha-IoU,SIoU
【日常训练--腾讯精选50】292. Nim 游戏
SAP Spartacus checkout 流程的扩展(extend)实现介绍
Nodejs get client IP
目标检测中的损失函数与正负样本分配:RetinaNet与Focal loss
原生小程序 之 input切換 text與password類型