ForkJoin It is an important knowledge and skill in concurrent programming ,ForkJoin The parallel framework can easily use the computing power of multi-core processors to split concurrent tasks , It is suggested to focus on @mikechen
I'll start with ForkJoin Overall design of frame 、 principle 、 Algorithm 、 And use cases to fully explain ForkJoin.
ForkJoin brief introduction
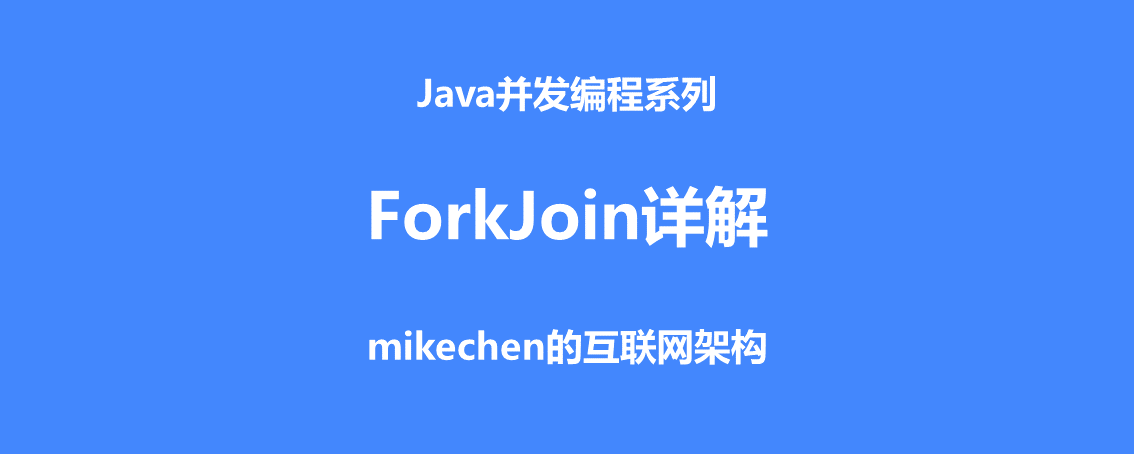
from JDK1.7 Start ,Java Provide ForkJoin The framework is used to perform tasks in parallel , Its idea is to divide a big task into several small tasks , Finally, summarize the results of each small task to get the results of this large task .
Job theft algorithm
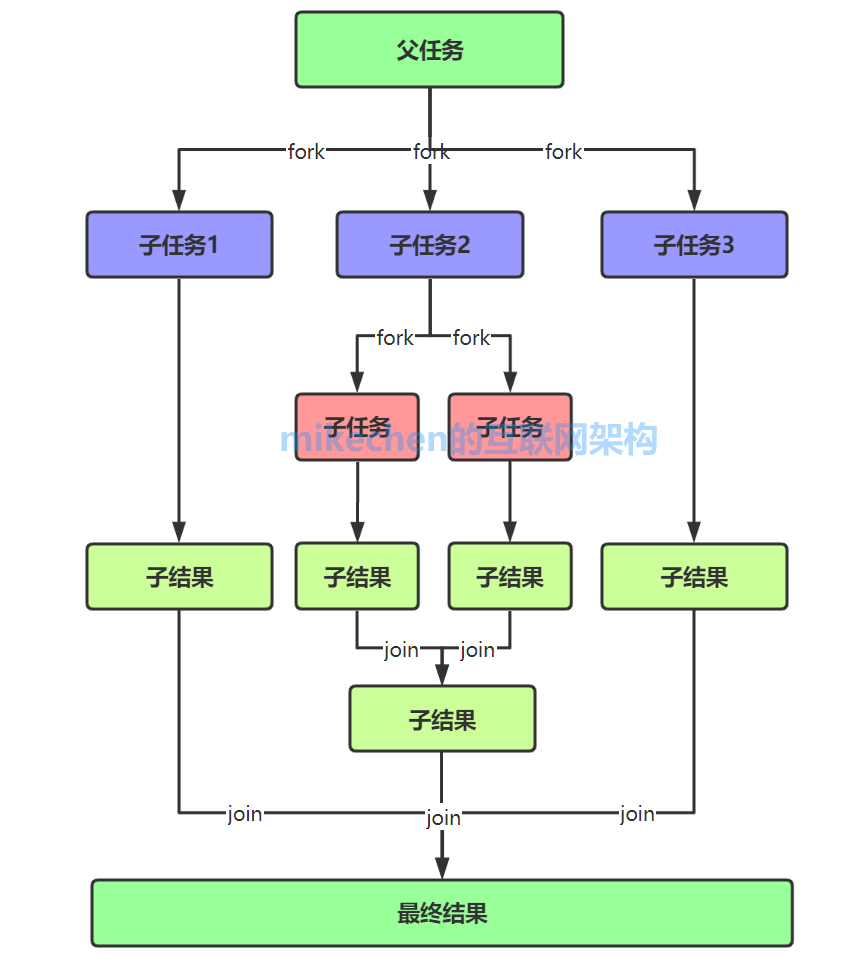
Fork/Join The framework adopts work stealing (work-stealing) Algorithm to achieve , The core of the algorithm is that a thread steals tasks from other queues to execute .
If we need to do a bigger task , We can divide this task into several independent sub tasks , To reduce the competition between threads , So I put these subtasks in different queues , And create a separate thread for each queue to perform the tasks in the queue , Threads and queues correspond one by one .
But some threads will finish the tasks in their queues first , There are tasks waiting to be processed in the queue corresponding to other threads , The thread that does the work is not waiting for , Why don't you help other threads , So it goes to the queue of other threads to steal a task to execute .
And at this point they access the same queue , So in order to reduce the competition between stealing task thread and being stolen task thread , We usually use a two terminal queue , The thread of the stolen task always takes the task from the head of the two terminal queue to execute , The thread that steals the task will always take the task from the end of the double end queue to execute , Its working principle is shown in the figure below :
Why use work stealing algorithm to realize ?
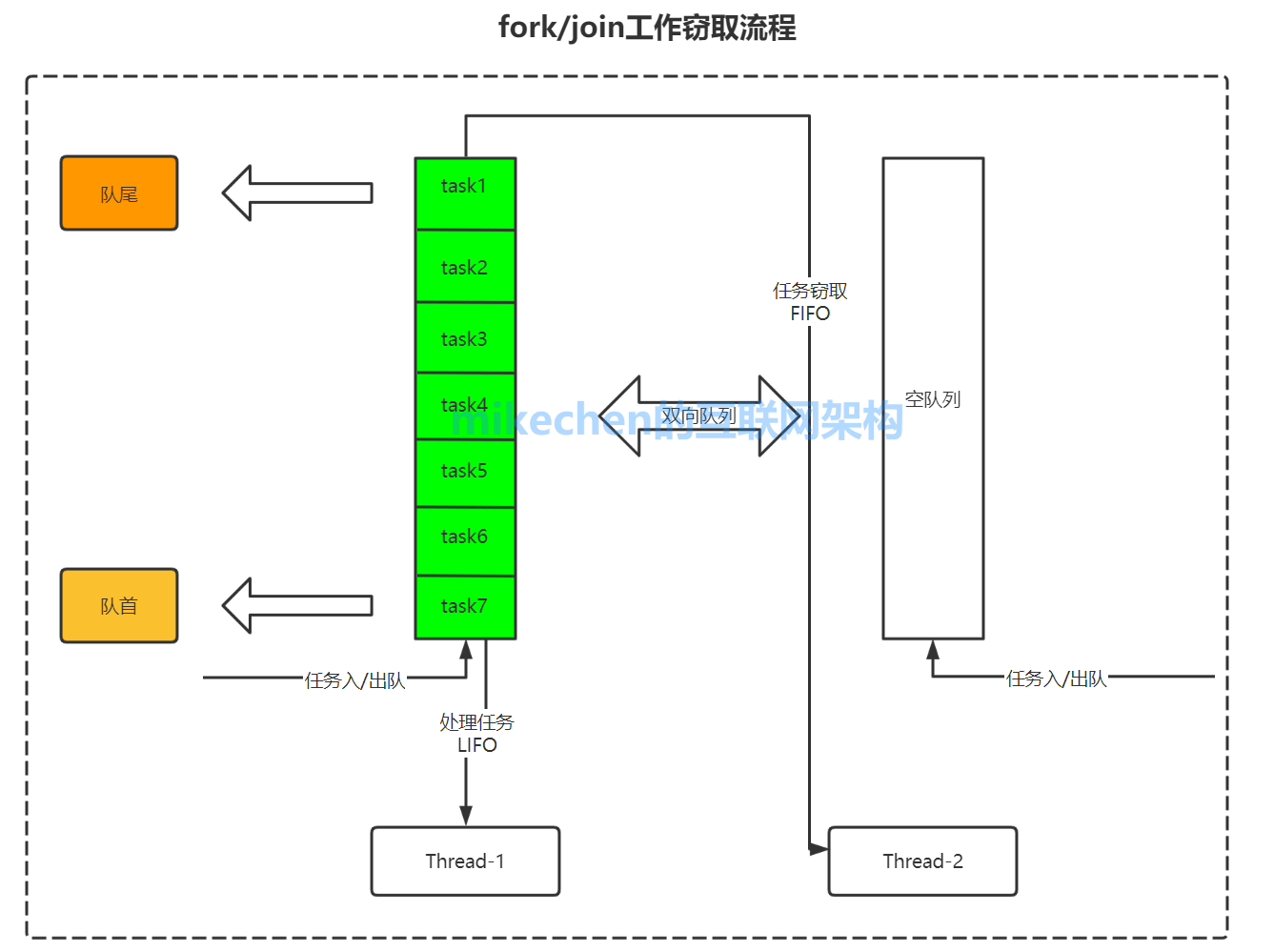
Because when we need to deal with a big task , We will divide this big task into several independent subtasks .
To reduce the competition between threads , We will put these subtasks in different queues , Then create a separate thread for each queue to execute the tasks in the queue , Threads and queues correspond one by one .
The execution efficiency of each thread varies , In order to improve efficiency , introduce “ Job theft algorithm ”, allow “ Fast thread ” steal “ Slow thread ” Task execution .
Work stealing algorithm makes full use of multithreading for Parallel Computing , Improved execution efficiency , At the same time, the use of double ended queues reduces the conflict and competition between threads , Then conflict cannot be completely avoided , For example, when there is only one task in a task queue , Two threads compete at the same time .
ForkJoin Core design
Except to understand ForkJoin The whole realization idea , You still need to understand ForkJoin What roles are defined to implement this framework , And understand the scope of these roles .
ForkJoin The core design class of the framework is : Mission (ForkJoinTask) And thread pool (ForkJoinPool), The flow chart of concurrent task execution is shown in the following figure :
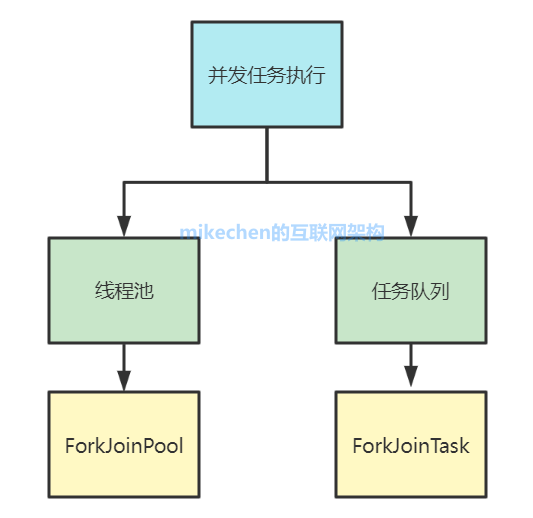
Now let's talk about the core functions of both .
ForkJoinPool
Since the task is gradually refined , Then you need to store these tasks in a pool , This pool is ForkJoinPool, act as fork/join Managers in the framework , The most primitive tasks can only be handled by it .
It is responsible for controlling the whole fork/join How many workerThread,workerThread The creation of , Activation is controlled by it .
It is also responsible for workQueue Creation and allocation of queues , Every time you create a workerThread, It is responsible for allocating the corresponding workQueue, Then it gives all the work it receives to workerThread To deal with , It can be said to be the whole frok/join The container of .
It is different from other ExecutorService The main difference is that it uses “ Job theft “, Main management ForkJoin The execution of threads in the framework .
ForkJoinTask
We're going to use ForkJoin frame , You must first create a ForkJoin Mission , And this class is one that will be in ForkJoinPool The base class of the task executed in .
ForkJoin The framework provides the ability to execute in one task fork and join Mechanism of operation and method of controlling task state .
Usually , In order to achieve Fork/Join Mission , You need to implement a subclass of one of the following two classes ( Inherited from ForkJoinTask).
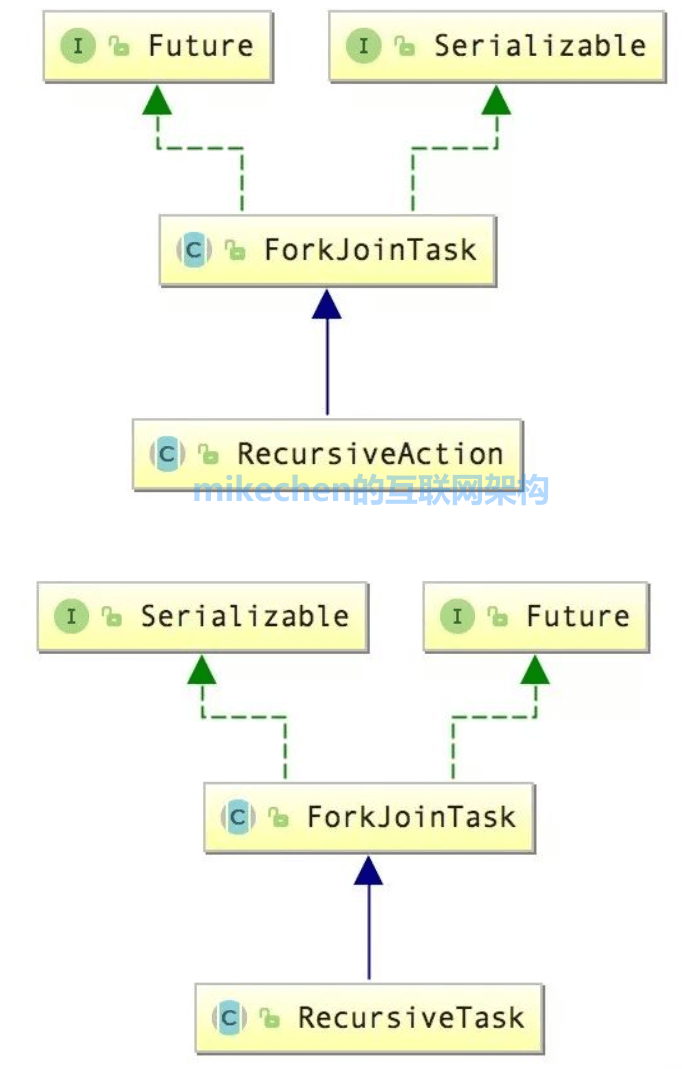
Its two subclasses are :RecursiveAction、RecursiveTask, Let's briefly talk about the difference between the two .
RecursiveAction: It is ready-made in the concurrent package ForkJoinTask Implementation one , Inherited from ForkJoinTask, Handle tasks that do not need to return results .
RecursiveTask: It is also ready-made in the concurrent package ForkJoinTask Implementation one , Inherited from ForkJoinTask, Be responsible for dealing with tasks that need to return results .
The difference between the two is RecursiveTask The task has a return value ,RecursiveAction no return value , The following is the class diagram relationship structure of the two :
The above mainly talks about ForkJoin The core design of concurrent task execution , Now let's see how to use ForkJoin.
ForkJoin Use case of
Before use , We need to remember two concepts :
ForkJoinTask, We need to define one of our own ForkJoinTask, Used to define the tasks we need to perform , It can inherit RecursiveAction perhaps RecursiveTask, To obtain fork and join Ability to operate , The former means that no return value is required , The latter requires a return value .
ForkJoinPool Similar to thread pool , The concept of connection pool ,ForkJoinTask All need to be handed over to ForkJoinPool To perform .
We use an example of summation to illustrate ForkJoin The process of , Now we have to be right 1 To 8 Sum the integers of , The code is as follows :
package com.mikechen.concurrent.other;import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;import java.util.concurrent.Future;import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask; /** * ForkJoin Calculation 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8 * * @author mikechen */public class ForkJoinTaskTest extends RecursiveTask<Integer> { public static final int threshold = 2; private int start; private int end; public ForkJoinTaskTest(int start, int end) { this.start = start; this.end = end; } @Override protected Integer compute() { int sum = 0; // If the task is small enough, calculate the task boolean canCompute = (end - start) <= threshold; if (canCompute) { for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { sum += i; } } else { // If the task is greater than the threshold , Split it into two subtasks int middle = (start + end) / 2; ForkJoinTaskTest leftTask = new ForkJoinTaskTest(start, middle); ForkJoinTaskTest rightTask = new ForkJoinTaskTest(middle + 1, end); // Perform subtasks leftTask.fork(); rightTask.fork(); // Its merge task is finished int leftResult = leftTask.join(); int rightResult = rightTask.join(); // Merge subtasks sum = leftResult + rightResult; } return sum; } public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool forkjoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); // Generate a calculation task , Calculation 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8 ForkJoinTaskTest task = new ForkJoinTaskTest(1, 8); // Perform a task Future<Integer> result = forkjoinPool.submit(task); try { System.out.println(result.get()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}We are compute Define the granularity of task splitting and the execution logic of minimum task , And pass fork and join Ability to achieve multithreading concurrency , When the subtask calls fork When , Will continue to perform the subtask compute, When the subtask calls join When , Will wait for the implementation results of all their descendants' tasks .
Here is the 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8 This big task was finally divided into four sub tasks , As shown in the figure below :
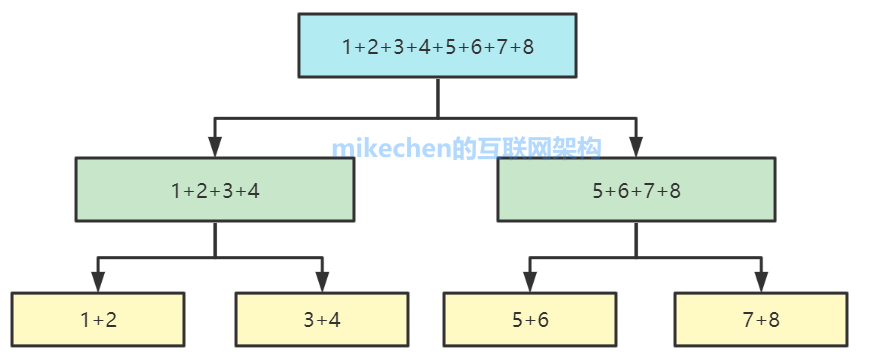
Recursion separately fork Keep splitting , Become four subtasks :
- 1+2
- 3+4
- 5+6
- 7+8
Finally, wait for the completion of the subtask , Merge to get the final execution result .
ForkJoin Summary
ForkJoin Using divide and conquer algorithm , The main principle is to split a large task into several small tasks and distribute them to several threads for processing , Finally, the results of several threads are summarized , So as to improve the calculation efficiency .
ForkJoin It is a simple and efficient design technology that can achieve good parallel performance , The purpose is to help us make better use of the parallel computing power of multiprocessors to improve the performance of applications .
I'll start from ForkJoin Design principle of 、 And then to the algorithm 、 And use cases for complete explanation , I hope it helped you !
ForkJoin It is an important knowledge and skill of concurrent programming , If you want to know more about Java Content of concurrent programming , You can click to view :Java Multi line and concurrent programming from 0 To 1 All collections
above !
Focus on 「mikechen Internet Architecture 」 official account , reply 【 framework 】 Get my original 《300 period +BAT Architecture technology series and 1000+ Answers to interview questions of Dachang 》

![R language [logic control] [mathematical operation]](/img/93/06a306561e3e7cb150d243541cc839.png)


![Paper reading [MM21 pre training for video understanding challenge:video captioning with pre training techniqu]](/img/9c/1f031400f0e201df47bd51547ff73f.png)