当前位置:网站首页>OSPF message details - LSA overview
OSPF message details - LSA overview
2022-07-06 11:56:00 【Gucheng 286】
Catalog
Two 、LSA message —— Link status notification
One 、OSPF Message details :
——【{ Second layer frame header }+{IP Head }+【{OSPF Head ]+{OSPF data }】
----【224.0.0.0~~224.0.0.255】 These are multicast addresses , Of these multicast addresses TTL All for 1
----hello message : Build and maintain OSPF Neighbor's , formation OSPF Neighborhood watch ; Purpose IP Address :224.0.0.5
----IP Inside the head : Purpose IP The address is 224.0.0.5,IP The priority defaults to 6;TTL The default is 1; Agreement No :89
(1)———OSPF Head analysis :
——version: 2---IPV4 Under the OPSF 3---ipv6 Under the OSPF
——message type: 1--hello 2--LSDBD 3---LSR 4--LSU 5--LSACK
——packet length: Packet size
——source OSPF router:. The sender's RID 【OSPF Between neighbors RID identical ,OSPF Neighbors can't get up 】
——area id: The area of the sender interface ID【 Direct link , Area ID atypism ( Two regions ),OSPF Neighbors can't get up 】
——packet check: Parity check
——auth type: 0-- No certification 1-- Plaintext Authentication ﹑2--MD5 authentication 【 Authentication type and key are inconsistent ,OSPF Neighbors can't get up 】
——auth data: What is stored is the authentication information
(2)———hello Field analysis :
—— Interface mask ; Interface IP The mask of the address 【 At the Ethernet interface , Masks between direct links are inconsistent OSPF Neighbors can't get up 】
——hello Sending interval :10/30 【10—— The radio type ,30——NBMA type ,hello The sending interval is inconsistent with the death timeout OSPF Neighbors can't get up 】
—— optional :DN O DC L NP MC E MT
—— Interface priority :1 If you need to choose DR and BDR, But the interface priority is 0, Neighbors can't get up
——hello The time of death :40/120
——DR The address of :
——BDR The address of :
—— neighbor ID:
—— Their own RID:
——————————————————————————-——-————-—————————-----————————
Two 、LSA message —— Link status notification
(1)——— brief introduction :
Describe which interfaces are enabled OSPF, This interface's OSPF Link type , Network segment and mask , cost Value and so on ;【 You can understand LSA It is a routing representative 】
LSA It represents a router routing entry , But this route entry is represented in the form of a database .
LSA Refresh time : This LSA Who produced , Who is responsible for every 30 Minutes for this LSA Regenerate an update ;
LSA Aging time : LSA The maximum storage time in the database ,1 Hours , Subtract... Every second 1, If you can't get a refresh in an hour , Aging time becomes 0, This LSA It will be deleted from the database and flooded , Inform others OSPF Neighbors delete this aging LSA【 Routing changes 】
LSA Update conditions : 1、 Every time 30 Minutes to refresh 2、 When my router is running OSPF The interface of has changed , It will also trigger incremental updates ,LSA Your serial number will +1( The interface has just been enabled OSPF Sometimes ), This is the latest LSA.
LSA Part of the ( Every LSA They all have the same LSA Header information ):
(2)——— Header information :
——LS age : Aging time 【1800 second (30 minute )~~~3600 second ( An hour )】, among 1800 It's cyclical LSA Refresh time ,3600 yes LSA Maximum aging time
——Options : optional DN O DC L NP MC E MT
——LS Type : What we are talking about is how many kinds of data are LSA
——Link State ID : Link state ID, It's a variable , According to LSA type , The values in this place are also different
——Advertising Router : Notification routing , This LSA Who made it , Just take this router RID Written here
——LS Seq Number : LSA The serial number of , Use this serial number to determine whose LSA Is the latest ,LSA Every update , Serial number +1
——Checksum : Parity sum , Used to verify the integrity of data transmission
——Length : It contains the total length of header information and data part
——Number of Links : Several interfaces of my router are enabled OSPF
(3)——— Data section :
LSA-1,LSA-2, LSA-3,LSA-4,LSA-5,LSA-7
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Five basic data packages :
| HELLO | The neighbor's discovery 、 establish 、 Keep alive |
|---|---|
| LSDBD | Database description package – Database directory information |
| LSR | Link status request |
| LSU | Link status update — Carry all kinds LSA |
| LSACK | Link status confirmation |
The above is only a personal point of view , If there is a mistake , Also please indicate ! Feel free to leave a comment !
边栏推荐
- MySQL and C language connection (vs2019 version)
- RT-Thread的main线程“卡死”的一种可能原因及解决方案
- Contiki源码+原理+功能+编程+移植+驱动+网络(转)
- TypeScript
- Using LinkedHashMap to realize the caching of an LRU algorithm
- C语言函数之可变参数原理:va_start、va_arg及va_end
- Stage 4 MySQL database
- E-commerce data analysis -- User Behavior Analysis
- 互联网协议详解
- Apprentissage automatique - - régression linéaire (sklearn)
猜你喜欢
![[Blue Bridge Cup 2017 preliminary] grid division](/img/e9/e49556d0867840148a60ff4906f78e.png)
[Blue Bridge Cup 2017 preliminary] grid division
wangeditor富文本引用、表格使用问题

B tree and b+ tree of MySQL index implementation
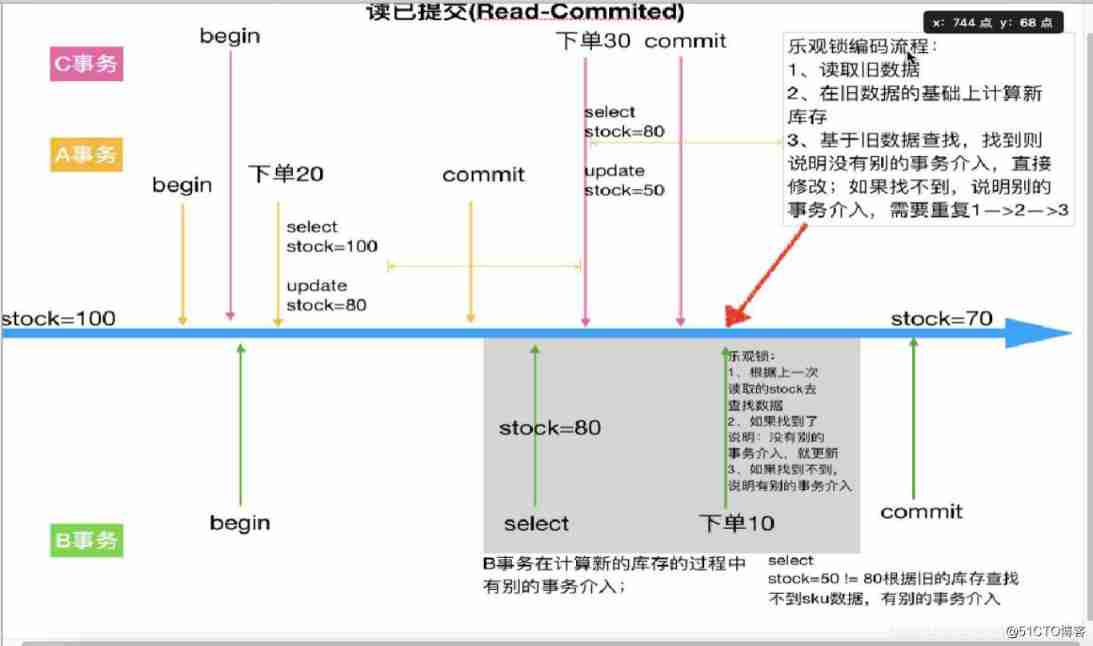
Mall project -- day09 -- order module

Connexion sans mot de passe du noeud distribué
Reading BMP file with C language

2019腾讯暑期实习生正式笔试
![[Flink] Flink learning](/img/2e/ff53e0795456e301f61da908c013af.png)
[Flink] Flink learning

Linux yum安装MySQL
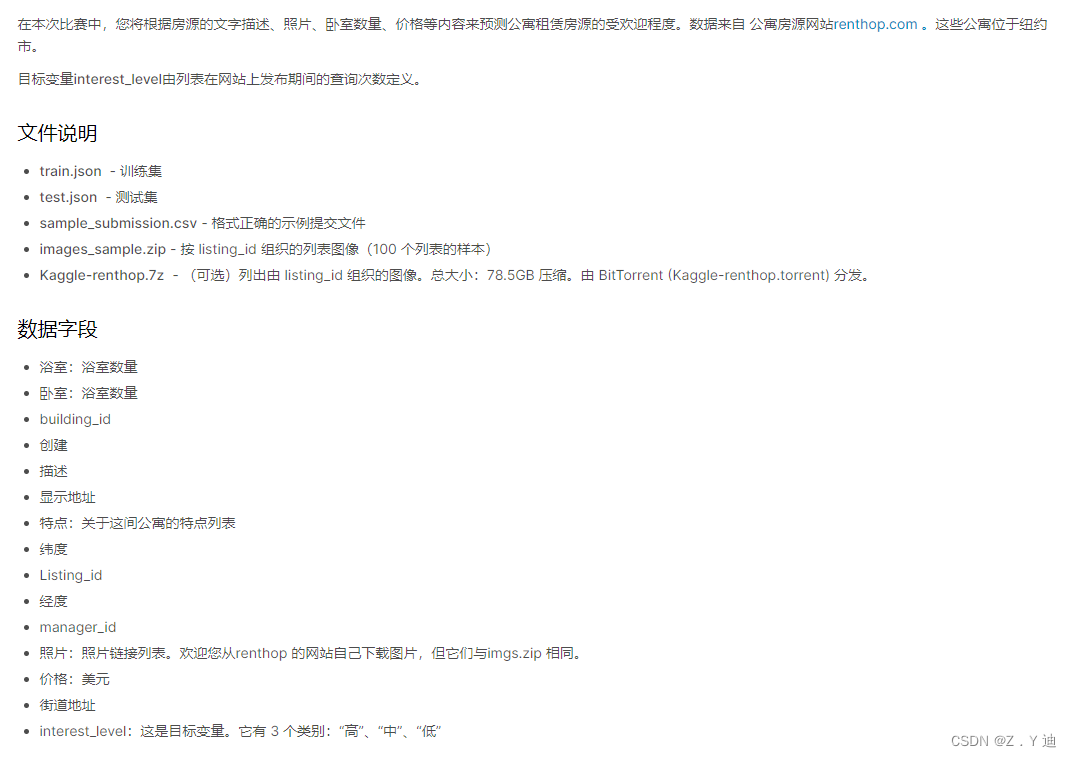
Kaggle竞赛-Two Sigma Connect: Rental Listing Inquiries
随机推荐
[BSidesCF_2020]Had_ a_ bad_ day
Gallery之图片浏览、组件学习
Mtcnn face detection
互聯網協議詳解
SQL时间注入
Pytorch-温度预测
2020 WANGDING cup_ Rosefinch formation_ Web_ nmap
Dependency in dependencymanagement cannot be downloaded and red is reported
MongoDB
C语言函数之可变参数原理:va_start、va_arg及va_end
Redis interview questions
优先级反转与死锁
Detailed explanation of express framework
XML file explanation: what is XML, XML configuration file, XML data file, XML file parsing tutorial
Vs2019 use wizard to generate an MFC Application
小L的试卷
E-commerce data analysis -- User Behavior Analysis
{一周总结}带你走进js知识的海洋
JS array + array method reconstruction
[Kerberos] deeply understand the Kerberos ticket life cycle