当前位置:网站首页>Matlab learning 2022.7.4
Matlab learning 2022.7.4
2022-07-05 13:49:00 【megaData】
I used my vacation time to pass 《MATLAB Application encyclopedia 》 And Related videos to learn matlab
Common commands :
clc Used to clear the contents of the command line window
clear Used to clear variables in the workspace
whos Used to display the details of variables
who Used to list the names of variables in the workspace
Use percent sign % Annotate the program
data type :
a1 = int8(6)
a2 = int16(-20)
%int32 int64 Is a signed integer
a3 = uint32(100)
a4 = uint64(200)
%uint8 uint16 Is an unsigned integer
b1 = single(3.5)
% Single precision floating point
b2 = 12
% The default is double precision floating point double
c1 = true
%logical Logical type
c2{1,1}=100
% Is the cell array type cell
c3='hello'
%char Is string type
c4.name='robin'
% Is the structure type
[email protected]
%function_handle Is the function handle type
value type :
stay matlab among , The default value type is double precision floating point
a = 24
% The default variable is double precision floating point
b1 = int8(a)
b2 = int16(a)
b3 = int32(a)
b4 = int64(a)
c = 'hello'
int8(c)
% Convert string to 8 An integer
By function intmin() and intmax() To get the value range of integers
Rounding function of floating point numbers :
round()、fix( towards 0 integer )、floor( Not greater than this number )、ceil( Not less than this number )
a1 = round(2.5)
a2 = round(-2.4)
a3 = round(-2.5)
b1 = fix(-3.6)
b2 = fix(-3.5)
c1 = floor(-4.2)
c2 = floor(4.9)
d1 = ceil(4.2)
d2 = ceil(-4.4)
a = 123.34
b = single(a)
c1 = double(a)
c2 = int16(a)
c3 = int32(a)
d1 = [realmin('single') realmax('single')]
d2 = [realmin('double') realmax('double')]
% By function realmin() and realmax() You can get the value range of single precision and double precision floating-point numbers Use complex(a,b) To create a complex number (a It is the real part ,b It is the imaginary part )
z1 = 3+4i
a1 = real(z1)
% Get the real part
a2 = imag(z1)
% Get the imaginary part
b1 = abs(z1)
% Get the module of the complex number
b2 = angle(z1)
c1 = conj(z1)
% Get conjugate complex
z2 = complex(1:3,2:4)
real(z2)
imag(z2)
Using functions format() To determine the display format of numeric type
The default display is :format short After decimal point 4 position
format short
a = 12.3456789
format short
a
format long
a
format long e
a
format short e
a
format bank
a
format +
a
format rational
a
format short
% Restore to the system default display format Logical type :
a1 = true
a2 = false
a3 = true(3,4)
a4 = false(3)
clear all
a = 3
logical(a)
b=0
logical(b)
c = [1.3 -3 0;2 0 4;0.01 9 1]
logical(c)
% Convert numeric type to logical type
character :
a = 'My name is zhangsan'
b = char([65 66 67 68])
c = int8('hello')
d =' Zhang '
clear all
Use function handles to call functions indirectly
% Function handle
f1 = @cos
t = 0:pi/5:pi
f1(t)
f2 = @complex
f2(3,4)
clear all
f1 = @char
s1 = func2str(f1)
f2 = str2func(s1)
functions(f1)
isa(f1,'function_handle')
isequal(f1,f2)
clear all
边栏推荐
- asp.net 读取txt文件
- redis6主从复制及集群
- 我为什么支持 BAT 拆掉「AI 研究院」
- MySQL get time
- 2022司钻(钻井)考试题库及模拟考试
- Binder communication process and servicemanager creation process
- ::ffff:192.168.31.101 是一个什么地址?
- Mmseg - Mutli view time series data inspection and visualization
- Parsing XML using Dom4j
- Kotlin协程利用CoroutineContext实现网络请求失败后重试逻辑
猜你喜欢
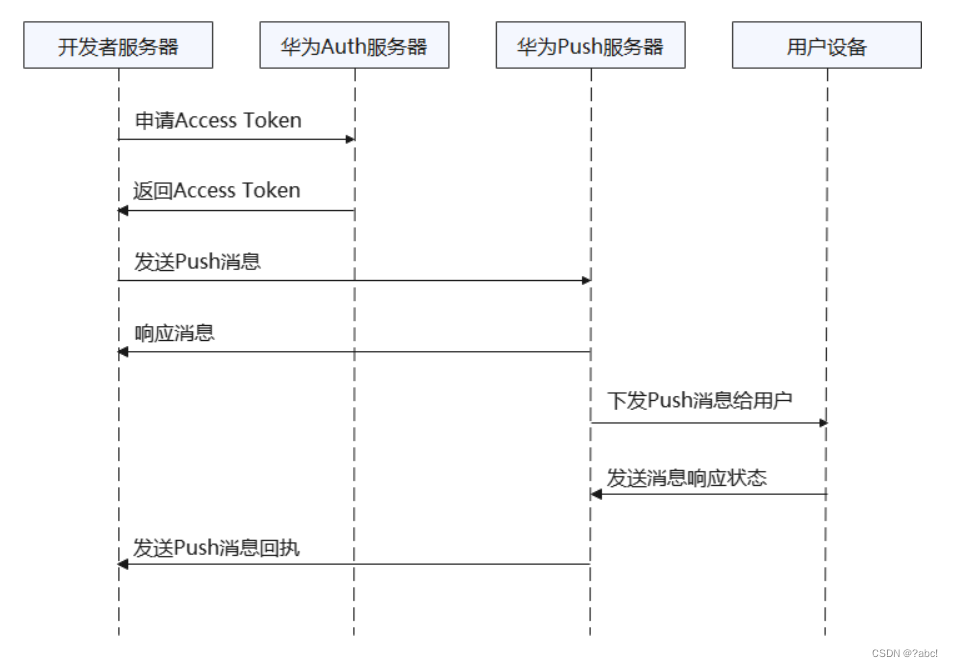
Huawei push service content, read notes
![Primary code audit [no dolls (modification)] assessment](/img/b8/82c32e95d1b72f75823ca91c97138e.jpg)
Primary code audit [no dolls (modification)] assessment
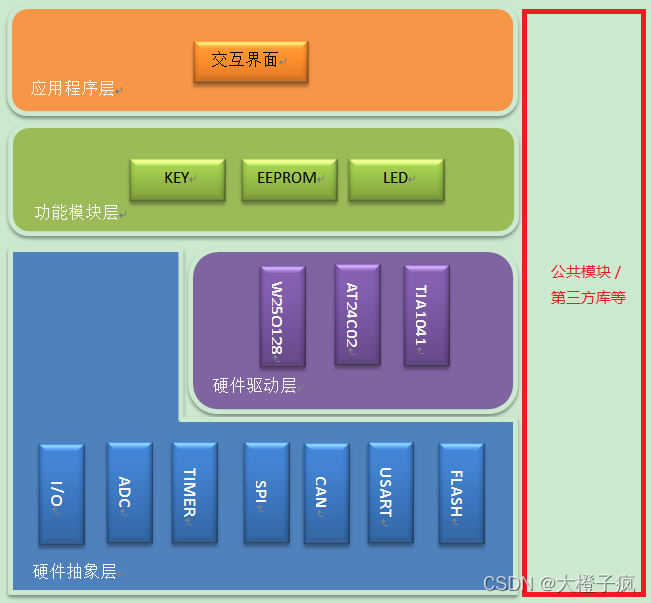
Embedded software architecture design - message interaction
TortoiseSVN使用情形、安装与使用

Those things I didn't know until I took the postgraduate entrance examination
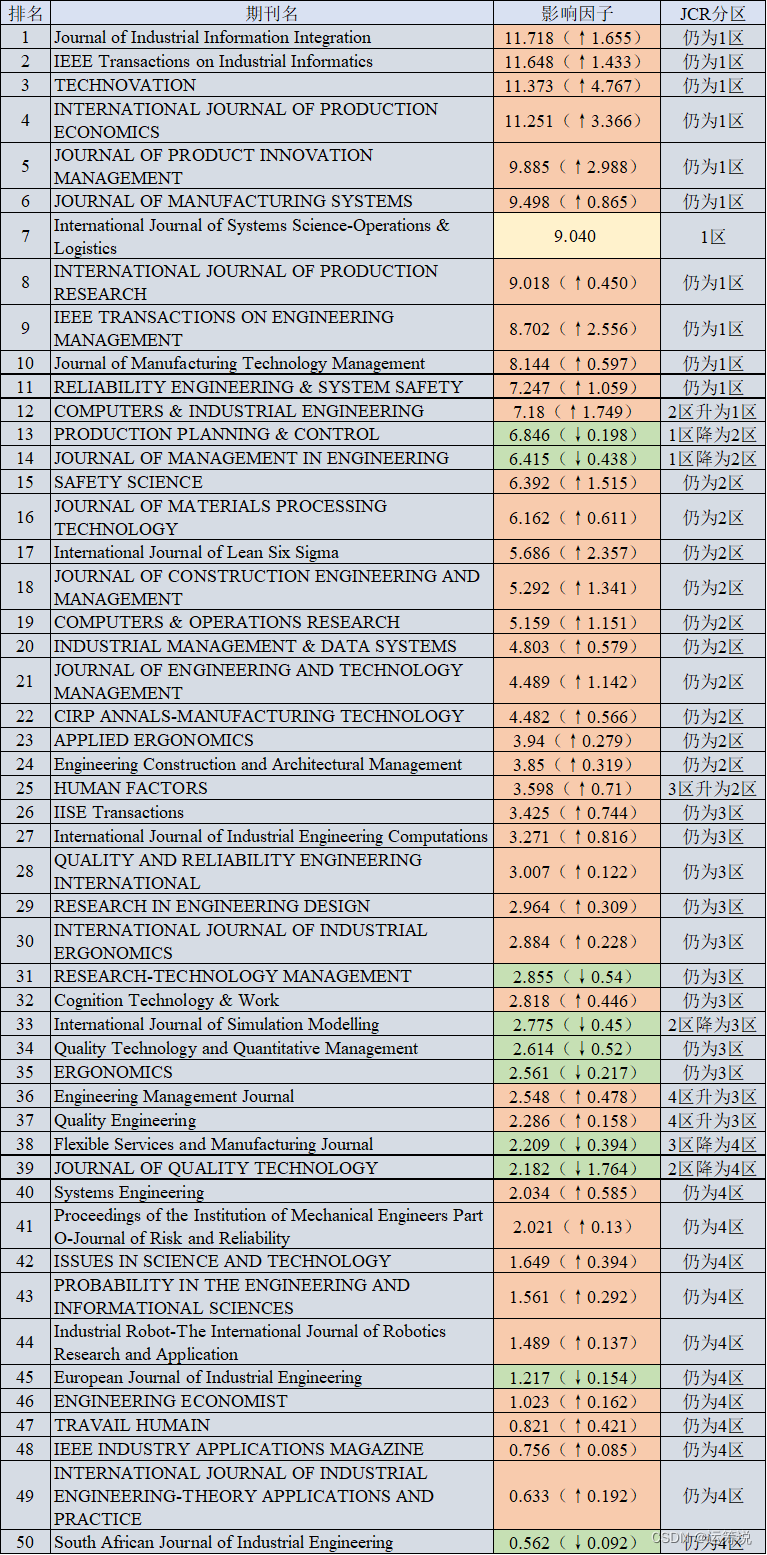
运筹说 第68期|2022年最新影响因子正式发布 快看管科领域期刊的变化

Kotlin协程利用CoroutineContext实现网络请求失败后重试逻辑

Solve the problem of invalid uni app configuration page and tabbar
How to apply the updated fluent 3.0 to applet development
stm32逆向入门
随机推荐
Data Lake (VII): Iceberg concept and review what is a data Lake
Kotlin协程利用CoroutineContext实现网络请求失败后重试逻辑
Self built shooting range 2022
Integer = = the comparison will unpack automatically. This variable cannot be assigned empty
2022司钻(钻井)考试题库及模拟考试
[notes of in-depth study paper]transbtsv2: wider instead of deep transformer for medical image segmentation
Nantong online communication group
::ffff:192.168.31.101 是一个什么地址?
MySQL if else use case use
Primary code audit [no dolls (modification)] assessment
Godson 2nd generation burn PMON and reload system
asp.net 读取txt文件
研究生可以不用学英语?只要考研英语或六级分数高!
aspx 简单的用户登录
web3.eth. Filter related
Attack and defense world web WP
zabbix 监控
Elk enterprise log analysis system
NFT value and white paper acquisition
[js] basic syntax - for loop