当前位置:网站首页>Redis6 master-slave replication and clustering
Redis6 master-slave replication and clustering
2022-07-05 13:31:00 【Do you know what a code monster is?】
Catalog
It's passed down from generation to generation
Master slave copy
After the host data is updated, according to the configuration and Policy , Automatic synchronization to the standby machine master/slaver Mechanism ,Master Write first ,Slave Mainly reading , It can realize the separation of reading and writing , Performance expansion . Disaster recovery and rapid response .
The host does write operations , Read from the machine .
Set up process
(1) stay Linux Create a new folder in the system , Copy a configuration file redis.conf Go to this folder . Will copy appendonly Set to no.
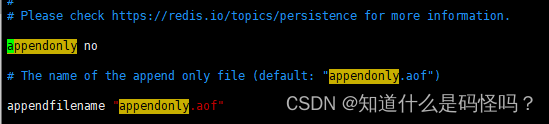
(2) In the file created in the first step , Create multiple redis The configuration file , introduce redis.conf, Set the port number port ,pid File name pidfile , Persistent file name dbfilename . Only the numbers in the three documents are different , The rest are the same .
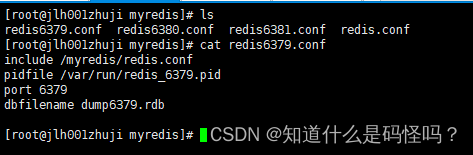
(3) Start created redis The server , Three session windows are connected separately 3 individual redis The server .
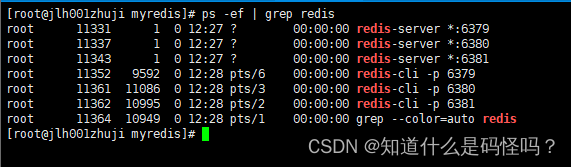
View system progress , Three redis The server has started and three connections have been established .
(4) Enter info replication Check the operation of the three hosts , It is found that there is no master-slave relationship , every last redis Servers are hosts .
info replication 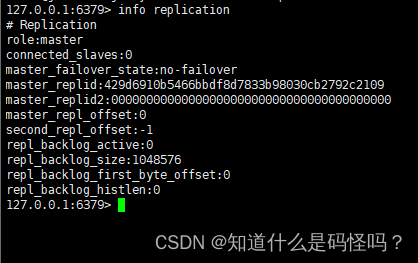
(5) Establish a master-slave relationship , Input slaveof host IP Port number .
slaveof < host IP> < Port number >Check the slave information again , It is found that there is already a host IP And port
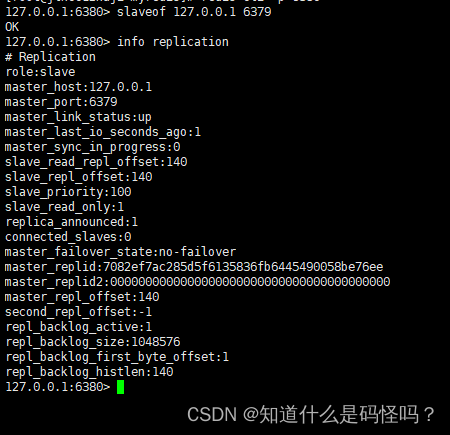
View host information , Display the number of slave connections 2 individual .
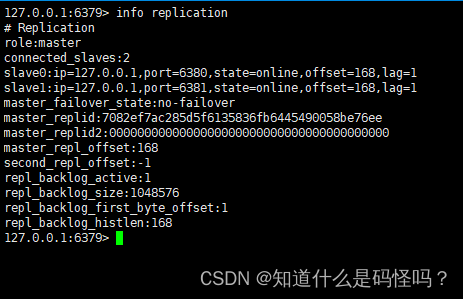
(6) The host writes , The slave can synchronize data , And the slave cannot write .
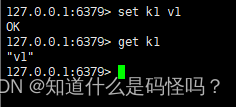
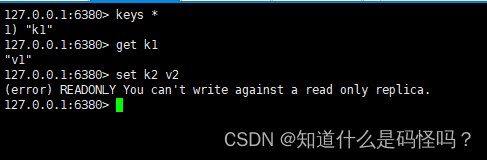
The principle of replication
Copy in full : After receiving the database file data from the slave , Save it and load it into memory .
Incremental replication : The host transmits all newly collected modification commands to the slave in turn , Complete synchronization .
One master and many servants
seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , One master connects multiple slaves .
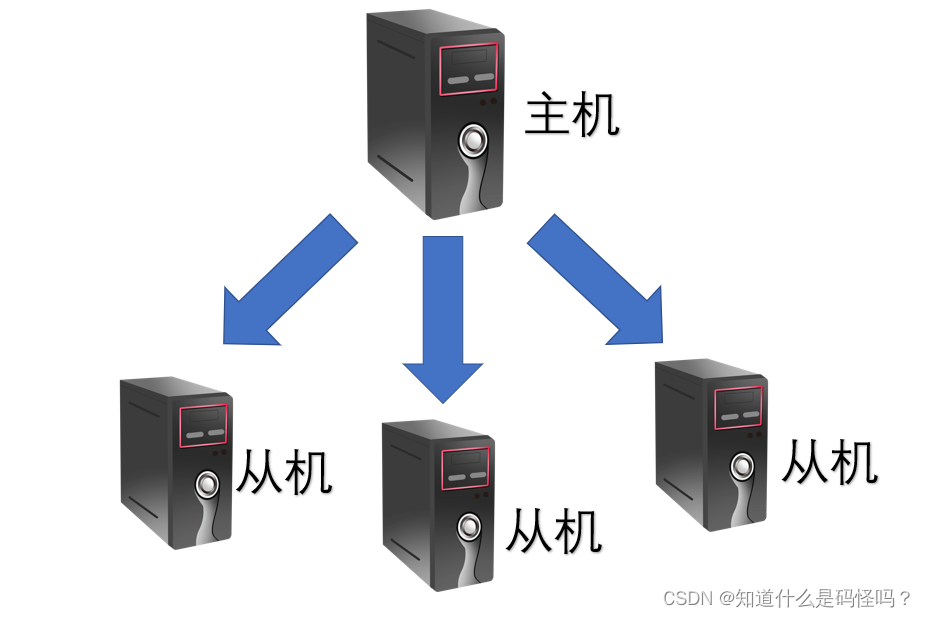
The copying process :(1) When the master-slave relationship is established between the slave and the host , The slave sends a data synchronization request to the host (2) The host will persist the current data after receiving the request , Then send the persistent file to the slave , Reading from the machine completes synchronization .(3) After the host adds data , The host sends the new data to the slave for data synchronization , The slave only applies for data synchronization when it is connected , In the rest of the time, the host takes the initiative to send .
It's passed down from generation to generation
The slave of the host can also be the host of other servers .
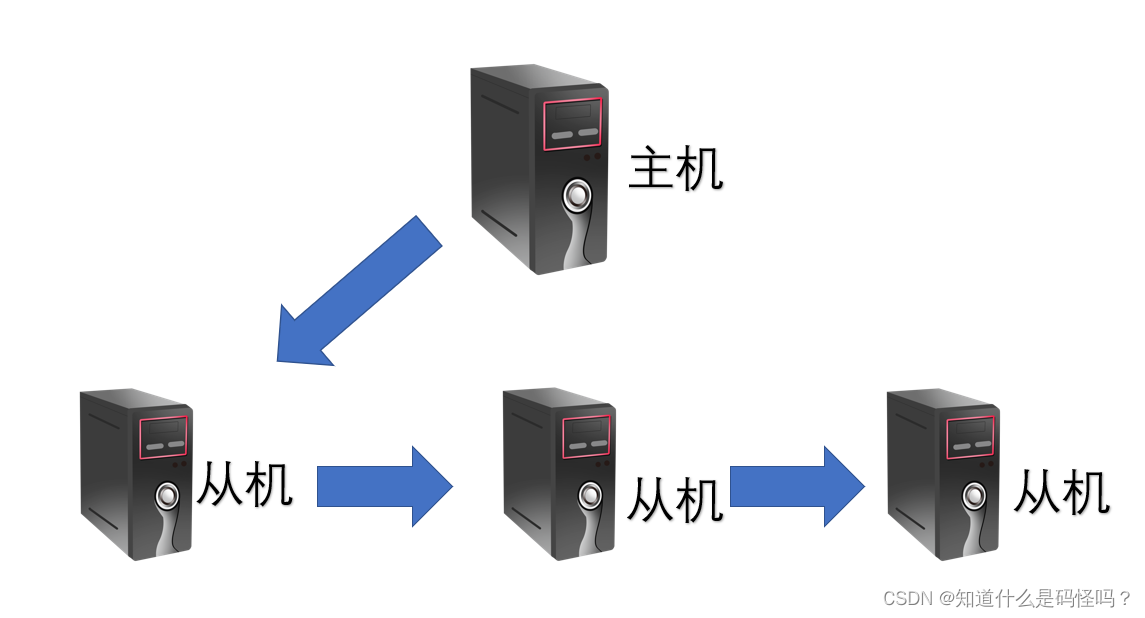
The copying process : The master is connected to the slave , The slave can also be the host of other servers . Be similar to java The inheritance relationship . When the host modifies the information , From the machine to update the data of other servers .
Going to
Host down , Slave host .
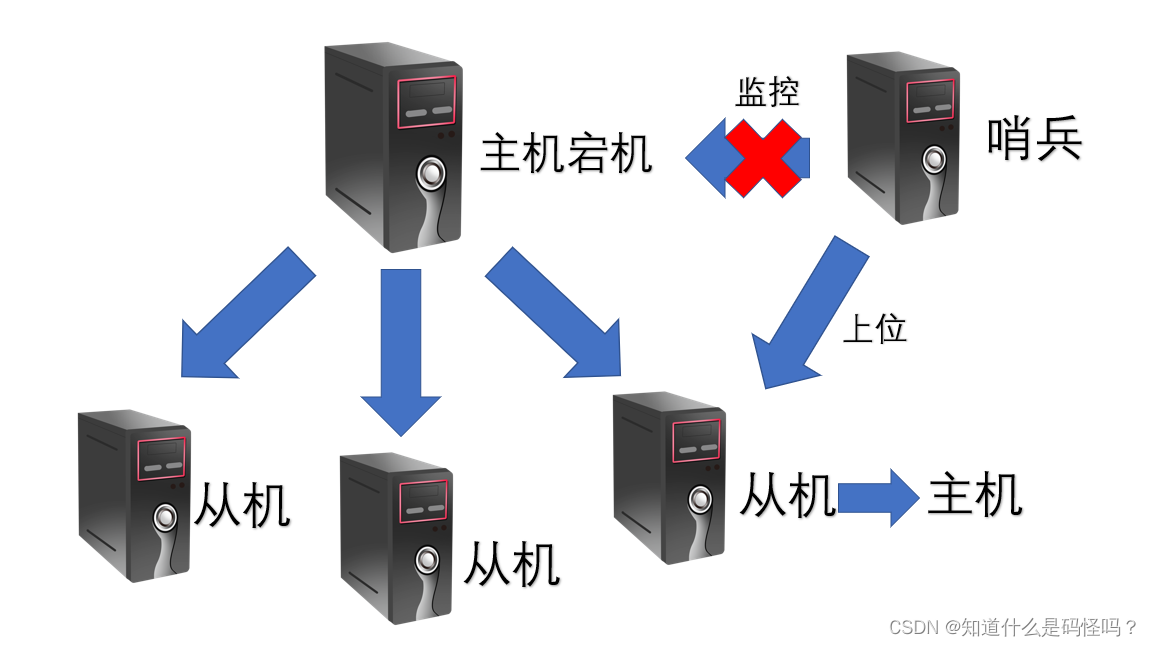
When the host goes down , The slave can be upgraded to the host , By inputting the following line of code in the slave .
slaveof no oneYou can automatically monitor the host by setting sentinels , When the host goes down, the slave is automatically promoted to the host , There is no need to set it manually .
Problem analysis
From the machine down
(1) After hanging up from the machine , Restart the slave , Slaves exist in the form of hosts , It is not the slave of the previous master .
(2) If the host adds new data during the period when the slave hangs up , After restarting the slave and establishing the master-slave relationship , The data of the slave is still consistent with that of the host .
(3) After the slave is restarted , The data added before the master-slave relationship is established with the host will disappear after the relationship is established , And then the data of the host will be preserved .
Host down
(1) After the host computer is down , The master remains unchanged in the slave display information , Just the state changes to down.
(2) Restart the host , Still the primary server .
colony
Redis The cluster has realized to Redis Horizontal expansion of , Start now N individual redis node , The entire database is distributed and stored here N A node in the , Each node stores the total data 1/N.
Redis Clusters are partitioned (partition) To provide a certain degree of usability (availability): Even if some nodes in the cluster fail or fail to communicate , The cluster can also continue to process command requests .
Set up the cluster
(1) Create a new folder in the master-slave relationship , modify redis6379.conf The content of the document , Add the following information . And copy 5 Share .
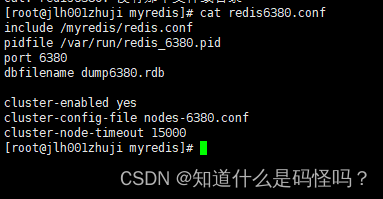
cluster-enabled yes Open cluster mode
cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf Set the node profile name
cluster-node-timeout 15000 Set the node loss time , Beyond that time ( millisecond ), The cluster automatically switches between master and slave .
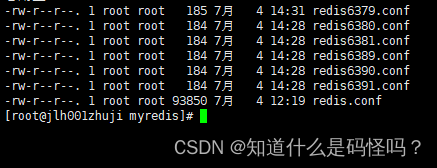
Modify the numbers in each copy of the data .
(2) Start this 6 individual redis service , And synthesize a cluster .
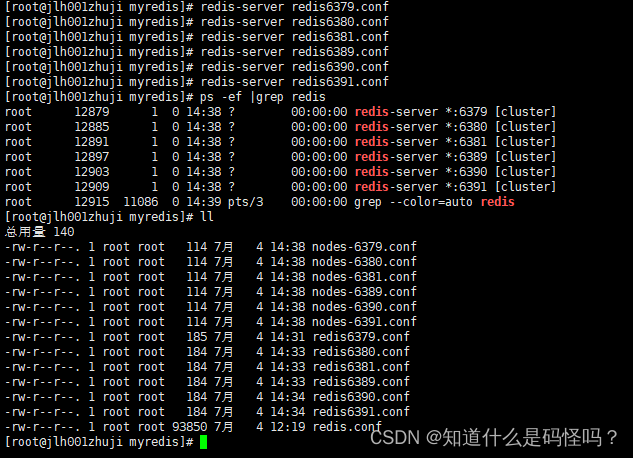
Enter into redis Install under directory src In the folder , Execute the following command , The command means to set up a cluster in the simplest way , A master node , A slave node corresponds one by one . The allocation principle tries to ensure that each master database runs on different servers IP Address , Each slave library and master library are not in one IP Address .
redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 <ip>:< port > <ip>:< port >Successful cluster construction
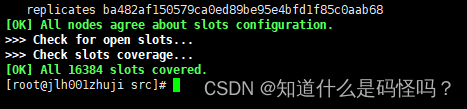
(3) Connect clusters , View cluster information .
Use the following instructions to connect to the cluster
redis-cli -c -p 6379Use the following instructions to view the cluster node information
cluster nodes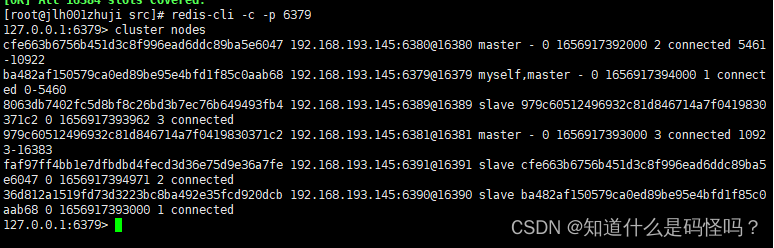
Cluster operation
After the cluster is built successfully ,redis The number of slots in this cluster will be displayed , namely slot.
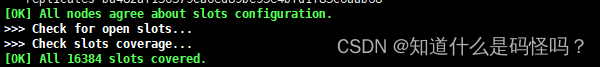
One Redis The cluster contains 16384 Slots (hash slot), Every key in the database belongs here 16384 One of the slots , The cluster uses the formula CRC16(key) % 16384 To calculate the key key Which slot does it belong to , among CRC16(key) Statements are used to evaluate keys key Of CRC16 The checksum .
Each node in the cluster is responsible for processing a portion of the slots . for instance , If a cluster can have a master node , among :
node A Responsible for handling 0 No. to 5460 Slot number .
node B Responsible for handling 5461 No. to 10922 Slot number .
node C Responsible for handling 10923 No. to 16383 Slot number .
Store the data
Test case 1 : Add data
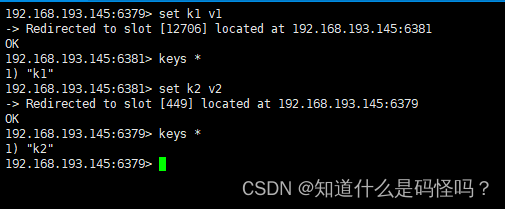
We are 6379 The port corresponds to redis Add data to the server , Finally added to 6381 Under port , stay 6381 Data added under port , Again 6379 Add below .
This is because redis take key adopt CRC16 Statement calculates the checksum , According to the checksum and 16384 To get the result of the remainder , To select different servers to add data .
Test case 2 : Multi key operation
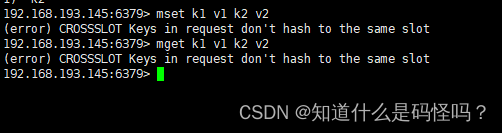
slot Different key values , Can't use mget,mset Wait for multi key operation .
Test case 3 : Group storage
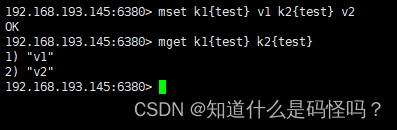
have access to {} To define the concept of a group , Give Way key in {} Key value pairs with the same content in the same slot in .
Reading data
Test case 1 : Reading data
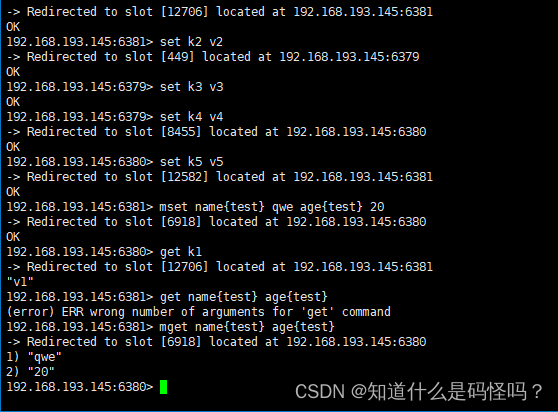
Different key, You need to get data from the corresponding node .
Test case 2 : of key and slot The operation of
see key Corresponding slot
cluster keyslot <key>see slot How many key( Only those within the current node can be viewed slot)
cluster countkeysinslot <slot>return count individual slot Key in groove ( Only those within the current node can be viewed slot)
cluster getkeysinslot <slot> <count> 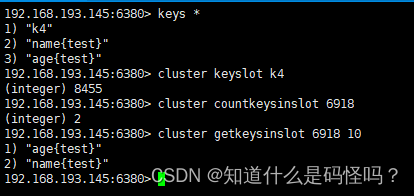
Fault recovery
(1) If a host goes down , The corresponding slave will be upgraded to the master .
(2) If you start the previous host again , Will become a slave .( It can be understood as Feng Shui turns , The boss takes turns to be )
(3) If both the master and slave are down , The cluster does not necessarily hang up . If redis.conf Parameters in cluster-require-coverage Set to yes , Then the cluster hangs up . If set to no , Then the slot data corresponding to this node cannot be used , Can't store .
边栏推荐
- Backup and restore of Android local SQLite database
- Integer = = the comparison will unpack automatically. This variable cannot be assigned empty
- C# 对象存储
- Shandong University Summer Training - 20220620
- What are the private addresses
- Apicloud studio3 API management and debugging tutorial
- mysql获得时间
- TortoiseSVN使用情形、安装与使用
- Sorry, we can't open xxxxx Docx, because there is a problem with the content (repackaging problem)
- Binder communication process and servicemanager creation process
猜你喜欢
Interviewer soul torture: why does the code specification require SQL statements not to have too many joins?

Binder通信过程及ServiceManager创建过程
stm32逆向入门
龙芯派2代烧写PMON和重装系统
Talk about seven ways to realize asynchronous programming

MySQL --- 数据库查询 - 排序查询、分页查询
Shandong University Summer Training - 20220620
Write macro with word

LB10S-ASEMI整流桥LB10S
先写API文档还是先写代码?
随机推荐
先写API文档还是先写代码?
DataPipeline双料入选中国信通院2022数智化图谱、数据库发展报告
RHCSA10
FPGA learning notes: vivado 2019.1 add IP MicroBlaze
mysql获得时间
Flutter 绘制波浪移动动画效果,曲线和折线图
49. 字母异位词分组:给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。 字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的字母得到的一个新单词,所有源单词中的字母通常恰好只用一次。
The "Baidu Cup" CTF competition was held in February 2017, Web: explosion-2
A detailed explanation of ASCII code, Unicode and UTF-8
Go pointer
Go array and slice
SAE international strategic investment geometry partner
山东大学暑期实训一20220620
[深度学习论文笔记]使用多模态MR成像分割脑肿瘤的HNF-Netv2
Huawei push service content, read notes
Interviewer soul torture: why does the code specification require SQL statements not to have too many joins?
Datapipeline was selected into the 2022 digital intelligence atlas and database development report of China Academy of communications and communications
南理工在线交流群
【服务器数据恢复】某品牌服务器存储raid5数据恢复案例
“百度杯”CTF比赛 九月场,Web:Upload