当前位置:网站首页>Oracle11g | getting started with database. It's enough to read this 10000 word analysis
Oracle11g | getting started with database. It's enough to read this 10000 word analysis
2022-07-04 10:53:00 【Eric%258436】
** If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting **
If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting , Please send a private message to the blogger , There is a red envelope for hard work , Worship “ one-word teacher ”.
Please find the paragraphs you need according to the table of contents
Introduction : This blog is organized for individuals Java Learning notes , If there is a mistake , Thank you for correcting . System learning , Welcome to continue to pay attention , Follow up updates
Java communication qq Group 383245788
Getting started with databases
brief introduction
The so-called database is actually a collection of data . Users can add data in the set 、 Inquire about 、 to update 、 Delete and other operations . The database is based on a - Store them together in a certain way 、 Can be Shared with multiple users 、 With as little redundancy as possible 、 Data sets independent of the application .
type
Relational type : Oracle、Mysql、PostgreSQL、DB2、Microsoft SQL Server、Microsoft Access
Non relational :Redis、Mongodb、Big Table
The difference between relational database and non relational data
Relational database :
The most typical data structure of relational database is table , A data organization consisting of two-dimensional tables and their connections . Support transaction consistency .
advantage :Easy to maintain : They all use the table structure , The format is consistent ;
Easy to use : SQL Common language ;
Complex operation : Support SQL, It can be used for very complex queries between one table and multiple tables ;shortcoming :
Poor performance : The reading and writing performance is poor , Especially the efficient reading and writing of massive data , For traditional relational databases , Hard disk IO It's a big bottleneck ;
Inflexible storage : Fixed watch structure , Less flexibility ;Non relational database :
A non relational database is not strictly a database , It should be a collection of data structured storage methods , You can document or key value equivalence . Transaction consistency feature is not supported .
advantage :Flexible format : The format for storing data can be key,value form 、 Document form 、 Picture form and so on ;
High scalability : Based on key value pair , The data is not coupled , Easy to expand ;
Fast : No need to go through sql Layer resolution , High read and write performance ;shortcoming :
I won't support it SQL: Does not provide sql Support , The cost of learning and using is high ;
Unsupported transaction : No transaction processing capability ; .
Complex queries are not supported : The data structure is relatively complex , It's a little bit less in terms of complex queries ;
Oracle introduction
Oracle Introduce
The collection of data stored in all relational databases is the files on disk .
Oracle A database is actually a collection of files .
Oracle The database consists of : Data files 、 Control documents 、 Log files .
Oracle file
Data files (.DBF)
The data file is a binary file , It is used to save user application data and Oracle File of internal data of the system , These files are ordinary operating system files in the operating system .Oracle Data files will be created while creating table spaces .
Control documents (.CTL)
The control file is a binary file , It mainly records the name of the database 、 Data file storage location and other information of the database . A control file can only belong to one database . If the control file is missing , The database cannot be operated .
Log files (LOG)
The log file is in Oracle The database is divided into redo logs (Redo Log) File and archive log file . Redo log file is Oracle An indispensable file for the normal operation of the database . The redo log file mainly records the database operation process . For backing up and restoring databases , To reach the latest state of the database .
Oracle Instance and database
example :
An instance is the memory allocated and the background process established after the database is started . After the database is closed , The physical file still exists , But the memory allocated by the instance and the process established ) There is no the .
An instance is a set of operating system processes ( Or a multithreaded process ) And some memory . These processes can manipulate databases ; The database is just a collection of files ( Including data files 、 Time file 、 Redo log files and control files )
At any moment , An instance can only have one set of related files ( Associate with a database ). Most of the time , And vice versa : Only one instance of a database operates on it .
Oracle Version Description
I: i representative Internet.8i Version on Internet Support for . therefore , After the version number , Added logo i.
G: g representative Grid grid .10g Added the function of Grid Computing , Therefore, the identification after the version number uses letters
C: c On behalf of the cloud (cloud) Computational design .12c Version indicates support for Cloud Computing .
Oracle Install and uninstall
install
link :https://pan.baidu.com/s/1GFfyj9YFvGaeNRXezd62mQ
Extraction code :qwer
database Under the folder is Oracle The installation files , edition 11G
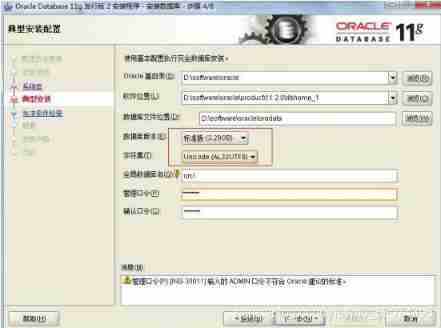
step 1 : double-click
step 2:
step 3:
step 4:
step 5:
step 6:
step 7: The installation time may be a little long , Wait patiently .
step 8:
uninstall
Oracle Installation and uninstallation of is troublesome , It is not recommended to uninstall easily .
step 1: Discontinue use oracle service , Enter computer management , in service , find oracle All the services at the beginning , Right click to select stop
step 2: Run uninstall Oracle Database program . Find... In the start menu Oracle Install the product , Click on the run Oracle Built in uninstaller Universal Installer Tool unload .
step 3: Delete use Oracle Service for . Start menu , find Universal Installer, function Oracle Universal Installer, Click uninstall product , In the product list window , Click expand all , except OraDb11g_home1 Outside , Check other items , Click delete , Click next as prompted .
step 4: Delete from the registry Oracle Related itemsIn the command window , Input regedit , Open the registry , In accordance with the Time exhibition open HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE, find oracle, Delete .
Expand one by one HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services in , Delete all oracle Items at the beginning .
Expand one by one ,HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Application, Delete all oracle Items at the beginning .
Extend delete ( The following is not a required registry deletion key ), If the installation is not successful, you can delete these yourself
stay HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, Delete with Ora、Oracle、Orcl or EnumOra Key for prefix .
Delete HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MenuOrder\Start Menu\Programs In the oracle Key at the beginning .
Delete except HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBCINST.INI in except MicrosoftODBC for Oracle Everything except the registry key contains Oracle Key .step 5: Delete Oracle Environmental Science . Right click on my computer –> attribute –> senior –> environment variable , Delete environment variables ORACLE_HOME、TNS_ADMIN And other environmental variables , Delete PATH Medium environmental variables Oracle Set the path information .
step 6: Delete “ Start ” The menu Oracle Catalog . Open Explorer , Enter in the address bar “%userprofile%\「 Start 」 menu \ Program ” enter , Remove installed Oracle Catalog . Then enter... In the address bar “%allusersprofile%\「 Start 」 menu \ Program ” enter , Remove installed Oracle Catalog
step 7: Restart the computer .
step 8: Delete Program Files\Oracle Catalog . If in Program Files\Oracle Directory exists , Delete Program Files\Oracle.
step 9: Delete Oracle The installation directory . Delete Oracle Installation directory app Such as catalog .
Oracle Directory structure
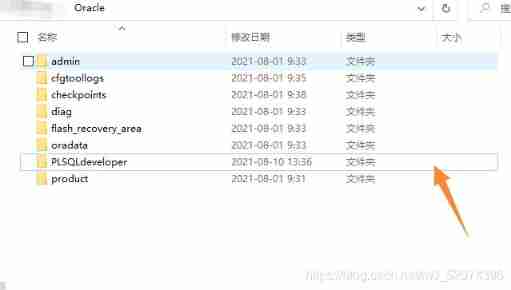
PS: The directory indicated by the arrow in the figure is the installation directory of the third-party client tools
admin Catalog
Record Oracle Instance configuration , Operation log and other files . One directory per instance .
SID: System IDentifer Abbreviation , yes Oracle Unique token of the instance . stay Oracle An instance in can only operate one database . If you install multiple libraries, there will be multiple instances , We can use examples SID To distinguish between . because Oracle The reason why an instance in can only operate one database oracle Also used in SID As the name of the Library .cfgtoollogs Catalog
The following subdirectories are respectively stored when running dbca, emca, netca And other graphical configuration procedures log.
checkpoints Catalog
Store checkpoint files
diag Catalog
Oraclellg A newly added reorganization directory . Subdirectories , Basically Oracle Each component has its own separate directory , stay Oracle10g We have been criticized log The problem of scattered documents has finally been solved , Whether it's asm still crs still rdbms, All components need to be used for diagnostics log The files are stored in this new directory .
flash_recovery_area( Flashback area ) Catalog
Flashback area : Assign a specific directory location to store - Some specific recovery files , For centralized and simplified management of database recovery . The flashback area can store complete data file backups 、 Incremental backup 、 Copy of data file 、 The current control file 、 Backup control file 、spfile file 、 Snapshot control file 、 Redo Log files 、 Archive log 、 Block trace file 、 Flash back to the log .
oradata Catalog : Storing data files
CONTROL01.CTL:Oracle Control file of database .
EXAMPLEO1.DBF:Oracle Database tablespace file .
REDO01.LOG:Oracle Redo log file of database .
SYSAUXO1.DBF:11g New table space . It mainly stores other data objects except data dictionary . Automatically maintained by the system .
SYSTEMO1.DBF: To hold Oracle All tables and data dictionary data in the system . such as , Table name 、 Name 、 User name, etc .
TEMPO1.DBF: Time table space file .
UNDOTBSO1.DBF: Undo tablespace file . Used to save rollback data .
USERSO1.DBF: User tablespace .product Catalog
Oracle RDBMS Software storage directory .RDBMS Relational database management system (Relational DatabaseManagement System).
Oracle System users
sys user
sys yes Oracle Super account in , You have the most permissions . It can complete all the management tasks of the database .
system user
system: No, sys Permission to big , It is usually used to create some user views Manage tables or views of information . Not recommended system Users can create some tables or views that have nothing to do with management .
scott user
scott: yes oracle Sample users provided , Provides some learning oracle Operation data table . Such as : emp、dept、salgrade、bonus surface
difference
sys and system In the login Oracle when ,sys Only as a system administrator ( sysdba) Or system operator ( sysoper) Login with permission of , and system Can log in directly (normal) .
Oracle Start and shut down
Oracle It is started through the service of the system .
OracleServiceORCL( Must be started )
OracleServiceORCL: Database services ( Database instance ), yes Oracle Core services this service , Is the foundation of database startup , Only this service starts ,Oracle The database can be started normally .
ORCL— Started instanceOracleOraDb11g home1TNSListener( Must be started )
OracleOraDb11g_ home1TNSListener: Listener service , The service can only be used when the database needs remote access PLSQL Developer Wait for third-party tools .
Use native It can be operated without starting OracleOracle ORCL VSS Writer Service( It is not necessary to start )
Oracle ORCL VSS Writer Service: Oracle Volume mapping copy write service ,VSS(Volume Shadow CopyService) Be able to make storage infrastructure ( This is like a disk , Array, etc ) Create a high fidelity point in time image , That is, mapping copies (shadow copy). It can create mapped copies on multiple or single volumes , At the same time, it will not affect the system performance .
OracleDBConsoleorcl( It is not necessary to start )
OracleDBConsoleorcl: Oracle Database console service , orcl yes Oracle The instance ID of , The default instance is orcl. Running Enterpise Manager( The enterprise management device OEM When , This service needs to be started .
OracleJobSchedulerORCL( It is not necessary to start )
OracleJobSchedulerORCL: Oracle Job scheduling ( timer service ,ORCL yes Oracle Instance ID .
OracleMTSRecoveryService( It is not necessary to start )
OracleMTSRecoveryService: Server control . The service allows the database to act as a Microsoft Transaction Server MTS、COMCOM+ Object and transaction resource manager in distributed environment .
close
close Oracle Just stop the service .
Oracle Client tools
Oracle Client tools SQL Plus
sys User login command : sys as sysdbalsysoper
system User login command : system
Use similar cmd Command line
Third party client tools PL/SQL Developer
Use operation without finishing , There are many related videos on the network , If you have leisure , Will produce tutorials
install : The installation file is in Baidu cloud link , The software comes from the network , Just share , If there is any infringement , Please contact us by private letter to delete .
Installation steps , It's just a fool installation , Other documents are used in Chinese , Sinicization is not recommended
step 1:
step 2:
step 3:
step 4:
step 5:
step 6:
Oracle Table space
classification
Permanent table space : Table space is the logical partition of database , A table space can only belong to one database . All database objects are stored in the specified table space . But the main storage is the watch , So it's called a table space .
Temporary table space :Oracle The temporary table space is mainly used for querying and storing some buffer data . The main reason for temporary table space consumption is the need to sort the intermediate results of the query . Restarting the database frees up temporary tablespaces .
Create persistent tablespaces
create tablespace Permanent tablespace name datafile ' Permanent tablespace physical file location / Physical disk location ' size 15M autoextend on next 10M permanent online;
Create user
1: adopt PL/SQL Developer Tools , Directly in user Under the table of contents new
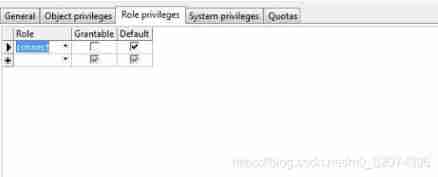
2: Assign user rights : User right click edit Assign user rightsObject permissions [Object privileges): Object permission refers to the permission or right to make actions on the specified table view sequence .
Role permissions (Role privileges): A role is a group that can grant users relevant permissions , This method makes the authorization revocation easier to manage .connect: Distribute connect Link role
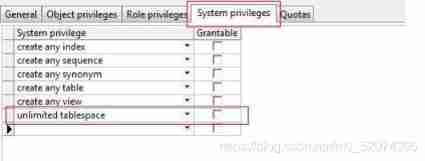
dba: To give dba jurisdictionSystem permissions [System privileges): Create tables for user assignments 、 Create user 、 Create view 、 Create stored procedures and other permissions .
create any table/view/sysnonym/index etc.
unlitimited tablespace
Oracle Link configuration
file location
Oracle Catalog \product\11.2.0\dbhome_1\NETWORK\ADMIN
sqlnet.ora
Name resolution . Use this file to decide how to find a connection string that appears in the connection .
Such as :sqlplus bjsxt/[email protected]
NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH= (TNSNAMES, EZCONNECT)
tnsnames.ora
Use in oracle client End , The alias parameters of the user configuration connection database are like hosts file .
ParametersORCL: The service alias used by the client to connect to the server . Be sure to write on the top line , Otherwise, the service alias will not be recognized .
PROTOCOL: Protocol for communication between client and server , It's usually TCP, Generally, the content does not need to be changed .
HOST:ORACLE Server side IP Address or hostname. Ensure that the monitoring on the server is started normally .
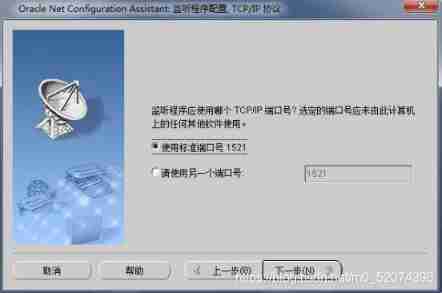
PORT: The database listens on the port it is listening on , here port The value of must be the same as the port on which the database is listening .
listener.ora
Use in oracle server End , Configurable Oracle Listening port of
ParametersLISTENER: Listen to the name , You can configure multiple listeners , Multiple listening port numbers should be distinguished .
PROTOCOL: snoopy protocol , Generally used TCP.
HOST: This machine IP Address or localhostname.
PORT: Listening port
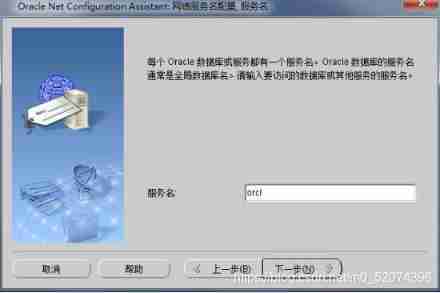
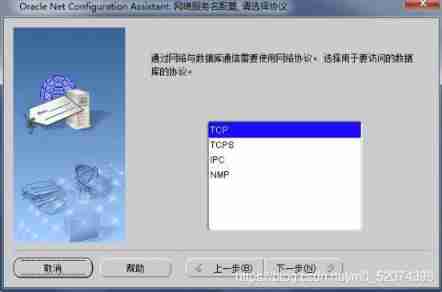
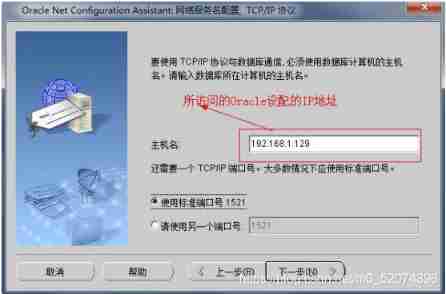
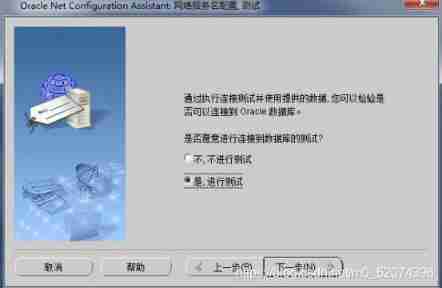
Net Configuration Assistant Tools
Oracle Tools provided , It can be used to configure the following :
This tool only provides a graphical operation interface , Directly configure the source code (.ora file ) Same effect
Monitor configuration Commonly used
Naming method configuration
Local network service name configuration Commonly used
Directory usage configuration
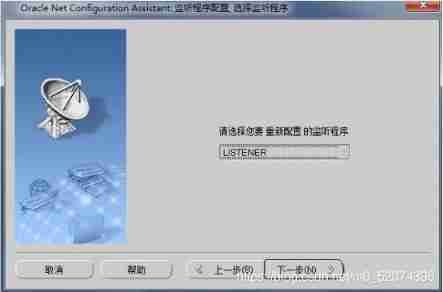
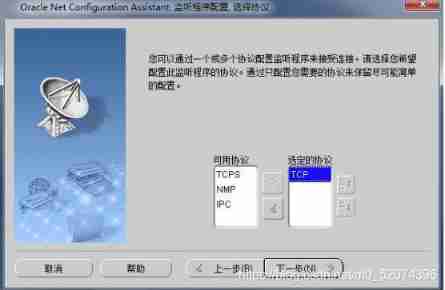
Configure listener
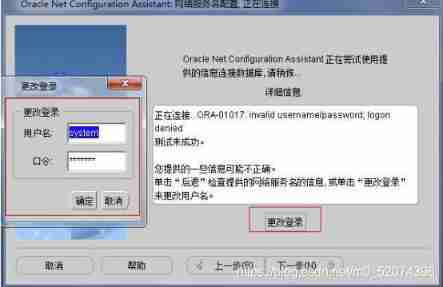
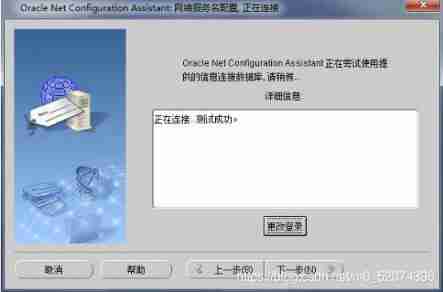
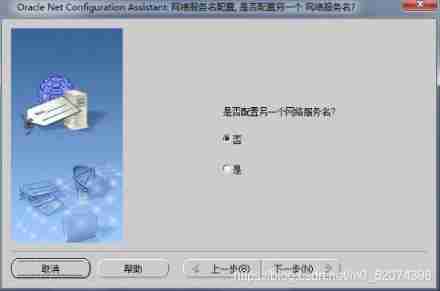
Just follow the diagram below , Stupid configuration
Local network service name configuration
Access the database through the network
Configure local network service requirements :
1: The firewall needs to be shut down
2: Each other can ping common
Configuration mode
Oracle data type
Character type
String data types can also be divided into fixed length types according to storage space (CHAR) And variable length types (VARCHAR2NVARCHAR2) Two kinds of .
CHAR type :CHAR type , Fixed length string , Will fill with spaces to reach its maximum length . Not NULL Of CHAR(12) Always include 12 Byte information .CHAR Fields can store up to 2,000 Byte information . If you create a table , Don't specify CHAR length , The default is 1.
VARCHAR2 type : Variable length string , And CHAR Different types , It does not use spaces to fill to the maximum length .VARCHAR2 Up to storage 4,000 Byte information .
NVARCHAR2 type : This is an inclusion of UNICODE Variable length string of format data .NVARCHAR2 Up to storage 4,000 Byte information .
Numeric type
NUMIBER type :NUMBER(P,S) Is the most common number type .P yes Precison English abbreviations , Precision abbreviation , Represents the number of significant digits , Not more than 38 A significant number .S yes Scale English abbreviations , The number of decimal digits .
INTEGER type :INTEGER yes NUMBER Subtypes of , It is equivalent to NUMBER (38,0) , Used to store integers . If inserted 、 The updated value has decimals , Will be rounded .
Floating point numbers
BINARY FLOAT type :BINARY_FLOAT yes 32 position 、 Single precision floating-point number data type . Can support at least 6 Bit precision each BINARY_FLOAT The value of needs 5 Bytes , Including length bytes .
BINARY DOUBLE:BINARY_DOUBLE Is for 64 position , Double precision floating-point number data type . Every BINARY_DOUBLE The value of needs 9 Bytes , Including length bytes .
date
DATE type :DATE Is the most commonly used data type , Date data types store date and time information . Although date and time information can be represented by character or number types , But the date data type has special relevance . For each date value , Oracle Store the following information : century 、 year 、 month 、 date 、 Hours 、 Minutes and seconds . General occupancy 7 Bytes of storage space .
TIMESTAMP type : This is a 7 Byte or 12 Fixed width date time data type of bytes . It is associated with DATE Different types of data , because TIMESTAMP It can contain decimal seconds , With decimal seconds TIMESTAMP You can keep at most on the right of the decimal point 9 position .
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE type : This is a TIMESTAMP Variants of type , It contains the value of the time zone offset .
TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE type : Store the time data after normalizing it in the time zone of the database
LOB type
CLOB type (Characfr Large Object): binary data , Store single byte and multi byte character data . Maximum length 4G.
BLOB type (Binary Large Object): It stores unstructured binary data large objects , It can be considered as a bit stream without character set semantics , General image 、 voice 、 Video and other documents . Maximum length 4G.
NCLOB data type : Storage UNICODE Data of type , Maximum length 4G.
LONG & RAW & LONG RAW type
LONG type : It stores variable length strings ( Super long string ), Up to 2G Character data of (2GB Refer to 2 gigabyte , instead of 2 Gigabit characters )
LONG RAW type : Energy storage 2GB Raw binary data , It can store multimedia image, sound, etc .
RAW type : Used to store binary or character type data , The length must be set . This data type stores data without character set conversion . It can store multimedia image, sound, etc .
Oracle Create table
Naming rules :
Must start with a letter
The length cannot exceed 30 Characters
Avoid using Oracle Key words of
Only use A-Z、z-Z、 0-9、#$Use table names with special symbols
Oracle When the table is created , Table names are automatically converted to uppercase .Oracle Insensitive to the case of table names . If the table name is defined with special symbols , Or to define the table name with lowercase letters, you need to add double quotation marks around the table name .
Oracle constraint
effect : Constraints are used to specify data rules in a table , If there is data behavior that violates the constraint , Behavior will be terminated by restraint .
Constraint type
Primary key constraint (Prjmay Key Constraint): Uniqueness , Non emptiness .
Unique constraint (Unique Constraint ): Uniqueness , Can be empty , But only one .
Check constraint ( Check Constraint): The range of data in this column 、 Format restrictions ( Such as : Age 、 Gender, etc ).
Non empty constraint (Not Null Constraint): This column is not allowed to contain null values .
Foreign key constraints (Foreign Key Constraint): You need to establish a relationship between the two tables and reference the columns of the main table .
Oracle Table relations
An important part of designing a relational database is to divide data elements into related tables , According to the relevance of the data itself , Aggregate data between different tables . Be careful : No matter what relationship is established between tables , It is not tables that determine whether there is a relationship between data , It's the data itself .
There are generally three relationships between tables , The one on one , One to many , Many to many relationship .
one-on-one : One to one relationship is based on one to many , Foreign keys can be on either side , You need to have a unique constraint on the foreign key side .
One to many : One to many Relationship is based on the relationship between two tables . One in a table Pieces of data can correspond to multiple pieces of data in another table . remember : Foreign keys are always in many ways . Foreign keys are allowed to repeat , Null values are allowed .
Many to many : You need to create an intermediate table , Create two columns in the middle table , Then you need to use these two columns as the joint primary key of the table , Then each column refers to the primary key of its own table as a foreign key .
At the end of the paper
This chapter is about Oracle The introductory explanation of comes to an end , Thank you for your attention , give the thumbs-up , Collection , Exploding the liver is not easy , Please support bloggers for more than three times .Oracle and MySQL As two mountains in China , Learning about them is very important , Subsequent bloggers will continue to update relevant articles .
边栏推荐
- How to use diff and patch to update the source code
- /*Rewrite the program, find the value of the element, and return the iterator 9.13: pointing to the found element. Make sure that the program works correctly when the element you are looking for does
- Static comprehensive experiment ---hcip1
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] set time synchronization of intranet server
- Software sharing: the best PDF document conversion tool and PDF Suite Enterprise version sharing | with sharing
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [server] soft RAID configuration
- DDL statement of MySQL Foundation
- VI text editor and user rights management, group management and time management
- [Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] build NFS to realize disk sharing
- [untitled]
猜你喜欢

TS type gymnastics: illustrating a complex advanced type
Rhsca day 11 operation
JMeter correlation technology
F12 clear the cookies of the corresponding web address
Using SA token to solve websocket handshake authentication
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (2)
Rhcsa day 9
RHCE day 3
Canoe - description of common database attributes
Personal thoughts on the development of game automation protocol testing tool
随机推荐
MPLS: multi protocol label switching
Canoe - the third simulation project - bus simulation - 2 function introduction, network topology
Communication layer of csframework
Rhsca day 11 operation
Linked list operation can never change without its roots
[test theory] test the dimension of professional ability
20 minutes to learn what XML is_ XML learning notes_ What is an XML file_ Basic grammatical rules_ How to parse
[Galaxy Kirin V10] [desktop] can't be started or the screen is black
Appscan installation steps
Hidden C2 tunnel -- use of icmpsh of ICMP
From programmers to large-scale distributed architects, where are you (2)
[advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing software development in 2022]
Personal thoughts on the development of game automation protocol testing tool
/*Rewrite the program, find the value of the element, and return the iterator 9.13: pointing to the found element. Make sure that the program works correctly when the element you are looking for does
Performance test method
How to quickly parse XML documents through C (in fact, other languages also have corresponding interfaces or libraries to call)
Locust learning record I
If you don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
Canoe: the fourth simulation project -- bug debugging experience
Performance test process