当前位置:网站首页>Rhcsa day 9
Rhcsa day 9
2022-07-04 10:17:00 【Attiude】
Just signed in Linux when , First start /etc/profile file , Then start... In the user directory ~/.bash_profile、~/.bash_login or ~/.profile One of the documents
Order of execution by :~/.bash_profile、~/.bash_login、 ~/.profile.
If ~/.bash_profile If the document exists , In general, it will also carry out ~/.bashrc file .
/etc/profile >>>> Of all users
.bash_profile>>>> Current user
/etc/.bashrc>>>> Home catalog

User's environment variable configuration :
[[email protected] ~]$ ls /root/.bashrc # It is recommended to set it in this file first
/root/.bashrc
[[email protected] ~]$ ls /root/.bash_profile
/root/.bash_profile
Global environment variable configuration :
[[email protected] ~]$ /etc/profile
[[email protected] ~]$ /etc/bashrc
[[email protected] ~]$ /etc/profile.d/
To initialize or display the loaded content after login , Put the script file in /etc/profile.d/ Then you can ( No need to load execution rights limit )
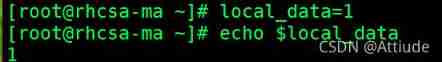
1. Create a normal variable local_data=1 And access
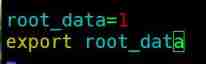
Create environment variables root_data, Only root Users can access
[[email protected] ~]# vim .bashrc
[[email protected] ~]# echo $root_data
1
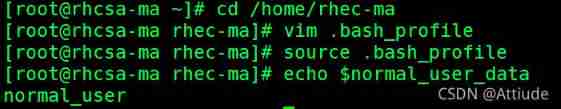
Create environment variables normal_user_data, Only ordinary users can access
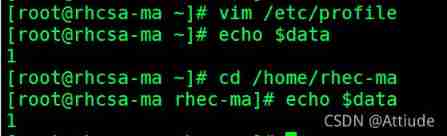
Create environment variables root Both users and ordinary users can access
2. establish 3 File test1.txt, test2.txt, test3.txt
Use find lookup test1.txt,test2.txt, test3.txt
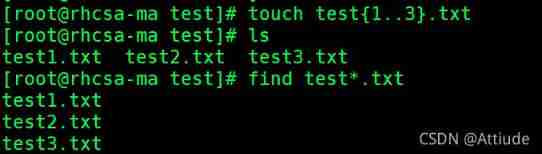
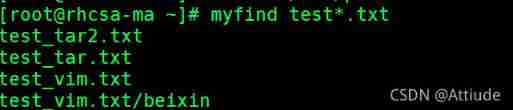
Use the alias : Name the above command myfind
To take effect automatically every time you log in , Add alias to /etc/profile or ~/.bashrc in . then # source ~/.bashrc . To make every user effective, alias , Add alias to /etc/bashrc Back most , then # source /etc/bashrc
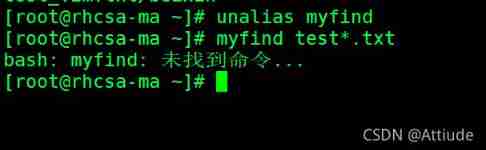
Remove alias
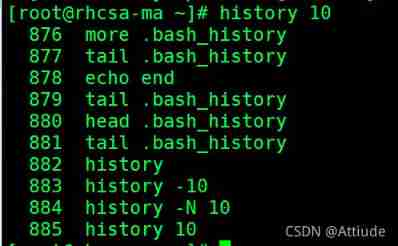
3. View recently used 10 Historical orders
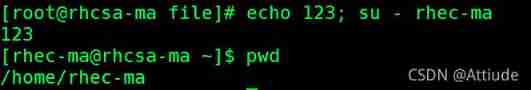
4. Print on one line 123 And from root Switch to normal user
5. Wildcard usage
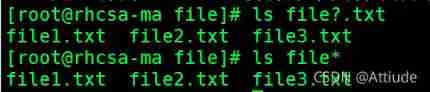
establish 3 File file1, file2, file3
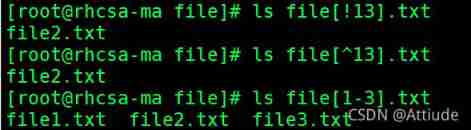
1.* To match 3 File 2.? matching 3 File
3.[] matching file1 and file3
4.[^] matching file2
5.[!] matching file2
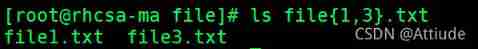
6.{} matching file1 and file3
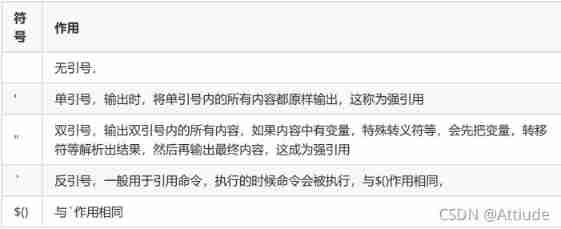
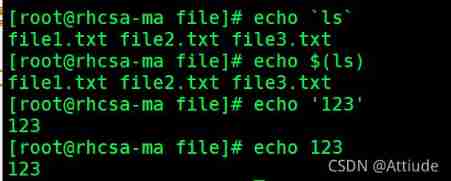
6. Examples of the use of quotation marks : No quotes , Single quotation marks , Double quotes , The quotation marks ,$()
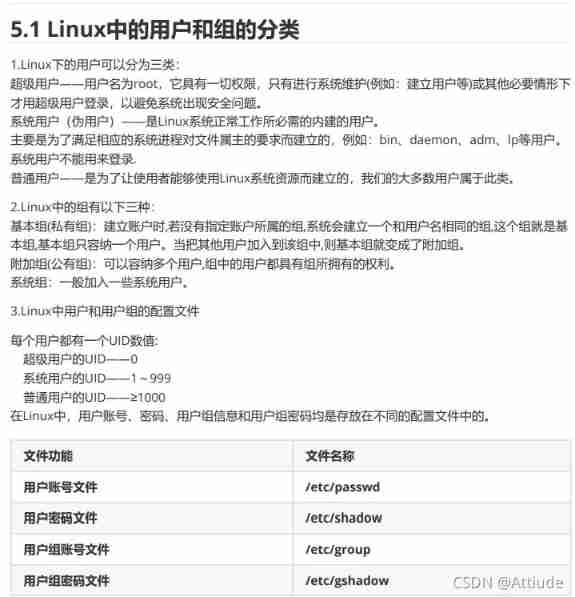
7.linux Type of user in
linux Type of user group in
Super user's UID——0
System user's UID——1~999
For ordinary users UID——≥1000
linux Which file stores user information in ? And what do the fields mean
User account file ——/etc/passwd passwd It's a text file , Used to define the user account of the system , Because all users are right passwd Have the right to read , So this file Only user accounts are defined in , Without saving the password .
passwd In file : Each line defines a user account Field meaning Login name Login name Encryption port Make Use SHA-512/SHA-256/MD5 The password encrypted by the algorithm ,
If it is empty , Indicates that the user can log in without a password ,
if “*” Indicates that the account cannot be used to log in to the system
if “!!” Indicates that the account password has been locked Finally Time modification Time Date of last password change , With distance 1970 year 1 month 1 The number of days in a day means At the very least Interval How many days can the password not be changed . The default value is 0, Means unrestricted Maximum time Interval How many days must the password be changed . The default value is 99999, It means that there is no restriction When warning between How many days in advance to warn users that the password will expire , The default value is 7 God ,0 Indicates that no warning is provided inactive Time How many days after the password expires, disable this user When the failure between Password expiration date , With distance 1970 year 1 month 1 The number of days in a day means , The default is empty. , Indicates permanently available sign Keep unused ,
For future development Each line by 7 Fields make up , Use... Between fields “:” Separate , The format is as follows :
Account name : password :UID:GID: The personal data : Home directory :Shell Field description :
Account name : The user login Linux The name of the system .
password : Previously, the location of the password was saved in an encrypted format , Now the password is saved in /etc/shadow In file , This is just a password placeholder “x” or “*”. if “x”, It means that the password has passed shadow The protection of the
UID: User's identity , It's a number , Use it to distinguish different users
GID: Identification of the basic group in which the user belongs , It's a number , Use it to distinguish different groups , The same group has the same GID.
The personal data : You can record the full name of the user 、 Address 、 Office phone 、 Personal information such as home phone .
Home directory : similar Windows Personal directory , Usually /home/username, here username Is the user name , User execution “cd~” Command, the current directory will switch to the personal home directory .
Shell: Define the number of users to activate after logging in Shell, The default is Bash Shell
linux What is the file in which the group information is stored ? And what do the fields mean ?
User group account file ——/etc/group Every file in the system has a user and a group owner .
Use “ls –l” The command can see the owner and group of each file .
Each group in the system , stay /etc/group There is a line in the file Any user can read the user group account information profile . The real password of the user group is saved in /etc/gshadow In profile .
边栏推荐
- Debug:==42==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address
- Dynamic address book
- Baidu R & D suffered Waterloo on three sides: I was stunned by the interviewer's set of combination punches on the spot
- Hands on deep learning (41) -- Deep recurrent neural network (deep RNN)
- What are the advantages of automation?
- 2. Data type
- Batch distribution of SSH keys and batch execution of ansible
- Number of relationship models
- 【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
- Histogram equalization
猜你喜欢
Debug:==42==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address
Hands on deep learning (37) -- cyclic neural network
Summary of small program performance optimization practice

Development guidance document of CMDB

Hands on deep learning (33) -- style transfer
Custom type: structure, enumeration, union

Servlet基本原理与常见API方法的应用
直方图均衡化
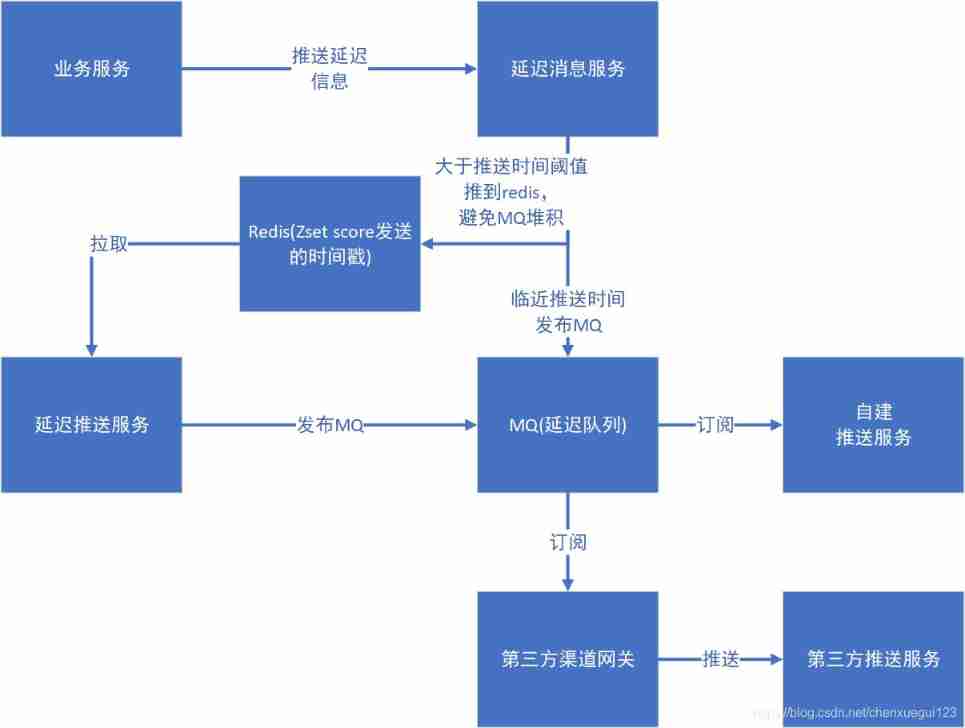
Delayed message center design

5g/4g wireless networking scheme for brand chain stores
随机推荐
Dynamic memory management
View CSDN personal resource download details
Latex insert picture, insert formula
libmysqlclient.so.20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
C # use smtpclient The sendasync method fails to send mail, and always returns canceled
Safety reinforcement learning based on linear function approximation safe RL with linear function approximation translation 2
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
C语言指针面试题——第二弹
Latex error: missing delimiter (. Inserted) {\xi \left( {p,{p_q}} \right)} \right|}}
Hands on deep learning (42) -- bi-directional recurrent neural network (BI RNN)
Exercise 7-2 finding the maximum value and its subscript (20 points)
2020-03-28
What is devsecops? Definitions, processes, frameworks and best practices for 2022
Machine learning -- neural network (IV): BP neural network
System.currentTimeMillis() 和 System.nanoTime() 哪个更快?别用错了!
C language pointer interview question - the second bullet
用数据告诉你高考最难的省份是哪里!
How to teach yourself to learn programming
使用 C# 提取 PDF 文件中的所有文字(支持 .NET Core)
Sword finger offer 31 Stack push in and pop-up sequence