当前位置:网站首页>C#,数值计算(Numerical Recipes in C#),线性代数方程的求解,LU分解(LU Decomposition)源程序
C#,数值计算(Numerical Recipes in C#),线性代数方程的求解,LU分解(LU Decomposition)源程序
2022-07-05 07:52:00 【深度混淆】
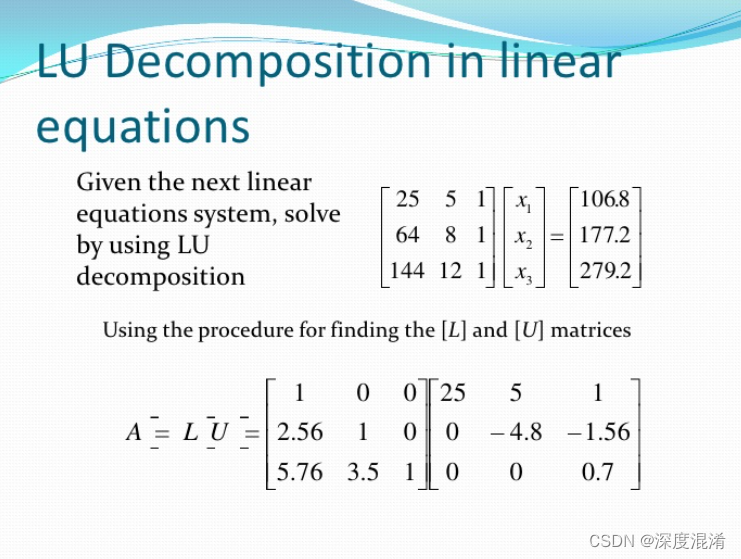
《Numerical Recipes in C++》原文摘要:

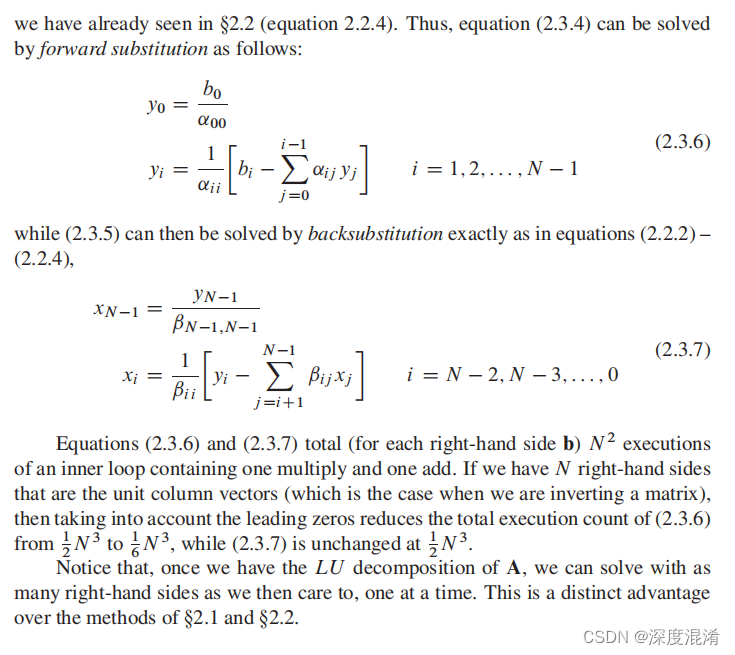
凑字数的狗屁不通的译文:
在线性代数中, LU分解(LU Factorization)是矩阵分解的一种,可以将一个矩阵分解为一个下三角矩阵和一个上三角矩阵的乘积(有时是它们和一个置换矩阵的乘积)。LU分解主要应用在数值分析中,用来解线性方程、求反矩阵或计算行列式。
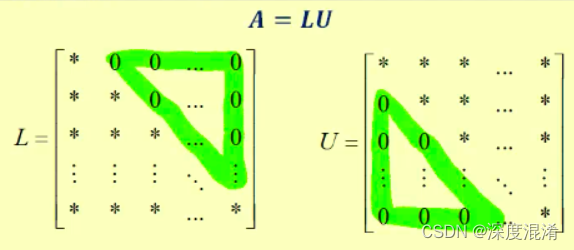
将系数矩阵A转变成等价两个矩阵L和U的乘积 ,其中L和U分别是单位下三角矩阵和上三角矩阵。当A的所有顺序主子式都不为0时,矩阵A可以唯一地分解为A=LU。其中L是下三角矩阵,U是上三角矩阵。
LU分解在本质上是高斯消元法的一种表达形式。实质上是将A通过初等行变换变成一个上三角矩阵,其变换矩阵就是一个单位下三角矩阵。这正是所谓的杜尔里特算法(Doolittle algorithm):从下至上地对矩阵A做初等行变换,将对角线左下方的元素变成零,然后再证明这些行变换的效果等同于左乘一系列单位下三角矩阵,这一系列单位下三角矩阵的乘积的逆就是L矩阵,它也是一个单位下三角矩阵。这类算法的复杂度一般在(三分之二的n三次方) 左右。
算法改进
(i)Doolittle分解
对于非奇异矩阵(任n阶顺序主子式不全为0)的方阵A,都可以进行Doolittle分解,得到A=LU,其中L为单位下三角矩阵,U为上三角矩阵;这里的Doolittle分解实际就是Gauss变换;
(ii)Crout分解
对于非奇异矩阵(任n阶顺序主子式不全为0)的方阵A,都可以进行Crout分解,得到A=LU,其中L为下三角矩阵,U为单位上三角矩阵;
(iii)列主元三角分解
对于非奇异矩阵的方阵A,采用列主元三角分解,得到PA=LU,其中P为一个置换矩阵,L,U与Doolittle分解的规定相同;
(iv)全主元三角分解
对于非奇异矩阵的方阵A,采用全主元三角分解,得到PAQ=LU,其中P,Q为置换矩阵,L,U与Doolittle分解的规定相同;
(v)直接三角分解
对于非奇异矩阵的方阵A,利用直接三角分解推导得到的公式(Doolittle分解公式或者Crout分解公式),可以进行递归操作,以便于计算机编程实现;
(vi)“追赶法”
追赶法是针对带状矩阵(尤其是三对角矩阵)这一大稀疏矩阵的特殊结构,得出的一种保带性分解的公式推导,实质结果也是LU分解;因为大稀疏矩阵在工程领域应用较多,所以这部分内容需要特别掌握。
(vii)Cholesky分解法(平方根法)和改进的平方根法
Cholesky分解法是是针对正定矩阵的分解,其结果是 A=LDLT=LD(1/2)D(1/2)LT=L1L1T。如何得到L1,实际也是给出了递归公式。
改进的平方根法是Cholesky分解的一种改进。为避免公式中开平方,得到的结果是A=LDLT=TLT, 同样给出了求T,L的公式。
小结:
(1) 从(i)~(iv)是用手工计算的基础方法,(v)~(vi)是用计算机辅助计算的算法公式指导;
(2) 这些方法产生的目的是为了得到线性方程组的解,本质是高斯消元法。
源程序(POWER BY 315SOFT.COM)
using System;
namespace Legalsoft.Truffer
{
/// <summary>
/// LU decomposition - PTC
/// Iterative Improvement of a Solution to Linear Equations
/// </summary>
public class LUdcmp
{
private int n { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Stores the decomposition
/// </summary>
private double[,] lu { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Stores the permutation.
/// </summary>
private int[] indx { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Used by det.
/// </summary>
private double d { get; set; }
private double[,] aref { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Given a matrix a[0..n - 1][0..n-1], this routine replaces it by the LU decomposition of a
/// rowwise permutation of itself.a is input.On output, it is arranged as in equation(2.3.14)
/// above; indx[0..n - 1] is an output vector that records the row permutation effected by the
/// partial pivoting; d is output as +/-1 depending on whether the number of row interchanges
/// was even or odd, respectively. This routine is used in combination with solve to solve linear
/// equations or invert a matrix.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>
public LUdcmp(double[,] a)
{
this.n = a.GetLength(0);
this.lu = a;
this.aref = a;
this.indx = new int[n];
const double TINY = 1.0e-40;
double[] vv = new double[n];
d = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double big = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double temp = Math.Abs(lu[i, j]);
if ((temp) > big)
{
big = temp;
}
}
//if (big == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(big) <= float.Epsilon)
{
throw new Exception("Singular matrix in LUdcmp");
}
vv[i] = 1.0 / big;
}
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
double big = 0.0;
int imax = k;
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
{
double temp = vv[i] * Math.Abs(lu[i, k]);
if (temp > big)
{
big = temp;
imax = i;
}
}
if (k != imax)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double temp = lu[imax, j];
lu[imax, j] = lu[k, j];
lu[k, j] = temp;
}
d = -d;
vv[imax] = vv[k];
}
indx[k] = imax;
//if (lu[k, k] == 0.0)
if (Math.Abs(lu[k, k]) <= float.Epsilon)
{
lu[k, k] = TINY;
}
for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
double temp = lu[i, k] /= lu[k, k];
for (int j = k + 1; j < n; j++)
{
lu[i, j] -= temp * lu[k, j];
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Solves the set of n linear equations A*x = b using the stored LU decomposition of A.
/// b[0..n - 1] is input as the right-hand side vector b, while x returns the solution vector x; b and
/// x may reference the same vector, in which case the solution overwrites the input.This routine
/// takes into account the possibility that b will begin with many zero elements, so it is efficient for
/// use in matrix inversion.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <param name="x"></param>
/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>
public void solve(double[] b, double[] x)
{
int ii = 0;
if (b.Length != n || x.Length != n)
{
throw new Exception("LUdcmp::solve bad sizes");
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
x[i] = b[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int ip = indx[i];
double sum = x[ip];
x[ip] = x[i];
if (ii != 0)
{
for (int j = ii - 1; j < i; j++)
{
sum -= lu[i, j] * x[j];
}
}
else if (sum != 0.0)
{
ii = i + 1;
}
x[i] = sum;
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
double sum = x[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
sum -= lu[i, j] * x[j];
}
x[i] = sum / lu[i, i];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Solves m sets of n linear equations A*X = B using the stored LU decomposition of A.The
/// matrix b[0..n - 1][0..m - 1] inputs the right-hand sides, while x[0..n - 1][0..m - 1] returns the
/// solution A^-1* B.b and x may reference the same matrix, in which case the solution overwrites
/// the input.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <param name="x"></param>
/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>
public void solve(double[,] b, double[,] x)
{
int m = b.GetLength(1);
if (b.GetLength(0) != n || x.GetLength(0) != n || b.GetLength(1) != x.GetLength(1))
{
throw new Exception("LUdcmp::solve bad sizes");
}
double[] xx = new double[n];
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
xx[i] = b[i, j];
}
solve( xx, xx);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
x[i, j] = xx[i];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Using the stored LU decomposition,
/// return in ainv the matrix inverse
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ainv"></param>
public void inverse(double[,] ainv)
{
//ainv.resize(n, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
ainv[i, j] = 0.0;
}
ainv[i, i] = 1.0;
}
solve( ainv, ainv);
}
/// <summary>
/// Using the stored LU decomposition,
/// return the determinant of the matrix A.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public double det()
{
double dd = d;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
dd *= lu[i, i];
}
return dd;
}
/// <summary>
/// Improves a solution vector x[0..n - 1] of the linear set of equations A*x= b.
/// The vectors b[0..n - 1] and x[0..n - 1] are input.On output, x[0..n - 1] is
/// modified, to an improved set of values.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <param name="x"></param>
public void mprove(double[] b, double[] x)
{
double[] r = new double[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double sdp = -b[i];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
sdp += (double)aref[i, j] * (double)x[j];
}
r[i] = sdp;
}
solve( r, r);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
x[i] -= r[i];
}
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- Define in and define out
- Record the torch encountered by win10 cuda. is_ False problem in available()
- Opendrive arc drawing script
- Global and Chinese markets for anesthesia, breathing and sleep apnea devices 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- II Simple NSIS installation package
- Cadence learning records
- A series of problems in offline installation of automated test environment (ride)
- MySQL blind note common functions
- Acwing - the collection of pet elves - (multidimensional 01 Backpack + positive and reverse order + two forms of DP for the answer)
- Numpy——1.數組的創建
猜你喜欢
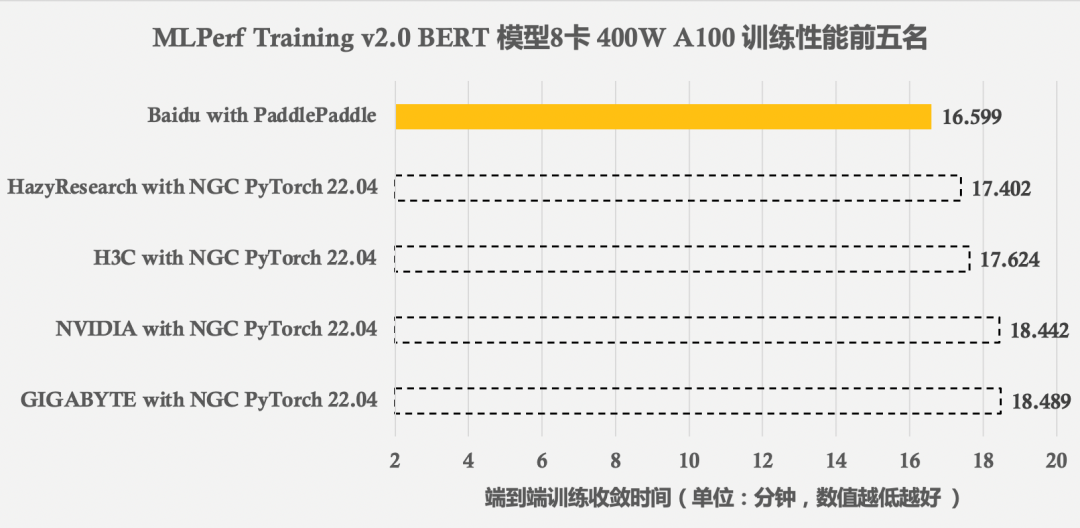
Mlperf training v2.0 list released, with the same GPU configuration, the performance of Baidu PaddlePaddle ranks first in the world
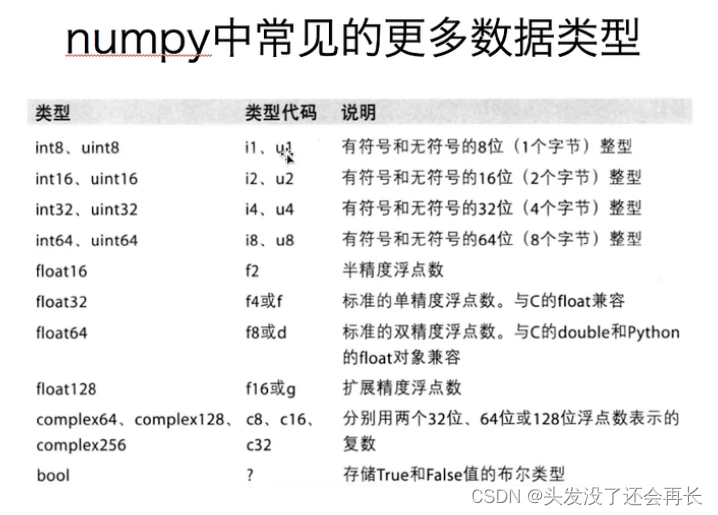
Numpy——1. Creation of array
![[neo4j] common operations of neo4j cypher and py2neo](/img/ff/8576d5784fcfa474eb1c0acd8a8065.jpg)
[neo4j] common operations of neo4j cypher and py2neo
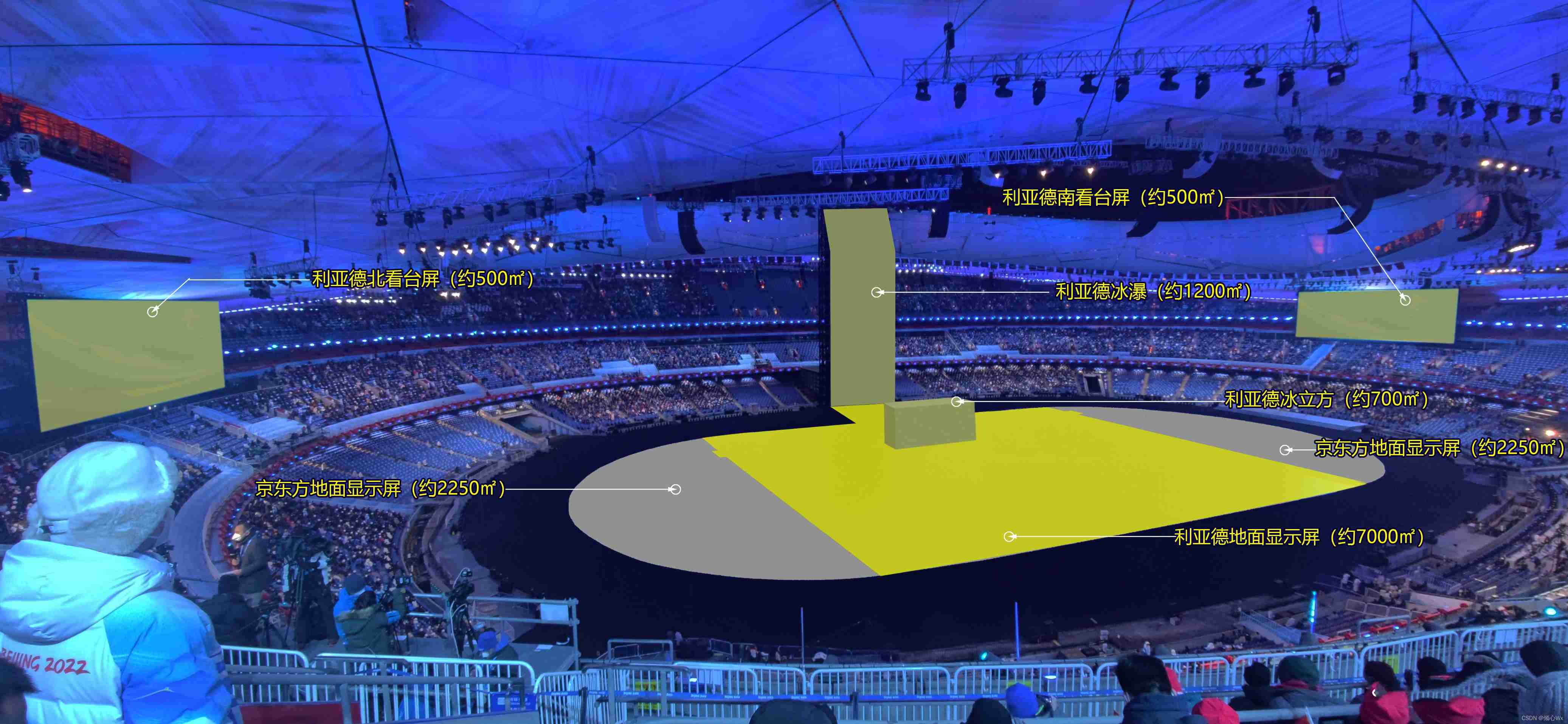

Record the opening ceremony of Beijing Winter Olympics with display equipment

Numpy——1.数组的创建

Record the visual shock of the Winter Olympics and the introduction of the screen 2
From then on, I understand convolutional neural network (CNN)
Can't find real-time chat software? Recommend to you what e-commerce enterprises are using!

P3D gauge size problem

A complete set of indicators for the 10000 class clean room of electronic semiconductors
随机推荐
Apple terminal skills
[MySQL] database knowledge record
STM32 learning method
Butterfly theme beautification - Page frosted glass effect
Screen record of the opening ceremony of the Beijing winter olympics 2
[untitled] record the visual shock of the Winter Olympics and the introduction of the display screen
研究發現,跨境電商客服系統都有這五點功能!
数字孪生实际应用案例-风机篇
2021-10-28
[neo4j] common operations of neo4j cypher and py2neo
Global and Chinese market of blackbody calibration source 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
NSIS finds out whether the file exists and sets the installation path
Pointnet++ classification practice
Altium Designer 19.1.18 - 导入板框
Mouse click fireworks explosion effect
Day09 how to create packages import package naming conventions Alibaba Development Manual
msys2
The research found that the cross-border e-commerce customer service system has these five functions!
A simple method to prove 1/t Fourier transform
1089 Insert or Merge 含测试点5