当前位置:网站首页>Getting started with MQ
Getting started with MQ
2022-07-02 03:22:00 【wuyanshen】
1. MQ introduction
1.1 What is? MQ
<font color=#b97e57>MQ</font>(Message Queue): Translated into <font color=#b97e57> Message queue </font>, Through typical <font color=#b97e57> producer </font> and <font color=#b97e57> consumer </font> Model , The producer keeps producing messages... To the message queue , Consumers keep getting messages from queues , Because the production and consumption of messages are asynchronous , And only care about the sending and receiving of messages , No intrusion of business logic , Easily realize decoupling between systems , An alias for <font color=#b97e57> Message middleware </font>, Through the use of efficient and reliable messaging mechanism for platform independent data exchange , And the integration of distributed system based on data communication .
1.2 MQ What are they?
There are many mainstream message middleware in the market today , Like the old brand ActiveMQ、RabbitMQ、 Hot at hand kafka、 Alibaba independently developed RocketMQ etc.
1.3 Different MQ characteristic
#
1.ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ yes Apache Produce , One of the most popular 、 Powerful open source message bus , It's a full support JMS Standard message middleware , rich API A variety of cluster architecture models make ActiveMQ Become an old message middleware in the industry , It's very popular in small and medium-sized enterprises .
#
2.Kafka
kafka yes LinkedIn Open source distributed Publishing - Subscribe to the messaging system , Belong to at present Apache Top projects .Kafka The main feature is based on Pull To handle message consumption , High throughput is required , The purpose at the beginning was to collect and transmit logs .0.8 The version began to support replication , Do not support things , Repetition of the message 、 The loss of 、 Mistakes are not strictly required .
#
3.RocketMQ
RocketMQ Alibaba's open source message middleware , It's pure Java Development , High throughput 、 High availability 、 Suitable for large-scale distributed applications ,RockerMQ Thought originated from Kafka, But it is not Kafka One of the Copy, It optimizes the reliable transmission of messages and the characteristics of things , At present, Alibaba group is widely used in transactions 、 Recharge 、 Flow calculation 、 Message push 、 Log streaming 、binglog Distribution and other scenarios .
#
4.RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ It's using Erlang Open source message queue system for voice development , be based on AMQP Protocol to implement ,AMQP The main feature is message oriented 、 queue 、 route ( Including point-to-point and release / subscribe )、 reliability 、 Security .AMQP Protocols are more used for data consistency within enterprise systems 、 Scenarios requiring high stability and reliability , The performance and throughput requirements are still second .
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
RabbitMQ Than kafka reliable ,kafka More suitable for IO High throughput processing , Generally used in big data log processing or on real-time ( Small delay ), reliability ( A small amount of lost data ) Use in a slightly lower level scenario , such as ELK Log collection
2. MQ actual combat
2.1 The first model ( Direct connection )

explain :
- P: producer , That is, the program to send messages
- C: consumer , Receiver of message , Will be waiting for the news to come
- queue: Message queue , The red part of the picture , It's like a mailbox , Can cache messages ; Producers can send messages to it , Consumers take messages out of it
Introduce dependencies
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>com.rabbitmq
</
groupId
>
<
artifactId
>amqp-client
</
artifactId
>
<
version
>5.14.0
</
version
>
</
dependency
>
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
Development producers
public
class
Producer {
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
batchProducer();
}
static
void
batchProducer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// The queue corresponding to the channel , No automatic creation | String queue, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete, Map<String, Object> arguments
channel.
queueDeclare(
"direct",
false,
false ,
false,
null);
// Release the news Parameters 1: Switch name Parameters 2: Queue name | String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body
channel.
basicPublish(
"",
"direct",
null, (
" Hello , I am the news. ").
getBytes());
channel.
close();
connection.
close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
Develop consumers
// consumer
public
class
Consumer1 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// The queue corresponding to the channel , No automatic creation | String queue, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete, Map<String, Object> arguments
channel.
queueDeclare(
"direct",
false,
false ,
false,
null);
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
"direct",
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
2.2 The second model (work queue)
<font color=#b97e57>Work queues</font>, Also known as (<font color=#b97e57>Toask queues</font>), Task model . When message processing is time consuming , Maybe the speed of producing messages will be much faster than that of consuming messages . In the long term , The news will pile up more and more , Can't handle in time . You can use work Model : Bind multiple consumers to a queue , Messages in the co consumption queue . Once the messages in the queue are consumed , Will disappear , So the task is not repeated .
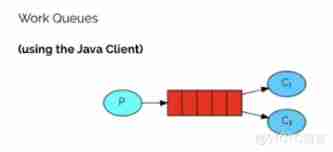
explain :
- P: producer : Publisher of task
- C1: consumer , Pick up the task and finish it , Let's say it's done slowly
- C2: consumer 2, Pick up the task and finish it , Let's say it's fast
Development producers ( Mass production messages )
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
batchProducer();
}
static
void
batchProducer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// The queue corresponding to the channel , No automatic creation
channel.
queueDeclare(
"hello",
false,
false ,
false,
null);
// Release the news
for (
int
i
=
1;
i
<=
20;
i
++) {
channel.
basicPublish(
"",
"work",
null, (
" Hello , I am the news. "
+
i).
getBytes());
}
channel.
close();
connection.
close();
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
Develop consumers 1 And consumers 2
public
class
Consumer2 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// The queue corresponding to the channel , No automatic creation
channel.
queueDeclare(
"work",
false,
false ,
false,
null);
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message
channel.
basicConsume(
"work",
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
try {
Thread.
sleep(
2000);
}
catch (
InterruptedException
e) {
e.
printStackTrace();
}
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
2.3 The third model (fanout)
<font color=#b97e57>fanout Fan out Also known as broadcast </font>
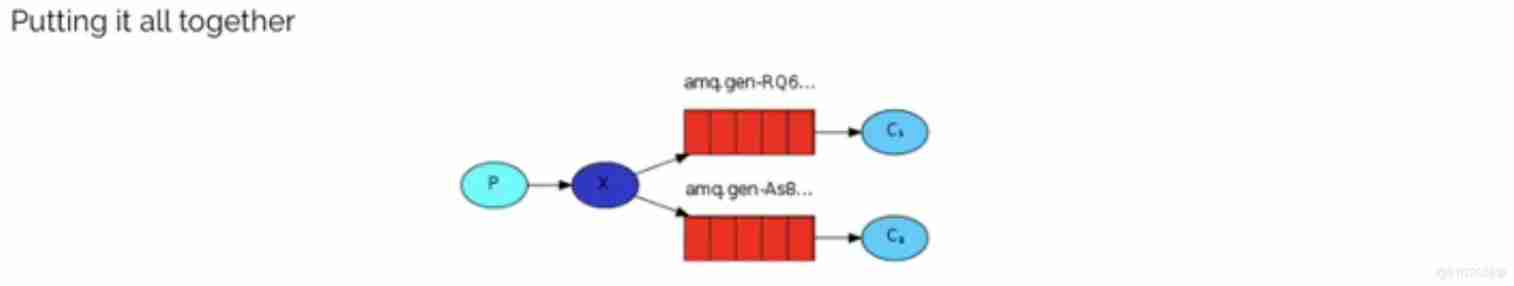
In broadcast mode , This is the message sending process :
- There can be multiple consumers
- Each consumer has its own queue( queue )
- Each queue is bound to the Exchange( Switch )
- Message sent by the producer , It can only be sent to the switch , The switch decides which queue to launch , The producer cannot decide
- The switch sends messages to all the queues it has bound
- Consumers in the queue can get messages . Realize that a message is consumed by multiple consumers
Development producers
public
class
Producer {
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
batchProducer();
}
static
void
batchProducer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// Declaration switch Parameters 1: Switch name Parameters 2: Switch type fanout The radio type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"logs",
"fanout");
// Release the news
for (
int
i
=
1;
i
<=
20;
i
++) {
// String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body
channel.
basicPublish(
"logs",
"",
null, (
" Hello , I am a fanout news "
+
i).
getBytes());
}
channel.
close();
connection.
close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
Develop consumers 1 And consumers 2
public
class
Consumer1 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// Channel bound switches | String exchange, String type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"logs",
"fanout");
// Declare temporary queue
String
queueName
=
channel.
queueDeclare().
getQueue();
// Bind switches and queues | String queue, String exchange, String routingKey
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"logs",
"");
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
queueName,
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time | long deliveryTag, boolean multiple
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
2.4 The fourth model (Routing)
2.4.1 Routing The subscription model of Internet -Direct( Direct connection )
<font color=#b97e57> stay Fanout In the pattern , A message , Will be consumed by all subscribed queues . however , In some cases , We want different messages to be consumed by different queues . It needs to be used Direct Type of Exchange.</font>
stay Direct Under the model :
- The binding of queues to switches , It can't be arbitrary binding , It's about specifying a <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font>( route key)
- The sender of the message is sending to Exchange When sending a message , You must also specify the <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font>.
- Exchange No longer give messages to each bound queue , It's based on the news <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font> Judge , There's only a line of <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font> With the news <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font> Exactly the same , To receive messages
technological process :
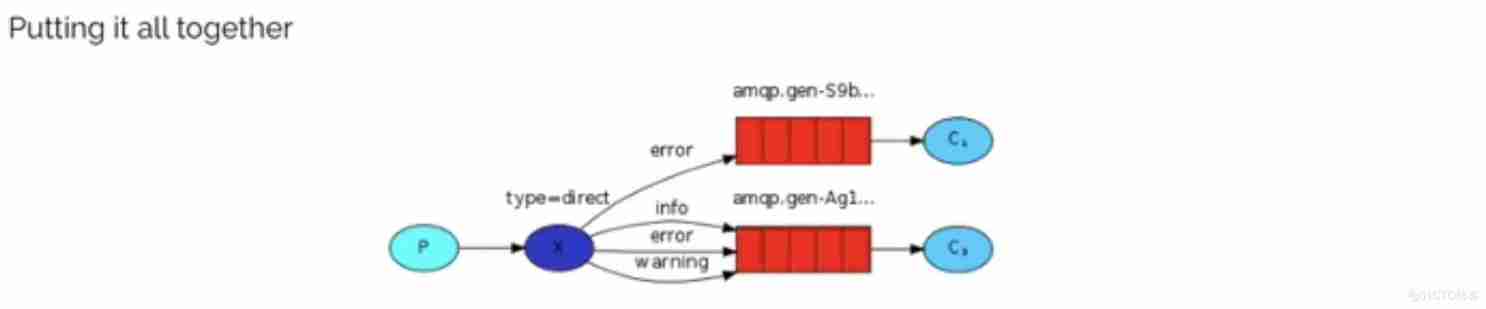
The illustration :
- P: producer , towards Exchange Send a message , When sending a message , Will specify a routingKey.
- X:Exchange( Switch ), Receive messages from producers , Then send the message to routingKey A perfectly matched queue
- C1: consumer , Its queue specifies the need for routingKey by error The news of
- C2: consumer , Its queue specifies the need for routingKey by info、error、warning
Development producers
public
class
Producer {
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
batchProducer();
}
static
void
batchProducer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// Declaration switch Parameters 1: Switch name Parameters 2: Switch type Routing mode
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"logs_direct",
"direct");
// Release the news
String
routingKey
=
"info";
for (
int
i
=
1;
i
<=
20;
i
++) {
// String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body
channel.
basicPublish(
"logs_direct",
routingKey,
null, (
" I am a direct Model publishing based on routingKey:"
+
routingKey
+
" Message sent "
+
i).
getBytes());
}
channel.
close();
connection.
close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
Develop consumers 1
consumer 1 Only routes can be received key by error The news of
public
class
Consumer1 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// Declaration switch | String exchange, String type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"logs_direct",
"direct");
// Declare temporary queue
String
queueName
=
channel.
queueDeclare().
getQueue();
// Bind switches and queues | String queue, String exchange, String routingKey
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"logs_direct",
"error");
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
queueName,
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time | long deliveryTag, boolean multiple
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
Develop consumers 2
consumer 2 Can receive routes key by info、warning、error The news of
public
class
Consumer2 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// Declaration switch | String exchange, String type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"logs_direct",
"direct");
// Declare temporary queue
String
queueName
=
channel.
queueDeclare().
getQueue();
// Bind switches and queues | String queue, String exchange, String routingKey
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"logs_direct",
"info");
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"logs_direct",
"warning");
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"logs_direct",
"error");
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
queueName,
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time | long deliveryTag, boolean multiple
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
2.4.1 Routing The subscription model of Internet -Topic
<font color=#b97e57>Topic</font> Type of <font color=#b97e57>Exchange</font> And <font color=#b97e57>Direct</font> comparison , All can be based on <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font> Route messages to different queues . It's just <font color=#b97e57>Topic</font> Type of <font color=#b97e57>Exchange</font> You can make the queue bind <font color=#b97e57>RoutingKey</font> When using wildcards ! This model <font color=#b97e57>Routingkey</font> It's usually made up of one or more words , More than one word to "." Separate , for example : <font color=#b97e57>item.insert</font>
<img src="https://minio.lvcoding.com/blog/1642488067454.png" alt="image-20220118144046584" style="zoom:50%;" />
#
wildcard
*
(
star)
No more, no less, just one word
#
Match one or more words
#
Such as :
audit.
#
matching audit.irs.corporate perhaps
audit.irs etc.
audit.
* Only match audit.irs
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
Development producers
public
class
Producer {
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
batchProducer();
}
static
void
batchProducer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// Declaration switch Parameters 1: Switch name Parameters 2: Switch type Routing mode
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"topics",
"topic");
// Release the news
String
routingKey
=
"user.save.delete";
for (
int
i
=
1;
i
<=
20;
i
++) {
// String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body
channel.
basicPublish(
"topics",
routingKey,
null, (
" I am a topic The dynamic routing model is based on routingKey:"
+
routingKey
+
" Message sent "
+
i).
getBytes());
}
channel.
close();
connection.
close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
Develop consumers 1
public
class
Consumer1 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// Declaration switch | String exchange, String type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"topics",
"topic");
// Declare temporary queue
String
queueName
=
channel.
queueDeclare().
getQueue();
// Bind switches and queues | String queue, String exchange, String routingKey
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"topics",
"user.*");
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
queueName,
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time | long deliveryTag, boolean multiple
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
Develop consumers 2
public
class
Consumer2 {
// consumer
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args)
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
amqpConsumer();
}
static
void
amqpConsumer()
throws
IOException,
TimeoutException {
{
ConnectionFactory
connectionFactory
=
new
ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.
setHost(
"localhost");
connectionFactory.
setPort(
5672);
connectionFactory.
setUsername(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setPassword(
"guest");
connectionFactory.
setVirtualHost(
"/");
// Connection object
Connection
connection
=
connectionFactory.
newConnection();
// Create channels
Channel
channel
=
connection.
createChannel();
// You can only consume one message at a time
channel.
basicQos(
1);
// Declaration switch | String exchange, String type
channel.
exchangeDeclare(
"topics",
"topic");
// Declare temporary queue
String
queueName
=
channel.
queueDeclare().
getQueue();
// Bind switches and queues | String queue, String exchange, String routingKey
channel.
queueBind(
queueName,
"topics",
"user.#");
// News consumption Parameters 2:true Automatic confirmation message false Manual confirmation message | String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback
channel.
basicConsume(
queueName,
false,
new
DefaultConsumer(
channel) {
// Parameters body Is the message taken from the message queue
public
void
handleDelivery(
String
consumerTag,
Envelope
envelope,
AMQP.
BasicProperties
properties,
byte[]
body)
throws
IOException {
System.
out.
println(
"body = "
+
new
String(
body));
// Parameters 1: To confirm which message in the queue ( Message flags ) Parameters 2: Whether to enable multiple parameter confirmation at the same time | long deliveryTag, boolean multiple
channel.
basicAck(
envelope.
getDeliveryTag(),
false);
}
});
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
3.Springboot Integrate RabbitMq
3.1 pom.xml
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>org.springframework.boot
</
groupId
>
<
artifactId
>spring-boot-starter-amqp
</
artifactId
>
</
dependency
>
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
3.2 hello Example
(
classes
=
AmqpDemoApplication.
class)
public
class
MqBoot {
private
RabbitTemplate
rabbitTemplate;
// hello
public
void
hello() {
rabbitTemplate.
convertAndSend(
"hello",
" Hello rabbitmq");
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
3.3 work Model
Test class
(
classes
=
AmqpDemoApplication.
class)
public
class
MqBoot {
private
RabbitTemplate
rabbitTemplate;
// worker Model , Default balanced consumption
public
void
worker() {
for (
int
i
=
0;
i
<
10;
i
++) {
rabbitTemplate.
convertAndSend(
"worker",
"worker Model "
+
i );
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
WorkListener consumer
public
class
WorkListener {
(
queuesToDeclare
=
(
value
=
"worker"))
public
void
worker1(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"worker1 = "
+
msg);
}
(
queuesToDeclare
=
(
value
=
"worker"))
public
void
worker2(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"worker2 = "
+
msg);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
3.4 fanout Broadcast model
Test class
(
classes
=
AmqpDemoApplication.
class)
public
class
MqBoot {
private
RabbitTemplate
rabbitTemplate;
// radio broadcast fanout Pattern
public
void
fanout() {
rabbitTemplate.
convertAndSend(
"logs",
"",
"fanout Model ");
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
FanoutListener consumer
public
class
FanoutListener {
(
bindings
= {
(
value
=
,
// Create a temporary queue
exchange
=
(
value
=
"logs",
type
=
"fanout")
// Binding switch
)
})
public
void
fanout1(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"fanout1 = "
+
msg);
}
(
bindings
= {
(
value
=
,
// Create a temporary queue
exchange
=
(
value
=
"logs",
type
=
"fanout")
// Binding switch
)
})
public
void
fanout2(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"fanout2 = "
+
msg);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
3.5 topic Subscription model
Test class
(
classes
=
AmqpDemoApplication.
class)
public
class
MqBoot {
private
RabbitTemplate
rabbitTemplate;
// subscribe topic Pattern Dynamic routing
public
void
topic() {
rabbitTemplate.
convertAndSend(
"topics",
"product.aa.bb.cc",
"topic Model ");
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
TopicListener consumer
public
class
TopicListener {
(
bindings
= {
(
value
=
,
// Create a temporary queue
exchange
=
(
value
=
"topics",
type
=
"topic"),
// Binding switch
key
= {
"user.save",
"user.*"}
)
})
public
void
topic1(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"topic1 = "
+
msg);
}
// * Match one ,# Match one or more
(
bindings
= {
(
value
=
,
// Create a temporary queue
exchange
=
(
value
=
"topics",
type
=
"topic"),
// Binding switch
key
= {
"order.#",
"product.#",
"user.*"}
)
})
public
void
topic2(
String
msg) {
System.
out.
println(
"topic2 = "
+
msg);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
4.Mq Application scenarios
4.1 Asynchronous processing
<font color=#b97e57> scene </font> : After user registration , Usually send SMS verification code and registration email , There are two traditional approaches :1. Serial mode 2. Parallel mode
- Serial mode
After writing the registration information to the database , Send registration email , Resend registration SMS , All the above three tasks are completed before returning to the client . There is a problem with this , mail , Texting is not necessary , It's just a notice , In fact, there is no need for the client to wait .

- Parallel mode
After writing the registration information to the database , While sending mail , Send a text message , After three tasks are completed , Return to the client , The parallel method can improve the processing time .

- Using message queuing
Suppose that three business nodes use 50ms, Serial usage time 150ms, Use time in parallel 100ms. Although parallelism has increased processing time , however , As I said before , Email and SMS have no impact on my normal use of the website , There is no need for the client Wait until the sending is completed before the registration is displayed , It should be written to the database and returned .
After using message queuing , Send email , SMS is not a necessary business logic asynchronous processing .

From this we can see that , After message queuing is introduced , The response time of the user is equal to the time of writing to the database + Time to write to message queue ( Negligible ), The response time is serial 3 times , It's parallel 2 times .
4.2 The application of decoupling
<font color=#b97e57> scene </font> : double 11 Shopping Festival , After the user orders , Order system needs to inform inventory system , The traditional way is that the order system calls the interface of the inventory system .

There is a drawback to this approach :
When the inventory system breaks down , The order will fail . High coupling between order system and inventory system .
Import message queue :

- <font color=#b97e57> Order system </font>: After the user orders , Order system completes persistent processing , Write message to message queue , Return to the user that the order was placed successfully .
- <font color=#b97e57> inventory system </font>: Subscribe to the message of the order , Get the order message , Perform library operations . Even if the inventory system breaks down , Message queue can also ensure the reliable delivery of messages , Will not result in the loss of messages .
4.3 Flow peak elimination
<font color=#b97e57> scene </font> : Seckill activity , Generally, it will be caused by excessive flow , Cause the app to hang up , Generally in The application front end joins the message queue
<font color=#b97e57> effect </font> :
- Can control the number of activities , Orders that exceed the threshold are directly discarded ( This may also be the reason why I didn't succeed in a second kill , Ha ha ha )
- It can alleviate the application of high flow crush in a short time ( The application gets the order according to its maximum processing capacity )

<font color=#b97e57> Scene description </font>:
- User's request , When the server receives it , Write message queue first , The length of joining the message queue exceeds the threshold , Then discard the user request or jump to the error page
- Seckill service according to the request information in the message queue , Follow up
边栏推荐
- Grpc quick practice
- venn图取交集
- Verilog 过程连续赋值
- Pointer array & array pointer
- Go执行shell命令
- What is the binding path of SAP ui5
- Verilog 过程赋值 区别 详解
- Retrofit's callback hell is really vulnerable in kotlin synergy mode
- Screenshot literacy tool download and use
- 2022 hoisting machinery command examination paper and summary of hoisting machinery command examination
猜你喜欢

The capacity is upgraded again, and the new 256gb large capacity specification of Lexar rexa 2000x memory card is added
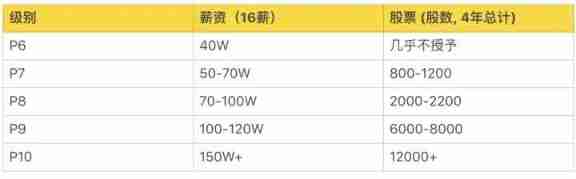
A list of job levels and salaries in common Internet companies. Those who have conditions must enter big factories. The salary is really high

Verilog 状态机
![[C Advanced] brother Peng takes you to play with strings and memory functions](/img/95/ab1bb0b3fa0b99e32233a5ca5d42a4.jpg)
[C Advanced] brother Peng takes you to play with strings and memory functions
How to establish its own NFT market platform in 2022

表单自定义校验规则

数据传输中的成帧

GB/T-2423.xx 环境试验文件,整理包括了最新的文件里面

命名块 verilog
![[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol](/img/03/83c883afb63b7c63f6879b5513bac3.jpg)
[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol
随机推荐
JS <2>
Discrimination between sap Hana, s/4hana and SAP BTP
JS introduction < 1 >
aaaaaaaaaaaaa
aaaaaaaaaaaaa
Golang configure export goprivate to pull private library code
Download and use of the super perfect screenshot tool snipaste
Gradle 笔记
Verilog 避免 Latch
[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol
OSPF LSA message parsing (under update)
JIT deep analysis
Form custom verification rules
GSE104154_ scRNA-seq_ fibrotic MC_ bleomycin/normalized AM3
Verilog state machine
Work hard all day long and be alert at sunset
Verilog timing control
Verilog wire type
Screenshot literacy tool download and use
Kotlin基础学习 17