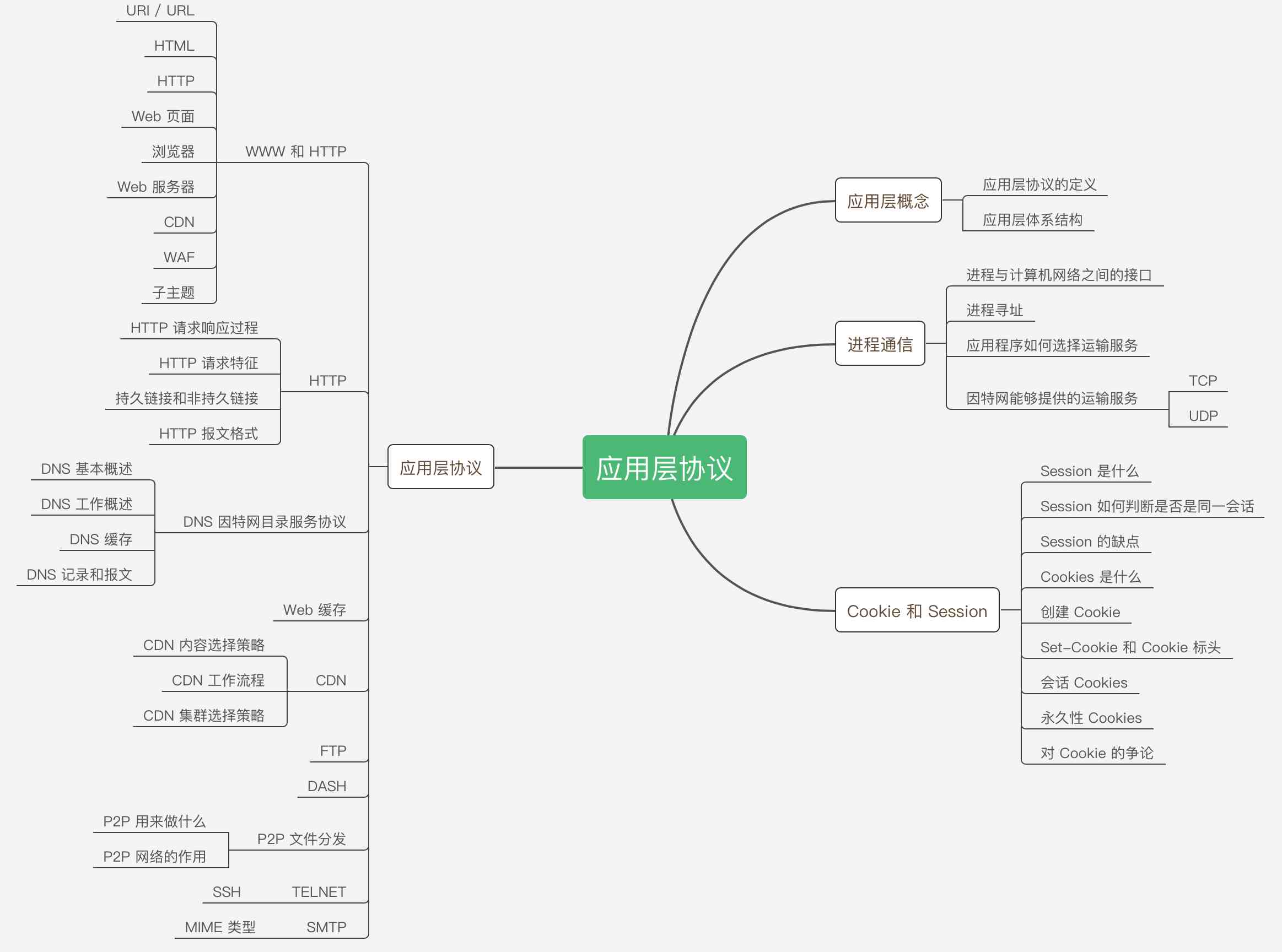
I believe used Koa、Redux or Express Our partners are familiar with middleware , Especially in learning Koa In the process of , You'll also be exposed to “ Onion model ”.
In this article, brother Bao will learn with you Koa Middleware , But I don't want to show you what's known in the first place “ Onion model ”, But let's first introduce Koa What is Middleware in ?
Learn more , You can visit A Bao Ge Github Personal home page
One 、Koa middleware
stay @types/koa-compose Under bag index.d.ts In the header file, we found the definition of middleware type :
// @types/koa-compose/index.d.ts
declare namespace compose {
type Middleware<T> = (context: T, next: Koa.Next) => any;
type ComposedMiddleware<T> = (context: T, next?: Koa.Next) => Promise<void>;
}
// @types/koa/index.d.ts => Koa.Next
type Next = () => Promise<any>; Through observation Middleware The definition of type , We can know in Koa in , Middleware is a common function , This function takes two arguments :context and next. among context Represent context object , and next Return after a call Promise Object function object .
To understand the Koa After what middleware is , Let's introduce Koa The core of middleware , namely compose function :
function wait(ms) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms || 1));
}
const arr = [];
const stack = [];
// type Middleware<T> = (context: T, next: Koa.Next) => any;
stack.push(async (context, next) => {
arr.push(1);
await wait(1);
await next();
await wait(1);
arr.push(6);
});
stack.push(async (context, next) => {
arr.push(2);
await wait(1);
await next();
await wait(1);
arr.push(5);
});
stack.push(async (context, next) => {
arr.push(3);
await wait(1);
await next();
await wait(1);
arr.push(4);
});
await compose(stack)({});Source of the above code : https://github.com/koajs/comp...
For the above code , We want to finish compose(stack)({}) After statement , Array arr The value of is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]. We don't care about compose How functions are implemented . Let's analyze , If an array is required arr Output the desired result , Above 3 The execution process of middleware :
1. Start with the 1 Middleware , Go to arr Array push in 1, here arr The value of the array is [1], And then wait 1 millisecond . In order to ensure arr The first of an array of 1 Items for 2, We need to call next After the function , Start with the 2 Middleware .
2. Start with the 2 Middleware , Go to arr Array push in 2, here arr The value of the array is [1, 2], Continue to wait for 1 millisecond . In order to ensure arr The first of an array of 2 Items for 3, We also need to call next After the function , Start with the 3 Middleware .
3. Start with the 3 Middleware , Go to arr Array push in 3, here arr The value of the array is [1, 2, 3], Continue to wait for 1 millisecond . In order to ensure arr The first of an array of 3 Items for 4, We require that we call 3 One in the middle next After the function , Be able to move on .
4. When the first 3 After the execution of middleware , here arr The value of the array is [1, 2, 3, 4]. So in order to guarantee arr The first of an array of 4 Items for 5, We need to be in the 3 After the execution of middleware , Back to page 2 Middleware next After the function, the statement begins to execute .
5. When the first 2 After the execution of middleware , here arr The value of the array is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. Again , In order to ensure arr The first of an array of 5 Items for 6, We need to be in the 2 After the execution of middleware , Back to page 1 Middleware next After the function, the statement begins to execute .
6. When the first 1 After the execution of middleware , here arr The value of the array is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].
In order to understand the above execution process more intuitively , We can think of each middleware as 1 A big task , Then in order to next Function is the cut-off point , Breaking down every big task into 3 individual beforeNext、next and afterNext 3 Small tasks .

In the diagram above , We start with middleware one beforeNext The task begins , Then follow the execution steps of the purple arrow to complete the task scheduling of middleware . stay 77.9K Of Axios What are the advantages of the project In this article , Brother Bao comes from Task registration 、 Task scheduling and task scheduling 3 Analyze... In every way Axios The implementation of interceptors . Again , Bao Ge will be from the above 3 Analyze... In every way Koa Middleware mechanism .
1.1 Task registration
stay Koa in , We created Koa After the application object , By calling the object's use Method to register middleware :
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const ms = Date.now() - start;
console.log(`${ctx.method} ${ctx.url} - ${ms}ms`);
}); Actually use The implementation of this method is very simple , stay lib/application.js In file , We found the definition of it :
// lib/application.js
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
constructor(options) {
super();
// Omitted code
this.middleware = [];
}
use(fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') throw new TypeError('middleware must be a function!');
// Omitted code
this.middleware.push(fn);
return this;
}
} From the above code we can see , stay use Inside the method, there will be fn Parameter type checking , When the check passes , Will be able to fn The directed middleware is saved to middleware Array , At the same time, it will return to this object , To support chain calls .
1.2 Task arrangement
stay 77.9K Of Axios What are the advantages of the project In this article , Brother Bao referred to Axios Interceptor design model , Extract the following general task processing model :

In this general model , A Bao Ge is by putting the front processor and the post processor into CoreWork Complete the task arrangement before and after the core task . And for Koa In terms of middleware mechanism , It is by putting the front processor and the post processor into await next() Before and after the sentence to complete the task arrangement .
// Middleware that counts request processing time
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const ms = Date.now() - start;
console.log(`${ctx.method} ${ctx.url} - ${ms}ms`);
});
1.3 Task scheduling
Through the previous analysis , We already know that , Use app.use Method registration middleware will be saved to the internal middleware Array . To complete the task scheduling , We need to constantly start from middleware Take out the middleware from the array to execute . The scheduling algorithm of middleware is encapsulated in koa-compose Under bag compose Function , The implementation of this function is as follows :
/**
* Compose `middleware` returning
* a fully valid middleware comprised
* of all those which are passed.
*
* @param {Array} middleware
* @return {Function}
* @api public
*/
function compose(middleware) {
// Omitted code
return function (context, next) {
// last called middleware #
let index = -1;
return dispatch(0);
function dispatch(i) {
if (i <= index)
return Promise.reject(new Error("next() called multiple times"));
index = i;
let fn = middleware[i];
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next;
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve();
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1)));
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err);
}
}
};
}compose The function takes a parameter , The type of the parameter is array , After calling this function, a new function will be returned . Next, we will take the previous example as an example , So let's analyze that await compose(stack)({}); Statement execution .
1.3.1 dispatch(0)
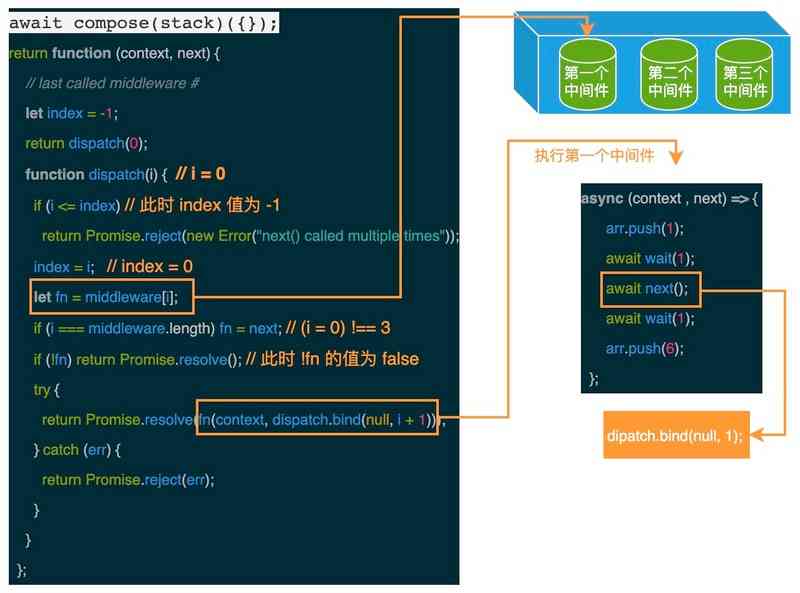
It can be seen from the above figure , When called inside the first middleware next function , In fact, it is to continue to call dispatch function , Now the parameters i The value of is 1.
1.3.2 dispatch(1)
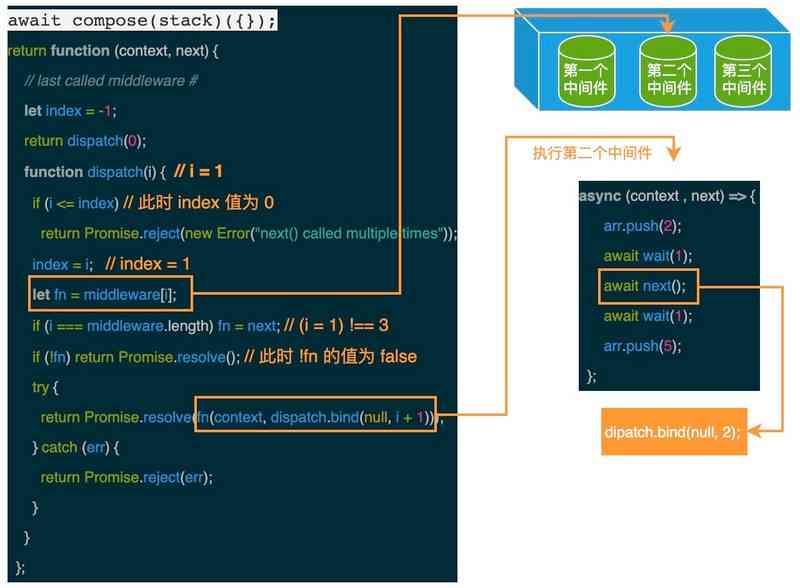
It can be seen from the above figure , When called inside the second middleware next function , Still call dispatch function , Now the parameters i The value of is 2.
1.3.3 dispatch(2)

It can be seen from the above figure , When called inside the third middleware next function , Still call dispatch function , Now the parameters i The value of is 3.
1.3.4 dispatch(3)

It can be seen from the above figure , When middleware After the middleware in the array starts to execute , If the schedule is not explicitly set next The value of the parameter , Will start to return next The statement after the function continues to execute . When the third middleware is executed , It will return to the second intermediate piece next The statement after the function continues to execute , Until all the statements defined in the middleware are executed .
Analysis finished compose Function implementation code , Let's take a look Koa How to use it internally compose Function to handle the registered middleware .
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// Respond to
app.use(ctx => {
ctx.body = ' Hello everyone , I'm brother Bao ';
});
app.listen(3000); Use the code above , I can quickly start a server . among use We have already analyzed the method , So let's analyze listen Method , The implementation of this method is as follows :
// lib/application.js
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
listen(...args) {
debug('listen');
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
return server.listen(...args);
}
} It's obvious that listen Methods the internal , Will be called first Node.js built-in HTTP Modular createServer Method to create the server , Then start listening to the specified port , Start waiting for the client to connect . in addition , Calling http.createServer Method creation HTTP Server time , The parameter we passed in is this.callback(), The implementation of this method is as follows :
// lib/application.js
const compose = require('koa-compose');
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
callback() {
const fn = compose(this.middleware);
if (!this.listenerCount('error')) this.on('error', this.onerror);
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fn);
};
return handleRequest;
}
} stay callback Methods the internal , We finally met the long lost compose Method . When calling callback After method , Returns the handleRequest Function objects are used to handle HTTP request . whenever Koa When the server receives a client request , Will be called handleRequest Method , In this method, a new Context object , Then the registered middleware is executed to process the received HTTP request :
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware) {
const res = ctx.res;
res.statusCode = 404;
const onerror = err => ctx.onerror(err);
const handleResponse = () => respond(ctx);
onFinished(res, onerror);
return fnMiddleware(ctx).then(handleResponse).catch(onerror);
}
}well ,Koa The content of middleware has been basically introduced , Yes Koa Partners interested in the kernel , You can study it yourself . Next, let's introduce the onion model and its application .
Two 、 Onion model
2.1 Introduction to onion model

( picture source :https://eggjs.org/en/intro/eg...)
In the diagram above , Each layer within the onion represents a separate middleware , For different functions , Like exception handling 、 Cache processing, etc . Each layer of middleware starts from the left side , After entering the innermost layer of middleware , It starts from the innermost layer of middleware and returns layer by layer . So for each layer of middleware , In a Requests and responses In cycle , There are two timing points to add different processing logic .
2.2 Onion model application
In addition to the Koa In addition to the onion model , The model is also widely used in Github On some good projects , such as koa-router And Alibaba's midway、umi-request Etc .
Introduction after Koa Middleware and onion model , According to his own understanding , Extract the following general task processing model :

The middleware shown in the figure above , Generally, it is a general function code that has nothing to do with business , For example, the middleware used to set the response time :
// x-response-time
async function responseTime(ctx, next) {
const start = new Date();
await next();
const ms = new Date() - start;
ctx.set("X-Response-Time", ms + "ms");
}For every middleware , Both the front processor and the post processor are optional . For example, the following middleware is used to set uniform response content :
// response
async function respond(ctx, next) {
await next();
if ("/" != ctx.url) return;
ctx.body = "Hello World";
}Although the two middleware described above are relatively simple , But you can also implement complex logic according to your own needs .Koa The kernel is very lightweight , The sparrow is all ready . It provides an elegant middleware mechanism , Let developers have the flexibility to extend Web The function of the server , This kind of design idea is worth learning and using for reference .
well , That's all for now , If there's a chance later , Brother Bao is introducing himself Redux or Express Middleware mechanism .