当前位置:网站首页>Understanding rotation matrix R from the perspective of base transformation
Understanding rotation matrix R from the perspective of base transformation
2022-07-05 08:54:00 【Li Yingsong~】
In understanding the camera coordinate system , We will definitely touch the camera's external parameter matrix R, It converts coordinates from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system :
P c = R ∗ P w + t P_c=R*P_w+t Pc=R∗Pw+t
This is actually a transformation between two coordinate systems , We know R R R A matrix is an orthogonal matrix , So it's 3 Row ( Column ) The vector is 3 A set of orthonormal bases in a vector space , And a set of orthonormal bases can be used as three basis vectors of a coordinate system . So our R R R How does a matrix relate to the basis vectors of two coordinate systems ?
Let's draw two coordinate systems first X w Y w Z w X_wY_wZ_w XwYwZw and X c Y c Z c X_cY_cZ_c XcYcZc: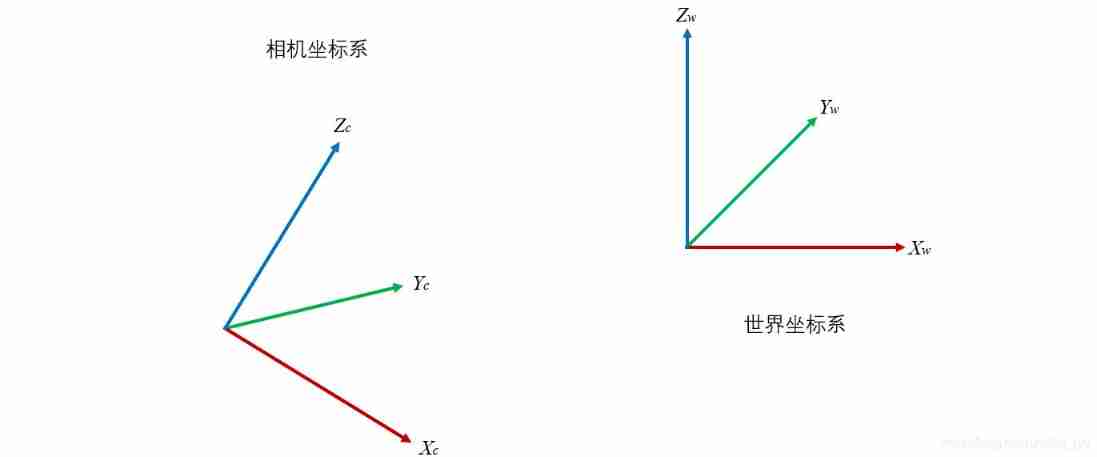
We're going to talk about how to put a certain point P P P Coordinates in the world coordinate system are converted into coordinates in the camera coordinate system .
Let's not consider the translation between the two coordinate systems , So move the origin of the camera coordinate system to the origin of the world coordinate system , like this :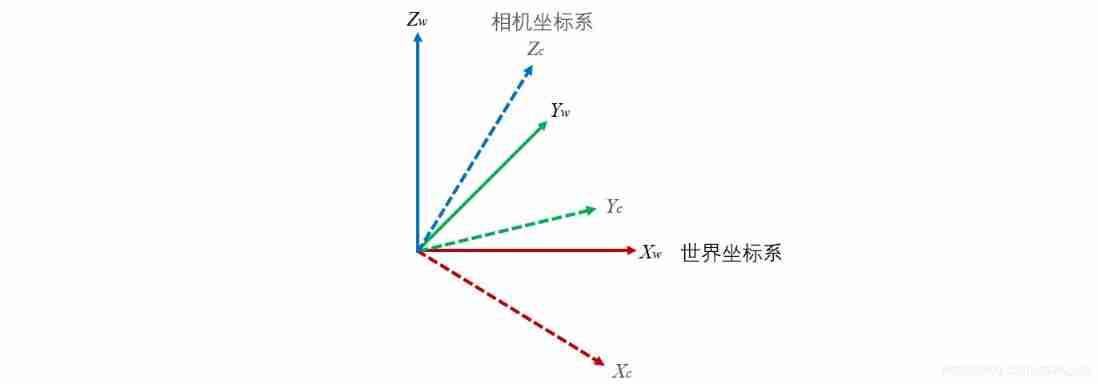
We can mark the set of basis vectors of two coordinate systems e w ( e ⃗ w x , e ⃗ w y , e ⃗ w z ) e_w(\vec{e}_{wx},\vec{e}_{wy},\vec{e}_{wz}) ew(ewx,ewy,ewz) and e c ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) e_c(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz}) ec(ecx,ecy,ecz). They're all in the world coordinate system .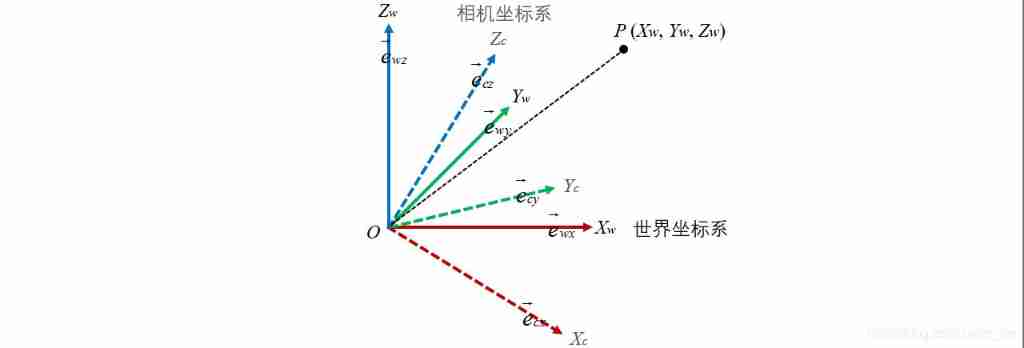
Next , And how to put a point in the world coordinate system P ( X w , Y w , Z w ) P(X_w,Y_w,Z_w) P(Xw,Yw,Zw) Convert to camera coordinates
P ( X w , Y w , Z w ) → P ( X c , Y w , Z w ) P(X_w,Y_w,Z_w)→P(X_c,Y_w,Z_w) P(Xw,Yw,Zw)→P(Xc,Yw,Zw)
In the world coordinate system , Basis vector set e w ( e ⃗ w x , e ⃗ w y , e ⃗ w z ) e_w(\vec{e}_{wx},\vec{e}_{wy},\vec{e}_{wz}) ew(ewx,ewy,ewz) Is the unit matrix , That is to say

among e ⃗ w x = ( 1 , 0 , 0 ) T \vec{e}_{wx}=(1,0,0)^T ewx=(1,0,0)T, e ⃗ w y = ( 0 , 1 , 0 ) T \vec{e}_{wy}=(0,1,0)^T ewy=(0,1,0)T, e ⃗ w z = ( 0 , 0 , 1 ) T \vec{e}_{wz}=(0,0,1)^T ewz=(0,0,1)T.
We know P P P The coordinates in the world coordinate system are actually a linear combination of the above three sets of basis vectors , namely P w = X w ∗ e ⃗ w x + Y w ∗ e ⃗ w x + Z w ∗ e ⃗ w x P_w=X_w*\vec{e}_{wx}+Y_w*\vec{e}_{wx}+Z_w*\vec{e}_{wx} Pw=Xw∗ewx+Yw∗ewx+Zw∗ewx

This is the base vector representation of coordinates .
So let's take P P P The coordinates of the points are transformed into a set of basis vectors e c ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) e_c(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz}) ec(ecx,ecy,ecz) Then we get the transformation in the camera coordinate system . let me put it another way , We're going to calculate P P P The point is in the base vector set e c ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) e_c(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz}) ec(ecx,ecy,ecz) The coordinates under P c = X c ∗ e ⃗ c x + Y c ∗ e ⃗ c x + Z c ∗ e ⃗ c x P_c=X_c*\vec{e}_{cx}+Y_c*\vec{e}_{cx}+Z_c*\vec{e}_{cx} Pc=Xc∗ecx+Yc∗ecx+Zc∗ecx.
From the perspective of the rotation matrix , The formula is :
P c = R P w P_c=RP_w Pc=RPw
Let's forget for a moment P P P, Let's think about the set of basis vectors e c ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) e_c(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz}) ec(ecx,ecy,ecz) adopt R R R What does a matrix look like in camera coordinates ?
The answer is obvious , It's a unit array E E E.
That is to say, by left multiplying the rotation matrix R R R, We can set the basis vectors e c ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) e_c(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz}) ec(ecx,ecy,ecz) Into a unit matrix E E E, The expression is as follows :
R ( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) = E R(\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz})=E R(ecx,ecy,ecz)=E
So we know
( e ⃗ c x , e ⃗ c y , e ⃗ c z ) = R − 1 = R T (\vec{e}_{cx},\vec{e}_{cy},\vec{e}_{cz})=R^{-1}=R^T (ecx,ecy,ecz)=R−1=RT
This is our rotation matrix R R R Understanding from the perspective of basis transformation , R R R The inverse matrix ( Or transpose matrix ) Three column vectors of , It is the coordinates of the three base vectors of the camera coordinate system in the world coordinate system .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Business modeling of software model | stakeholders
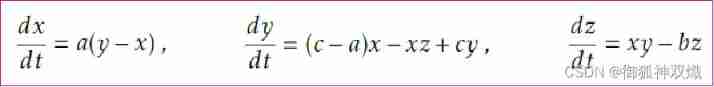
Solutions of ordinary differential equations (2) examples

Guess riddles (10)
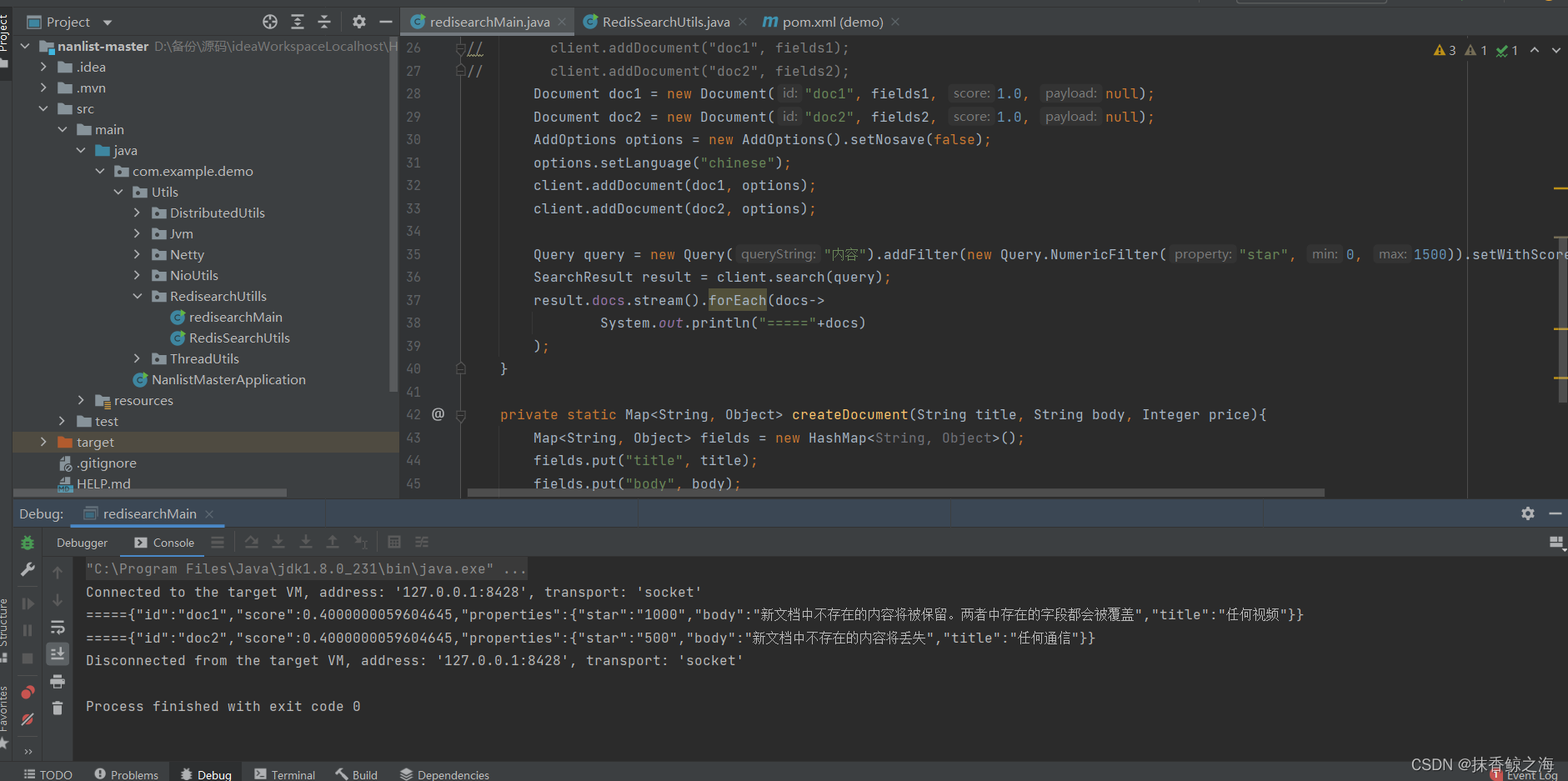
Redis实现高性能的全文搜索引擎---RediSearch

牛顿迭代法(解非线性方程)
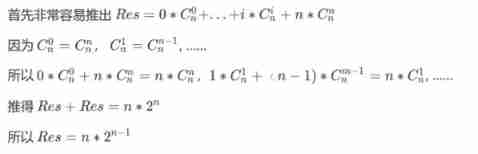
Solution to the problems of the 17th Zhejiang University City College Program Design Competition (synchronized competition)

RT-Thread内核快速入门,内核实现与应用开发学习随笔记

图解八道经典指针笔试题

Halcon blob analysis (ball.hdev)
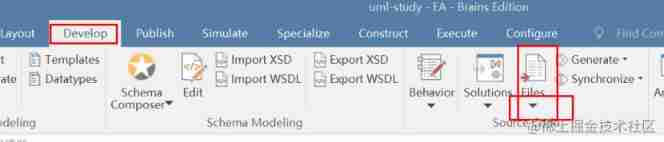
EA introduction notes
随机推荐
js异步错误处理
Hello everyone, welcome to my CSDN blog!
The first week of summer vacation
My experience from technology to product manager
Characteristic Engineering
LLVM之父Chris Lattner:为什么我们要重建AI基础设施软件
GEO数据库中搜索数据
Codeforces Round #648 (Div. 2) E.Maximum Subsequence Value
JS asynchronous error handling
【日常訓練--騰訊精選50】557. 反轉字符串中的單詞 III
Solutions of ordinary differential equations (2) examples
某公司文件服务器迁移方案
asp. Net (c)
Halcon snap, get the area and position of coins
notepad++
ROS learning 1- create workspaces and function packs
Shift operation of complement
c#比较两张图像的差异
Ros-10 roslaunch summary
[牛客网刷题 Day4] JZ35 复杂链表的复制