当前位置:网站首页>Handwritten promise [05] - exception capture of promise method and optional parameters of then method implementation
Handwritten promise [05] - exception capture of promise method and optional parameters of then method implementation
2022-06-11 06:25:00 【Geek student】
1. Capture customization LyPromise Mistakes in
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class LyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
} catch(error) {
this.reject(error);
}
}
status = PENDING;
value = undefined;
reason = undefined;
// Successful callback
successCallback = [];
// Failed callback
failCallback = [];
resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
// Determine whether a successful callback exists , If there is Call the successful callback
// this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value);
while (this.successCallback.length) {
this.successCallback.shift()(this.value); // perform
}
}
reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
// Determine whether the failed callback exists , If there is Call the failed callback
// this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason)
while (this.failCallback.length) {
this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason)
}
}
then(successCallback, failCallback) {
let Promise2 = new LyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// Q: Why want to use reject
// A: call chaining then Method time , The last one that went wrong then Need to be in the next then Method
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else {
// When the actuator operates asynchronously ,status still pending,
// So at this time, we don't know whether it is a success or a failure callback , So here we need to call back these two
// Store it
this.successCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
this.failCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
}
})
return Promise2;
}
}
function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError("Promise Referenced circularly !!!"))
}
if (x instanceof LyPromise) {
// promise object
x.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
// Common value
resolve(x);
}
}
module.exports = LyPromise;
2. then Method becomes an optional parameter
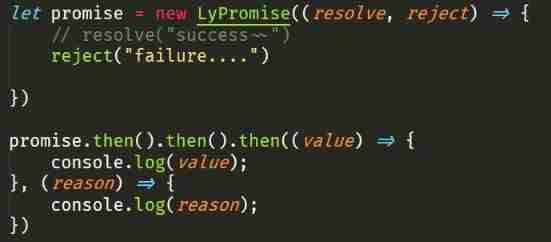
stay Promise in then Methods Successful callback and Failed callback Is an optional parameter , It belongs to what can be written but not written .
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reiect) => {
resolve(100);
});
promise
.then()
.then()
.then()
.then((value) => {
console.log(value); // 100
});
When in the previous then When no parameters are passed in the method , In fact, it is equivalent to passing a Returned to himself Callback function for :
So just judge this then It should be ok if the method passes parameters , If no parameters are passed , Then give him a parameter .
then(successCallback, failCallback) {
successCallback = successCallback ? successCallback : value => value;
failCallback = failCallback ? failCallback : reason => reason;
let Promise2 = new LyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// Q: Why want to use reject
// A: call chaining then Method time , The last one that went wrong then Need to be in the next then Method
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else {
// When the actuator operates asynchronously ,status still pending,
// So at this time, we don't know whether it is a success or a failure callback , So here we need to call back these two
// Store it
this.successCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
this.failCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
}
})
return Promise2;
}
Test it :

3. All current codes
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class LyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
try {
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
} catch(error) {
this.reject(error);
}
}
status = PENDING;
value = undefined;
reason = undefined;
// Successful callback
successCallback = [];
// Failed callback
failCallback = [];
resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
// Determine whether a successful callback exists , If there is Call the successful callback
// this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value);
while (this.successCallback.length) {
this.successCallback.shift()(this.value); // perform
}
}
reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status !== PENDING) return;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
// Determine whether the failed callback exists , If there is Call the failed callback
// this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason)
while (this.failCallback.length) {
this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason)
}
}
then(successCallback, failCallback) {
let Promise2 = new LyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
// Q: Why want to use reject
// A: call chaining then Method time , The last one that went wrong then Need to be in the next then Method
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0)
} else {
// When the actuator operates asynchronously ,status still pending,
// So at this time, we don't know whether it is a success or a failure callback , So here we need to call back these two
// Store it
this.successCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = successCallback(this.value);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
this.failCallback.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = failCallback(this.reason);
resolvePromise(Promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 0);
});
}
})
return Promise2;
}
}
function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(new TypeError("Promise Referenced circularly !!!"))
}
if (x instanceof LyPromise) {
// promise object
x.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
// Common value
resolve(x);
}
}
module.exports = LyPromise;
边栏推荐
- Learn C language well from keywords
- CCF 2013 12-5 I‘m stuck
- Chapter 6 of machine learning [series] random forest model
- Print sparse arrays and restore
- 关于SIoU的原理和代码实现(回顾IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU)
- How to treat the ethical issues arising from driverless Technology
- Learn a trick to use MySQL functions to realize data desensitization
- Training and testing of super score model in mmediting
- 617. 合并二叉树
- Squid agent
猜你喜欢

Shandong University machine learning experiment VI k-means

235-二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先

MATLAB realizes mean filtering and FPGA for comparison, and uses Modelsim waveform simulation

How to use the markdown editor
![[]==![]](/img/65/ab724c74b080da319ed5c01c93fdb7.png)
[]==![]

Matlab实现均值滤波与FPGA进行对比,并采用modelsim波形仿真

Review Servlet

Topic collection of FIFO minimum depth calculation

Shandong University machine learning experiment 5 SVM

Servlet
随机推荐
CCS安装编译器的方法
Solve the problem that ffmpeg obtains aac audio files with incorrect duration
FPGA interview notes (IV) -- sequence detector, gray code in cross clock domain, ping-pong operation, static and dynamic loss reduction, fixed-point lossless error, recovery time and removal time
Quantitative understanding (Quantitative deep revolutionary networks for effective information: a whitepaper)
通过两种方式手写一个消息队列
[TP5 online export picture generation excel detailed explanation example]
Detailed steps for installing mysql-5.6.16 64 bit green version
Handwritten promise [04] - then method chain call to recognize promise object self return
jenkins-凭证管理
Simple understanding of XML and JSON
Shandong University machine learning experiment 7 pca+ SVM face recognition
The classification effect of converting video classification data set to picture classification data set on vgg16
This point of arrow function
call和apply和bind的区别
Docker installation of MySQL and redis
Training and testing of super score model in mmediting
FPGA设计——乒乓操作实现与modelsim仿真
Using Metasploit Trojan horse for remote control
MySQL implements over partition by (sorting the data in the group after grouping)
Use of constructors