当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to network basics
Introduction to network basics
2022-07-06 22:47:00 【GSX_ MI】
One . In Architecture , Location of the network
1. Understand through examples in life
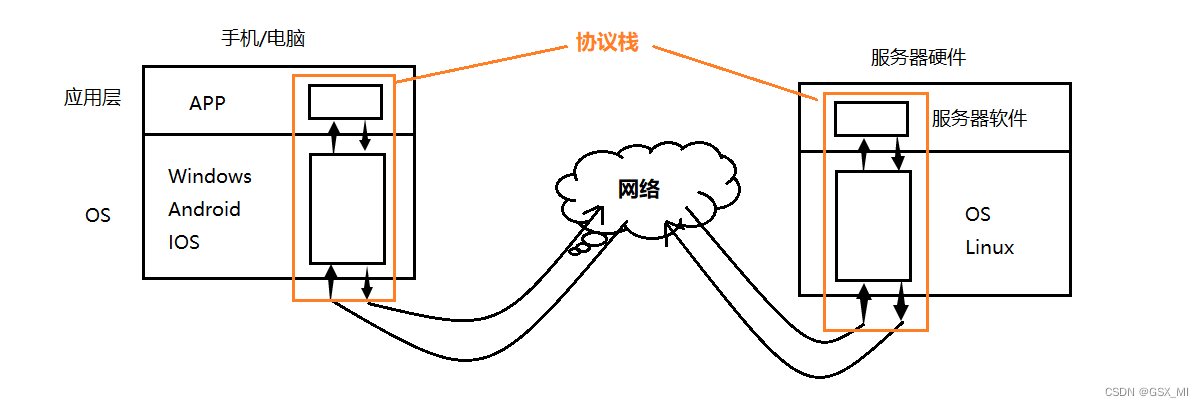
- We usually use it on mobile phones or computers APP They all run in the application layer . When a user initiates a request at the application layer , Will eventually be released to OS,OS There is an embedded software protocol stack inside , The protocol stack packs the user's request data layer by layer , Transfer data to the network through the network card , Data is forwarded through various routes within the network , Finally, the data is transmitted to the target server .
- The target server itself is also a computer , The operating system of the computer is Linux, When accessing the target server, we may use Windows/ Android /IOS Isooperating system . Besides , The peer server also has its own protocol stack , The peer server will get the data through the protocol stack for various unpacking operations, and then submit it to the service software of the application layer , The software server performs various analysis and processing on the received user requests , Then return the corresponding data to the user in the same way
2. All layers of the network protocol stack are OS Position in
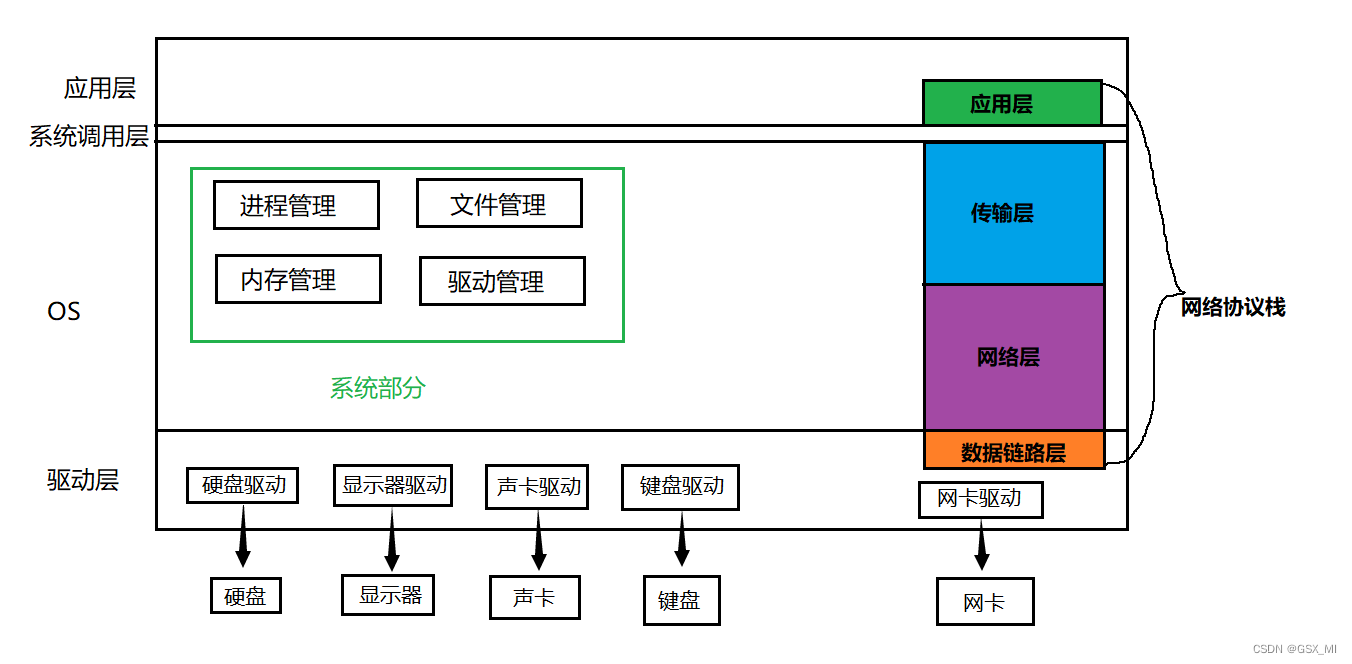
- The application layer is located in the user layer : This part of the code is written by the developer of the network protocol , such as HTTP agreement 、HTTPS Agreement and SSH Agreements, etc .
- The transport layer and network layer are located at the operating system layer : The most classic protocol of transport layer is called TCP agreement , The most classic protocol in the network layer is called IP agreement , namely TCP/IP agreement .
- The data link layer is located in the driver layer : It is responsible for real data transmission
3. Functions between layers of network protocol stack
- Data link layer and physical layer : To realize communication, we must first be able to send data , The data link layer and the physical layer are Responsible for the real data transmission process .
- The network layer : Supported by data link layer and physical layer , Now you can send data , But we should also know where the data should be sent , What the network layer does is forward data , Solved the problem of where the data goes .
- Transport layer : Now you have the ability to send data , Also know where the data should be sent , However, we cannot guarantee that the sent data can successfully reach the opposite host , For example, packet loss or shutdown of the opposite host may occur during transmission , Even the end-to-end server makes mistakes , Cause data transmission problems . The work of the transport layer is to deal with the problems encountered in transmission , Mainly to ensure data reliability .
- application layer : The lower three layers of the network protocol stack can ensure the delivery of data to the opposite host , But now we need to be clear , What is the purpose of sending data to the opposite host , This is the problem to be solved by the application layer . The application layer needs to be based on the specific communication purpose , Analyze and process the data , To achieve a certain business purpose .
Conclusion : The main work of the lower three layers of the network protocol stack is to deal with the communication details , The application layer mainly completes some specific business details .
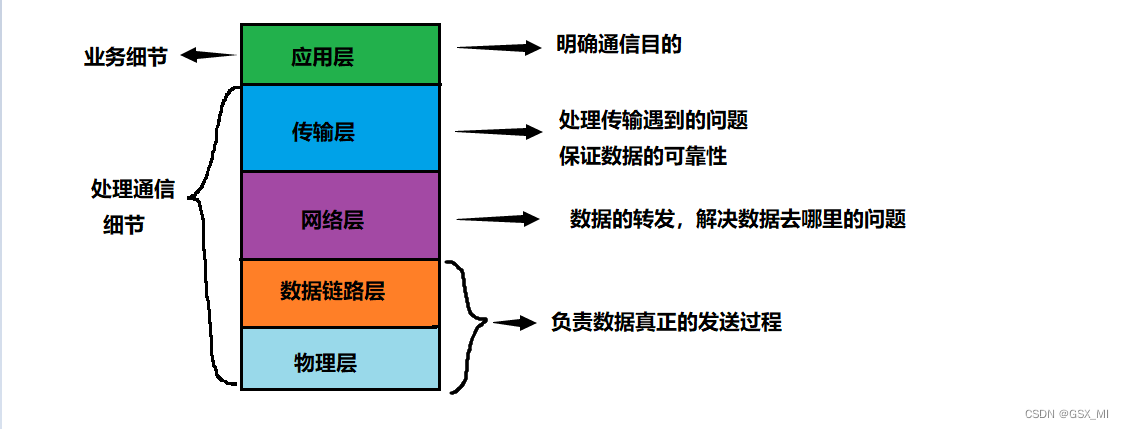
4. Network protocol layering
(1) The essence of layered structure : Decoupling in software engineering
- Between layers , Only the mutual transfer relationship of interfaces
- Increase the maintainability and extensibility of the code
(2) About maintainability and extensibility
- Suppose one day you think that the functions of the data link layer can no longer afford the ability of communication , Then we can replace it with a new protocol , The protocols corresponding to other layers do not need to be changed , This is called scalability .
- And if there is a problem with one layer of the protocol stack , We just need to determine which floor is wrong , You can go directly to the corresponding layer to find the problem , This is called code maintainability .
Two . The background of computer network development
1. Network development
(1) Independent mode : Computers perform tasks independently
In the early days , Computers are independent of each other , At this time, if multiple computers want to cooperate to complete a certain business , Then you can only wait for one computer to process and then transfer the data to the next computer , Then the next computer will carry out the corresponding business processing , Very inefficient .
(2) Network interconnection : Multiple hosts are connected , Data sharing
Then someone tried to connect these computers together , When a business needs to be completed by multiple computers , The shared data can be put into the server for centralized management , At this point, each computer can obtain these shared data , Therefore, each business can be switched at any time during processing .

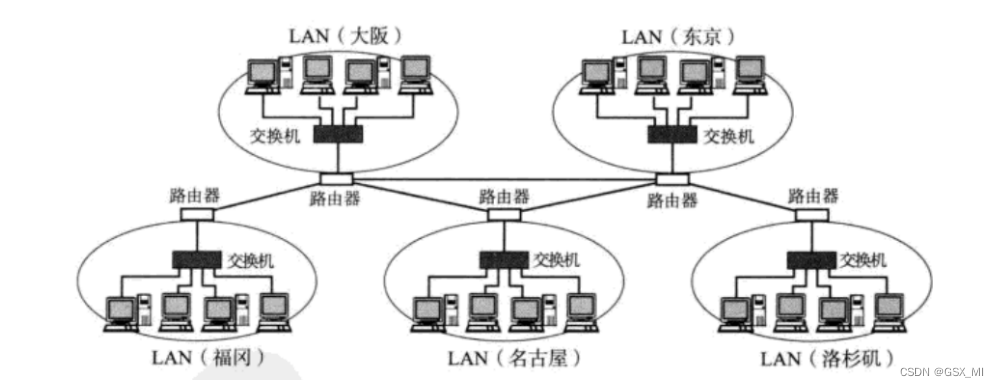
(3) LAN LAN: There are more computers , It's connected to a router through a switch
The local area networks are connected with each other through routers , It forms a larger network structure , We call it wan . Actual LAN and WAN are relative concepts , We can also regard Wan as a relatively large lan
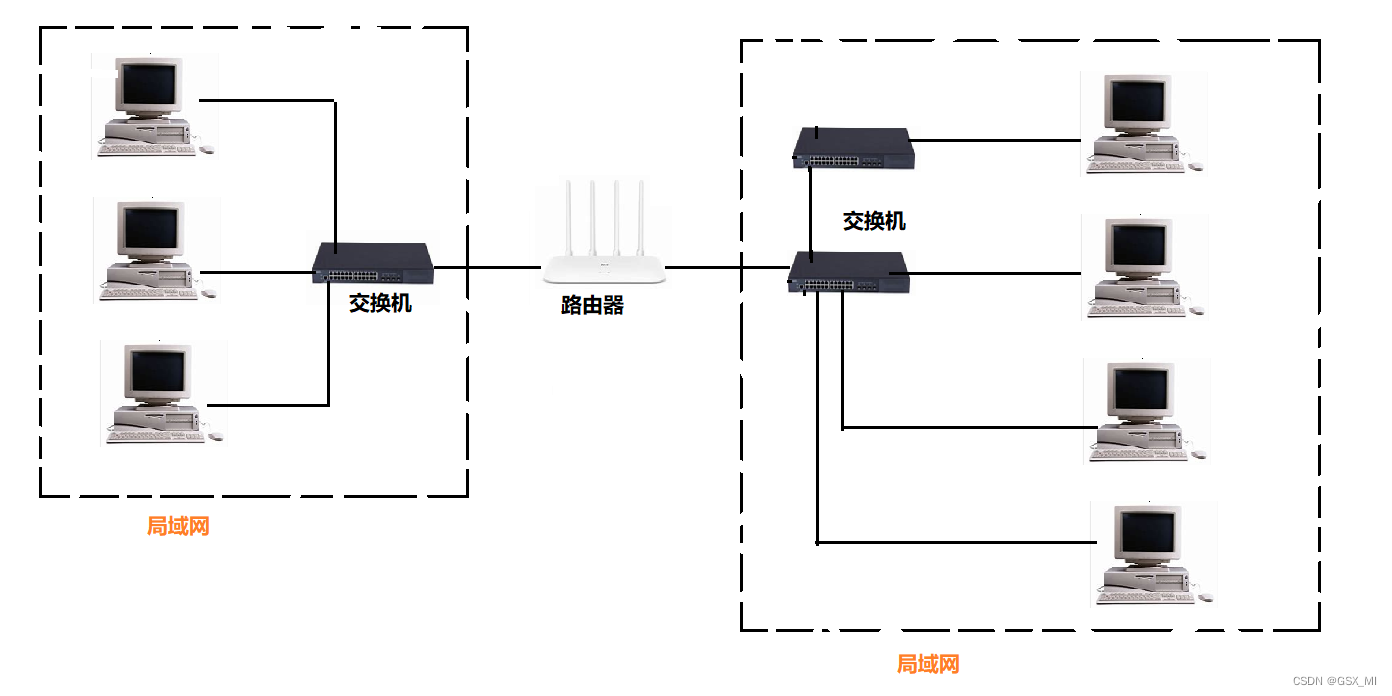
(4) Wide area network WAN: Connecting computers thousands of miles away
The local area networks are connected with each other through routers , It forms a larger network structure , We call it wan . Actual LAN and WAN are relative concepts , We can also regard Wan as a relatively large lan .
2. know " agreement "
- “ agreement ” The essence is a kind of agreement , As long as the two sides of the communication have made some agreement , Then you can use this Convention to accomplish something . The network protocol is a set of agreements that both sides of the communication computer must abide by , Therefore, we must express this agreement in computer language , At this time, the computers of both parties can recognize the relevant contents of the agreement .
- Computers want to define that the essence of a protocol is a pile of information , Organized in a specific structure , The first message sent by both parties when communicating is called protocol message ,— Once you recognize the agreement information, you will know what you want to do .
- The transmission medium between computers is optical signal and electric signal . adopt " frequency " and “ Strong and weak " To express 0 and 1 Such information . To deliver all kinds of different messages , We need to agree on the data format of both parties .
- The greatest strength of the so-called agreement is to make everyone think that the agreement is reasonable , In this way, a consensus is formed . We call the standard commonly followed in the industry network protocol .
- The express bill is — Kind of agreement , The express delivery received is more than the actual items , The extra part can be regarded as an agreement .
3、 ... and . Network protocol initialization
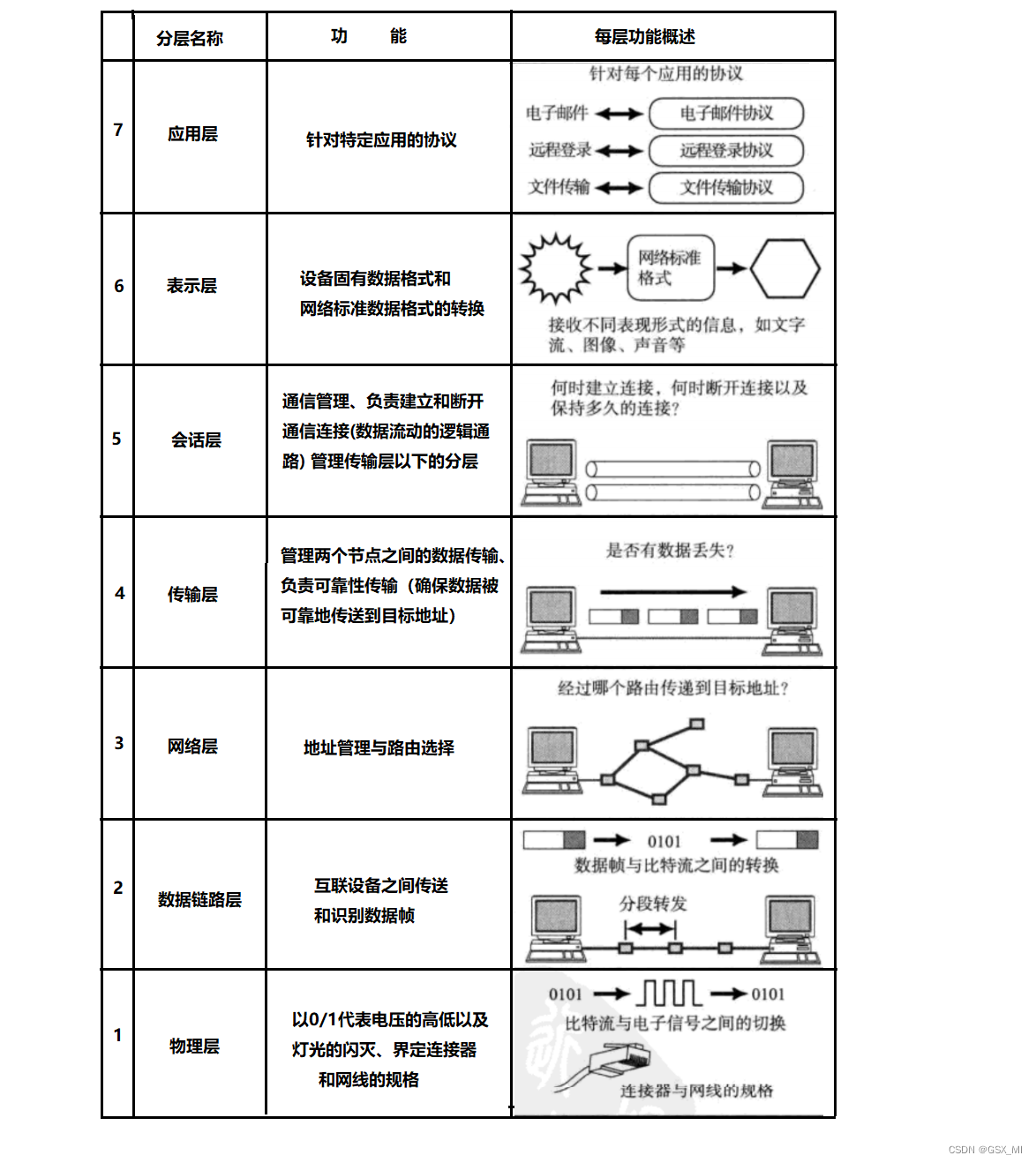
1.OSI Seven layer model
- OSI(Open System Interconnection, Open systems interconnection ) The seven layer network model is called the open mode system interconnection reference model , It's a logical definition and specification .
- OSI Logically divide the network into seven layers , Each floor has related 、 The corresponding physical device , Like a router , Switch .
- OSI The seven layer model is a framework design method , Its main function is to help different types of hosts realize data transmission , For example, data transmission between mobile phone and TV .
- OSI The biggest advantage of the seven layer model is that service 、 Interfaces and protocols These three concepts are clearly separated , The concept is clear , The theory is also relatively complete , Through seven hierarchical structure models, the reliable communication between different systems and different networks can be realized .
- OSI The seven layer model is both complex and impractical , So later, it was adjusted when it was implemented , So there is what we see now TCP/IP Four layer protocol .
2.TCP/IP Five floors ( Or four floors ) Model
TCP/IP Is a synonym for a group of agreements , It also includes many agreements , Together TCP/IP Protocol cluster .TCP/IP The communication protocol adopts a five layer hierarchical structure , Each layer calls the network provided by its next layer to fulfill its own needs .
- The physical layer : Responsible for light / How electrical signals are transmitted . For example, the current Ethernet network cable ( Twisted pair )、 Coaxial cable used in early Ethernet ( Now it's mainly used in cable TV )、 Optical fiber , current WiFi The electromagnetic waves used in wireless networks belong to the concept of physical layer . The capacity of the physical layer determines the maximum transmission rate 、 transmission distance 、 Anti interference, etc . A hub (Hub) It works in the physical layer .
- Data link layer : Responsible for the transmission and identification of data frames between devices . For example, drivers of network card devices 、 Frame synchronization 、 Collision detection ( Automatically resend if a conflict is detected )、 Data error checking, etc . There are many network communication standards at the bottom of the data link layer , Ethernet 、 Token ring network 、 wireless LAN etc. . Switch (Switch) It works in the data link layer .
- The network layer : Responsible for address management and routing . For example, in IP Agreement , adopt IP Address to identify a host , The data transmission line between the two hosts is planned by means of routing table ( route ). Router (Router) Is working at the network layer .
- Transport layer : Responsible for data transmission between two hosts . For example, transmission control protocol (TCP), It can ensure the reliable sending of data from the source host to the target host .
- application layer : Responsible for communication between applications . For example, simple e-mail transmission (SMTP)、 File transfer protocol (FTP)、 Network remote access protocol (Telnet) etc. . Our network programming is mainly aimed at the application layer .
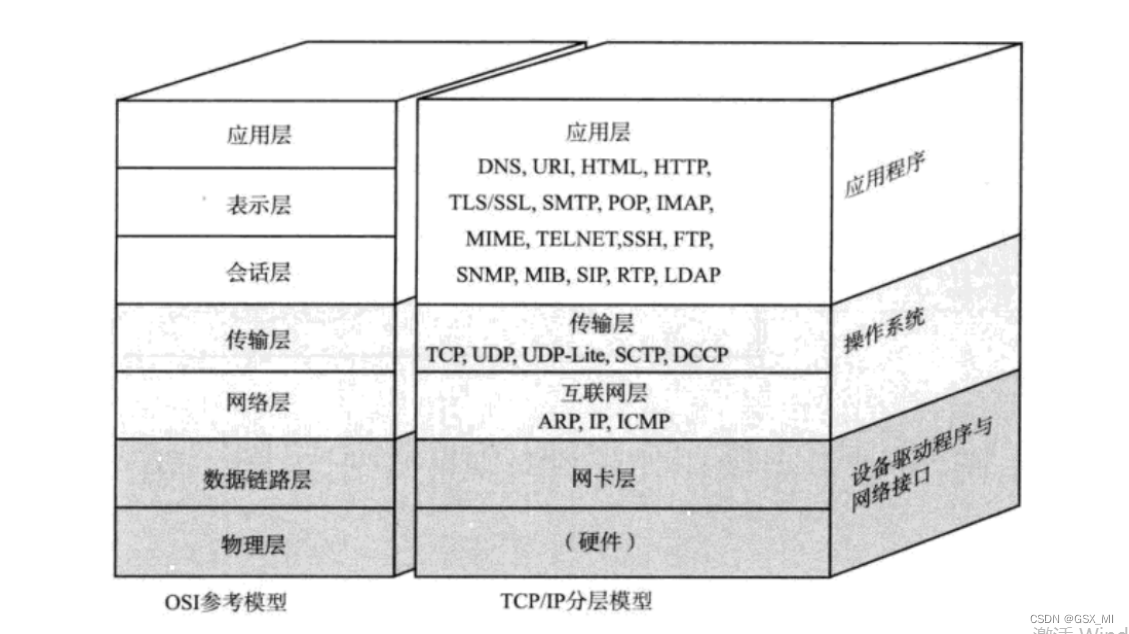
(1) generally speaking :
- For a host , Its operating system kernel implements content from transport layer to physical layer .
- For a router , It realizes the content from network layer to physical layer .
- For a switch , It realizes the content from data link layer to physical layer .
- For hubs , It only implements the content of the physical layer .
But this is not absolute , For example, many switches also realize network layer forwarding , Many routers ( Today's routers are very powerful ) It also realizes part of the content of the transport layer ( For example, port forwarding )
(2) interview :OSl and TCP/IP The difference of the four layers in the layered structure ?
OSI The upper three layers are compressed into one application layer , The others make no difference .
(3) For hubs ( Switch ) A supplement to :
- For hubs , He simply connects the wires between the hosts , Nothing else is done , So all connected hosts will form a conflict domain . That means : When a host is sending data , No other host can send data anymore , Because sending two pieces of media at the same time will cause conflicts . So this is a way to share bandwidth , The price is that the conflict domain becomes larger .
- Electromagnetic signal will be attenuated in the process of long-distance transmission , The main function of the hub is to regenerate, shape and amplify the received signal , To expand the transmission distance of the network , At the same time, all nodes are concentrated on the nodes centered on it .
- It should be noted that , Hub belongs to the bottom equipment of pure hardware network , There is basically no switch like “ Intelligent memory ” Ability and “ Study ” Ability , Nor does it have the characteristics of a switch MAC Address table , So when it sends data, it's not targeted , It's broadcast , in other words , When the hub wants to send data to a node , Instead of sending data directly to the destination node , Instead, send packets to all nodes connected to the hub .
Four . The basic flow of network transmission
1. Communicate with two hosts in the LAN
The first thing to be clear is , Hosts in the same LAN can communicate directly , Because the purpose of the original LAN Design , Is to enable the host in the LAN to communicate .
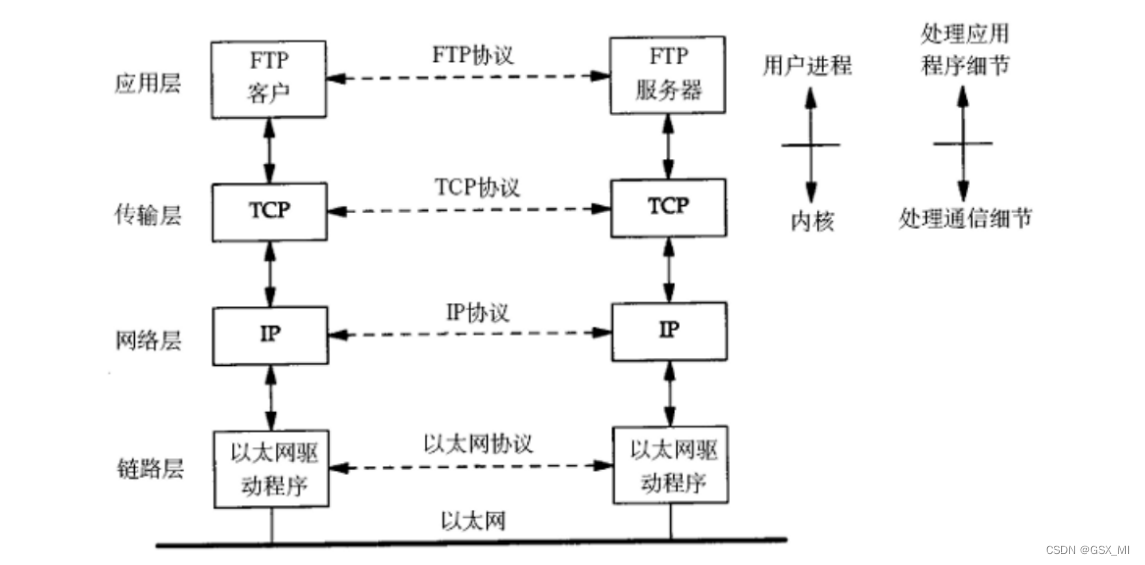
(1) The concept of packet encapsulation and distribution
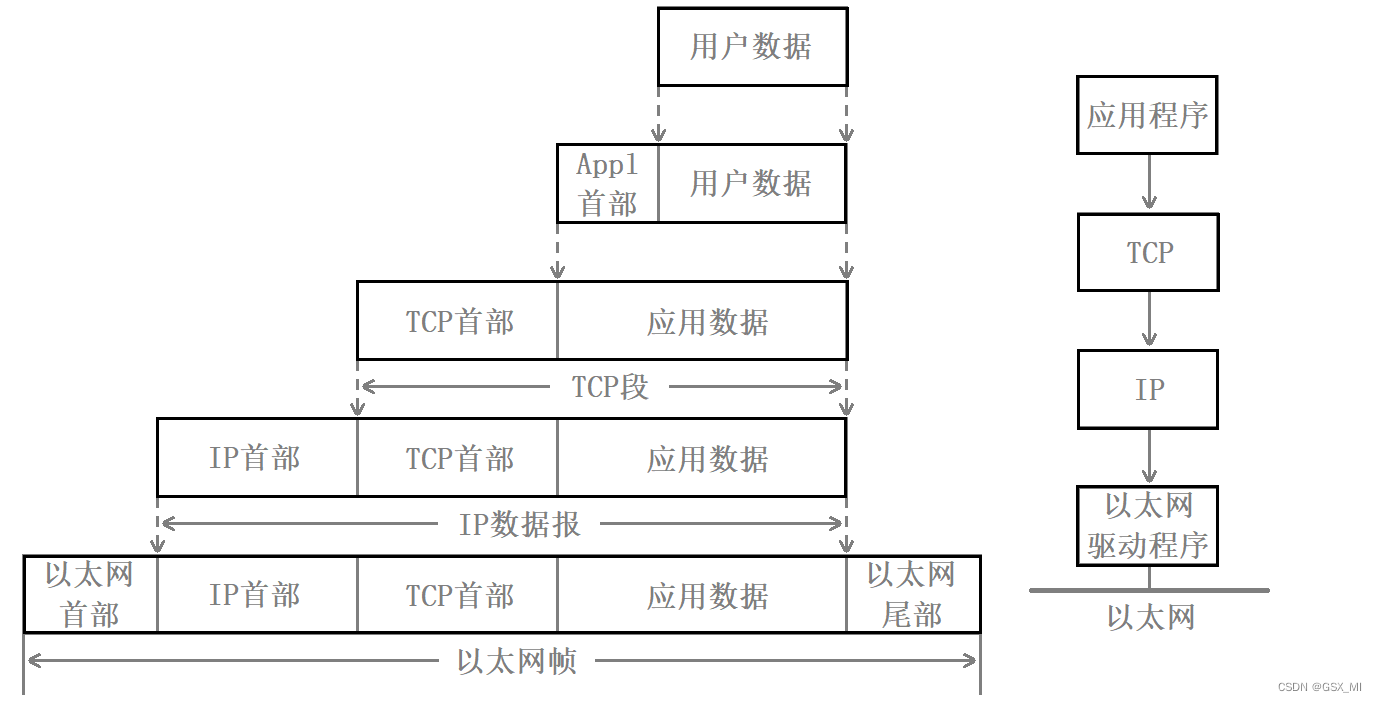
- Different protocol layers have different terms for data packets , At the transport layer, it's called segments (segment), In the network layer, it's called datagram (datagram), In the link layer, it's called frames (frame).
- Application layer data is sent to the network through the protocol stack , Each layer of protocol has to add a data header (header), It's called encapsulation (Encapsulation).
- The first message contains something similar to how long the first one is , load (payload) How long is , What is the upper layer protocol .
- Data is packaged into frames and sent to the transmission medium , After reaching the destination host, the corresponding header of each layer protocol is stripped , According to the first part of “ Upper layer protocol field ” The data is handed over to the corresponding upper layer protocol for processing .
① encapsulation
② Divide up
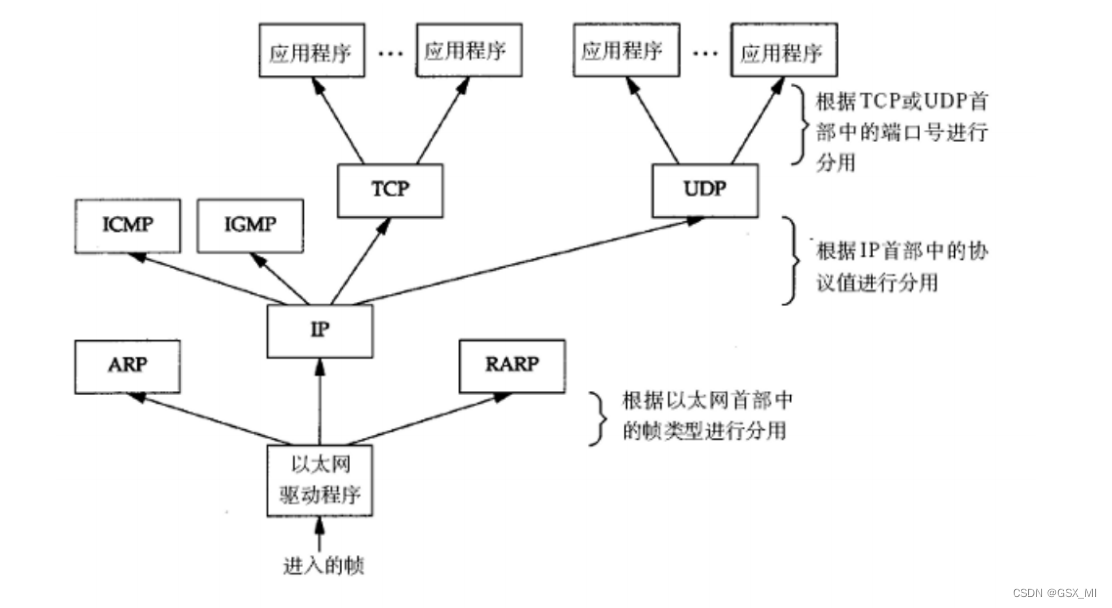
(2) The specific process of packaging and unpacking
When the user wants to transfer the file to another host , The file data needs to be encapsulated through the network protocol stack :
- The file data is handed over to the application layer first , The application layer adds the header information corresponding to the application layer protocol , Pass the data to the transport layer .
- After the transport layer receives the data , Then add the header information corresponding to the transport layer protocol , And continue to deliver the data down .
- After the network layer receives the data , Then add the header information corresponding to the network layer protocol , Then the data is handed over to the link layer .
- After the link layer receives the data , Finally, add the header information corresponding to the link layer protocol , So far, the data encapsulation is completed .
After the data is encapsulated, it can be sent to the opposite host through the LAN , When the opposite host receives the data , Correspondingly, it is also necessary to unpack and distribute the data through the network protocol stack :
- After the link layer receives the data , First, the header information corresponding to the link layer protocol in the data is extracted , Then give the rest of the data to the network layer .
- After the network layer receives the data , Then extract the header information corresponding to the network layer protocol in the data , Then continue to deliver the remaining data up .
- After the transport layer receives the data , Then extract the header information corresponding to the transport layer protocol in the data , Then deliver the remaining data to the application layer .
- After the application layer receives the data , Finally, the header information corresponding to the application layer protocol in the data is extracted , So far, the unpacking and distribution of data have been completed .
Before any host sends data , The data must first run through the protocol stack from top to bottom to complete the data encapsulation , In the process , Each layer of protocol will add the corresponding header information ; And after any host receives the data , It is necessary to run through the protocol stack from bottom to top to complete the unpacking and distribution of data , In the process , Each layer protocol will extract the corresponding header information .
(3) Header and payload : When packaging downward , When the upper layer protocol encapsulates the data into a whole and hands it over to the next layer protocol , This whole is the payload for the underlying protocol .
(4) Each layer of agreement should be able to do two things :
① How to separate the header from the payload
- Each layer of the protocol stack should extract the corresponding header information from the data , The header in the data should be extracted , First, we need to clarify the boundary between the header and the payload , So that they can be separated . When adding a header in each layer, the header is added to the header of the data , So we just need to know the size of the header , The header and payload can be separated .
- In fact, every protocol should provide a method , Let's get the size of the header , In this way, we can separate the header from the payload when unpacking .
There are usually two ways to get the header size :
- Fixed length header . As the name suggests, the size of the header is fixed .
- Self description field . A field is provided in the header , Used to indicate the length of the header .
② The agreement delivered to the upper layer after unpacking
In fact, in the header of each protocol , Almost always contain a field , Indicate which protocol we should deliver the separated payload to the upper layer , This is the process of distribution .
(5) Communicate in the same LAN, and all hosts in the LAN can receive
① One to one communication
LAN is equivalent to a classroom . Everyone stands up and says a word that everyone can hear , Zhang San and Li Si can also be heard by others . When the teacher asks a classmate, it is equivalent to a network communication ( Of course, others heard it, but didn't stand up ); There are two students discussing other topics when asking questions, and we will interfere with each other ( This is called data collision ), As a result, no one can communicate with each other . Will generate garbage data , Recognized by everyone , The sending host will detect and then send ( This is called LAN collision detection ); There may still be a collision in the process of re sending , Avoid collision , And we are constantly checking whether there is anyone sending it . Collision avoidance After that, it is possible to collide, but the probability is reduced .
② One to many communication
radio broadcast : Everyone received the data , All have to be handled , Agreed broadcast address . One to many
(6) Collision
- But when all hosts in the same LAN communicate , All use a common communication channel , Therefore, if multiple hosts in the LAN communicate at the same time , At this time, these data may interfere with each other .
- Every LAN can be regarded as a collision domain , If there is interference between the data sent by one host and the data sent by other hosts , We call the two hosts colliding in the collision domain .
(7) The host can actually... In some way , Know whether the data sent has collided ; The more data in a LAN, the more likely it is to have collision problems , It's like a classroom is so big , The more people there are, the more collisions there will be ; The bottom layer has collision avoidance algorithm .
(8) How does each host determine whether the data is sent to itself ?
- The data sent in the LAN is actually called MAC Data frame , In this MAC The header of the data frame will contain two fields , They are called source MAC Address and purpose MAC Address .
- Each computer is equipped with at least one network card , Each network card has a built-in... When it leaves the factory 48 Bit's serial number , We call this sequence “MAC Address ”, This MAC The address is the only one in the world .
- When communicating in the LAN , Each host receives a MAC After the data frame , Will extract the MAC Header of data frame , Find the corresponding purpose MAC Address and own MAC Address comparison . If it's time to MAC Address and own MAC Address mismatch , Then directly put the MAC Data frame discarding , Only MAC When the address matches , The host will continue to deliver the payload of the data frame upward for processing .
(9) How to divide collision domain ?
There is a device switch in the LAN , Its function is when a certain area of ours collides , Collision messages don't need to be forwarded , Only legal messages will be forwarded .
(10) How to hack the LAN after knowing the principle ?
The principle of hacking LAN , I keep stuffing garbage data into the LAN , Any data sent out will touch me . Everyone's data can't be sent out , The upper layer shows that the LAN is connected but not yet available . But based on the user layer, garbage data is stuffed into the LAN , The bottom driver has collision avoidance algorithm . But some can be avoided Mac Collision avoidance algorithm of frames .
2. Communication between two hosts across the network
- Local area networks are connected through routers , Therefore, a router can span at least two LANs .
- A router is a host in this LAN , Therefore, the router can communicate directly with any host in these LANs .
(1) How do hosts communicate in a LAN using two different communication standards
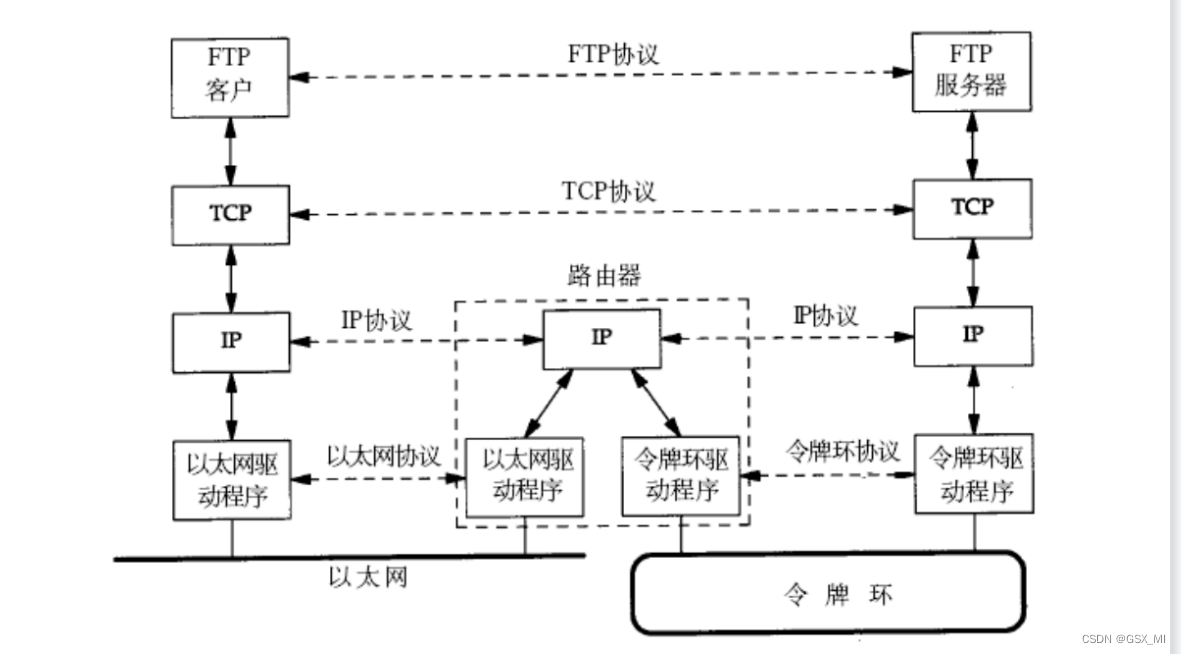
① Because Ethernet and token ring network are different communication standards , They also add different headers to the data , Therefore, the host in token ring network cannot unpack the data frame in Ethernet .
② The protocol stack structure of router
③ Specific communication process
When data is to be sent from the Ethernet host to the token ring host , The host package in Ethernet is sent to the router , Then the router unpacks from the data link layer to the physical layer and gets the destination at the network layer IP Lookup routing table , After a series of data analysis at the network layer , Then deliver the data down to the link layer , At this time, the header information corresponding to the token ring will be added to the data in the link layer , Then send the data to the token ring , At this time, the data can be transmitted in the token ring network .
④ Router forward for
- A router may connect multiple LANs , When the router needs to forward the data from one LAN to another , How does the router know which LAN the data should be forwarded to ?
- Router is actually through IP Address to determine the forwarding direction of data , Every computer on the Internet has a unique IP Address , When data is encapsulated downward , The header encapsulated in the network layer will contain two fields , Are the source IP Address and purpose IP Address .
- When the router needs to forward the data from one LAN to another , In the link layer of the router, the underlying header of the data corresponding to the current LAN will be removed first , Then deliver the remaining data up to the network layer , At this time, the corresponding purpose of the data can be obtained at the network layer IP Address , Then the router can according to the IP The address is searched in the routing table , Finally, we can confirm which LAN the data should be sent to .
⑤“ shielding ” Underlying differences
IP The existence of addresses in addition to help data “ route ” outside , There is also a very important role , That is to shield the differences between the underlying networks . For both sides of the communication host IP Layer and its upward protocol , They don't need to care whether Ethernet or token ring network is adopted at the bottom , They think that as long as the source is filled in IP Address and purpose IP Address can send data , So now the mainstream network is also called “IP The Internet ”.
There are similar technologies :
- Virtual address space : Masked the difference between memory , Let all processes see the same piece of memory , And the layout of this memory is the same .
- Everything is a document : Through the scheme of file structure and function pointer , Allows us to treat certain resources as files .
5、 ... and . Address management in the network
1. know IP Address
- IP The address is at IP Agreement , Address used to identify different hosts in the network .
- about IPv4 Come on ,IP The address is a 4 byte ,32 An integer .
- We usually use “ dotted decimal ” String representation of IP Address , for example 192.168.0.1, Each number divided by dots represents a byte , The scope is 0-255.
- It should be noted that ,IP There are two versions of the agreement , Namely IPv4 and IPv6.IPv4 use 32 Bits to identify IP Address , and IPv6 use 128 Bits to identify IP Address .
2. know MAC Address
- MAC Address is used to identify the nodes connected in the data link layer .
- The length is 48 position , And 6 Bytes , It's usually used 16 A decimal number plus a colon to indicate ( for example :08:00:27:03:fb:19).
- In the network card factory to determine , Do not modify .MAC The address is usually unique ( In the virtual machine MAC The address is not real MAC Address , There may be conflict , Some network cards support user configuration MAC Address )
3.IP vs MAC
The relationship between the two is like : Tang's monk scriptures
- From the eastern Tang Dynasty -> Buddhist paradise : From where to where IP
- On — A place to -> Next place : mac Address
4.Linux View in MAC Address
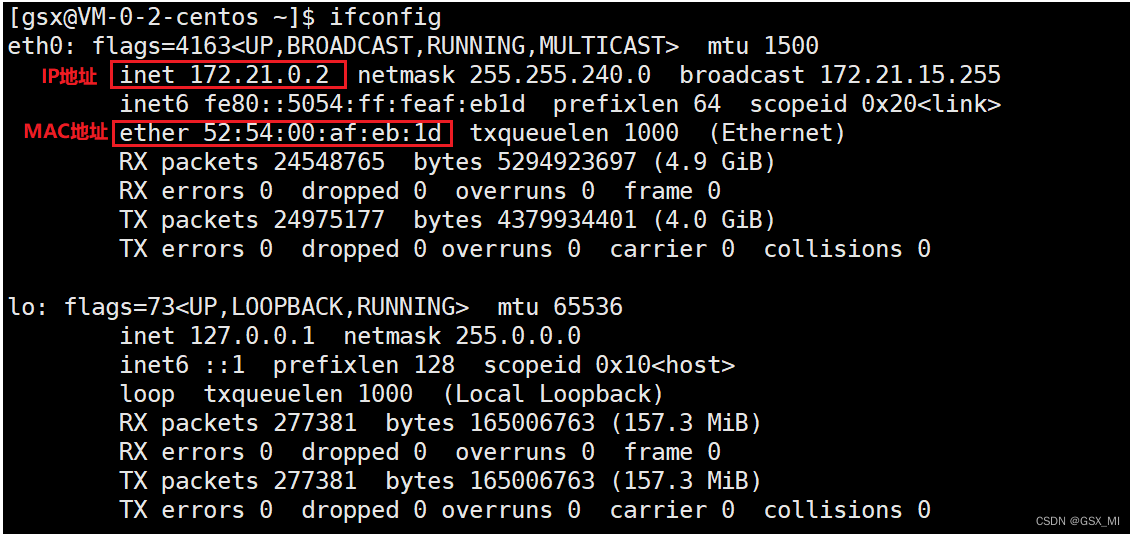
ifconfig You can view the network card information corresponding to the current host
On the cloud server MAC The address may not be real MAC Address , The MAC The address may be simulated .
边栏推荐
- 自定义 swap 函数
- General implementation and encapsulation of go diversified timing tasks
- BasicVSR_PlusPlus-master测试视频、图片
- How to achieve text animation effect
- TypeScript获取函数参数类型
- Puppeter connects to the existing Chrome browser
- UDP编程
- extern关键字
- const关键字
- ICLR 2022 | pre training language model based on anti self attention mechanism
猜你喜欢

树的先序中序后序遍历
关于声子和热输运计算中BORN电荷和non-analytic修正的问题
Aardio - 不声明直接传float数值的方法
Balanced Multimodal Learning via On-the-fly Gradient Modulation(CVPR2022 oral)
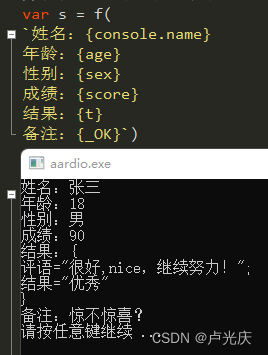
Aardio - integrate variable values into a string of text through variable names
视图(view)
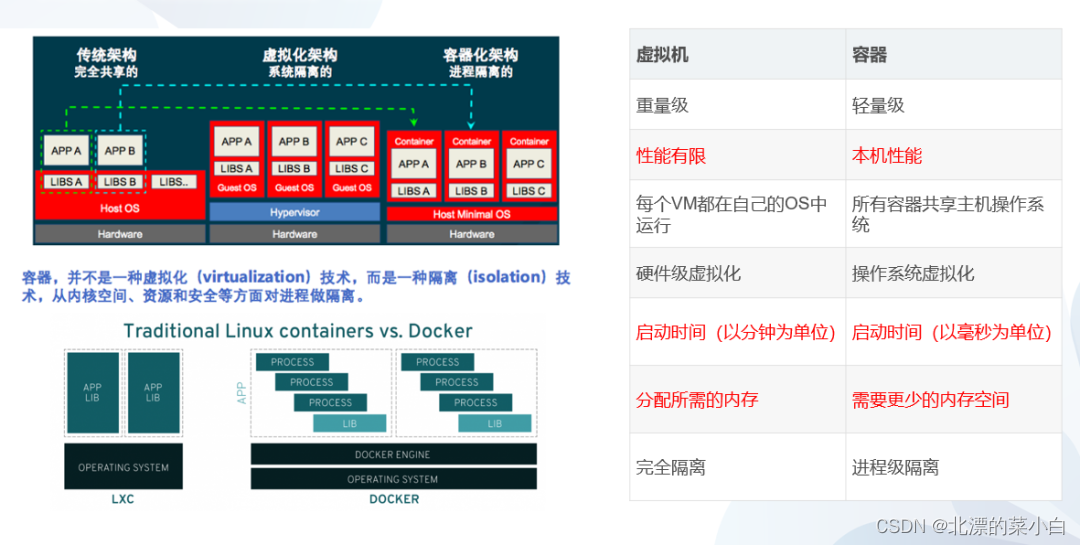
Cloud native technology container knowledge points
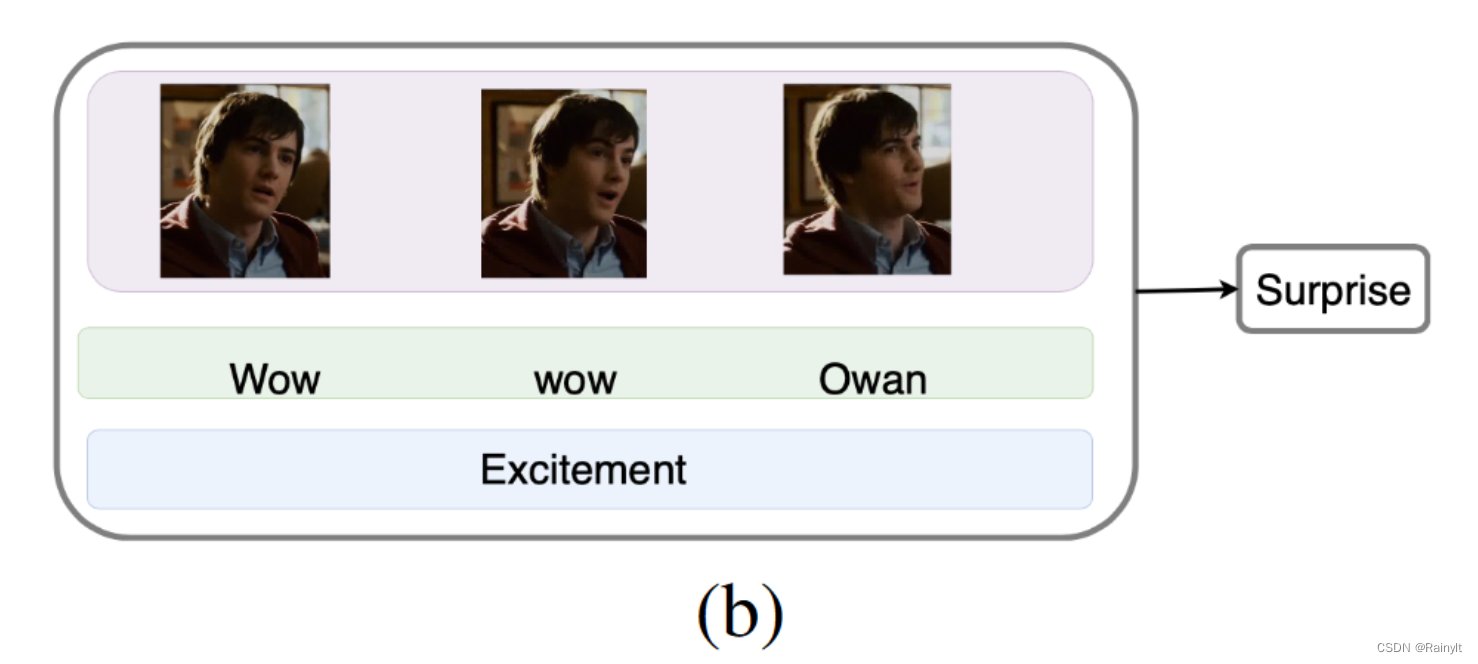
Improving Multimodal Accuracy Through Modality Pre-training and Attention
DR-Net: dual-rotation network with feature map enhancement for medical image segmentation
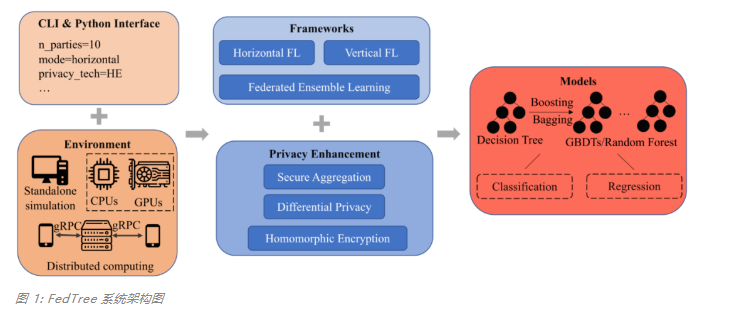
Designed for decision tree, the National University of Singapore and Tsinghua University jointly proposed a fast and safe federal learning system
随机推荐
自定义 swap 函数
Self made j-flash burning tool -- QT calls jlinkarm DLL mode
AdaViT——自适应选择计算结构的动态网络
MySQL----初识MySQL
柔性数组到底如何使用呢?
OpenSSL: a full-featured toolkit for TLS and SSL protocols, and a general encryption library
General implementation and encapsulation of go diversified timing tasks
专为决策树打造,新加坡国立大学&清华大学联合提出快速安全的联邦学习新系统
The ceiling of MySQL tutorial. Collect it and take your time
[IELTS speaking] Anna's oral learning record part1
Leetcode exercise - Sword finger offer 26 Substructure of tree
【无标题】
Windows Auzre 微软的云计算产品的后台操作界面
Aardio - construct a multi button component with customplus library +plus
欧洲生物信息研究所2021亮点报告发布:采用AlphaFold已预测出近1百万个蛋白质
#DAYU200体验官# 首页aito视频&Canvas绘制仪表盘(ets)
允许全表扫描 那个语句好像不生效set odps.sql.allow.fullscan=true;我
项目复盘模板
How big is the empty structure?
Motion capture for snake motion analysis and snake robot development