当前位置:网站首页>1. First knowledge of C language (1)
1. First knowledge of C language (1)
2022-07-06 13:43:00 【It's Wang Jiujiu】
First time to know C Language
Catalog
1. What is? C Language ? Why study C Language ?
The scope and life cycle of variables
5. character string 、 Escape character
1. What is? C Language ? Why study C Language ?
What is? C Language ?
C Language is a universal language Computer programming language , Widely used in the underlying development .C The design goal of the language is to provide a way to compile 、 Processing low-level memory 、 Generate a small amount of machine code and a programming language that can run without any support of the running environment .
Even though C Language provides many low-level processing functions , But it still has good cross platform characteristics , Written in a standard specification C Language programs can be compiled on many computer platforms , It even includes some embedded processors ( Single chip computer MCU) And super Level computer and other operating platforms .
The 1980s , In order to avoid the use of C There are differences in language grammar , By the National Bureau of standards C Language has developed a complete set of American national standard grammar , be called ANSI C, As C The original standard of language . [1] at present 2011 year 12 month 8 Japan , International Organization for Standardization (ISO) And the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) released C11 standard yes C The third official standard of language , It's also C The latest standard of language , The standard better supports Chinese character function names and Chinese character identifiers , To a certain extent, Chinese character programming is realized .
C Language is a language Process oriented Computer programming language , And C++,Java etc. object-oriented Different programming languages .
Its compiler mainly includes Clang、GCC、WIN-TC、SUBLIME、MSVC、Turbo C etc. .
Why study C Language ?
Before understanding programming , Most people always think that programming is the business of programmers , It has nothing to do with your study and work . But that's not the case : For most science and engineering subjects , With programming, the computer can deal with a large number of 、 Complex data , Time saving and labor saving . And liberal arts students can also exercise their logical thinking by learning programming , And use some simple functions to record 、 Deal with a large number of documents .
In the undergraduate graduation stage , If you can master a programming language , Will be able to stand out from many candidates ; And during graduate study , Programming is the foundation of learning , All theoretical knowledge should be realized on the computer through programming in the end .
C The basis of language learning content 、 System , also C The fast running speed of the language can meet the needs of most science and engineering majors . As the saying goes C All living things , Through the study C Language has a good programming foundation , Then it will be very easy to transfer to other programming languages .
Any learning process is not achieved overnight ,C Language learning is even more so . I'm learning C You need to practice repeatedly during the language 、 Constantly consolidate and review 、 And cultivate blogging , A good habit of recording your learning process .C Language learning takes about a year , I believe that this year's efforts will eventually bring you rich returns .
2. first C Language program
#include<stdio.h>// Import header file
int main()// Main function entry , A project can only have one main function
{
printf("Hello World\n");// Print “Hello World”
return 0;// Returns an integer , And int echo
}The header file : If you want to call a function in the header file , for example “printf”, You need to start with #include Import header file , If the header file is not referenced, execute the program , The compiler will report an error :“printf” Undefined .
The main function : The main function represents the entry of the program , A project can only have one main function main, new edition C Language use int To define the main function , Return an integer value at the end to echo , The general default return value is 0, return 0 It means that the program is successful , Not 0 False report .( In the old textbook void main() No longer applicable )
3. data type
char // Character data type
short // Short
int // plastic
long // Long integer
long long // Longer plastic surgery
float // Single-precision floating-point
double // Double precision floating point So many data types , To cope with various values in life . In the process of writing code , Try to assign appropriate data types to our variables . adopt sizeof Operators can query the size of these data types , Unit is byte .
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(char));//1
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(short));//2
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(int));//4
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(long));//4
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(long long));//8
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(float));//4
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(double));//8
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(long double));//8
return 0;
}notes :sizeof The returned value is an unsigned integer , When printing, you can use %d, The program can run successfully without error , But there will be a warning . All you have to do is %d Change it to %zu that will do .( This is a C99 standard )
4. Variable 、 Constant
seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , The amount of change is called a variable ( height 、 weight 、 Age 、 balance ), Constant quantities are called constants ( PI , ID number ).
How to define variables
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ch = 'a';// Single characters in single quotes
char name1[] = " Wang Jiujiu ";// String in double quotation marks
int age = 23;
return 0;
}notes : When you define variables , If you don't need to assign values to variables at first , It is best to initialize variables . example :int age =0; Some old textbooks like to use int age; This method , Do not initialize variables , It is easy to appear in the later programming process bug.
Classification of variables
Variables are divided into global variables and local variables .
Global variables : Variables defined outside the function are global variables .
local variable : Variables defined inside a function are called global variables .
#include<stdio.h>
int num = 100;// Global variables
int main()
{
int num = 99;// local variable
printf("%d\n", num);// When local variables and global variables conflict , Local variables take precedence , This shows num Yes. 99
return 0;
}
Use of variables
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;// Defining variables , And initialization
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);// use scanf The function inputs two integers , The two numbers are separated by spaces .& To get the address symbol , Pass the input parameters to the variables a,b
c = a + b;
printf("%d\n", c);
}notes : When you name a variable , It's best to give meaning , Convenient for future use without confusion .
The scope and life cycle of variables
Scope :
Scope (scope) It's a programming concept , Generally speaking , The names used in a program are not always valid / Usable .
Scope of global variables : For the whole project , Global variables can be used anywhere in the entire project , And modify it .
The scope of a local variable : Is the local range of the variable , That is, the function in which the variable is located .
Life cycle :
The life cycle of a variable is the period between the creation of a variable and its destruction .
The life cycle of global variables : For the whole project life cycle .
The life cycle of a local variable : Enter the scope lifecycle begins , Out of scope life cycle ends .
notes : When programming , Global variables should be used as little as possible , Use more local variables . Global variables can be accessed by the whole project 、 modify , Poor safety ; Local variables can only be used within the scope , Out of scope, you cannot access 、 modify , High safety .
Constant
C Constants in languages are divided into the following :
- Literal constants
- #define Defined identifier constant
- Enumeration constants
- const Modified constant variable
Literal constants :
100;
3.14;// Constant cannot be changed #define Defined identifier constant :
#include <stdio.h>
#define pass 60
#define good 80
#define excellent 90
//define Variables defined
int main()
{
int num = 0;// initialization
scanf("%d", &num);// Input
if (num<pass)
{
printf(" fail, ");
}
else if (num >=pass && num <good)
{
printf(" pass ");
}
else if (num >= good && num < excellent)
{
printf(" good ");
}
else if (num >= excellent)
{
printf(" good ");
}
return 0;
}notes : If the full score of roll noodles is 150 branch , Just change the above define Part of the definition , There is no need to change the value inside the function , Very convenient .
Enumeration constants :
#include<stdio.h>
enum color// Enumeration constants
{
red,//0 Enumeration constants are from... By default 0 Start , Increase in descending order 1
yellow,//1
blue//2
};
int main()
{
enum color a = red;// use enum color Create a variable a, The assignment is red
enum color b = yellow;
enum color c = blue;
printf("%d\n", a);//0
printf("%d\n", b);//1
printf("%d\n", c);//2
return 0;
}notes : Except for color , Gender 、 hobby 、 Regions and so on can be expressed by enumerating constants .
const Modified constant variable :
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10;
a = 20;// Regular defined variables can be modified
const int b = 10;//const Defined constant variables have constant properties , Can't change , But its essence is constant .
return 0;
}5. character string 、 Escape character
character string
A string of characters enclosed in double quotation marks is called a string
The end flag of the string is ‘\0’, When calculating the length of string, it will not be included . When entering a string with double quotation marks , The default ending is \0, No manual input . however , If you enter a string of characters in consecutive single quotation marks , The result must add ‘\0’.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr1[] = "hello";// You can create an array without defining space , Automatically define according to the input
char arr2[] = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0' };
char arr3[] = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' };
printf("%s\n", arr1);
printf("%s\n", arr2);
printf("%s\n", arr3);
return 0;
}The result of the above code execution is shown in the following figure :

Array arr3 Because there is no ‘\0’, The compiler does not recognize the end flag , After printing hello Will continue to print garbled .
Besides , When defining space for an array , The two methods are also different .
char arr1[5] = "hello";
char arr2[6] = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0' };// When entering in this way , When defining space, you need to consider ‘\0’ Take up a byte , and arr1 You don't need to Escape character
Escape character | paraphrase |
\? | Use... When writing multiple consecutive question marks , Prevent them from being parsed into three letter words |
\' | Used to represent character constants ' |
\“ | Double quotation marks used to represent the inside of a string |
\\ | Used to indicate a backslash , Prevent it from being interpreted as an escape sequence character . |
\a | Warning characters , Beep |
\b | Back space |
\f | Paper in |
\n | Line break |
\r | enter |
\t | Horizontal tabs |
\v | Vertical tabs |
\ddd | ddd Express 1~3 Eight octal numbers . Such as : \130 X |
\xdd | dd Express 2 Hexadecimal numbers . Such as : \x30 0 |
Compiler at compile time , It is read from left to right , Sometimes the content you want to print is confused with the content of escape characters , Result in failure to compile , Then join in front \ that will do .
for example :
Print a character ’, How to print ?
Print a string , The content of the string is ”, How to print ?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%c\n", '\'');// Print a single character '
printf("%s\n", "\"");// Print string , Its content is "
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- List set map queue deque stack
- The latest tank battle 2022 full development notes-1
- MySQL中count(*)的实现方式
- A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews
- 关于双亲委派机制和类加载的过程
- 2022 Teddy cup data mining challenge question C idea and post game summary
- 【九阳神功】2020复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
- JS interview questions (I)
- (超详细onenet TCP协议接入)arduino+esp8266-01s接入物联网平台,上传实时采集数据/TCP透传(以及lua脚本如何获取和编写)
- 最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-1
猜你喜欢

9. Pointer (upper)
A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews

【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
凡人修仙学指针-1
Leetcode.3 无重复字符的最长子串——超过100%的解法
View UI plus released version 1.3.0, adding space and $imagepreview components

这次,彻底搞清楚MySQL索引
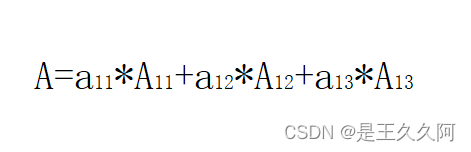
3. C language uses algebraic cofactor to calculate determinant
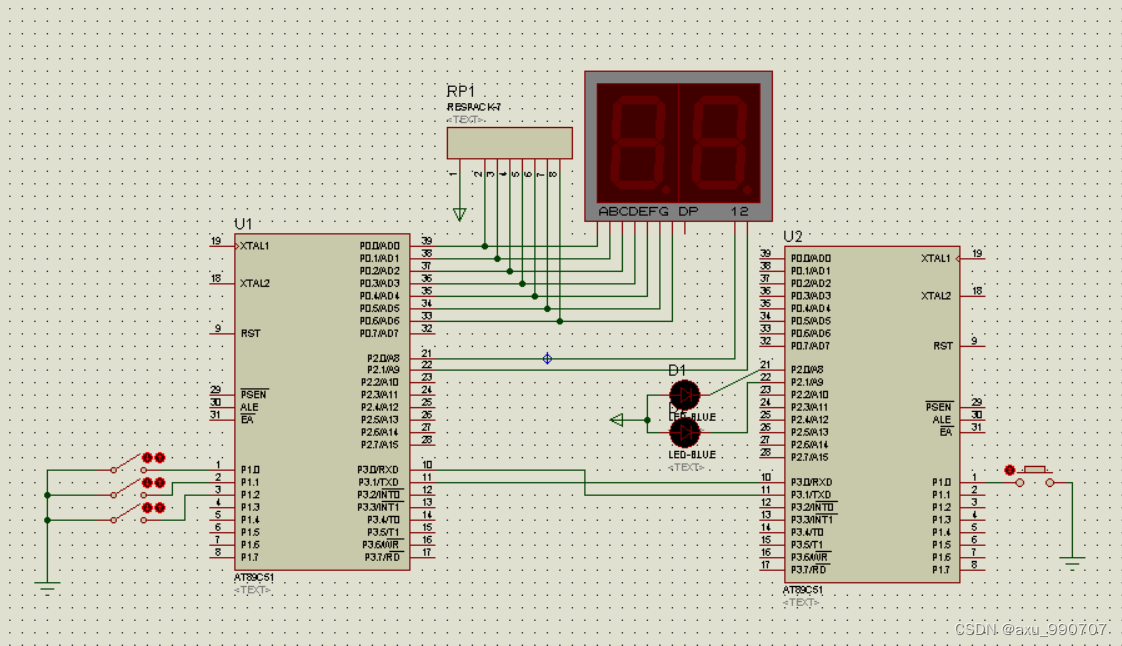
甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1
A piece of music composed by buzzer (Chengdu)
随机推荐
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (III)
6.函数的递归
简单理解ES6的Promise
Zatan 0516
This time, thoroughly understand the MySQL index
JS interview questions (I)
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(二)
5.函数递归练习
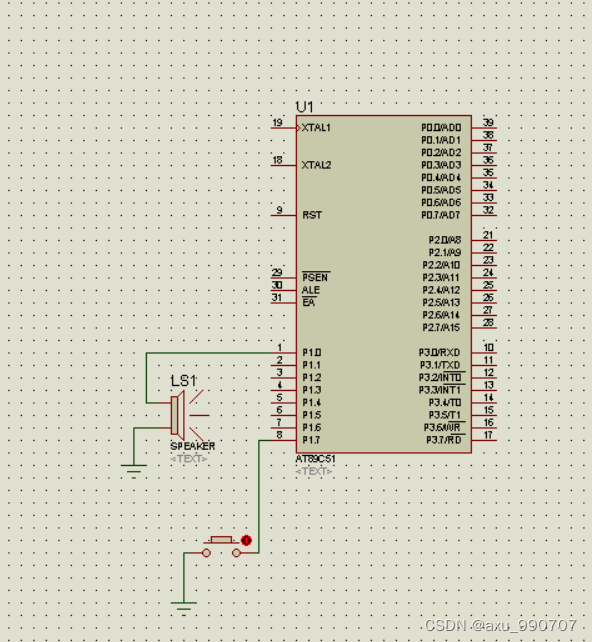
A piece of music composed by buzzer (Chengdu)
5月27日杂谈
Reinforcement learning series (I): basic principles and concepts
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-1
Implement queue with stack
Change vs theme and set background picture
C language Getting Started Guide
There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
Have you encountered ABA problems? Let's talk about the following in detail, how to avoid ABA problems
简述xhr -xhr的基本使用
仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(三)
canvas基础1 - 画直线(通俗易懂)