当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2) D. Cut and Stick
Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2) D. Cut and Stick
2022-07-05 05:30:00 【solemntee】
obviously :
For an interval, we only need to deal with the element that appears most times
( We call the remaining elements other elements )
The optimal strategy is to take two maximum elements and one other element to form a sequence
So the answer to a certain interval is
m a x ( most many element plain individual Count − Its He element plain , 1 ) max( Maximum number of elements - Other elements ,1) max( most many element plain individual Count − Its He element plain ,1)
So for a single interval , We just need to find out the number of elements that appear most often .
This is easy to make .
Because each time add a number or delete a number , The number of elements with the highest number of occurrences in the interval will only increase or decrease by one , So we only need one c n t [ i ] cnt[i] cnt[i] Record i i i Number of occurrences , r n k [ i ] rnk[i] rnk[i] The number of occurrences recorded is i i i Number of elements of times .
Every maintenance c n t [ i ] cnt[i] cnt[i] and r n k [ i ] rnk[i] rnk[i] that will do .( You can know that the complexity of this is very low , Because of the above " The number of elements with the most occurrences will only increase or decrease by one ")
At the same time, because the inquiry is a continuous interval , So I think of Mo team , The complexity can be controlled within O ( n n ) O(n\sqrt n) O(nn) within .
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn=3e5+50;
int n,q;
int a[maxn],ans[maxn],rnk[maxn],cnt[maxn];
int nowl=1,nowr=0,nowans=0;
struct qu
{
int l,r,num;
}query[maxn];
bool cmp(qu a,qu b)
{
int t=sqrt(n);
if(a.r/t!=b.r/t)return a.r/t<b.r/t;
return a.l<b.l;
}
void add(int x)
{
if(cnt[a[x]]>0)rnk[cnt[a[x]]]--;
cnt[a[x]]++;
rnk[cnt[a[x]]]++;
nowans=max(nowans,cnt[a[x]]);
}
void del(int x)
{
rnk[cnt[a[x]]]--;
cnt[a[x]]--;
rnk[cnt[a[x]]]++;
while(rnk[nowans]==0)nowans--;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&query[i].l,&query[i].r);
query[i].num=i;
}
sort(query+1,query+1+q,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
while(nowr<query[i].r)
{
nowr++;
add(nowr);
}
while(nowl>query[i].l)
{
nowl--;
add(nowl);
}
while(nowr>query[i].r)
{
del(nowr);
nowr--;
}
while(nowl<query[i].l)
{
del(nowl);
nowl++;
}
// cout<<nowans<<' '<<"aa"<<endl;
if(nowans<=(query[i].r-query[i].l+1+1)/2)ans[query[i].num]=1;
else ans[query[i].num]=max(1,nowans-(query[i].r-query[i].l+1-nowans));
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
But as far as this topic is concerned, we can do many things , There are two kinds of feelings that are very meaningful .
1、 If a number in the interval exceeds ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 Time , Then it must appear in some sub interval more than ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 Time ( Otherwise, the contradiction ), So we only need to use the segment tree to deal with each interval exceeding ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 The number of times , And then separately c h e c k check check that will do .
2、 If a number in the interval exceeds ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 Time , Then let's take a random position , The probability of randomly reaching this number is greater than 1 / 2 1/2 1/2, So we randomly n n n Time , c h e c k check check Value obtained each time , The probability of finding this number is very high .
notes :check Just a simple two-point subscript ~
Also learned by the way , For occurrences greater than ( n + 1 ) / 2 (n+1)/2 (n+1)/2 We have a Moore voting algorithm that can O ( n ) O(n) O(n) Find out …
b y t h e w a y by\,the\,way bytheway We can also review some cold knowledge about the median , For an interval, we can divide it into two numbers , Then count the number of numbers greater than this number and less than this number , Come on c h e c k check check, Complexity is O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn).
边栏推荐
- Acwing 4301. Truncated sequence
- Drawing dynamic 3D circle with pure C language
- [speed pointer] 142 circular linked list II
- Fragment addition failed error lookup
- YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2
- [merge array] 88 merge two ordered arrays
- Web APIs DOM节点
- Add level control and logger level control of Solon logging plug-in
- 卷积神经网络简介
- Summary of Haut OJ 2021 freshman week
猜你喜欢
Palindrome (csp-s-2021-palin) solution
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
Little known skills of Task Manager
Support multi-mode polymorphic gbase 8C database continuous innovation and heavy upgrade
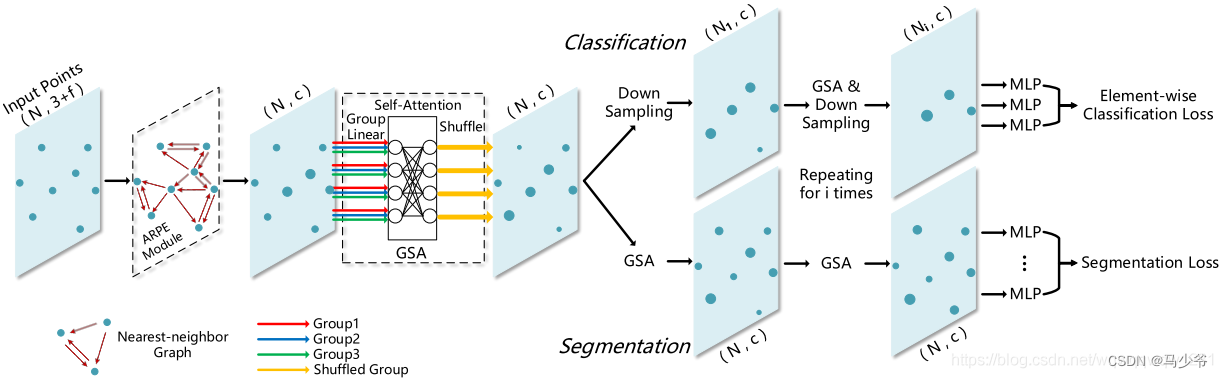
Pointnet++的改进
![[turn to] MySQL operation practice (I): Keywords & functions](/img/b1/8b843014f365b786e310718f669043.png)
[turn to] MySQL operation practice (I): Keywords & functions
![[to be continued] [depth first search] 547 Number of provinces](/img/c4/b4ee3d936776dafc15ac275d2059cd.jpg)
[to be continued] [depth first search] 547 Number of provinces
![[to be continued] [UE4 notes] L3 import resources and project migration](/img/81/6f75f8fbe60e037b45db2037d87bcf.jpg)
[to be continued] [UE4 notes] L3 import resources and project migration

Yolov5 adds attention mechanism
SAP method of modifying system table data
随机推荐
Solon Auth 认证框架使用演示(更简单的认证框架)
Introduction to tools in TF-A
用STM32点个灯
Gbase database helps the development of digital finance in the Bay Area
Haut OJ 1316: sister choice buys candy III
Yolov5 adds attention mechanism
Pointnet++学习
浅谈JVM(面试常考)
卷积神经网络简介
Solon Logging 插件的添加器级别控制和日志器的级别控制
Summary of Haut OJ 2021 freshman week
room数据库的使用
26、 File system API (device sharing between applications; directory and file API)
Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
剑指 Offer 06.从头到尾打印链表
读者写者模型
Csp-j-2020-excellent split multiple solutions
lxml.etree.XMLSyntaxError: Opening and ending tag mismatch: meta line 6 and head, line 8, column 8
Solon 框架如何方便获取每个请求的响应时间?
远程升级怕截胡?详解FOTA安全升级