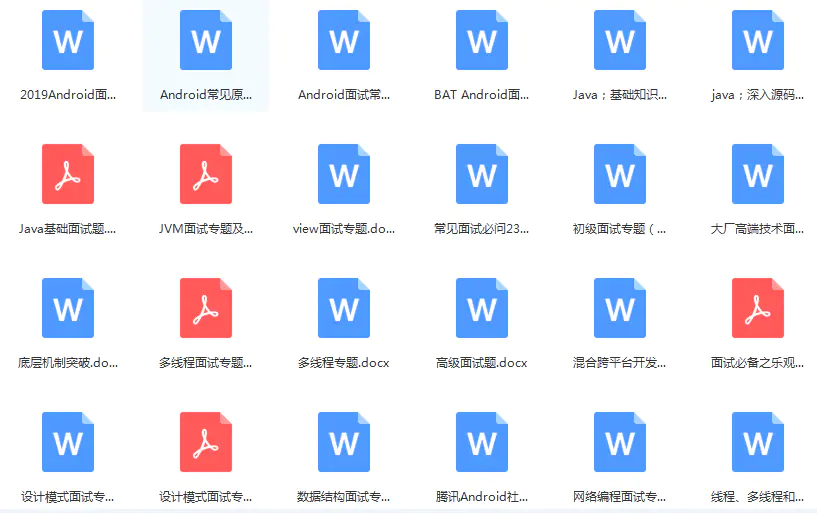
当前位置:网站首页>Skimage learning (3) -- gamma and log contrast adjustment, histogram equalization, coloring gray images
Skimage learning (3) -- gamma and log contrast adjustment, histogram equalization, coloring gray images
2022-07-07 16:57:00 【Original knowledge】
1、Gamma and log Contrast adjustment
This example adjusts the image contrast by performing gamma and logarithmic correction on the input image .
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from skimage import data, img_as_float
from skimage import exposure
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 8
def plot_img_and_hist(image, axes, bins=256):
# Draw the image and its histogram and cumulative histogram .
image = img_as_float(image)# Convert to floating point
ax_img, ax_hist = axes # axes by 2 That's ok 3 Column block , First act ax_img , Second behavior ax_hist
ax_cdf = ax_hist.twinx() #twinx() The function represents shared x Axis twiny() It means sharing y Axis The shared representation is the second row of all coordinate systems x The axis uses the same scale mark
# Display image
ax_img.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax_img.set_axis_off()
''' Cmap yes MATLAB The function used to set and obtain the current color map , You can set the following color chart : hot Smooth transition from black to red 、 Orange and yellow background colors , Then go to white . cool Contains shades of turquoise and magenta . From turquoise to magenta . gray Returns the linear grayscale color map . bone Grayscale color map with high blue component . This color map is used to add an electronic view to the grayscale map . white All white monochromatic graph . spring Contains magenta and yellow shadow colors . summer Contains green and yellow shadow colors . autumn Smooth change from red to orange , Then go to yellow . winter Contains shades of blue and green . '''
# Display histogram
ax_hist.hist(image.ravel(), bins=bins, histtype='step', color='black')
# bins Is the number of columns in the histogram image.ravel() Stretch the matrix into a one-dimensional array
# histtype: Histogram Type ,‘bar’, ‘barstacked’, ‘step’, ‘stepfilled’
ax_hist.ticklabel_format(axis='y', style='scientific', scilimits=(0, 0))
# Set up y Axis
# sytle: sci or scientific Scientific enumeration plain: Natural number
# sclimits (m, n) The value range of the axis 10 Of m Power to 10 Of n Power (0,0) Means unlimited
ax_hist.set_xlabel('Pixel intensity')## Set up x Axis labels : Pixel strength
ax_hist.set_xlim(0, 1)# Set up x Axis range 0 To 1
ax_hist.set_yticks([])
# set_xticks And set_yticks Method can be used to set the position of the label
# ax.set_xticks([0.25, 0.5, 0.75])
# ax.set_xticklabels(['a', 'b', 'c'], fontsize=18)
# Display cumulative distribution
# Returns the cumulative distribution function of a given image (cdf) mg_cdf: The value of the array cumulative distribution function .bin_centers: Array center .
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(image, bins)
ax_cdf.plot(bins, img_cdf, 'r')
ax_cdf.set_yticks([])
return ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf
# Load an example image
img = data.moon()
# Gamma
gamma_corrected = exposure.adjust_gamma(img, 2)
''' Adjustment of image brightness and contrast , It's on the skimage Bag exposure Inside the module gamma adjustment principle :I=Ig For the pixels of the original image , Perform power operation , Get the new pixel value . Formula g Namely gamma value . If gamma>1, The new image is darker than the original image If gamma<1, The new image is brighter than the original image The function format is :skimage.exposure.adjust_gamma(image, gamma=1) gamma The parameter defaults to 1, The original image does not change . Gamma transform is low for image contrast , And the overall brightness value is high ( For camera overexposure ) In this case, the image enhancement effect is obvious . '''
# logarithm
logarithmic_corrected = exposure.adjust_log(img, 1)
''' log Expression of function : y=alog(1+x), a Is an amplification factor ,x It is also the input pixel value , The value range is [0−1], y Is the output pixel value . The logarithmic transformation has a better effect on the image with low overall contrast and low gray value . '''
# Show results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
axes = np.zeros((2, 3), dtype=np.object)#axes The values of two rows and three columns are 0
axes[0, 0] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
axes[0, 1] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 2, sharex=axes[0, 0], sharey=axes[0, 0])
axes[0, 2] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 3, sharex=axes[0, 0], sharey=axes[0, 0])
axes[1, 0] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
axes[1, 1] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
axes[1, 2] = plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img, axes[:, 0])# The first column of the canvas
ax_img.set_title('Low contrast image')# Low contrast images
y_min, y_max = ax_hist.get_ylim()
ax_hist.set_ylabel('Number of pixels')# The number of pixels
ax_hist.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, y_max, 5))#y Axis 5 Equal division , Mark the equal value
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(gamma_corrected, axes[:, 1])
ax_img.set_title('Gamma correction')# Gamma correction
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(logarithmic_corrected, axes[:, 2])
ax_img.set_title('Logarithmic correction')# Logarithmic correction
ax_cdf.set_ylabel('Fraction of total intensity')# Percentage of total strength
ax_cdf.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, 1, 5))# Set up y Axis labels
# prevent overlap of y-axis labels
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
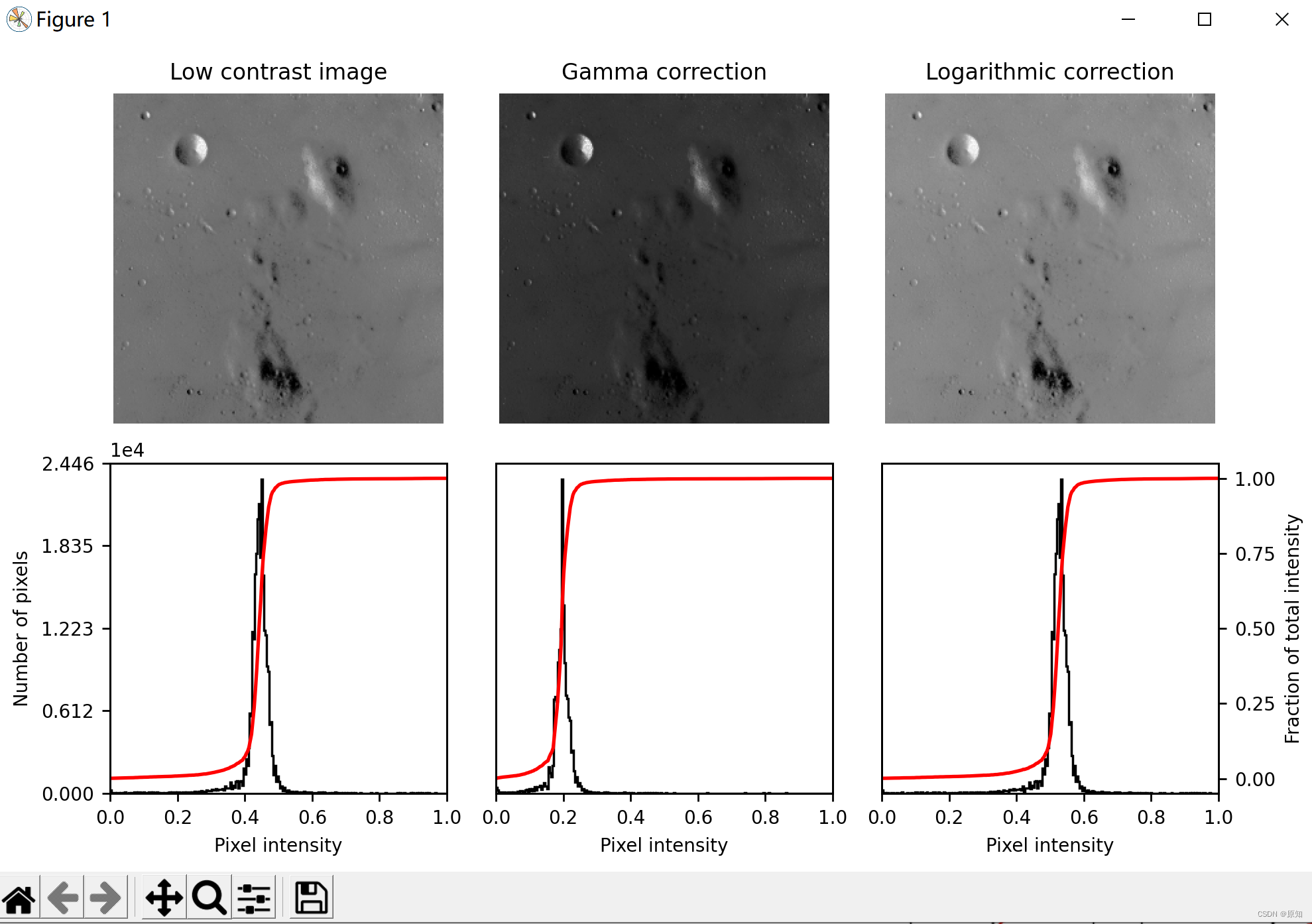
2、 Histogram equalization
This example uses a method called histogram equalization to enhance low contrast images , The method In the image 1 in “ Expand the most frequent intensity value ” . The equalized image has a roughly linear cumulative distribution function .
Although histogram equalization has the advantage of not requiring parameters , But sometimes it will produce images that look unnatural . The other way is Contrast stretch , Where the image is rescaled to include falling on the 2 And the 98 All intensities within the percentile .
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from skimage import data, img_as_float
from skimage import exposure
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 8
def plot_img_and_hist(image, axes, bins=256):
""" Draw the image and its histogram and cumulative histogram . """
image = img_as_float(image)
ax_img, ax_hist = axes
ax_cdf = ax_hist.twinx()
# Show pictures
ax_img.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax_img.set_axis_off()
# Show histogram
ax_hist.hist(image.ravel(), bins=bins, histtype='step', color='black')
ax_hist.ticklabel_format(axis='y', style='scientific', scilimits=(0, 0))
ax_hist.set_xlabel('Pixel intensity')
ax_hist.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax_hist.set_yticks([])
# Show cumulative distribution
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(image, bins)
ax_cdf.plot(bins, img_cdf, 'r')
ax_cdf.set_yticks([])
return ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf
# Load a sample image
img = data.moon()
# Contrast stretch , Contrast stretching is a method of image enhancement , It also belongs to grayscale transformation operation
p2, p98 = np.percentile(img, (2, 98))# What to calculate (2,98) Number sequence . Calculates the second of the data along the specified axis q One hundredth
img_rescale = exposure.rescale_intensity(img, in_range=(p2, p98))# The original pixel value does not want to be stretched , Just wait for the scale to shrink
''' numpy.percentile:https://www.cjavapy.com/article/1087/ exposure.rescale_intensity:https://blog.csdn.net/PresleyR/article/details/116200390 '''
# equilibrium
img_eq = exposure.equalize_hist(img)
# Adaptive equalization
img_adapteq = exposure.equalize_adapthist(img, clip_limit=0.03)
# Show results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
axes = np.zeros((2, 4), dtype=np.object)
axes[0, 0] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 1)
for i in range(1, 4):
axes[0, i] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 1+i, sharex=axes[0,0], sharey=axes[0,0])
for i in range(0, 4):
axes[1, i] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 5+i)
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img, axes[:, 0])
ax_img.set_title('Low contrast image')
y_min, y_max = ax_hist.get_ylim()
ax_hist.set_ylabel('Number of pixels')
ax_hist.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, y_max, 5))
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_rescale, axes[:, 1])
ax_img.set_title('Contrast stretching')# Contrast stretch
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_eq, axes[:, 2])
ax_img.set_title('Histogram equalization')# Histogram equalization
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_adapteq, axes[:, 3])
ax_img.set_title('Adaptive equalization')# Adaptive equalization
ax_cdf.set_ylabel('Fraction of total intensity')# Fraction of total intensity
ax_cdf.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, 1, 5))
# prevent y Axis labels overlap
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3、 Color grayscale images
It is very useful to artificially color an image with a certain color , It can highlight specific areas of the image , It can also make grayscale images vivid .
This example is scaled RGB Value and in HSV Adjust colors in color space to demonstrate image shading .
stay 2D in , Color images are usually used 2D Array of RGB-3 The layer said , this 3 Layers represent the ed、(G) green and (B)lue passageway .
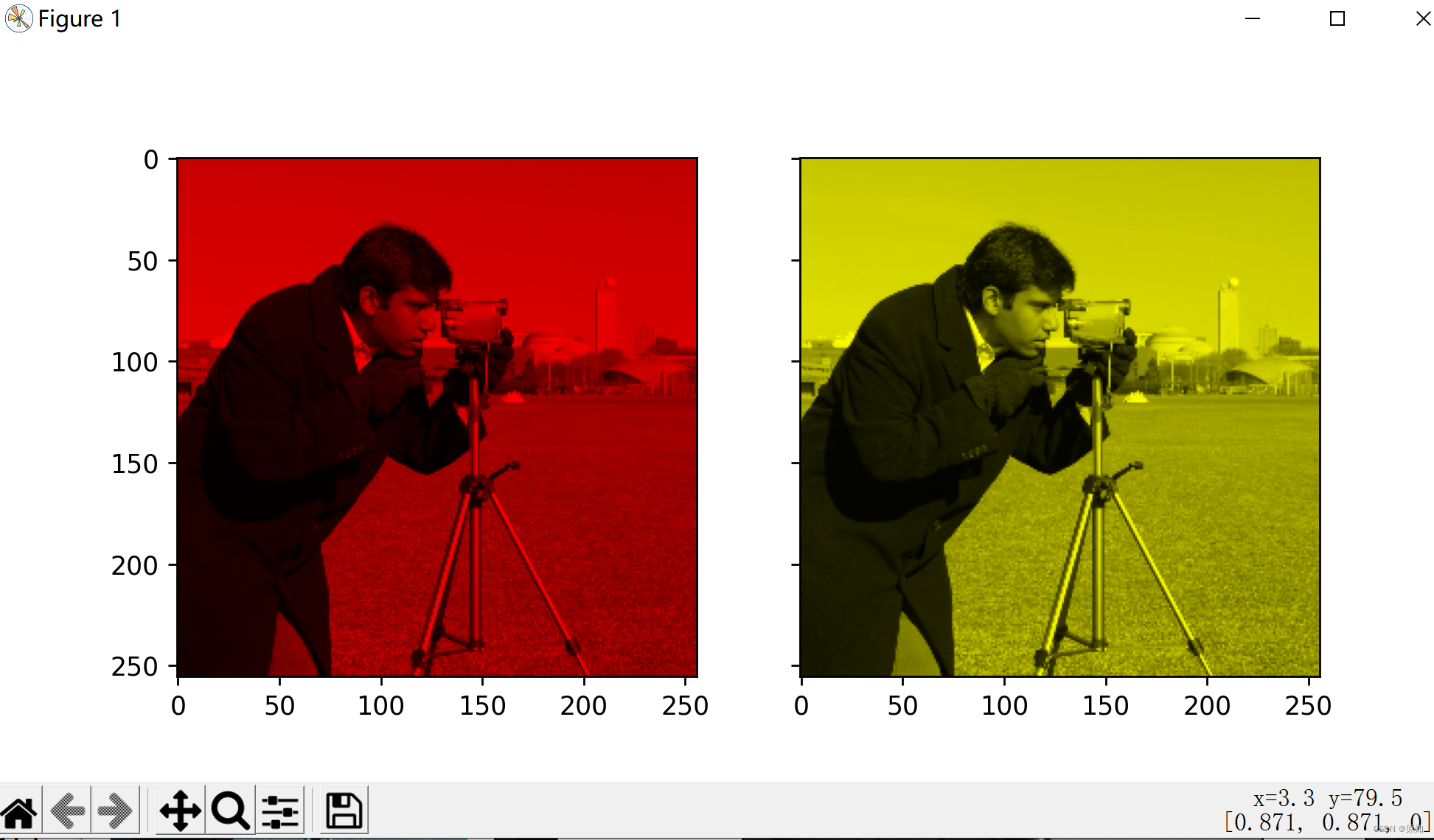
The easiest way to get a shaded image is to put each RGB Channels are set to grayscale images scaled by different multipliers for each channel .
''' for example , Multiply the green and blue channels by 0 Only red channels will be left and bright red images will be produced . Again , Zero the blue channel , Only red and green channels are left , They combine to form a yellow channel . '''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage import color
from skimage import img_as_float
grayscale_image = img_as_float(data.camera()[::2, ::2])# Floating point grayscale
image = color.gray2rgb(grayscale_image)# Create a grayscale image RGB Express .
red_multiplier = [1, 0, 0]
yellow_multiplier = [1, 1, 0]
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(8, 4),
sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax1.imshow(red_multiplier * image)# Multiply the green and blue channels by 0 Only red channels will be left and bright red images will be produced
ax2.imshow(yellow_multiplier * image)# Zero the blue channel , Only red and green channels are left , They combine to form a yellow channel
''' in many instances , Handle RGB The value may not be ideal . Because of that , There are many other color spaces that can be used to represent color images . A popular color space is called HSV, It represents hue (~ Color )、 saturation (~ Chromaticity ) And the value (~ brightness ). for example , A color ( tonal ) It may be green , But its saturation is green intensity —— Olive is at the low end , Neon lights are at the high end . In some implementations ,HSV The hue in the is from 0 To 360, Because the hue is surrounded by a circle . However , stay scikit-image in , The hue is from 0 To 1 Floating value of , So tone 、 Saturation and value share the same scale . below , We draw a linear gradient in the hue , Saturation and value rise all the way : '''
import numpy as np
hue_gradient = np.linspace(0, 1)# Again 0、1 The generation length between is 50 Array of
hsv = np.ones(shape=(1, len(hue_gradient), 3), dtype=float)# Return length is 1, Wide for 50, High for 3 Array of
hsv[:, :, 0] = hue_gradient
all_hues = color.hsv2rgb(hsv)# Create a grayscale image RGB Express
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 2))
# Set the image range , Change the hue from 0 To 1, Image is a good aspect ratio .
ax.imshow(all_hues, extent=(0 - 0.5 / len(hue_gradient),
1 + 0.5 / len(hue_gradient), 0, 0.2))
ax.set_axis_off()
''' Create a small utility function to get RGB Images , also : 1. take RGB Image to HSV 2. Set hue and saturation 3. take HSV Image conversion back to RGB '''
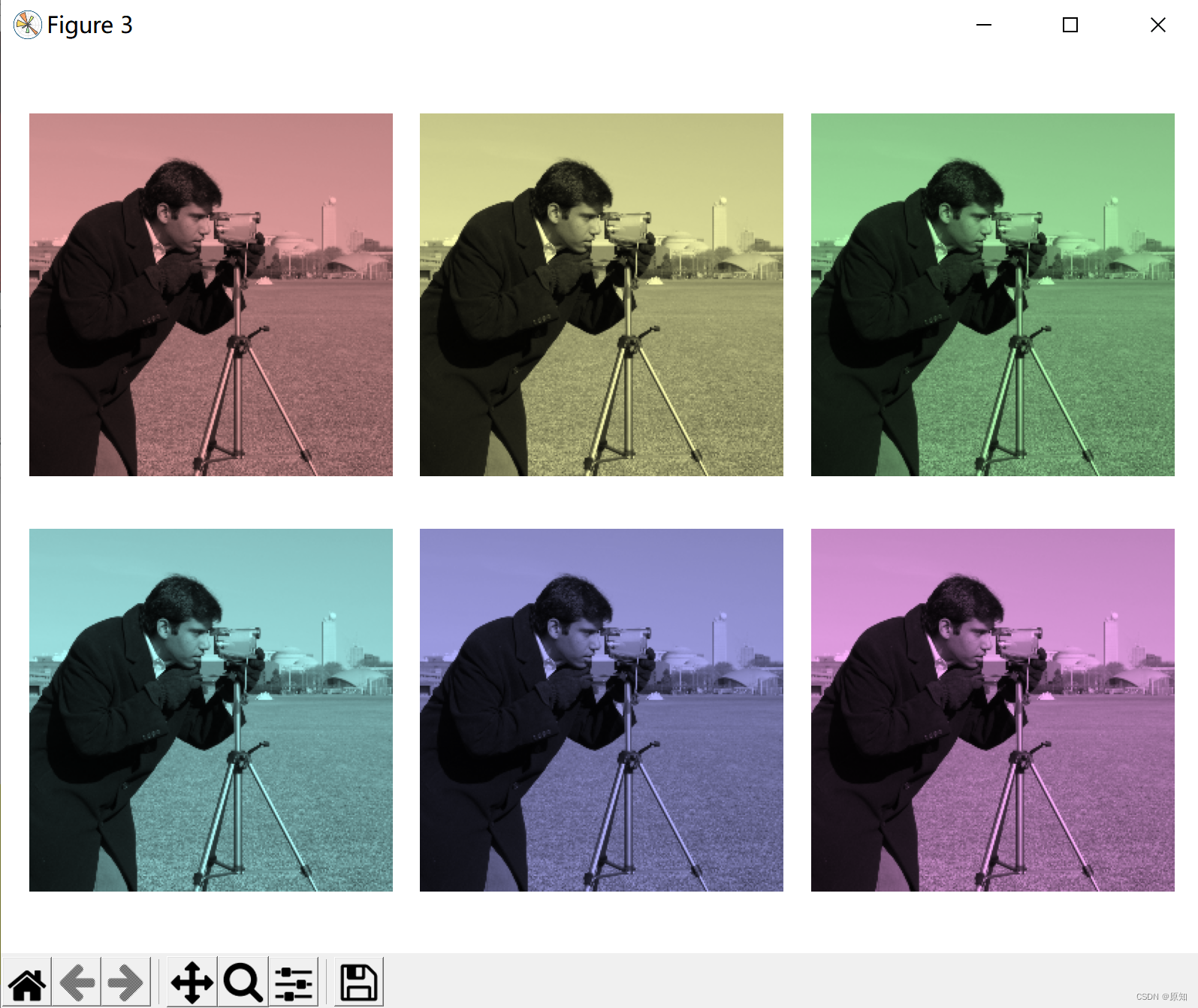
def colorize(image, hue, saturation=1):
""" Add the color of the given hue to RGB Image . By default , Saturation is set to 1, So that the color pops up ! """
hsv = color.rgb2hsv(image)
hsv[:, :, 1] = saturation# saturation (S)
hsv[:, :, 0] = hue# tonal (H)
return color.hsv2rgb(hsv)
''' Please note that , We need to increase saturation ; Images with zero saturation are grayscale , So we need a non-zero value to really see the color we set . Use the function above , We drew six images with linear gradient hue and non-zero saturation : '''
hue_rotations = np.linspace(0, 1, 7)# Return length is 6, stay 0、1 An array evenly divided between
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=3, sharex=True, sharey=True)
for ax, hue in zip(axes.flat, hue_rotations):
# Turn down the saturation to give it that vintage look.
tinted_image = colorize(image, hue, saturation=0.3)# The saturation is 0.3,hue=hue_rotations
ax.imshow(tinted_image, vmin=0, vmax=1)
ax.set_axis_off()
fig.tight_layout()
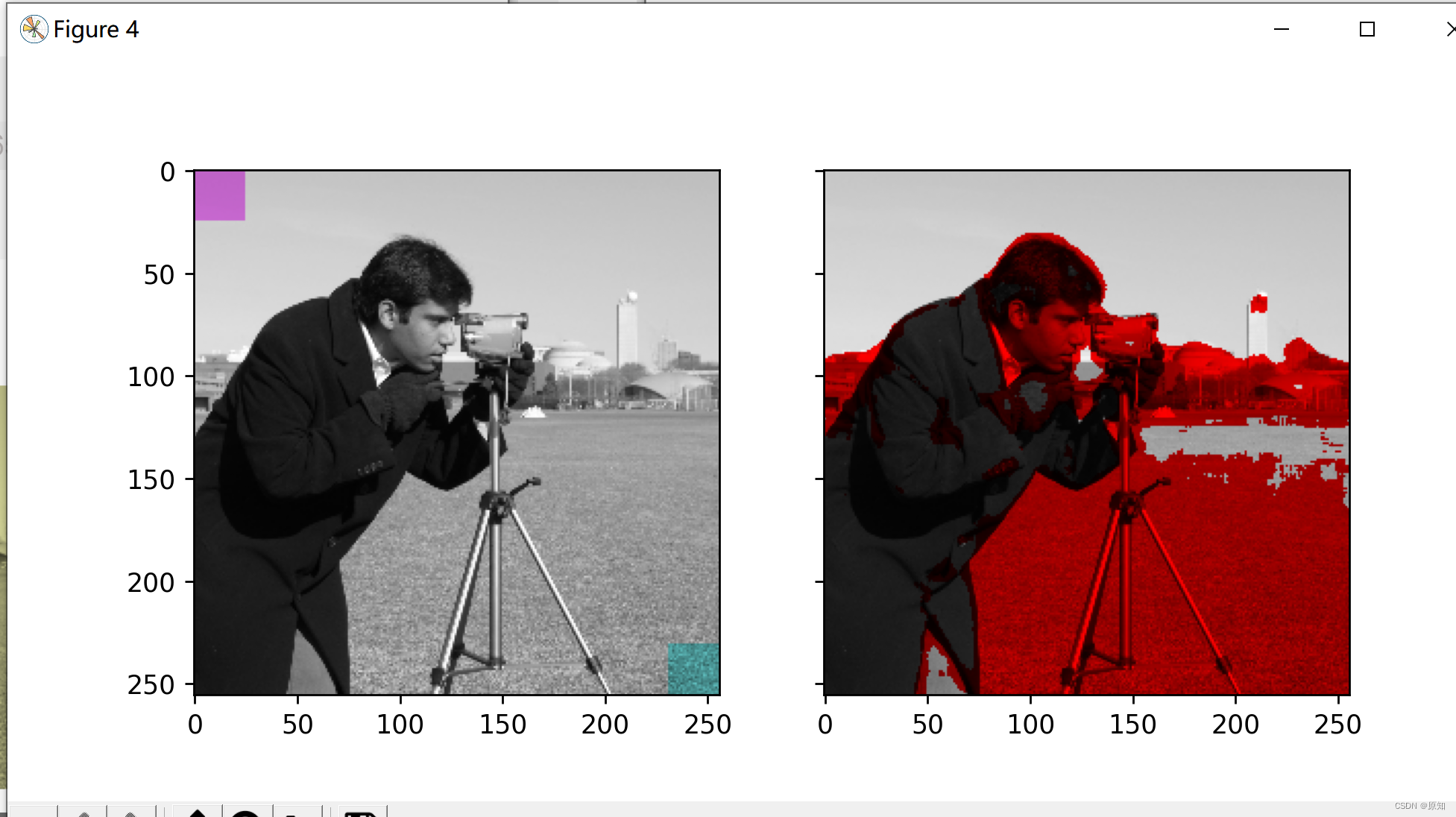
''' Compare this shading effect with numpy Slicing and fine indexing , To selectively color your image . In the following example , We use slices to set the hue of some rectangles , And scale some pixels found by threshold processing RGB value . In practice , You may want to define a shaded area according to the segmentation result or the speckle detection method . '''
from skimage.filters import rank
# A square area defined as a slice on the first two dimensions .
top_left = (slice(25),) * 2#slice() Function to implement slicing objects ,x Axis and y Axis
bottom_right = (slice(-25, None),) * 2
print("top_left:",top_left)
print("bottom_right:",bottom_right)
#top_left: (slice(None, 25, None), slice(None, 25, None))
#bottom_right: (slice(-25, None, None), slice(-25, None, None))
sliced_image = image.copy()
sliced_image[top_left] = colorize(image[top_left], 0.82, saturation=0.5)# Section staining
sliced_image[bottom_right] = colorize(image[bottom_right], 0.5, saturation=0.5)
# Create a mask selection area with interesting textures .
noisy = rank.entropy(grayscale_image, np.ones((9, 9)))
''' skimage.filters.rank.entropy(image,footprint,out = None,mask = None,shift_x = False,shift_y = False,shift_z = False) Entropy is used in 2 Base logarithm calculation , That is, the filter returns the minimum number of bits required to encode the local gray distribution Parameters : 1、image([P,] M, N) ndarray (uint8, uint16) The input image . 2、footprint:ndarray The neighborhood is expressed as 1 and 0 Of ndarray. 3、out ([P,] M, N) Array ( Same as input dtype) without , Then allocate a new array . 4、mask:ndarray( Integer or floating point number ), Optional Define the image contained in the local neighborhood (>0) Mask array of regions . without , Then use the complete image ( Default ). 5、shift_x, shift_y, shift_z int The offset added to the center point of the package .Shift Limited by package size ( The center must be within the given package ). Return value : out ([P,] M, N) ndarray (float) Output image . '''
textured_regions = noisy > 4.25# Screening , and text_3 The usage of is similar to
''' Note the use of colorize It is a little hard , Because use rgb2hsv Expect one RGB Images ( Height x Width x passageway ), But the indexed index returns A group of RGB Pixels (# pixels x channel). '''
masked_image = image.copy()
masked_image[textured_regions, :] *= red_multiplier
# I guess , The meaning here should be to redden part of the gray-scale image according to certain rules
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=1, figsize=(8, 4),
sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax1.imshow(sliced_image)
ax2.imshow(masked_image)
plt.show()




边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
最新2022年Android大厂面试经验,安卓View+Handler+Binder
Personal notes of graphics (4)

Temperature sensor chip used in temperature detector
最新高频Android面试题目分享,带你一起探究Android事件分发机制

如何快速检查钢网开口面积比是否符合 IPC7525

浅浅理解.net core的路由
最新Android高级面试题汇总,Android面试题及答案
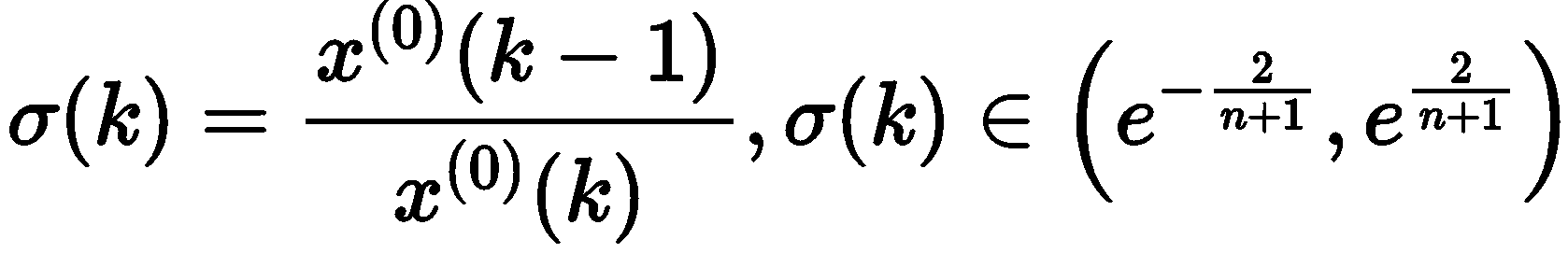
Prediction - Grey Prediction
The difference and working principle between compiler and interpreter
掌握这个提升路径,面试资料分享
随机推荐
打造All-in-One应用开发平台,轻流树立无代码行业标杆
[designmode] facade patterns
Read PG in data warehouse in one article_ stat
Laravel changed the session from file saving to database saving
【Android -- 数据存储】使用 SQLite 存储数据
Cesium(3):ThirdParty/zip. js
ORACLE进阶(六)ORACLE expdp/impdp详解
LeetCode 213. 打家劫舍 II 每日一题
Introduction and use of gateway
第九届 蓝桥杯 决赛 交换次数
Sort out several important Android knowledge and advanced Android development interview questions
node:504报错
OpenGL personal notes
Three. JS series (2): API structure diagram-2
低代码(lowcode)帮助运输公司增强供应链管理的4种方式
ByteDance Android gold, silver and four analysis, Android interview question app
[C language] question set of X
应用在温度检测仪中的温度传感芯片
LeetCode 1986. 完成任务的最少工作时间段 每日一题
Record the migration process of a project