当前位置:网站首页>[advanced C language] array & pointer & array written test questions
[advanced C language] array & pointer & array written test questions
2022-07-04 22:00:00 【Muxixi】
Hello, I'm Mu Xixi

List of articles

Preface
The pointer
Memory –》 Memory unit (1byte byte )–》 Number –》 Address –》 The pointer
So the pointer is an address ( Number ) nothing more .
The pointer in spoken language generally refers to : Pointer to the variable . Pointer variable is just a variable , It's just a memory space , Pointer variables are used to store addresses .
Pointer variable in x32 The size under the platform is 4 Bytes , stay x64 The size under the platform is 8 Bytes .
Pointer operations include :
1. Plus or minus positive numbers
2. The pointer - The pointer
3. The relational operation of pointers
The pointer is the memory address , Pointer variables are variables used to store memory addresses , In the same CPU Under Framework , Different types of pointer variables occupy the same length of storage unit , Depending on the type of data stored in the variable , The amount of storage space used is also different . With the pointer , Not only the data itself , You can also operate on the variable address where the data is stored .
stay C/C++ In language , Pointers are generally considered pointer variables , The content of a pointer variable stores the first address of the object it points to , The object pointed to can be Variable ( Pointer variables are also variables ), Array , Functions and other entities occupying storage space .
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;//pa It's a pointer variable ,int* It's a pointer variable pa The type of
//* explain pa It's a pointer variable ,int Explain pointer variables pa The type of the variable that is pointed to
*pa = 20;//*pa Dereference operation
printf("%d\n",a);//20
The meaning of pointer type
char ch = 'w';
char* pc = &ch;// Character pointer
float a = 3.14f;
float* pf = &a;// Floating point pointer
1. Pointer variables are used in addition and subtraction integer operations , The pointer variable type determines how many bytes the pointer variable skips ( step ).
2. When dereferencing pointer variables , The type of pointer variable determines how many characters the pointer variable accesses at a time ( jurisdiction ).
Pointer array
Pointer array : It's essentially arrays , Stored in the array are pointers ( Address ).
int* pa = NULL;// Pointer variables need to be initialized , Otherwise, it is a wild pointer
int* pb = NULL;
int* pc = NULL;
int* pd = NULL;
int* arr[4] = {
pa,pb,pc,pd};// Pointer array
Array name
1. Array names in most cases represent : First element address .
But there are two exceptions , The following two array names represent the entire array :
1.sizeof( Array name );// It is the memory size of the whole array in the space
// The array list is included in sizeof Inside
2.& Array name // It takes out the address of the entire array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[3] = {
1,2,3 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));//12
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));//4 perhaps 8// The size of the address is 4 perhaps 8,x32 yes 4,x64 yes 8
}
A function pointer
Functions also have addresses , Then you can use pointer variables to store the address of the function , Convenient for future function calls .
#include<stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*pa)(int, int) = &Add;
// The address of the function is stored in the pointer variable of the function
int (*pb)(int, int) = Add;
int ret = (*pa)(2, 3);
int sum = pb(2, 3);
printf("%p\n", &Add);
printf("%p\n", pa);
printf("%p\n", pb);
printf("%d\n", ret);
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}

Function pointer can realize callback function . A callback function is a function called through a function pointer .
A callback function is a function called through a function pointer . If you put a pointer to a function ( Address ) Pass as argument to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function . The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to respond to the event or condition .
Function pointer array
Function pointer array refers to : It's essentially an array , An array for storing function pointers .
int (*pf)(int , int ) = Add;
int (*pfArr[4])(int ,int );//int(*)(int ,int ) Is the type of function pointer array
pfArr The type of each element of the array is :int(*)(int ,int );
pfArr The array can store four types int(*)(int ,int ) Function pointer of .
Bubble sort simulation qsort function
#include <stdio.h>
int int_cmp(const void* p1, const void* p2)
{
return (*(int*)p1 - *(int*)p2);
}
void _swap(void* p1, void* p2, int size)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
char tmp = *((char*)p1 + i);
*((char*)p1 + i) = *((char*)p2 + i);
*((char*)p2 + i) = tmp;
}
}
void bubble(void* base, int count, int size, int(*cmp)(void*, void*))
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < count - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < count - i - 1; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * size, (char*)base + (j + 1) * size) > 0)
{
_swap((char*)base + j * size, (char*)base + (j + 1) * size, size);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 0 };
//char *arr[] = {"aaaa","dddd","cccc","bbbb"};
int i = 0;
bubble(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), sizeof(int), int_cmp);
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Array of written questions
The platform used by Xiaomu is x32 In the environment
Written test question 1
Code
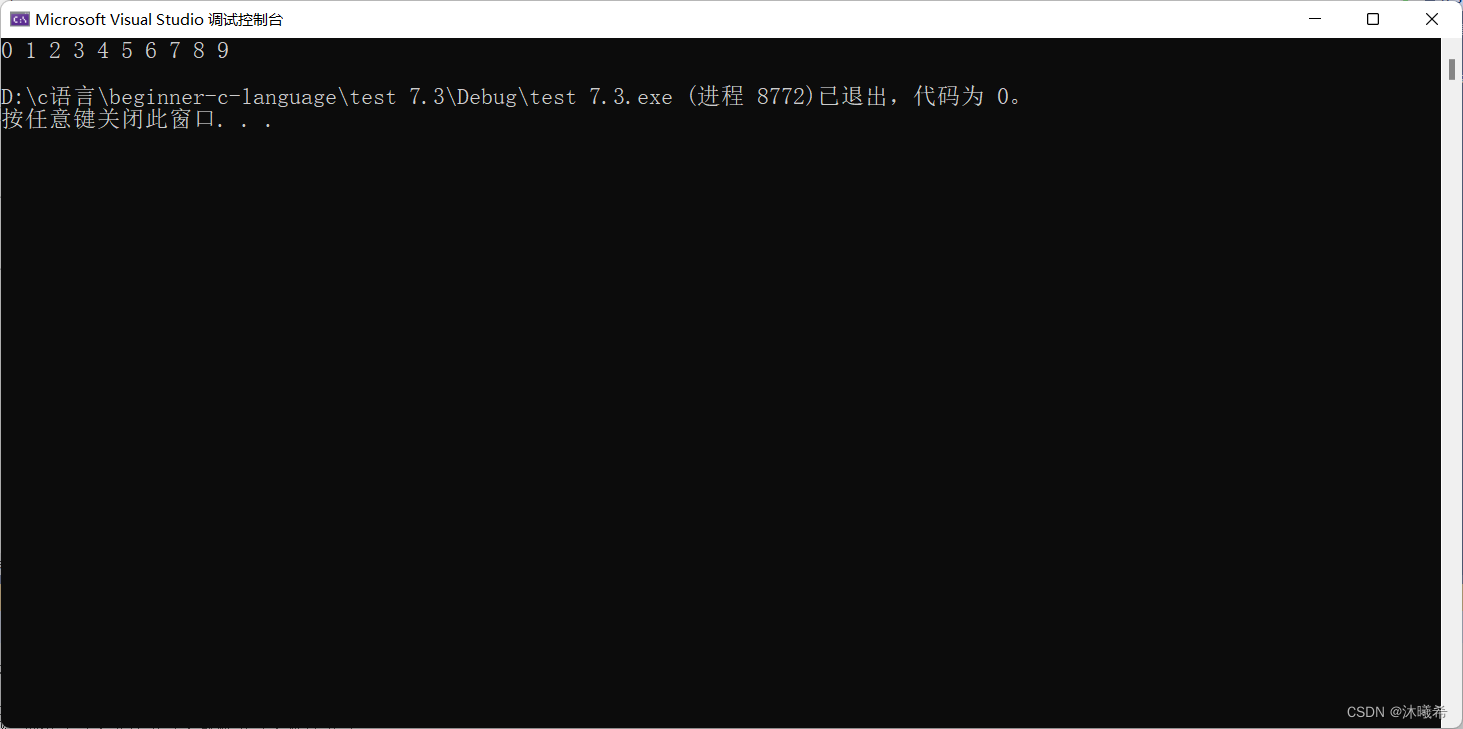
// One dimensional array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1,2,3,4 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 0));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[1]));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&a));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0]));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));
return 0;
}
analysis
1.sizeof( Array name ), At this point, the array name represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array , Unit is byte . So it's 16 Bytes
2.a+0 Array name in a Not alone sizeof Inside , There is no address symbol , therefore a Is the first yuan address ,a+0 Or the first element address , The size of the address is 4 perhaps 8 Bytes . So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes
3.*a Array name in a Is the address of the first element of the array ,*a Is to dereference the address of the first element , What you find is the first element , Because the type of the first element is int integer , So the size of the first element is 4 Bytes . So it's 4 Bytes
4.a+1 Medium a Is the address of the first element of the array ,a+1 Is the address of the second element ,sizeof(a+1) Is the size of the address 4 perhaps 8. So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
5.a[1] It represents the second element , so sizeof(a[1]) It calculates the memory size of the second element . So it's 4 Bytes
6.&a The address of the extracted array , Address of array , It's just an address , And the size of the address is 4 perhaps 8. So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
7.*&a Medium &a The type is int(*)[4],&a What you get is the address of the array name , The type is int(*)[4], Is an array pointer , Array pointer dereference finds an array , That is equivalent to * and & Offset each other , namely *&a Equivalent to a, The o sizeof(a), and a Represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array , Unit is byte . So it's 16 Bytes .
8.&a+1 Medium &a What we get is the address of the array ,&a The array pointer type of is int(*)[4],&a+1 Is from an array a The address of skipped a backward (4 Of an integer element ) Size of array ,&a+1 Or the address , Yes, the address is 4/8 byte . So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
9.&a[0] in &a[0] It's the address of the first element , It calculates the size of the address . So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
10.&a[0]+1 in &a[0]+1 Is the address of the second element , Size is 4/8 Bytes ,&a[0]+1 amount to &a[1]. So it's 4 Bytes .
result
Question 2 of the written examination
Code
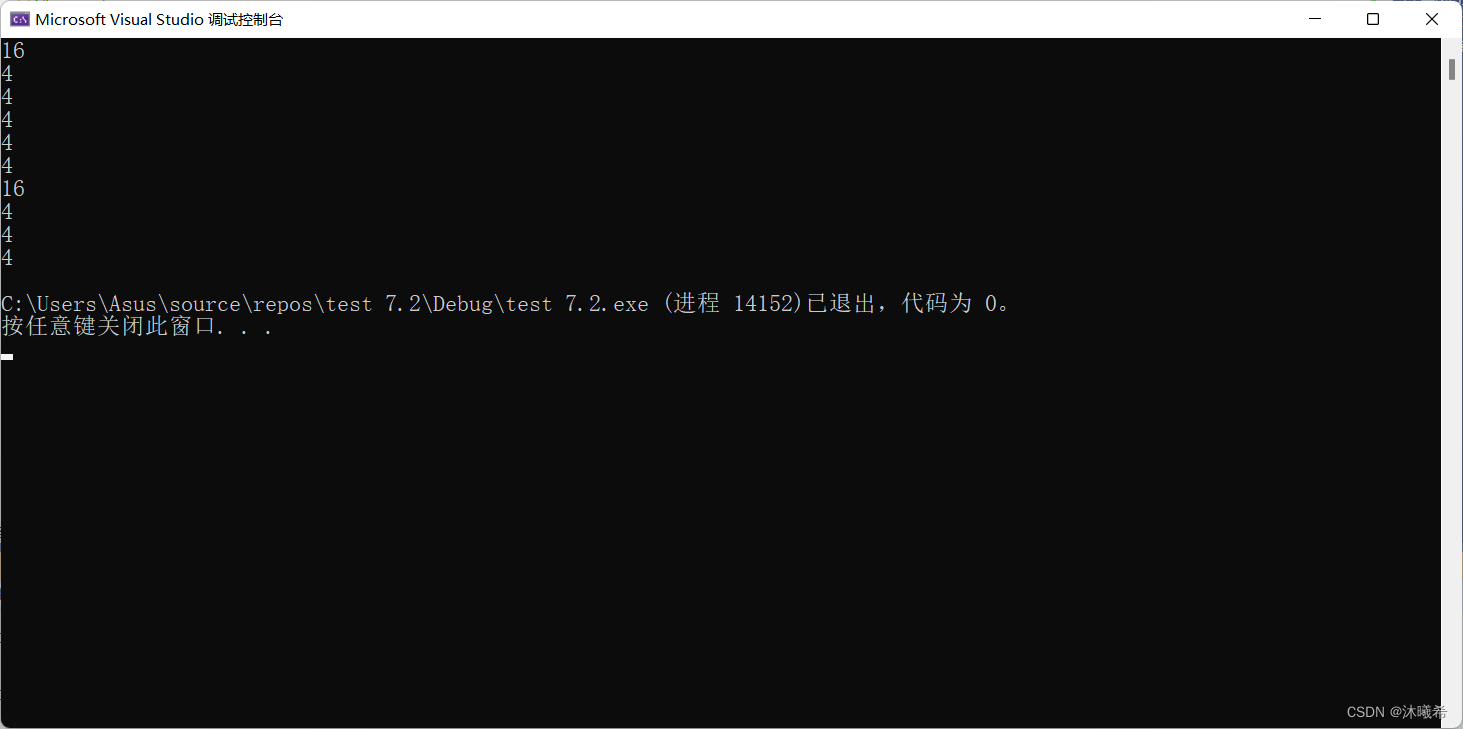
// A character array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
'a','b','c','d','e','f' };
//6 Elements
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr + 0));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr + 1));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0] + 1));
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr + 0));
//printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));//error
//printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));//error
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr + 1));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0] + 1));
return 0;
}
analysis

strlen Find the string length , Focus on... In the string ‘\0’, The calculation is ’\0’ The number of strings that appear before , It's a library function , For strings only .
sizeof Only pay attention to the size of memory space , Don't care what's stored in memory , It's the operator .
1.sizeof( Array name ), At this point, the array name represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array , Unit is byte . So it's 6 Bytes
2.arr+0 in arr + 0 Is the address of the first element of the array , The size of the address is 4 perhaps 8. So it's 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
3.*arr in arr Represents the address of the first element ,*arr Represents the first element , The size is 1 Bytes , So it's 1 Bytes .
4.arr[1] Represents the second element , The size is one byte .
5.&arr Take the address of the whole array , The size of the address is 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
6.&arr+1 Is the address after skipping an array , The size of the address is 4 perhaps 8 Bytes .
7.&arr[0]+1 amount to arr[1], That is, the second element , The size is one byte .
8.strlen(arr) It means that ‘\0’(0) The number of previous elements , So it's a random value
9.strlen(arr+0) amount to strlen(arr), Therefore, it is still a random value
10.strlen(arr) amount to strlen(‘a’), And it's equivalent to strlen(97), It's a wild pointer , So it's wrong .
11.strlen(arr[1]) amount to strlen(‘b’), And it's equivalent to strlen(98), It's a wild pointer , So it's wrong .
12.strlen(&arr) Get the address of the entire array , Count from the first element , To ’\0’ end , Random value .
13.strlen(&arr+1) Indicates skipping a type of char()[6] Array of , Therefore, it is a random value -6.
14.strlen(&arr[0]-1) Indicates the number starting from the second element , To ’\0’ end , Random value -1.The random values above are equal
result
Written test question 3
Code
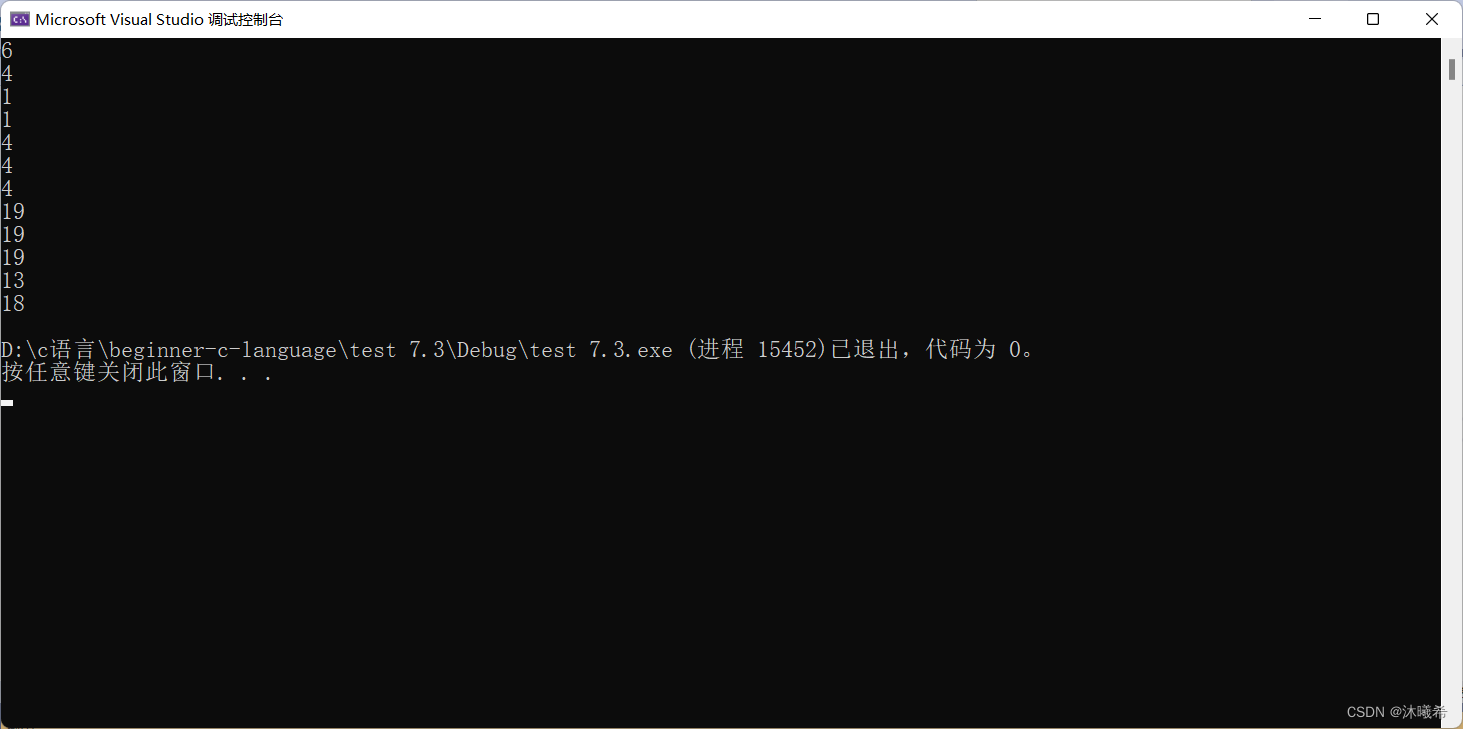
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
//7 Elements
//[a b c d e f \0]
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));//7
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr + 0));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));//1
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));//1
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr + 1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0] + 1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr + 0));//6
//printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));//error
//printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));//error
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr + 1));// Random value
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0] + 1));5
return 0;
}
result
Written test question 4
Code
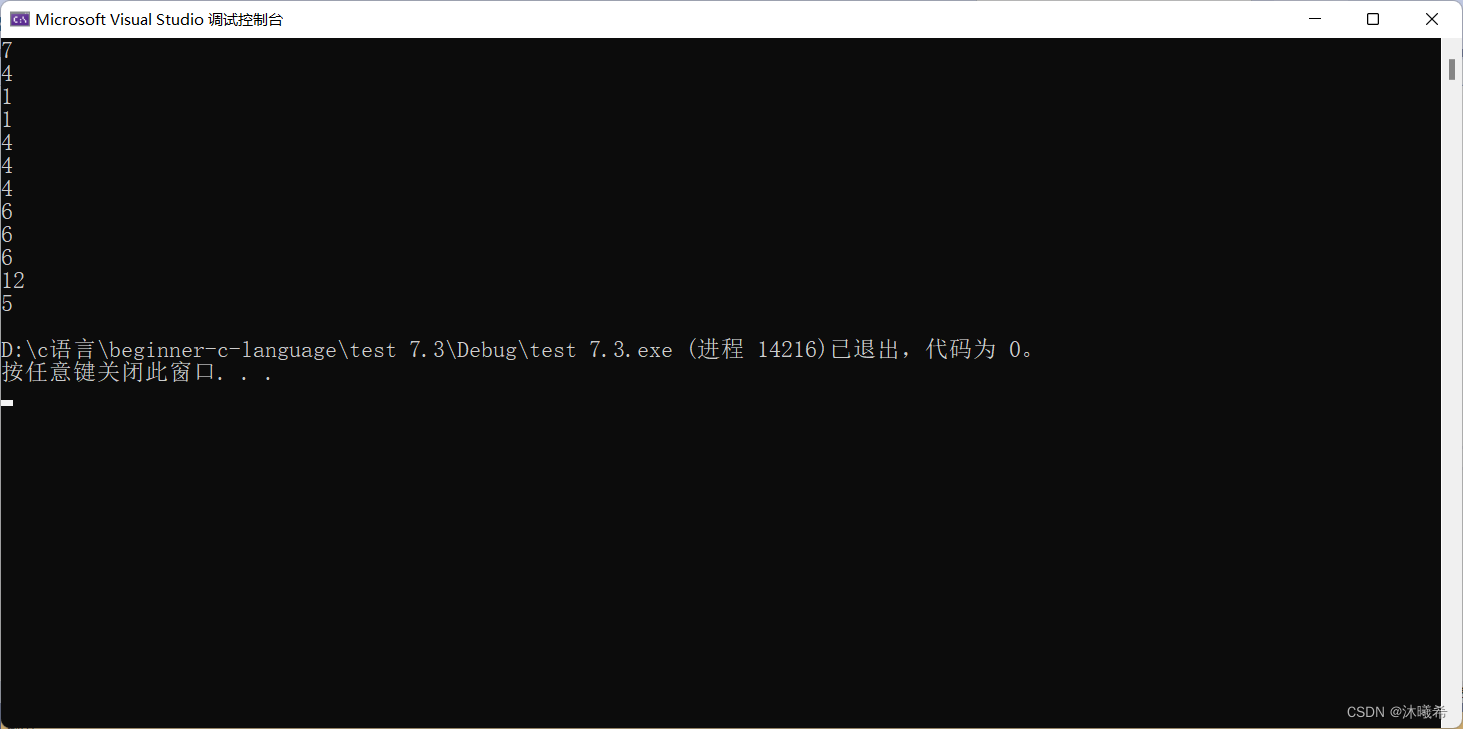
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char* p = "abcdef";
//7 Elements
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p + 1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*p));//1
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p[0]));//1
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p + 1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p[0] + 1));//4/8
printf("%d\n", strlen(p));//6
printf("%d\n", strlen(p + 1));//5
//printf("%d\n", strlen(*p));//error
//printf("%d\n", strlen(p[0]));//p[0]-->*(p+0)//error
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p));// Random value
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p + 1));// Random value
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p[0] + 1));//5
return 0;
}
result
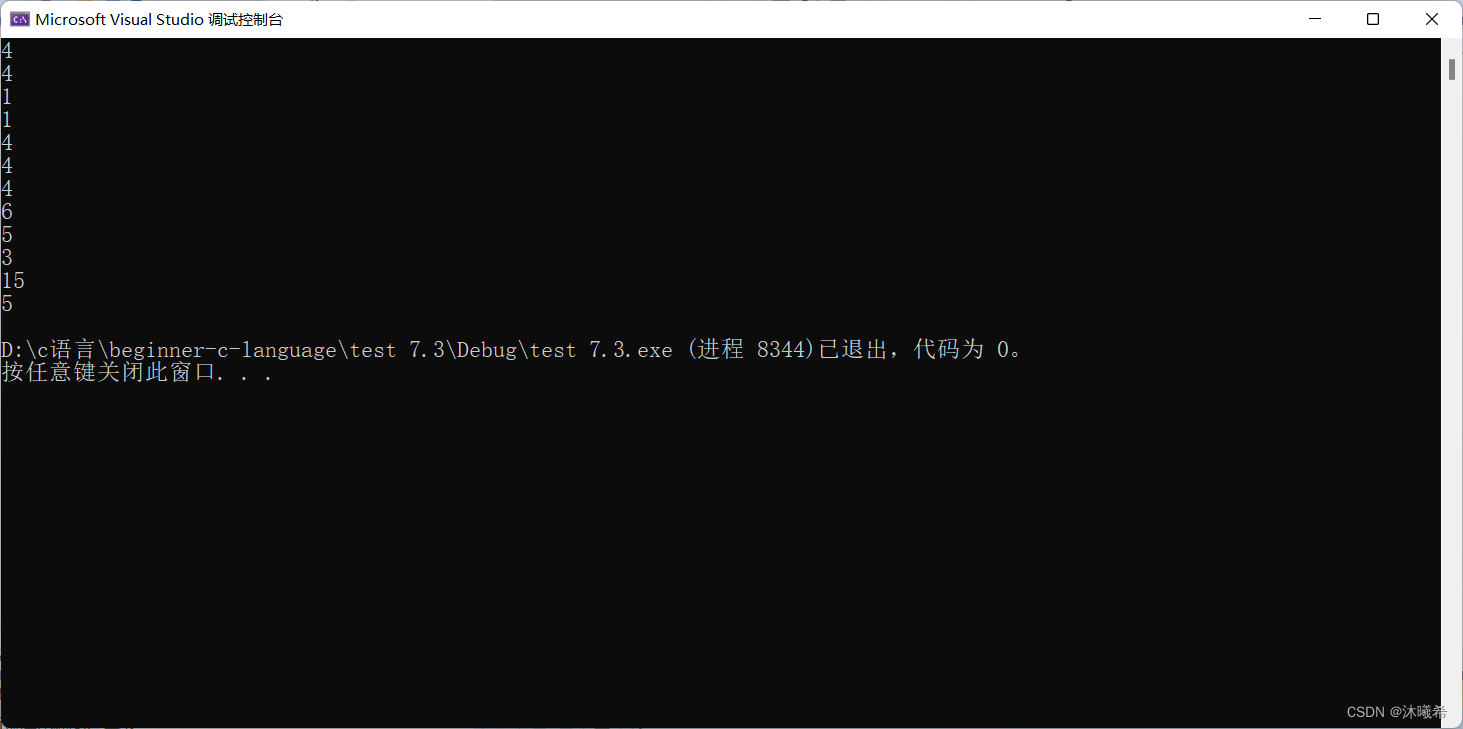
Written test question five
Code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[3][4] = {
0 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));//3*4*4=48
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0][0]));4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0]));
//a[0] Is the array name of this one-dimensional array in the first line , Put it alone sizeof Inside ,a[0] Represents the first entire one-dimensional array
//sizeof(a[0]) Calculate the size of the first row
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0] + 1));
//a[0] Not alone in sizeof Inside , I didn't take the address ,a[0] It means the address of the first element
// Is the address of the first element of the first row of this one-dimensional array ,a[0] + 1 Is the address of the second element in the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a[0] + 1)));
//a[0] + 1 Is the address of the second element in the first line
//*(a[0] + 1)) It's the second element in the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));
//a Although it is the address of a two-dimensional array , But it is not placed alone sizeof Inside , I didn't take the address
//a Represents the address of the first element , The first element of a two-dimensional array is its first row ,a It's the address on the first line
//a+1 Just skip the first line , Indicates the address of the second line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a + 1)));
//*(a + 1) Is the dereference of the address in the second line , I got the second line
//*(a+1)-->a[1]
//sizeof(*(a+1))-->sizeof(a[1])
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));
//&a[0] - Address the array name in the first row , Take out the address on the first line
//&a[0]+1 - What you get is the address on the second line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(&a[0] + 1)));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));
//a Represents the address of the first element , It's the address on the first line
//*a Is the dereference of the address in the first line , What you get is the first line
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[3]));
return 0;
}
result
summary
The meaning of array names :
- sizeof( Array name ), The array name here represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array .
- & Array name , The array name here represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array .
- In addition, all array names represent the address of the first element .
At the end
Friends who think it's good can pay attention to , Like or collect ! Thank you for your support .
Yours ️ Praise is the source of my creative power
Your collection is the direction of my struggle
Your attention is my greatest support
Yours ️ Comments are a bright light for me to move forward
It's not easy to create , I hope you can support Xiaomu
边栏推荐
- Kubedm initialization error: [error cri]: container runtime is not running
- 解决异步接口慢导致的数据错乱问题
- 淘宝商品评价api接口(item_review-获得淘宝商品评论API接口),天猫商品评论API接口
- Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]
- gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(2)什么是测试夹具/装置(test fixture)
- 类方法和类变量的使用
- 【C语言进阶篇】数组&&指针&&数组笔试题
- Bizchart+slider to realize grouping histogram
- 保证接口数据安全的10种方案
- 哈希表(Hash Tabel)
猜你喜欢
做BI开发,为什么一定要熟悉行业和企业业务?
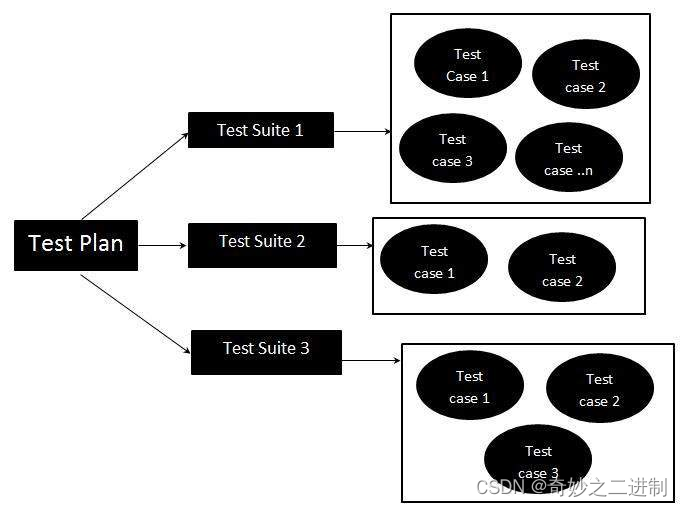
gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(3)什么是test suite和test case

创客思维在高等教育中的启迪作用

At the right time, the Guangzhou station of the city chain science and Technology Strategy Summit was successfully held
OMS系统实战的三两事
Bizchart+slider to realize grouping histogram
TCP三次握手,四次挥手,你真的了解吗?
![[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox](/img/ef/65379499df205c068ee9bc9df797ac.png)
[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox
![[C language] deep understanding of symbols](/img/4b/26cf10baa29eeff08101dcbbb673a2.png)
[C language] deep understanding of symbols

如何借助自动化工具落地DevOps
随机推荐
Flutter WebView示例
Open3D 曲面法向量计算
Why do you have to be familiar with industry and enterprise business when doing Bi development?
如何借助自动化工具落地DevOps
How was MP3 born?
旋变串判断
力扣98:验证二叉搜索树
如何使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue做一个缓存队列
How to use concurrentlinkedqueue as a cache queue
历史最全混合专家(MOE)模型相关精选论文、系统、应用整理分享
bizchart+slider实现分组柱状图
TCP协议三次握手过程
MP3是如何诞生的?
Caduceus从未停止创新,去中心化边缘渲染技术让元宇宙不再遥远
Shutter textfield example
Which securities company is better to open an account? Is online account opening safe
gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(3)什么是test suite和test case
Flutter 返回按钮的监听
Go语言循环语句(第10课中3)
Exclusive interview of open source summer | new committer Xie Qijun of Apache iotdb community