当前位置:网站首页>Pytorch Summary - Automatic gradient
Pytorch Summary - Automatic gradient
2022-06-29 09:21:00 【TJMtaotao】
Find the gradient of the function (gradient).PyTorch Provided autograd package Be able to lose ⼊ And the forward propagation process to automatically build the calculation diagram , And hold ⾏ Row back propagation .
Tensor Is the core class of this package , If its attribute .requires_grad Set to True , It will begin to chase
Trace (track) All operations on it ( This will benefit 利⽤ Use the chain rule to enter ⾏ That's ok 行 The gradient propagates 了). After the calculation , It can be adjusted
⽤ use .backward() To complete all gradient calculations . this Tensor The gradient of will accumulate to .grad attribute in .
Pay attention to y.backward() when , If y It's scalar 量, be 不 Need to be for backward() Pass on ⼊ Enter any parameter ; otherwise , need
Pass on ⼊ With a y Homomorphic Tensor
If 不 Want to be tracked , It can be adjusted ⽤ .detach() Separate it from the tracking record , This will prevent ⽌ Future plans
Be tracked , So the gradient can't pass 了. Besides , You can also use with torch.no_grad() Will not 不 Operation generation that wants to be tracked
Code block wrapped , This method is often used when evaluating models , Because when evaluating the model , We don't 不 Need to calculate trainable parameters
( requires_grad=True ) Gradient of .
Function It's another ⼀ A very important class . Tensor and Function Combined with each other, you can build a record with the entire calculation
Directed acyclic graph of a process (DAG). Every Tensor There are ⼀ One .grad_fn attribute , The property creates the Tensor Of
Function , That is to say Tensor yes 不 Is obtained by some operation , if , be grad_fn return ⼀ One is associated with these operations
Closed object , It is None.
TENSOR
Create a Tensor And set up requires_grad=True :
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
print(x)
print(x.grad_fn)
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
None
Do another operation :
y = x + 2
print(y)
print(y.grad_fn)
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]], grad_fn=<AddBackward>)
<AddBackward object at 0x1100477b8>
Be careful x It's created directly , So it doesn't have grad_fn , and y It's through ⼀ Created by an addition operation , So it has a name for
<AddBackward> Of grad_fn . image x This direct creation is called a leaf node , The leaf node corresponds to grad_fn yes None .
print(x.is_leaf, y.is_leaf) # True False
More complexity operations :
z = y * y * 3
out = z.mean()
print(z, out)
tensor([[27., 27.],
[27., 27.]], grad_fn=<MulBackward>) tensor(27., grad_fn=
<MeanBackward1>)
adopt .requires_grad_() To use in-place Of ⽅ Type change requires_grad attribute :
a = torch.randn(2, 2) # Default... If missing requires_grad = False
a = ((a * 3) / (a - 1))
print(a.requires_grad) # False
a.requires_grad_(True)
print(a.requires_grad) # True
b = (a * a).sum()
print(b.grad_fn)
False
True
<SumBackward0 object at 0x118f50cc0>
gradient
because out yes ⼀ A target 量, So call backward() when 不 The derivation variable needs to be specified 量:
out.backward() # Equivalent to out.backward(torch.tensor(1.))
Let's see out About x Gradient of 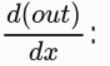
print(x.grad)
tensor([[4.5000, 4.5000],
[4.5000, 4.5000]])
We make out by o , because



and torch.autograd This package is used to calculate ⼀ The product of some Jacobian matrices .
example 例 Such as , If v yes ⼀ Of scalar functions 

So according to the chain rule, we have ![]() About
About ![]() Of Jacques ⽐ The matrix is :
Of Jacques ⽐ The matrix is :

Be careful :grad It is cumulative in the process of back propagation (accumulated), This means that every shipment ⾏行 Back propagation , Gradients will be tired
Plus the gradient before , therefore ⼀ Generally, the gradient needs to be cleared before back propagation .
Back propagation again , Be careful grad It's cumulative
out2 = x.sum()
out2.backward()
print(x.grad)
out3 = x.sum()
x.grad.data.zero_()
out3.backward()
print(x.grad)
tensor([[5.5000, 5.5000],
[5.5000, 5.5000]])
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
边栏推荐
- train_ on_ Batch save the image of the loss function change
- 查找字符串中重复次数最多的元素
- 记微信小程序setData动态修改字段名
- Verilog shift operator
- DevOps到底是什么意思?
- GPU训练云平台记录
- Pytorch summary learning series - operation
- Mysql database and table splitting strategy and application scenarios
- PAT (Basic Level) Practice (中文)1003 我要通过! (20分) C语言实现
- 使用GPU训练kernel切换
猜你喜欢

Wechat applet sub components transfer values to the page (communication between parent and child components) with source code

promise方法的简单使用

调试H5页面-vConsole
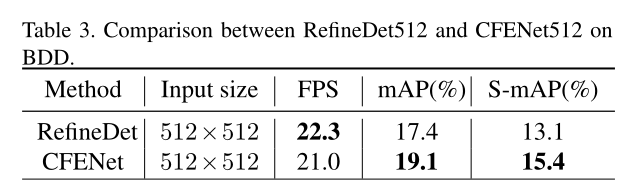
SSD改进CFENet

【目标检测】|指标 A probabilistic challenge for object detection

Mongodb persistence

Pytorch summary learning series - operation

SSD improvements cfenet

What is hyperfusion? What is the difference with traditional architecture

微信小程序底部导航栏中间突出
随机推荐
Wechat applet latest canvas2d handwritten signature
Augfpn: amélioration de l'apprentissage des caractéristiques à plusieurs échelles pour la détection des cibles
Highlight in the middle of the navigation bar at the bottom of wechat applet
GPU training cloud platform record
Training kernel switching using GPU
Handwriting Redux thunk
Hb5470 combustion test of non-metallic materials in civil aircraft cabin
ServerApp. iopub
HB5470民用飞机机舱内部非金属材料燃烧测试
Detailed version of two-stage target detection principle
Unity C # e-learning (12) -- protobuf generation protocol
Verilog data type
调试H5页面-weinre及spy-debugger真机调试
专业结构record
微信小程序项目:微信小程序页面布局
Summary of 3DMAX jamming, white screen and rendering crash
微信小程序搜索关键字高亮和ctrl+f搜索定位实现
微信小程序跳转公众号图文内容
Simple use of promise method
What exactly does Devops mean?