当前位置:网站首页>C语言 -- 操作符详解
C语言 -- 操作符详解
2022-08-04 05:18:00 【稚子】
本节重点:
- 各种操作符的介绍
- 表达式求值
操作符分类:
- 算术操作符 + - * / %
/ 两边若都为整数,则得到的也为整数;两边有一个为小数,得到的即为小数。
% 操作符的两个操作数必须为整数,返回的是整除之后的余数。
- 移位操作符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// >> 右移操作符
// << 左移操作符
// 移动的为二进制位
int main()
{
int a = 16;
// 16的二进制0001 0000
int b = a >> 1;
printf("%d\n", a);
printf("%d\n", b);
return 0;
}
/*
右移操作符:
1.算术右移
右边丢弃,左边补原符号位;
2.逻辑右移
右边丢弃,左边补0
*/整数的二进制表示有 :原码、反码、补码,存储到内存的是补码
- 位操作符
& 按位与
| 按位或
^ 按位异或
注:他们的操作数必须是整数
练习:交换两个变量的值,不使用中间变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
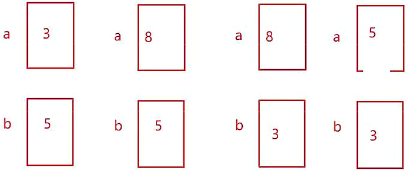
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
// 加减法
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
printf("after : a = %d b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
练习:求一个整数存储在内存中的二进制中1的个数
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
scanf("%d",&num);
// 统计num的补码中有几个1
int count = 0; // 计数
while (num)
{
if (num % 2 == 1)
count++;
num = num / 2;
}
printf("二进制中1的个数 = %d\n", count);
return 0;
}- 赋值操作符
变量在创建时给它一个值,叫做初始化,之后叫赋值
- 单目操作符
单目操作符,只有一个操作数,例如!
双目操作符,两个操作数
&a 取地址操作符,一般与指针结合使用
*p 解引用操作符
*p = &a
// 变量的赋值与使用
int a = 10;
int *p_a = &a;
*p_a = 20;sizeof计算的变量是所占内存空间的大小,单位是字节
int 4个字节
char 1个字节
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
short s = 0;
int a = 10;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(s = a+5)); // s为short,2个字节
printf("%d\n",s); // sizeof 不参与运算,只计算空间的大小
return 0;
}++a 前置++,先++,后使用
a++ 后置++,先使用,再++
强制类型转换
int a = (int)3.14 //正确用法
int a = int(3.14) //错误用法- 关系操作符
- 逻辑操作符
&& 注:只要左边结果为假,右边不管结果是什么都不再计算
int i = 0,a=0,b=2,c=3,d=4;
i = a++ && ++b && d++
printf("a = %d\n b= %d\n c=%d\n d = %d\n",a,b,c,d);
// 输出结果 1 2 3 4|| 只要左边为真,右边就不需要计算了
- 条件操作符
- 逗号操作符
逗号表达式就是用逗号隔开的多个表达式,从左向右依次执行,整个表达式的结果是最后一个表达式的结果。
- 下标引用、函数调用和结构成员
下标引用操作符:一个数组名+一个索引值
函数调用操作符(),接受一个或多个操作数;第一个操作数是函数名,剩余的操作数就是传递给函数的参数。
访问一个结构成员(重要)
结构体变量.成员名
#include <stdio.h>
// 学生
// 创建一个结构体类型
struct stu{
char name[20];
int age;
char id[20];
};
// 结构体对象s1,并初始化,实例化
struct stu s1 = {"张三",20,"20131532"};
int main()
{
printf("%s\n",s1.name);
printf("%d\n",s1.age);
printf("%s\n",s1.id);
return 0;
}结构体指针->成员名
#include <stdio.h>
// 学生
// 创建一个结构体类型
struct stu{
char name[20];
int age;
char id[20];
};
// 结构体对象s1,并初始化,实例化
struct stu s1 = {"张三",20,"20131532"};
struct stu *ps = &s1; // 结构体指针
int main()
{
printf("%s\n",ps->name);
printf("%d\n",ps->age);
printf("%s\n",ps->id);
//以下效果相同
printf("%s\n",(*ps).name);
printf("%d\n",(*ps).age);
printf("%s\n",(*ps).id);
return 0;
}表达式求值
表达式求值的顺序一部分是由操作符的优先级和结合性决定,同样有些表达式的操作数在求值的过程中可能需要转换为其他类型。
隐式类型转换
C的整型算术运算总是至少以缺省整型类型的精度来进行的。为了获得这个精度,表达式中的字符和短整型操作数在使用之前被转换为普通整型,这种转换称为整型提升
整型提升是按照变量的数据类型的符号位来提升的
边栏推荐
- About yolo7 and gpu
- SLSA 框架与软件供应链安全防护
- Jenkins export and import Job Pipeline
- 【流程图】
- Plus版SBOM:流水线物料清单PBOM
- 【21 Days Learning Challenge】Direct Insertion Sort
- 信息学奥赛一本通 1312:【例3.4】昆虫繁殖
- QT 如何识别文件的编码格式
- [Cloud Native--Kubernetes] Pod Resource Management and Probe Detection
- C Expert Programming Chapter 5 Thinking about Linking 5.1 Libraries, Linking and Loading
猜你喜欢

《看见新力量》第四期免费下载!走进十五位科技创业者的精彩故事
【云原生--Kubernetes】Pod资源管理与探针检测
![[C language advanced] program environment and preprocessing](/img/ac/a13dd2cc47136d4938b6fc7fad660c.png)
[C language advanced] program environment and preprocessing
某母婴小程序加密参数解密
day13--postman接口测试
The idea setting recognizes the .sql file type and other file types
![[One step in place] Jenkins installation, deployment, startup (complete tutorial)](/img/f2/15fb546eb864d7ff40b5507d5c7aa5.png)
[One step in place] Jenkins installation, deployment, startup (complete tutorial)
For Qixi Festival, I made a confession envelope with code
ADC噪声全面分析 -03- 利用噪声分析进行实际设计

详解八大排序
随机推荐
docker安装mysql与宿主机相差8小时的问题。
自动化测试的成本高效果差,那么自动化测试的意义在哪呢?
Converts XML tags to TXT format (voc conversion for yolo convenient training)
基于gRPC编写golang简单C2远控
[SemiDrive source code analysis] [MailBox inter-core communication] 47 - Analysis of RPMSG_IPCC_RPC mode limit size of single transmission and limit bandwidth test
As soon as flink cdc is started, the CPU of the source Oracle server soars to more than 80%. What is the reason?
力扣:343. 整数拆分
[C language advanced] program environment and preprocessing
获取单选框选中内容
Interesting Kotlin 0x0E: DeepRecursiveFunction
el-Select 选择器 底部固定
C专家编程 第5章 对链接的思考 5.3 函数库链接的5个特殊秘密
备份工具pg_dump的使用《postgres》
TSF微服务治理实战系列(一)——治理蓝图
[One step in place] Jenkins installation, deployment, startup (complete tutorial)
5个开源组件管理小技巧
文献管理工具 | Zotero
21 days learning challenge 】 【 sequential search
深度学习21天——卷积神经网络(CNN):实现mnist手写数字识别(第1天)
深度学习环境配置