当前位置:网站首页>Calculation example of matlab program iEEE9 node system for power flow calculation of AC-DC hybrid system based on alternate iteration method
Calculation example of matlab program iEEE9 node system for power flow calculation of AC-DC hybrid system based on alternate iteration method
2022-07-31 07:52:00 【Electromagnetic MATLAB】
Power flow calculation of AC-DC hybrid system based on alternate iteration methodmatlab程序iEEE9节点系统算例
参考文献:
As the receiving end load continues to increase,The voltage stability performance of the DC transmission receiving system has naturally attracted people's attention.目前,The voltage stability analysis of the AC/DC hybrid grid is roughly divided into two categories,Namely static voltage stability analysis and dynamic voltage stability analysis,This book focuses on the former.in traditional analysis,Effective short-circuit ratio evaluates the strength of AC and DC grids,VSIThe index evaluates the voltage stability of the receiving end grid,But both failed to reveal the mechanism of the voltage instability of the receiving end grid.
1 Equivalent models of AC and DC systems
As shown in the figure, it is a schematic diagram of the equivalent value of the AC and DC system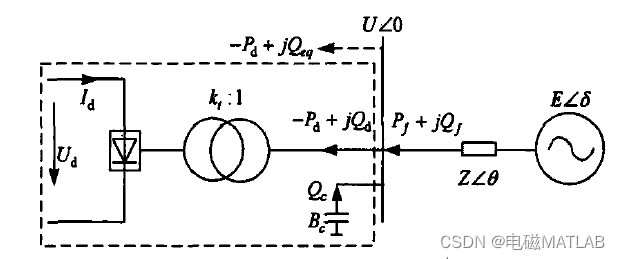
Its basic characteristic equation can be expressed as formula
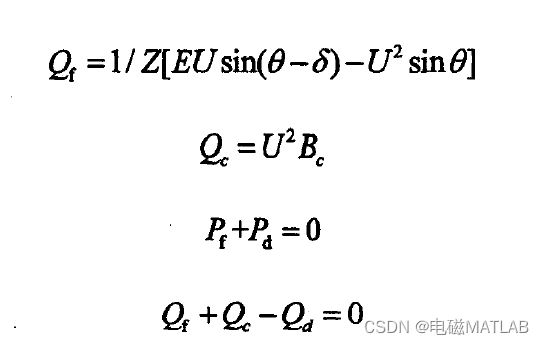

1.1 Rectifier constant current inverter constant voltage(CC-CU)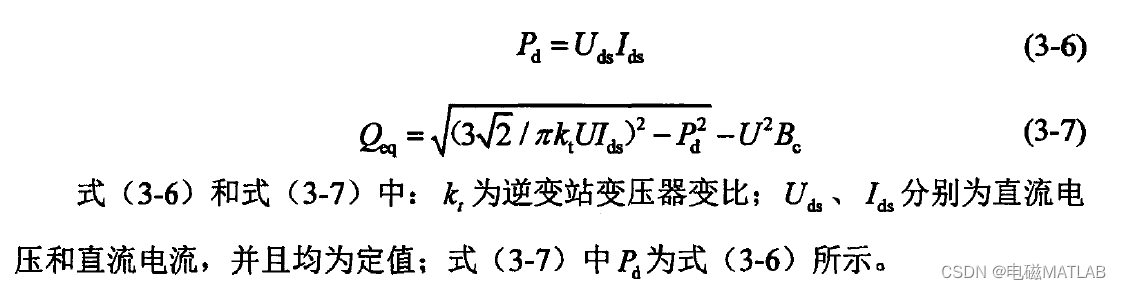
1.2 Rectifier constant current inverter constant off angle(CC-CIA)
1.3 Rectifier constant power inverter constant voltage(CP-CU)
1.4 The rectifier has a constant power and the inverter has a constant turn-off angle(CP-CIA)
2 iEEE9节点系统算例
7与8The node is changed to a DC branch.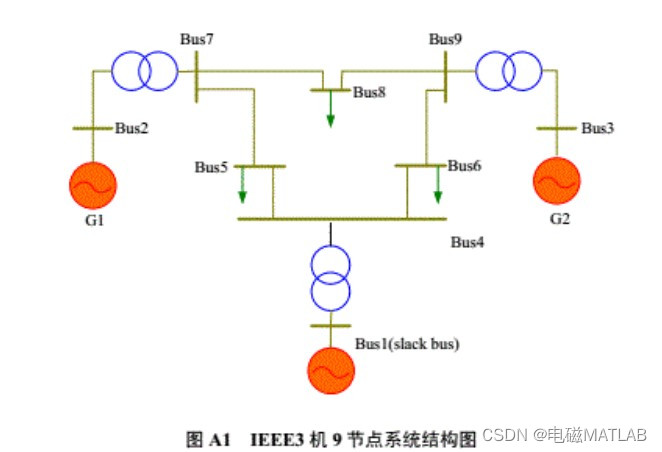
3 matlab程序运行结果
4 matlab程序
1)主函数
//Power flow calculation of AC-DC hybrid system based on alternate iteration methodmatlab程序iEEE9节点系统算例
%% 5种控制模式,The DC unknown is UD ID SD PD QD Contrl_ang Refer to Wang Yunpeng's article on the attachment control method
%function flow_calculation
clear;
clc;
close all
tic
eval('case9')
T=0.00001;
%% 参数
kk=1;%迭代次数
line=size(Line.con,1);%number of branches
n=max(Bus.con(:,1));%找出第1,2列的最大值,即节点数
TT=ones(n,1)*T;%Convergence error settings
%% Create an admittance matrixY
Y=zeros(n);%Create an admittance matrixY
U=ones(n,1);
dU=zeros(n,1);
U(PV.con(:,1))=PV.con(:,5);
U(SW.con(:,1))=SW.con(:,4);
th=zeros(n,1);
dth=zeros(n,1);
Pg=zeros(n,1);
Pl=zeros(n,1);
Ql=zeros(n,1);
Qg=zeros(n,1);
Pg(PV.con(:,1))=PV.con(:,4);
Pl(PQ.con(:,1))=PQ.con(:,4);
Ql(PQ.con(:,1))=PQ.con(:,5);
%% 计算导纳矩阵
for m=1:line
a=Line.con(m,1);%首节点a
b=Line.con(m,2);%末节点b
z=Line.con(m,8)+1i*Line.con(m,9);%节点abimpedance between
y2=1i*Line.con(m,10)/2;%导纳/2
if real(z)==0
k=Line.con(m,7)*Bus.con(b,2)/Bus.con(a,2);%变比K
else
k=1;
end
Y(a,b)=-1/k/z;%abmutual admittance
Y(b,a)=Y(a,b);
Y(a,a)=Y(a,a)+y2+(k-1)/(k*z)+1/k/z;%Seek self-admission
Y(b,b)=Y(b,b)+y2+(1-k)/k^2/z+1/k/z;
% C(a)=data(m,7);%输入节点a,bCompensation capacitance admittance
% C(b)=data(m,8);
end
%Separates the real and imaginary parts of the nodal admittance
B=imag(Y);
G=real(Y);
%判断PQ、PV、The number of balanced nodes
PQn=size(PQ.con,1);
PVn=size(PV.con,1);
SWn=size(SW.con,1);
%% DC node number
DCn=Hvdc.con(:,[1 2])';%DC node number
ACn=setdiff(1:n,union(DCn,SW.con(1,1)))';
Ndc=size(DCn,1);%The number of DC nodes
Nac=size(ACn,1);%The number of communication nodes
pn=setdiff(1:n,SW.con(1,1))';
qn=setdiff(pn,PV.con(:,1));
Pn=intersect(ACn, pn);%exchange nodePEquation node
Qn=intersect(ACn, qn);%exchange nodeQEquation node
p=size(Pn,1); %exchange nodeP方程个数
q=size(Qn,1); %exchange nodeQ方程个数
% YK=zeros(p+q);
DPa=zeros(p,1);
DQa=zeros(q,1);
DPt=zeros(Ndc,1);
DQt=zeros(Ndc,1);
Dd1=zeros(Ndc,1);
Dd2=zeros(Ndc,1);
Dd3=zeros(Ndc,1);
Dd4=zeros(Ndc,1);
Dd5=zeros(1,1);
H=zeros(p+Ndc);
N=zeros(p+Ndc,q+Ndc);
M=zeros(q+Ndc,p+Ndc);
L=zeros(q+Ndc);
JRX=zeros(9,9);
%% DC iteration initial value setting+控制方式
Vd=ones(Ndc,1)*1.1562;%DC voltage initial value
Id=0.5;
% fai=ones(Ndc,1)*30/180*pi;%Initial value of power factor angle30°
Pd=0.6.*ones(Ndc,1);
Qd=0.3.*ones(Ndc,1);
Sd=0.5.*ones(Ndc,1);
Control_ang=[20/180*pi;17/180*pi];%Inverter control angle,第一个为alpha,第二个为gama
% Control_ang(2)=30/180*pi;
W=cos(Control_ang);
Kt=ones(Ndc,1);%Transformer ratio setting at both ends of the DC branch
%% DC parameter settings
% ku=0.995;%Commutation effect constant,Wang Xifan181页
Rdc=0.0625;%直流电阻
Xc=[0.1345;0.1257];%Rectifier and inverter side transformer reactance,Write the real value
disp('Please enter a control method:')
disp('方式1:Rectifier side constant current,Inverter side constant voltage')
disp('方式2:Rectifier side constant current,The arc extinguishing angle is fixed on the inverter side')
disp('方式3:Constant power on the rectifier side,Inverter side constant voltage')
disp('方式4:Constant power on the rectifier side,The arc extinguishing angle is fixed on the inverter side')
disp('方式5:The firing angle is fixed on the rectifier side,Inverter side constant current')
Controlmode=input('方式:');
%% AC and DC calculation main loop
for mm=1:1000
H=zeros(p+Ndc);
N=zeros(p+Ndc,q+Ndc);
M=zeros(q+Ndc,p+Ndc);
L=zeros(q+Ndc);
%求ΔPa,ΔQa,ΔPt,ΔQt
Pu=0;Qu=0;
for m=1:p
for k=1:n
Pu=Pu+U(Pn(m))*U(k)*(G(Pn(m),k)*cos(th(Pn(m))-th(k))+B(Pn(m),k)*sin(th(Pn(m))-th(k)));
end
DPa(m)=Pg(Pn(m))-Pl(Pn(m))-Pu;
Pu=0;
end
for m=1:q
for k=1:n
Qu=Qu+U(Qn(m))*U(k)*(G(Qn(m),k)*sin(th(Qn(m))-th(k))-B(Qn(m),k)*cos(th(Qn(m))-th(k)));
end
DQa(m)=Qg(Qn(m))-Ql(Qn(m))-Qu;
Qu=0;
end
for m=1:Ndc
for k=1:n
Pu=Pu+U(DCn(m))*U(k)*(G(DCn(m),k)*cos(th(DCn(m))-th(k))+B(DCn(m),k)*sin(th(DCn(m))-th(k)));
Qu=Qu+U(DCn(m))*U(k)*(G(DCn(m),k)*sin(th(DCn(m))-th(k))-B(DCn(m),k)*cos(th(DCn(m))-th(k)));
end
if any(DCn(m)==Hvdc.con(:,1))
DPt(m)=Pg(DCn(m))-Pl(DCn(m))-Pu-Pd(m);
DQt(m)=Qg(DCn(m))-Ql(DCn(m))-Qu-Qd(m);
else
DPt(m)=Pg(DCn(m))-Pl(DCn(m))-Pu+Pd(m);
DQt(m)=Qg(DCn(m))-Ql(DCn(m))-Qu-Qd(m);%%Think carefully about the positive and negative signs of DC reactive power
end
Pu=0;
Qu=0;
end
%矩阵H的形成
for x=1:(p+Ndc)
for y=1:(p+Ndc)
if pn(x)==pn(y)
for m=1:n
H(x,x)=H(x,x)+U(pn(x))*U(m)*(G(pn(x),m)*sin(th(pn(x))-th(m))-B(pn(x),m)*cos(th(pn(x))-th(m)));
end
H(x,x)=H(x,x)-U(pn(x))*U(pn(x))*(G(pn(x),pn(x))*sin(th(pn(x))-th(pn(x)))-B(pn(x),pn(x))*cos(th(pn(x))-th(pn(x))));
else
H(x,y)=-U(pn(x))*U(pn(y))*(G(pn(x),pn(y))*sin(th(pn(x))-th(pn(y)))-B(pn(x),pn(y))*cos(th(pn(x))-th(pn(y))));
end
end
end
Haa=H(Pn-1,Pn-1);
Hat=H(Pn-1,DCn-1);
Hta=H(DCn-1,Pn-1);
Htt=H(DCn-1,DCn-1);
H=[Haa,Hat;Hta,Htt];
%矩阵N的形成
for x=1:(p+Ndc)
for y=1:(q+Ndc)
if pn(x)==qn(y)
for m=1:1:n
N(x,y)=N(x,y)-U(pn(x))*U(m)*(G(pn(x),m)*cos(th(pn(x))-th(m))+B(pn(x),m)*sin(th(pn(x))-th(m)));
end
N(x,y)=N(x,y)+U(pn(x))*U(pn(x))*(G(pn(x),pn(x))*cos(th(pn(x))-th(pn(x)))+B(pn(x),pn(x))*sin(th(pn(x))-th(pn(x))))-2*U(pn(x))^2*G(pn(x),pn(x));
else
N(x,y)=-U(pn(x))*U(qn(y))*(G(pn(x),qn(y))*cos(th(pn(x))-th(qn(y)))+B(pn(x),qn(y))*sin(th(pn(x))-th(qn(y))));
end
end
end
% N(pn==DCn(1),qn==DCn(1))=N(pn==DCn(1),qn==DCn(1))-3*sqrt(2)/pi*cos(Control_ang(1))*Id;
% N(pn==DCn(2),qn==DCn(2))=N(pn==DCn(2),qn==DCn(2))-3*sqrt(2)/pi*cos(Control_ang(2))*Id;
Naa=N(Pn-1,Qn-Qn(1)+1);
Nat=N(Pn-1,DCn-Qn(1)+1);
Nta=N(DCn-1,Qn-Qn(1)+1);
Ntt=N(DCn-1,DCn-Qn(1)+1);
N=[Naa,Nat;Nta,Ntt];
%矩阵M的形成
for x=1:(q+Ndc)
for y=1:(p+Ndc)
if qn(x)==pn(y)
for m=1:1:n
M(x,y)=M(x,y)-U(qn(x))*U(m)*(G(qn(x),m)*cos(th(qn(x))-th(m))+B(qn(x),m)*sin(th(qn(x))-th(m)));
end
M(x,y)=M(x,y)+U(qn(x))*U(qn(x))*(G(qn(x),qn(x))*cos(th(qn(x))-th(qn(x)))+B(qn(x),qn(x))*sin(th(qn(x))-th(qn(x))));
else
M(x,y)=U(qn(x))*U(pn(y))*(G(qn(x),pn(y))*cos(th(qn(x))-th(pn(y)))+B(qn(x),pn(y))*sin(th(qn(x))-th(pn(y))));
end
end
end
Maa=M(Qn-Qn(1)+1,Pn-1);
Mat=M(Qn-Qn(1)+1,DCn-1);
Mta=M(DCn-Qn(1)+1,Pn-1);
Mtt=M(DCn-Qn(1)+1,DCn-1);
M=[Maa,Mat;Mta,Mtt];
%矩阵L的形成
for x=1:(q+Ndc)
for y=1:(q+Ndc)
if qn(x)==qn(y)
for m=1:1:n
L(x,y)=L(x,y)-U(qn(x))*U(m)*(G(qn(x),m)*sin(th(qn(x))-th(m))-B(qn(x),m)*cos(th(qn(x))-th(m)));
end
L(x,y)=L(x,y)+U(qn(x))*U(qn(x))*(G(qn(x),qn(x))*sin(th(qn(x))-th(qn(x)))-B(qn(x),qn(x))*cos(th(qn(x))-th(qn(x))))+2*U(qn(x))^2*B(qn(x),qn(x));
else
L(x,y)=-U(qn(x))*U(qn(y))*(G(qn(x),qn(y))*sin(th(qn(x))-th(qn(y)))-B(qn(x),qn(y))*cos(th(qn(x))-th(qn(y))));
end
end
end
% L(qn==DCn(1),qn==DCn(1))=N(qn==DCn(1),qn==DCn(1))-3*sqrt(2)/pi*cos(Control_ang(1))*Id*tan(fai(1));
% L(qn==DCn(2),qn==DCn(2))=N(qn==DCn(2),qn==DCn(2))-3*sqrt(2)/pi*cos(Control_ang(2))*Id*tan(fai(2));
Laa=L(Qn-Qn(1)+1,Qn-Qn(1)+1);
Lat=L(Qn-Qn(1)+1,DCn-Qn(1)+1);
Lta=L(DCn-Qn(1)+1,Qn-Qn(1)+1);
Ltt=L(DCn-Qn(1)+1,DCn-Qn(1)+1);
L=[Laa,Lat;Lta,Ltt];
%求Δd1----Δd3
for m=1:Ndc
Dd1(m)=Vd(m)-3*sqrt(2)/pi*U(DCn(m))*W(m)+3/pi*Xc(m)*Id;
Dd2(m)=Pd(m)-Vd(m)*Id;
Dd3(m)=Sd(m)-3*sqrt(2)/pi*U(DCn(m))*Id;
Dd4(m)=Sd(m).^2-Pd(m).^2-Qd(m).^2;
end
Dd5=(1/Rdc*Vd(1)-1/Rdc*Vd(2))-Id;
%% JPX JQX JRV JRX
switch Controlmode
case 1
JRX_1=eye(2);
JRX_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRX_3=zeros(2);
JRX=[[1;0],JRX_2,zeros(2,6);[-Id;0],JRX_3,JRX_1,JRX_3,JRX_3;[0;0],JRX_3,JRX_3,JRX_1,JRX_3;...
[0;0],JRX_3,[-2*Pd(1),0;0,-2*Pd(2)],[2*Sd(1),0;0,2*Sd(2)],[-2*Qd(1),0;0,-2*Qd(2)];1/Rdc,zeros(1,7),0];
%%To make the Jacobian matrix non-singular,将JRX对角线元素为0设为1
JPX=zeros(2,9);
JPX(1,4)=-1;
JPX(2,5)=1;
JQX=zeros(2,9);
JQX(1,8)=-1;
JQX(2,9)=-1;
JRV_1=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRV_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(2))];
JRV=[JRV_1;zeros(2);JRV_2;zeros(3,2)];
J=[H,N,[zeros(6,9);JPX];M,L,[zeros(4,9);JQX];zeros(9,8),zeros(9,4),JRV,JRX];
DD=-inv(J)*[DPa;DPt;DQa;DQt;Dd1;Dd2;Dd3;Dd4;Dd5];
%Add the increment to U th上
dth(Pn)=DD(1:6);
dth(DCn)=DD(7:8);
dU(Qn)=DD(9:12).*U(Qn);
dU(DCn)=DD(13:14).*U(DCn);
dVd=DD(15);
dW=DD(16:17);
dPd=DD(18:19);
dSd=DD(20:21);
dQd=DD(22:23);
th=th+dth;
U=U+dU;
Vd(1)=Vd(1)+dVd;
W=W+dW;
Pd=Pd+dPd;
Sd=Sd+dSd;
Qd=Qd+dQd;
case 2
JRX_1=eye(2);
JRX_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1));0];
JRX_3=zeros(2);
JRX=[JRX_1,JRX_2,zeros(2,6);[-Id,0;0,-Id],[0;0],JRX_1,JRX_3,JRX_3;[0;0],JRX_3,JRX_3,JRX_1,JRX_3;...
[0;0],JRX_3,[-2*Pd(1),0;0,-2*Pd(2)],[2*Sd(1),0;0,2*Sd(2)],[-2*Qd(1),0;0,-2*Qd(2)];1/Rdc,-1/Rdc,zeros(1,7)];
%%To make the Jacobian matrix non-singular,将JRX对角线元素为0设为1
JPX=zeros(2,9);
JPX(1,4)=-1;
JPX(2,5)=1;
JQX=zeros(2,9);
JQX(1,8)=-1;
JQX(2,9)=-1;
JRV_1=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRV_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(2))];
JRV=[JRV_1;zeros(2);JRV_2;zeros(3,2)];
J=[H,N,[zeros(6,9);JPX];M,L,[zeros(4,9);JQX];zeros(9,8),zeros(9,4),JRV,JRX];
DD=-inv(J)*[DPa;DPt;DQa;DQt;Dd1;Dd2;Dd3;Dd4;Dd5];
%Add the increment to U th上
dth(Pn)=DD(1:6);
dth(DCn)=DD(7:8);
dU(Qn)=DD(9:12).*U(Qn);
dU(DCn)=DD(13:14).*U(DCn);
dVd=DD(15:16);
dW=DD(17);
dPd=DD(18:19);
dSd=DD(20:21);
dQd=DD(22:23);
th=th+dth;
U=U+dU;
Vd=Vd+dVd;
W(1)=W(1)+dW;
Pd=Pd+dPd;
Sd=Sd+dSd;
Qd=Qd+dQd;
case 3
JRX_1=eye(2);
JRX_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRX_3=zeros(2);
JRX=[[1;0],JRX_2,zeros(2,1),JRX_3,JRX_3,[3/pi*Xc(1);3/pi*Xc(2)];[-Id;0],JRX_3,[0;1],JRX_3,JRX_3,[-Vd(1);-Vd(2)];[0;0],JRX_3,[0;0],JRX_1,JRX_3,[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1));-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(2)*U(DCn(2))];...
[0;0],JRX_3,[0;-2*Pd(2)],[2*Sd(1),0;0,2*Sd(2)],[-2*Qd(1),0;0,-2*Qd(2)],[0;0];1/Rdc,zeros(1,7),-1];
%%To make the Jacobian matrix non-singular,将JRX对角线元素为0设为1
JPX=zeros(2,9);
JPX(2,4)=1;
JQX=zeros(2,9);
JQX(1,7)=-1;
JQX(2,8)=-1;
JRV_1=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRV_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(2))];
JRV=[JRV_1;zeros(2);JRV_2;zeros(3,2)];
%% 雅可比矩阵
J=[H,N,[zeros(6,9);JPX];M,L,[zeros(4,9);JQX];zeros(9,8),zeros(9,4),JRV,JRX];
DD=-inv(J)*[DPa;DPt;DQa;DQt;Dd1;Dd2;Dd3;Dd4;Dd5];
%Add the increment to U th上
dth(Pn)=DD(1:6);
dth(DCn)=DD(7:8);
dU(Qn)=DD(9:12).*U(Qn);
dU(DCn)=DD(13:14).*U(DCn);
dVd=DD(15);
dW=DD(16:17);
dPd=DD(18);
dSd=DD(19:20);
dQd=DD(21:22);
dId=DD(23);
th=th+dth;
U=U+dU;
Vd(1)=Vd(1)+dVd;
W=W+dW;
Pd(2)=Pd(2)+dPd;
Sd=Sd+dSd;
Qd=Qd+dQd;
Id=Id+dId;
case 4
JRX_1=eye(2);
JRX_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1));0];
JRX_3=zeros(2);
JRX=[JRX_1,JRX_2,zeros(2,1),JRX_3,JRX_3,[3/pi*Xc(1);3/pi*Xc(2)];[-Id,0;0,-Id],[0;0],[0;1],JRX_3,JRX_3,[-Vd(1);-Vd(2)];[0;0],JRX_3,[0;0],JRX_1,JRX_3,[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(1)*U(DCn(1));-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(2)*U(DCn(2))];...
[0;0],JRX_3,[0;-2*Pd(2)],[2*Sd(1),0;0,2*Sd(2)],[-2*Qd(1),0;0,-2*Qd(2)],[0;0];1/Rdc,-1/Rdc,zeros(1,6),-1];
%%To make the Jacobian matrix non-singular,将JRX对角线元素为0设为1
JPX=zeros(2,9);
JPX(2,4)=1;
JQX=zeros(2,9);
JQX(1,7)=-1;
JQX(2,8)=-1;
JRV_1=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRV_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(2))];
JRV=[JRV_1;zeros(2);JRV_2;zeros(3,2)];
%% 雅可比矩阵
J=[H,N,[zeros(6,9);JPX];M,L,[zeros(4,9);JQX];zeros(9,8),zeros(9,4),JRV,JRX];
DD=-inv(J)*[DPa;DPt;DQa;DQt;Dd1;Dd2;Dd3;Dd4;Dd5];
%Add the increment to U th上
dth(Pn)=DD(1:6);
dth(DCn)=DD(7:8);
dU(Qn)=DD(9:12).*U(Qn);
dU(DCn)=DD(13:14).*U(DCn);
dVd=DD(15:16);
dW=DD(17);
dPd=DD(18);
dSd=DD(19:20);
dQd=DD(21:22);
dId=DD(23);
th=th+dth;
U=U+dU;
Vd=Vd+dVd;
W(1)=W(1)+dW;
Pd(2)=Pd(2)+dPd;
Sd=Sd+dSd;
Qd=Qd+dQd;
Id=Id+dId;
case 5
JRX_1=eye(2);
JRX_2=[0;-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Kt(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRX_3=zeros(2);
JRX=[JRX_1,JRX_2,zeros(2,1),JRX_3,JRX_3,[3/pi*Xc(1);3/pi*Xc(2)];[-Id,0;0,-Id],[0;0],[1,0;0,1],JRX_3,JRX_3;[0;0],JRX_3,JRX_3,JRX_1,JRX_3;...
[0;0],JRX_3,[-2*Pd(1),0;0,-2*Pd(2)],[2*Sd(1),0;0,2*Sd(2)],[-2*Qd(1),0;0,-2*Qd(2)];1/Rdc,-1/Rdc,zeros(1,6),0];
%%To make the Jacobian matrix non-singular,将JRX对角线元素为0设为1
JPX=zeros(2,9);
JPX(2,4)=1;
JQX=zeros(2,9);
JQX(1,7)=-1;
JQX(2,8)=-1;
JRV_1=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(1)*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*W(2)*U(DCn(2))];
JRV_2=[-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(1)),0;0,-3*sqrt(2)/pi*Id*U(DCn(2))];
JRV=[JRV_1;zeros(2);JRV_2;zeros(3,2)];
%% 雅可比矩阵
J=[H,N,[zeros(6,9);JPX];M,L,[zeros(4,9);JQX];zeros(9,8),zeros(9,4),JRV,JRX];
DD=-inv(J)*[DPa;DPt;DQa;DQt;Dd1;Dd2;Dd3;Dd4;Dd5];
%Add the increment to U th上
dth(Pn)=DD(1:6);
dth(DCn)=DD(7:8);
dU(Qn)=DD(9:12).*U(Qn);
dU(DCn)=DD(13:14).*U(DCn);
dVd=DD(15:16);
dW=DD(17);
dPd=DD(18:19);
dSd=DD(20:21);
dQd=DD(22:23);
th=th+dth;
U=U+dU;
Vd=Vd+dVd;
W(2)=W(2)+dW;
Pd=Pd+dPd;
Sd=Sd+dSd;
Qd=Qd+dQd;
end
AP=abs(DD);%取模值
%判断是否收敛
if(max(AP)<1e-5) %Eis the zero matrix defined earlier
break;
end
kk=kk+1;
end
if mm==200
disp('注意:结果不收敛!');
end
disp(' 迭代次数:')
kk
disp('电压幅值:')
U
toc
.......略
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
【微服务】 微服务学习笔记二:Eureka注册中心的介绍及搭建

Fund investment advisory business

科普 | “大姨太”ETH 和 “小姨太”ETC的爱恨情仇
任务及任务切换

Machine Learning - Notes and Implementation of Linear Regression, Logistic Regression Problems

【第四章】详解Feign的实现原理
Environment_Variable_and_SetUID

Yu Mr Series 】 【 2022 July 022 - Go Go teaching course of container in the dictionary
解决安装 Bun 之后出现 zsh compinit: insecure directories, run compaudit for list. Ignore insecure directorie
双倍数据速率同步动态随机存储器(Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, DDR SDRAM)- 逻辑描述部分
随机推荐
【 TA - frost Wolf _may - "one hundred plan" 】 art 2.3 hard surface
Chapter 9 Exceptions try...except...else...finally
2022.07.14_每日一题
项目 - 如何根据最近30天、最近14天、最近7天、最近24小时、自定义时间范围查询MySQL中的数据?
bcos简介及自序
【第四章】详解Feign的实现原理
HighTec 的安装与配置
CNN--各层的介绍
多进程全局变量失效、变量共享问题
2022.07.20_Daily Question
解决安装 Bun 之后出现 zsh compinit: insecure directories, run compaudit for list. Ignore insecure directorie
mysql的建表语句_三种常用的MySQL建表语句
2022.7.29 Array
从 Google 离职,前Go 语言负责人跳槽小公司
基于LSTM的诗词生成
在 ASP.NET Core 应用程序启动时运行代码的 3 种方法
Automatic translation software - batch batch automatic translation software recommendation
【网络攻防】常见的网络攻防技术——黑客攻防(通俗易懂版)
2022.07.20_Daily Question
单点登录 思维导图