当前位置:网站首页>Principle and usage of extern
Principle and usage of extern
2022-07-06 17:53:00 【TABE_】
Here's the catalog title
extern It can be used to specify links ; It can also be placed in front of variables or functions , A function defined in a file or other variable , Prompt the compiler to look for its definition in other modules when it encounters this variable and function .
Say something reasonable. , It has the following two functions :
- And “C” Continuous use , Such as extern “C” void fun(); Tell the compiler to press C The rules to translate
- Global variable or function declaration , Its declared variables and functions can be found in other modules ( file ) Use in , Be careful , This is just a statement, not a definition , The specific definition should be completed in the specific module
And “C” Continuous use ( Link assignment )
stay CPP You can often see code in the following form in the file :
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/**** some declaration or so *****/
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif /* end of __cplusplus */
that , What's the use of this way of writing ? actually , This is to make CPP Can and C Interface . The reason for this is , It is because of some differences between the two languages .
because CPP Support polymorphism , That is, functions with the same function name can complete different functions ,CPP It is usually through parameters to distinguish which function is called . At compile time ,CPP The compiler concatenates the parameter type with the function name , So after the program is compiled into the object file ,CPP The compiler can directly link multiple object files into one object file or executable file according to the symbol name in the object file . But in C In language , Because there is no concept of polymorphism ,C When compiling, the compiler will add an underscore in front of the function name , Do nothing ( At least that's what many compilers do ). For this reason , When CPP And C Mixed programming , There could be problems .
Suppose such a function is defined in a header file :
int foo(int a, int b);
The implementation of this function is located in a .c In file , meanwhile , stay .cpp The function is called in the file. . that , When CPP When the compiler compiles this function , It is possible to change the function name to _fooii, there ii Indicates that the first and second parameters of the function are integers . and C The compiler may compile the function name into _foo. in other words , stay CPP In the target file obtained by the compiler ,foo() The function consists of _fooii Symbols to reference , And in the C In the target file generated by the compiler ,foo() The function consists of _foo Referring to .
But when the linker works , It doesn't matter what language the upper level uses , It recognizes only symbols in the target file . therefore , The connector will be found in .cpp Called in foo() function , But it can't be found in other target files _fooii This symbol , Therefore, an error is prompted in the connection process .extern “C” {} This grammatical form is used to solve this problem .
Global variable or function declaration
for instance , We want to declare a long int runtime_minute Variables are used by multiple modules :
//time.h
#ifndef TIME_H
#define TIME_H
// First of all we have time.h Make the following statement :
extern long int runtime_minute;
#endif //TIME_H
Pass... In the header file extern Declared variables are not defined , So we need to time.cpp The definition of :
//time.cpp
#include "time.h"
// stay time.cpp Give in runtime_minute Specific definition of variables :
long int runtime_minute = 0;
At this time , If you want to time2.cpp Use this definition in time.cpp Medium runtime_minute Variable , Just include time.h This header file is enough :
//time2.cpp
#include "time.h"
#include <iostream>
// stay time.cpp Give in runtime_minute Specific definition of variables :
int main(){
runtime_minute++;
std::cout<<runtime_minute<<std::endl;
// Output is 1
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- FMT开源自驾仪 | FMT中间件:一种高实时的分布式日志模块Mlog
- OpenEuler 会长久吗
- HMS Core 机器学习服务打造同传翻译新“声”态,AI让国际交流更顺畅
- Unity tips - draw aiming Center
- The easycvr platform reports an error "ID cannot be empty" through the interface editing channel. What is the reason?
- 【MySQL入门】第三话 · MySQL中常见的数据类型
- node の SQLite
- [introduction to MySQL] third, common data types in MySQL
- Easy introduction to SQL (1): addition, deletion, modification and simple query
- Xin'an Second Edition; Chapter 11 learning notes on the principle and application of network physical isolation technology
猜你喜欢

Unity tips - draw aiming Center
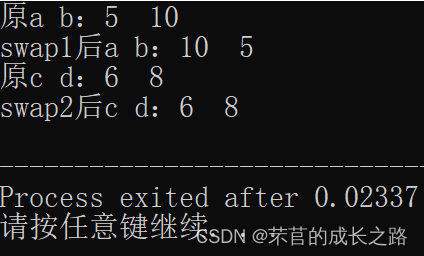
C语言通过指针交换两个数

Today in history: the mother of Google was born; Two Turing Award pioneers born on the same day
Kali2021 installation and basic configuration
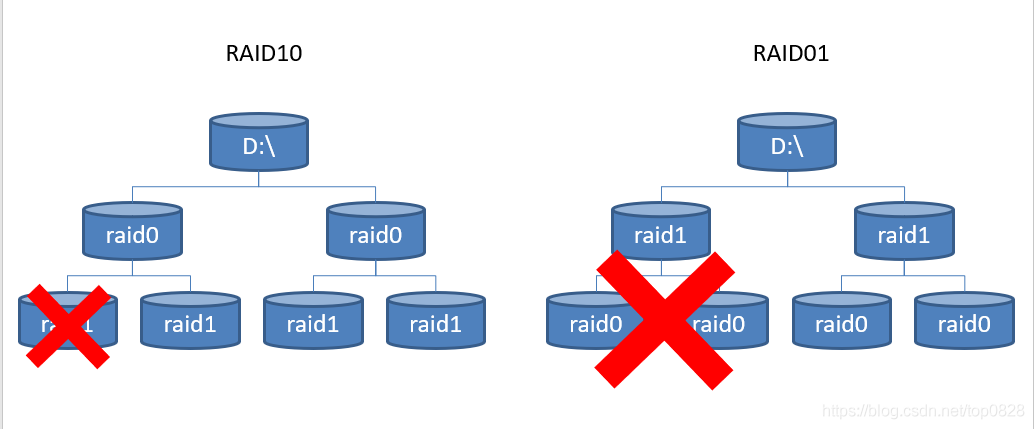
基本磁盘与动态磁盘 RAID磁盘冗余阵列区分
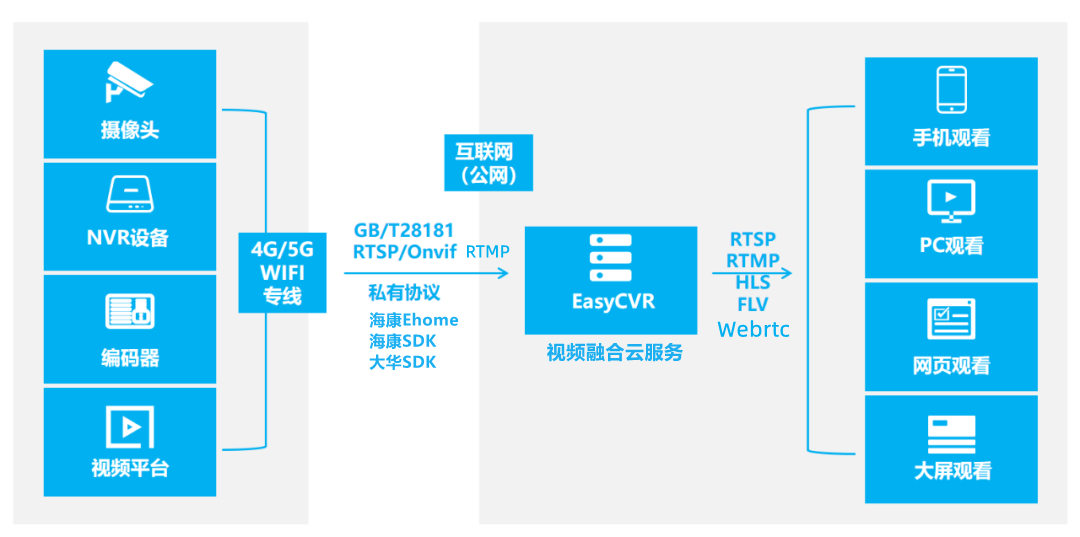
EasyCVR授权到期页面无法登录,该如何解决?
SAP UI5 框架的 manifest.json

李书福为何要亲自挂帅造手机?

Summary of Android interview questions of Dachang in 2022 (II) (including answers)
Pyspark operator processing spatial data full parsing (4): let's talk about spatial operations first
随机推荐
The shell generates JSON arrays and inserts them into the database
2022年大厂Android面试题汇总(一)(含答案)
MarkDown语法——更好地写博客
EasyCVR接入设备开启音频后,视频无法正常播放是什么原因?
分布式不来点网关都说不过去
Alibaba brand data bank: introduction to the most complete data bank
一体化实时 HTAP 数据库 StoneDB,如何替换 MySQL 并实现近百倍性能提升
Codeforces Round #803 (Div. 2)
EasyCVR授权到期页面无法登录,该如何解决?
Summary of Android interview questions of Dachang in 2022 (I) (including answers)
视频融合云平台EasyCVR增加多级分组,可灵活管理接入设备
Unity tips - draw aiming Center
Olivetin can safely run shell commands on Web pages (Part 1)
The art of Engineering (3): do not rely on each other between functions of code robustness
Growth of operation and maintenance Xiaobai - week 7
Example of batch update statement combining update and inner join in SQL Server
【ASM】字节码操作 ClassWriter 类介绍与使用
Binary search strategy
Interview shock 62: what are the precautions for group by?
PyTorch 提取中间层特征?