当前位置:网站首页>MySQL high frequency interview 20 questions, necessary (important)
MySQL high frequency interview 20 questions, necessary (important)
2022-07-06 06:37:00 【Share and summary】
List of articles
- One 、MySQL High frequency interview 30 ask
- 1.1 MySQL The three paradigms of ?
- 1.2 MyISAM And InnoDB difference ?
- 1.3 The difference between clustered index and non clustered index ?
- 1.4 char and varchar The difference between ?
- 1.5 Innodb Why is auto increment recommended ID?
- 1.6 What is index ?
- 1.7 Index type ?
- 1.8 Index the underlying data structure ?
- 1.9 B Trees and B+ Tree difference ? Why B+ Trees ?
- 1.10 The index field is int Good or not varchar good ?
- 1.11 Index design principles ( Quick query , Take up less space )
- 1.12 Index failure scenario ?
- 1.13 How to create an index ?
- 1.14 Will non clustered index return to table query ?
- 1.15 Rules for establishing joint index ?
- 1.16 Left most matching principle ?
- 1.17 One sql The reason for the slow implementation ?
- 1.18 SQL Examples of optimization ?
- 1.19 COUNT()
- 1.20 What is? mysql Business ? What are the four characteristics of a transaction ?
One 、MySQL High frequency interview 30 ask
1.1 MySQL The three paradigms of ?
Normal form is the norm we should follow when creating tables . The paradigm that meets the minimum requirements is the first paradigm 1NF, What meets more specifications on the basis of the first paradigm is called the second paradigm 2NF, Third normal form 3NF And so on .
1NF: The first normal form is that the columns of the table are atomic , You can't split , That is, the information of the column can no longer be decomposed into sets and arrays . As long as it is a relational database, it will automatically meet 1NF. If a field in a table has multiple values, it must be split into different attributes . Generally speaking, a field can only store one information .
2NF: The second paradigm is based on the first paradigm , Therefore, when the premise of the second paradigm is satisfied, the first paradigm is satisfied . The second paradigm requires that each instance or row in the database table must be uniquely different . We usually need to design a primary key to realize . Popular understanding is that one field in a table can only rely on another field .
3NF: The third paradigm must satisfy the second paradigm . The third paradigm requires that a database table does not contain non primary key fields that have been included in other tables . The non primary key columns in the table are completely dependent on the primary key , Some attributes cannot depend on other attributes . When there is a transfer dependency, you should create a table for the columns that do not depend on the primary key to manage .
1.2 MyISAM And InnoDB difference ?
InnoDB Cluster index ,MyISAM Nonclustered index
InnoDB The data is saved with the index .ibd,MyISAM Table structure .frm Indexes .myi data .myd
InnoDB Support transactions 、 Foreign keys 、 Row lock table lock ,MyISAM Unsupported transaction 、 Foreign keys 、 Only table locks are supported
select count(*)
MyISAM Better query ,InnoDB Update better
All are B+tree Indexes
MyISAM Full text index support ,InnoDB5.6 Post support
MyISAM:
Unsupported transaction , But every query is atomic
Support table level lock , Lock the whole table every time
Store the total number of tables
One MyISAM The table has three files : Table structure .frm Indexes .myi data .myd
Using nonclustered indexes , The data field of the index file stores the pointer to the data file . The secondary index is basically the same as the primary index , But secondary indexes don't guarantee uniqueness .
Innodb:
Support ACID Business , Four isolation levels are supported
Supports row level locks and foreign key constraints , Therefore, write concurrency is supported
Do not store total rows
The primary key index adopts the clustered index ( The indexed data field stores the data file itself ), The data field of the secondary index stores the value of the primary key ; So look up the data from the secondary index , You need to find the primary key value through the secondary index first , Visit the secondary index ; It's better to use auto primary key , Prevent data insertion , To maintain B+ Tree structure , A big adjustment of the document .
1.3 The difference between clustered index and non clustered index ?
Cluster index : Put data storage and index together , Find the index and find the data .
Nonclustered index : Store data in index separated structure , The leaf node of the index structure points to the corresponding row of the data ,myisam adopt key_buffer Cache the index into memory first. When you need to access data ( Access data by index ), Search the index directly in memory , Then find the corresponding data of the disk through the index , That's why the index isn't there key buffer Hit, , The reason for the slow speed .
The difference between primary key index and common index : The primary key index only needs to search ID This B+Tree You get the data . The ordinary index searches the index first to get the primary key value , Search the primary key index tree again ( Back to the table ).
Clustering index is unique , Because clustering index is to put data and index structure together , So a table has only one clustered index .
1.4 char and varchar The difference between ?
1.CHAR The length of is immutable , and VARCHAR The length of is variable , in other words , Define a CHAR[10] and VARCHAR[10], If the deposit is ‘ABCD’, that CHAR The total length is still 10, Except for the characters ‘ABCD’ Outside , Followed by six spaces , and VARCHAR And the length of it becomes 4 了 , When taking data CHAR The type should use trim() Remove the extra space , and VARCHAR Type is not required .
2、CHAR Access speed is faster than VARCHAR Much faster , Because its length is fixed , Convenient program storage and search ; however CHAR It pays the price of space , Because its length is fixed , So it's inevitable that there will be extra spaces to occupy the space , It can be said that space is exchanged for time efficiency , and VARCHAR Space efficiency is the first priority .
3、CHAR The storage mode of is , One English character (ASCII) Occupy 1 Bytes , A Chinese character takes up two bytes ; and VARCHAR The storage mode of is , One English character occupies 2 Bytes , A Chinese character also takes up 2 Bytes .
1.5 Innodb Why is auto increment recommended ID?
① It's going to fill the pages in almost the order of the primary keys , Improved the maximum fill rate of the page , There will be no waste of pages .
② The newly inserted row must be next to the original maximum data row ,mysql Location and addressing are fast , There is no additional cost to calculate the position of the new row .
③ Reduced page fragmentation and fragmentation .
UUID: A lot of random IO+ Page splitting causes a lot of data to be moved + The data will be fragmented .
summary : Self increasing ID Orderly , Will be inserted last in order , and UUID disorder , Random generation , Insert randomly , It will cause frequent page splitting , Memory fragmentation , A lot of random IO.
1.6 What is index ?
Ordered data structure , Can help quickly find data .
Advantages and disadvantages : Index can improve query speed , Queries use optimization hiders to improve performance , But it also takes up physical space , Reduce the speed of addition, deletion and modification , Because I have to operate the index file .
1.7 Index type ?
Overlay index + Back to the table + Index push down + Joint index
1. General index : Can be repeated
2. unique index : only , May be empty , There is only one primary key index in the table , Multiple unique indexes can be
3. primary key : only , Not empty , The leaf node saves row record data , A primary key index is also called a clustered index , The value of the primary key stored in the leaf node corresponding to the non primary key index ( Secondary indexes ), Using a secondary index to look up a table requires a table return operation ( Find the primary key according to the secondary index , Then check the primary key index according to the primary key ) Self increasing primary key is generally recommended , Ensure space utilization , Reduce page splits
4. Full-text index
5. Overlay index : The index field covers the fields involved in the query statement , Directly through the index file, you can return the data required by the query , You don't have to go back to the table .
6. Back to the table : Find the primary key through the index , According to the primary key id Query the primary key index .
7. Index push down : In the process of query by index, some records are filtered out according to the query conditions , Reduce the last table return operation .
If you execute select * from stu where name=? and age=? There is no index push down before the storage engine name Filter data returned to server layer , then server Layer according to age Filter . Direct index push down name and age Filter the results at the storage engine layer .
1.8 Index the underlying data structure ?
B+ Trees 、hash
hash The bottom layer is the hash table implementation , Equivalent query , Can quickly locate , Generally, the efficiency is very high , unstable , When a large number of key duplicate hash conflicts occur , Decline in efficiency , Range query is not supported , Cannot be used to sort groups , Cannot obfuscate query , Leftmost prefix matching principle of multi column index , Always return to the table, etc .
1.9 B Trees and B+ Tree difference ? Why B+ Trees ?
B+ Trees : Non leaf nodes do not exist data, Only exist key, More stable query , Increased breadth (B+ The tree is more out , The trees are tall and short , Small node , disk IO low repetition ); The next level pointer of the leaf node ( Range queries ); Index redundancy .B Tree non leaf nodes can also store data ,B+ All data of the tree is stored on the leaf node , Non leaf nodes do not store data . Leaf nodes are connected by a two-way linked list, which is suitable for range query .
Compared with the red and black trees :
Fewer queries :B+ The tree is more out , The tree is lower , Fewer queries
Disk read ahead principle : In order to reduce the IO operation , Often not read strictly on demand , It's a preview .B+ The leaf nodes of the tree are stored adjacent to each other , Reading will be faster .
Store more index nodes :B+ Trees store data only at leaf nodes , Non leaf node index , A node is a memory page on the disk , The memory page size is fixed , So compared B These trees can · Save more index nodes , More out , The trees are tall and short , Fewer queries , disk IO Less .
1.10 The index field is int Good or not varchar good ?
int Take up less memory innodb Storage engine uses b+ Each node of the tree is 16k(show variables like ‘innodb_page_size’;)16438 That means less memory b+ Tree nodes can store more pointers, so B+ Trees can better control the height of trees , Reduce io.
1.11 Index design principles ( Quick query , Take up less space )
1. Appear in the where Clause or join the columns in the clause
2. Tables with small cardinality are not necessary
3. Use short index , If the index is a long string column , Prefix length should be specified
4. Define the index of the data column with foreign key
5. Don't over index
6. Frequent updates are not suitable for
7. Those with low discrimination are not suitable for , Such as gender
8. Expand the index as much as possible , Don't create a new index , Such as (a)->(a,b)
9. String field indexing method
1、 Create a full index directly , This may take up more space ;
2、 Create prefix index , Save a space , But it will increase the number of query scans , And the overlay index cannot be used ;
3、 Backward storage , Then create a prefix index , The problem of not enough indexing to bypass the prefix of the string itself ;
4、 Index with an additional field , Additional computational overhead
summary : The index design principle requires fast query , Take up less space ; Usually built in where Conditions , High matching ; The base number is required to be large , High discrimination , Don't over index , Try to expand , Use union index , Frequent updates are not suitable for 、 Use short index .
1.12 Index failure scenario ?
1. With “%” At the beginning like sentence , Invalid index , suffix “%” No effect
2.or The index is not used before and after the statement
3. Column type is string , Be sure to quote the data in quotation marks in the condition , Otherwise, it will fail ( Implicit conversion )
4. If mysql It is estimated that full table scanning is faster than indexing , No index ( Few key values , There is too much duplicate data )
5. The combination index should abide by the leftmost prefix principle —— Do not use the first column index invalid
6. Use... On index fields not,<>,!= ( The processing is full table scanning )
7. Calculate the index field , Field use functions also fail
8.is null
1.13 How to create an index ?
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX index_name (column_list);
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_list);
stay create table Created on
1.14 Will non clustered index return to table query ?
All query fields hit the index , Overlay index , Don't go back to your watch , Get results directly from the index , Don't check the data file
summary : Overwrite the index without going back to the table
1.15 Rules for establishing joint index ?
Put the columns with frequent query requirements or high field selectivity in front
Index reuse , You can maintain fewer indexes (a)->(a,b)
If there is an existing union query , Also based on a、b What about their own queries ? The principle of consideration is space , Index small items separately
1.16 Left most matching principle ?
Match from left to right , Until you encounter a range query . Set up a joint index (a,b,c) The index is based on a Sort ,a Phase at the same time b Orderly ,a Different disorder , And so on . In short, stop when you encounter a range query .
(a,b) Joint index [(2,4),(),()]
\|/ \|/
[(1,1),(1,2),(2,1)] [(2,4),(3,1),(3,2)]
law :a In order (1,1,2,2,2,3,3)b lack order ,a Phase at the same time b And in order , Different a Between b There is no order , therefore a=1,b>2 Let's go ;a>1,b>2 Don't walk index .
select * from table_name where a = '1' and b = '2' and c = '3'
// Full value matching query , Use index , It has nothing to do with order , Query optimizer , It will automatically optimize the query order
select * from table_name where a = '1'
select * from table_name where a = '1' and b = '2'
select * from table_name where a = '1' and b = '2' and c = '3'
// When matching the columns on the left , Index is used
select * from table_name where b = '2'
select * from table_name where c = '3'
select * from table_name where b = '1' and c = '3'
// No index is used
select * from table_name where a = '1' and c = '3'
//a Index is used ,b、c Not to
select * from table_name where a > 1 and a < 3 and b > 1;
// Only a Use index , stay 1<a<3 Within the scope of b Is chaotic , No index , find 1<a<3 After recording , Only according to the conditions b > 1 Continue to filter one by one
select * from table_name where a = 1 and b > 3;
// a=1 Under the circumstances b Is ordered , The range lookup takes the federated index go a b Indexes (a Phase at the same time b Orderly )
1.17 One sql The reason for the slow implementation ?
One SQL The execution is slow , We will discuss it in two situations :
1、 Most of the time it's normal , Sometimes it's slow , There are the following reasons
(1)、 The database is refreshing dirty pages , for example redo log Full write needs to be synchronized to disk .
(2)、 When it comes to execution , Encounter lock , Like a watch lock 、 Row lock .
(3)、sql The writing is rotten
2、 This article SQL Statement execution is slow all the time , There are the following reasons
(1)、 If the index is not used or the index fails : For example, this field has no index ; Because of the operation on the field 、 Function operation makes index unavailable .
(2)、 An index may go through a full table scan
How to judge whether to scan the whole table :
Index differentiation ( The more different the values of the index , The more distinguishable ), It's called cardinality , When the amount of data is large, it is impossible to scan all the data to get the base number , Instead, it samples part of the data for prediction , That may be wrong , Cause full table scanning .
1.18 SQL Examples of optimization ?
1、 Try to avoid full scan , Consideration should be given to where And order by Index the columns involved .
2. Should try to avoid in where Field in the clause null Value judgement , Failing to do so will cause the engine to abandon the index for a full table scan , Such as :select id from t where num is null Can be in num Set the default value on 0, Make sure the table num No column null value , And then query like this select id from t where num=0.
3. Should try to avoid in where Used in clauses != or <> The operator , Otherwise, the engine will discard the index and scan the whole table .
4. Should try to avoid in where Used in clauses or To join the conditions , Failing to do so will cause the engine to abandon the index for a full table scan , Such as :
select id from t where num=10 or num=20 You can query like this :select id from t where num=10 union all select id from t where num=20
5.in and not in Be careful with , Otherwise, it will result in a full table scan
6. For continuous values , It works between Don't use in 了
7. The query will also result in a full table scan select id from t where name like ‘%abc%’
8. Don't use... Anywhere select * from t , Replace... With a specific list of fields “*”, Do not return any fields that are not available .
9. Try to avoid large transaction operations , Improve system concurrency .
1.19 COUNT()
1、COUNT There are several uses ?
count() count( Name ) count(1) Three uses . Alibaba java The development manual mentions : Force not to use count( Name ) count(1) Instead of count()
count(*) yes sql92 Defined syntax for counting rows , Follow null And non null irrelevant .
2、COUNT( Field name ) and COUNT() What's the difference between the query results of ?
count( Field name ) If the field is null So he doesn't count null Ignore null value count() take null Values are also counted , contain null The number of rows for the value
count( Field ) When making statistics, the whole field will be judged as non empty , Efficient than count(*) low
3、COUNT(1) and COUNT() What's the difference between ?
COUNT( Constant ) and COUNT() Represents the number of rows in the database table that directly query the matching conditions . and COUNT( Name ) Represents the value of the qualified column in the query
Not for NULL The number of rows .
4、COUNT(1) and COUNT() Which is more efficient ?
about COUNT(1) and COUNT(),MySQL The optimization of is exactly the same , There is no one who is faster !
5、 Why? 《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 It is recommended to use COUNT()
It is recommended to use COUNT()! Because this is SQL92 The syntax for defining the number of standard statistics lines
6、MySQL Of MyISAM Engine pair COUNT() What optimizations have been made ?
MyISAM Made a simple optimization , That is, it can record the total number of tables separately , If you use... From a table COUNT() When querying
You can directly return the recorded value , Of course , The premise is that there can be no where Conditions .
1.20 What is? mysql Business ? What are the four characteristics of a transaction ?
Transactions are the basic unit of recovery and concurrency control . It's a group of atomic sql Inquire about , Or a separate unit of work . All statements in a transaction either succeed or fail .
Four characteristics of transactions :
Atomicity (Atomicity)
Uniformity (Consistency)
Isolation, (Isolation)
persistence (Durability)
Atomicity ( adopt undolog Log to achieve ):
A transaction must be treated as an indivisible minimum unit of work , All operations in the entire transaction either all commit successfully , or
All failed rollback , For a transaction , It is impossible to perform only some of these operations , That's the atomicity of the transaction
Uniformity ( Consistency is the ultimate pursuit of affairs , Consistency is achieved through three other features ):
Databases are always moving from one consistent state to another .( In the previous example , Consistency ensures , namely
Make the system crash during the transfer process , There's no loss in checking accounts 200 dollar , Because the transaction didn't commit in the end , So what you do in a transaction
Your changes will not be saved to the database .)
Isolation, ( adopt mvcc+ Lock to achieve ):
Generally speaking , The modification operation made by a transaction is before the transaction is committed , Invisible to other transactions .( In the previous example
Zizhong , When the third statement is executed 、 Before the fourth sentence begins , At this point, another account aggregation program starts to run , be
He saw that the balance of the checking account had not been subtracted 200 dollar .)
persistence ( adopt redo log Log to achieve ):
Once the transaction is committed , Its changes will be permanently saved to the database .
explain : Transactions can ensure the integrity and consistency of data , Make the user's operation more secure .
边栏推荐
- [web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis
- (practice C language every day) reverse linked list II
- [ 英語 ] 語法重塑 之 動詞分類 —— 英語兔學習筆記(2)
- 【MQTT从入门到提高系列 | 01】从0到1快速搭建MQTT测试环境
- [no app push general test plan
- Apple has open source, but what about it?
- Office-DOC加载宏-上线CS
- Day 246/300 ssh连接提示“REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! ”
- 英语论文翻译成中文字数变化
- Financial German translation, a professional translation company in Beijing
猜你喜欢

It is necessary to understand these characteristics in translating subtitles of film and television dramas
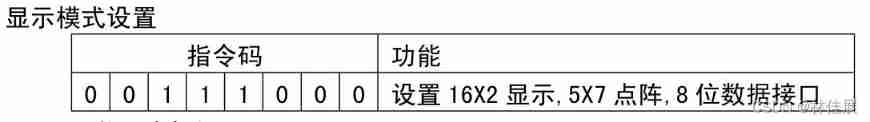
Lecture 8: 1602 LCD (Guo Tianxiang)
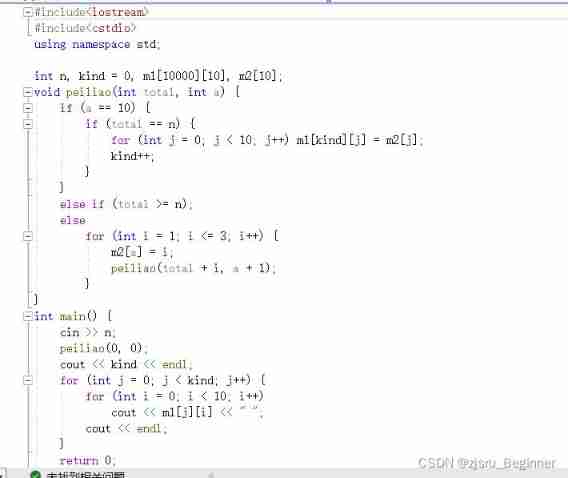
Luogu p2089 roast chicken
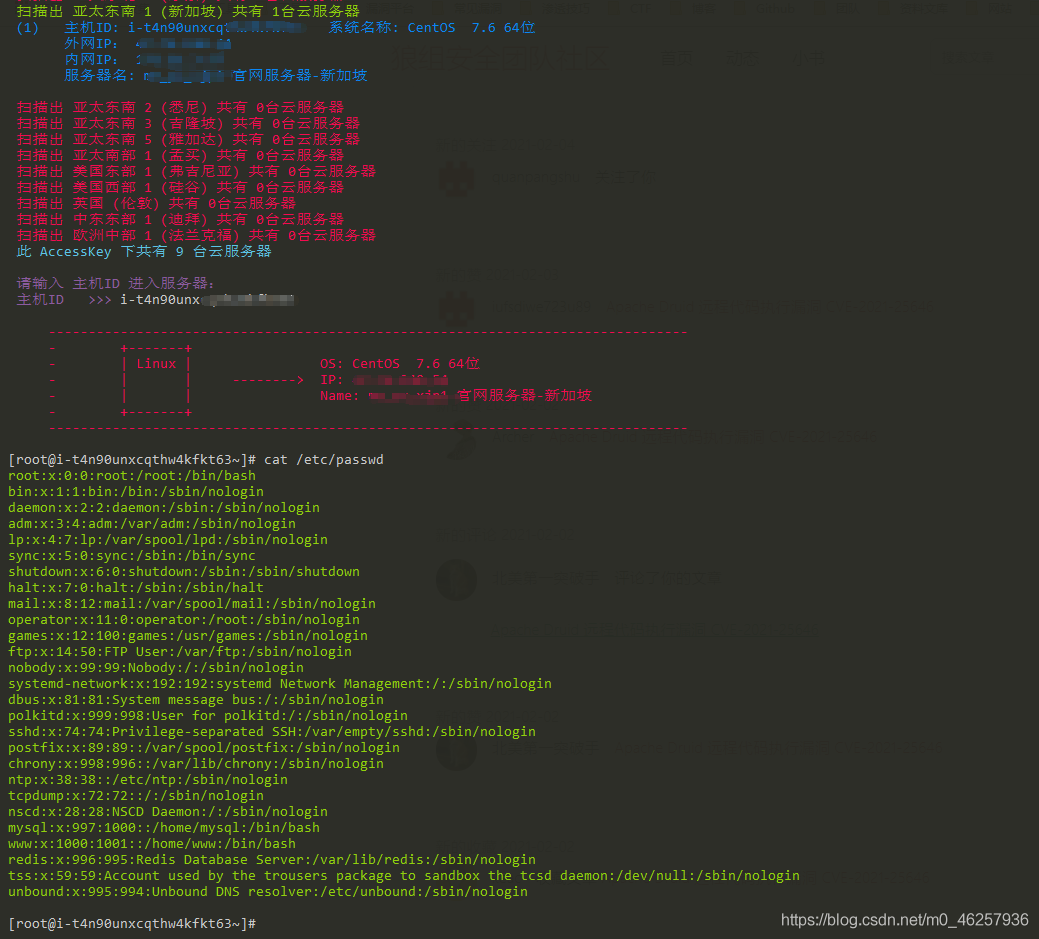
云服务器 AccessKey 密钥泄露利用
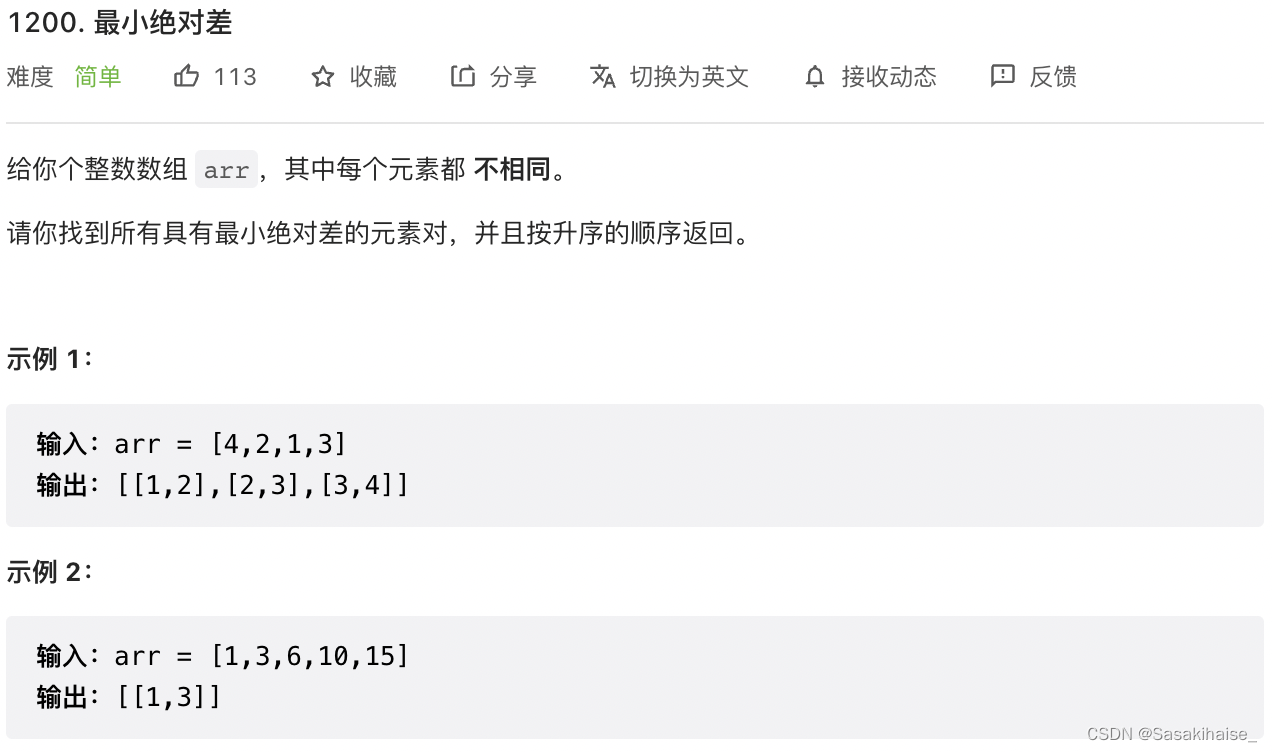
LeetCode 1200. Minimum absolute difference

Changes in the number of words in English papers translated into Chinese
keil MDK中删除添加到watch1中的变量
[no app push general test plan
Selenium source code read through · 9 | desiredcapabilities class analysis
Grouping convolution and DW convolution, residuals and inverted residuals, bottleneck and linearbottleneck
随机推荐
My seven years with NLP
MFC on the conversion and display of long string unsigned char and CString
Drug disease association prediction based on multi-scale heterogeneous network topology information and multiple attributes
keil MDK中删除添加到watch1中的变量
The internationalization of domestic games is inseparable from professional translation companies
Day 248/300 关于毕业生如何找工作的思考
Defense (greed), FBI tree (binary tree)
Py06 dictionary mapping dictionary nested key does not exist test key sorting
記一個基於JEECG-BOOT的比較複雜的增删改功能的實現
Traffic encryption of red blue confrontation (OpenSSL encrypted transmission, MSF traffic encryption, CS modifying profile for traffic encryption)
Advanced MySQL: Basics (1-4 Lectures)
[web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis
Modify the list page on the basis of jeecg boot code generation (combined with customized components)
(practice C language every day) reverse linked list II
Biomedical localization translation services
[mqtt from getting started to improving series | 01] quickly build an mqtt test environment from 0 to 1
The whole process realizes the single sign on function and the solution of "canceltoken" of undefined when the request is canceled
【MQTT从入门到提高系列 | 01】从0到1快速搭建MQTT测试环境
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1143 Longest common subsequence
Financial German translation, a professional translation company in Beijing