当前位置:网站首页>Operating system principle --- summary of interview knowledge points
Operating system principle --- summary of interview knowledge points
2022-07-08 00:12:00 【chengwei1128】
List of articles
- 1. The difference between a process and a thread
- 2. The state of the process and its transitions
- 3. Synchronization and mutual exclusion of processes
- 4. What are the modes of communication between processes ?
- 5. Homework ( process ) What are the scheduling algorithms of ?
- 6. What is a deadlock ? The cause of deadlock ? The necessary conditions for deadlock ? How to prevent deadlock ? How to avoid deadlock ? How to unlock ?
1. The difference between a process and a thread
- Fundamental difference : Process is the basic of operating system resource allocation ( Minimum ) Company , And thread is the basic of task scheduling and execution ( Minimum ) Company .
- In terms of expenses : Each process has its own code and data space , Switching between programs can be costly ; For threads , The same class of threads share code and data space , Each thread has its own running stack and program counter , The cost of switching between threads is small .
- environment : It can run multiple processes simultaneously in the operating system ( Program ); In the same process, multiple threads execute at the same time ( adopt CPU Dispatch , There is only one thread executing in each time slice ).
- Memory allocation : When the system is running, it will allocate different memory space for each process ; And for threads , except CPU Outside , The system does not allocate memory for threads ( The resource used by a thread comes from the resource of the process it belongs to ), Only resources can be shared between thread groups .
- Inclusion relation : A process consists of at least one thread .
2. The state of the process and its transitions
The status of the process can be basically divided into the following 3 class :
| state | explain |
|---|---|
| The ready state | The process is ready to run , however CPU Not assigned yet ; |
| Running state | Process occupation CPU, And in CPU Up operation ; |
| Blocking state | The process is temporarily unable to run because it is waiting for something to happen ; |
Process in a lifetime , Are in the above 3 One of the States .
3 A state transition diagram :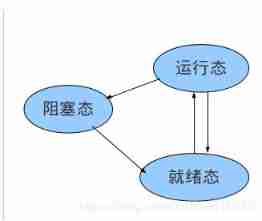
According to mathematical reasoning , If the above three states can be converted to each other , Should have 6 In this case , But actually only 4 Kind of , rest 2 Kind of impossible .
First introduced Can happen 4 There are two conversion situations , See the table below .
| State transition | explain |
|---|---|
| The ready state ----> Running state | The running process ran out of time slices , The scheduling goes to the ready queue and selects the appropriate process to assign to CPU. |
| Running state ----> The ready state | This is caused by scheduling , When the process occupies CPU Too long , Will be turned into ready . |
| Running state ----> Blocking state | It happened. I/O Ask or wait for something to happen . |
| Blocking state ----> The ready state | The event that the process is waiting for occurs , Go to the ready queue . |
Impossible conversion :
| State transition | explain |
|---|---|
| Blocking state ----> Running state | Even if the blocking process is assigned CPU, Can't execute , The operating system will not load the blocking queue for selection when scheduling , The selection object of its scheduling is the ready queue . |
| The ready state ----> Blocking state | Because the ready state is not run at all , How to enter the blocking state . |
The above describes the basic state of the process , But in the specific implementation of the operating system , The details are as follows 5 States . See the table below .
| state | explain |
|---|---|
| 1. Operational state | Combination of running state and ready state , Indicates that the process is running or ready to run ,Linux Use in TASK_RUNNING Macro represents this state . |
| 2. Light sleep | Also known as interruptible sleep state . The process is sleeping ( Blocked ), Wake up when waiting for resources , You can also wake up through other process signals or clock interrupts . Wake up and enter the ready queue .Linux Use TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE Macro represents this state . |
| 3. Deep sleep | Also known as non interruptible sleep state . It's basically similar to light sleep , But one thing is not to be awakened by other process signals or clock interrupts . Processes in this state can only use wake_up() Function wake up .Linux Use TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE Macro represents this state . |
| 4. Pause state | The process is suspended for some processing . If the process being debugged is in this state .Linux Use TASK_STOPPED Macro represents this state . |
| 5. A dead state | The process has ended but not released PCB.Linux Use TASK_ZOMBIE Macro represents this state . |
Linux Diagram of interprocess state transition and kernel call :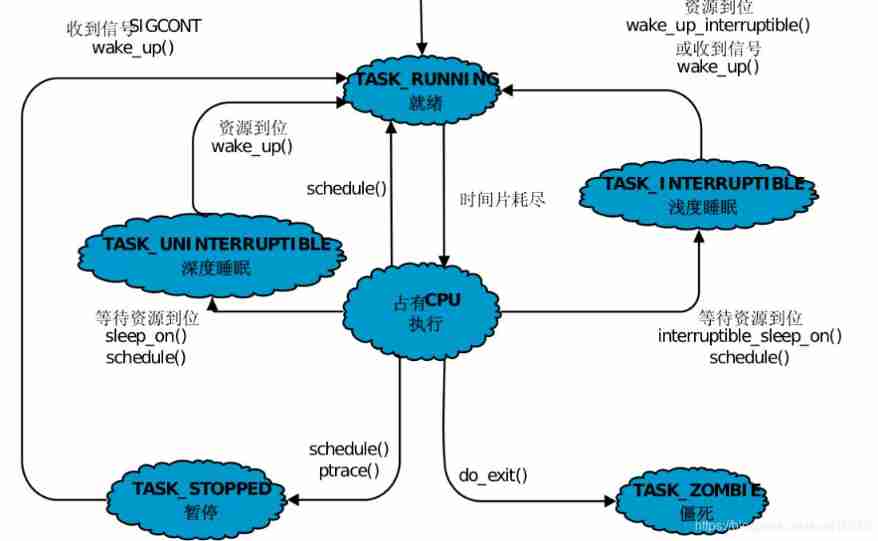
3. Synchronization and mutual exclusion of processes
Mutually exclusive : It means that only one visitor is allowed to access a resource at the same time , It is unique and exclusive . But mutual exclusion can't limit the order in which visitors access resources , That is, access is out of order .
Sync : On the basis of mutual exclusion ( In most cases ), Through other mechanisms, visitors can access resources orderly . in the majority of cases , Synchronization has achieved mutual exclusion , In particular, all write resources must be mutually exclusive . In a few cases, multiple visitors can be allowed to access resources at the same time .
To put it simply : Synchronization embodies a kind of cooperation , Wheezing embodies a kind of exclusivity .
4. What are the modes of communication between processes ?
| classification | explain |
|---|---|
| The Conduit ( Anonymous pipeline 、 name pipes ) | The essence of pipeline is a Kernel buffer , The function of the pipe is just like its name , The two processes that need to communicate are at both ends of the pipe , Processes use pipes to pass information . A pipe is a process at both ends of a pipe , It's a document , But this file is special , It doesn't belong to the file system and only exists in memory . |
| The signal | Signal is a simulation of interrupt mechanism at software level , Is an asynchronous communication mode , The process does not have to wait for the signal to arrive through any operation . Signals can interact directly between user space processes and the kernel , The kernel can use signals to inform user space processes of what system events have occurred . |
| Semaphore | A semaphore is essentially a counter that identifies the number of available resources , Its value is always a nonnegative integer . And only 0 and 1 The semaphores with two values are called binary semaphores ( Or binary semaphore ), Available is used to identify whether a resource is available . Mainly as a means of synchronization between processes and different threads in the same process . |
| Message queue | The message queue is a linked list of messages , Have a specific lattice , Stored in memory and identified by the message queue identifier , And allows one or more processes to write and read messages to it . Message queuing overcomes the problem of less signaling messages , The pipeline can only support unformatted byte stream and the buffer size is limited . |
| Shared memory | So that multiple processes can directly read and write the same block of memory space , It is designed for the low efficiency of other communication mechanisms . |
| Socket | Socket is a more basic mechanism of interprocess communication , Unlike other ways , Sockets can be used for interprocess communication between different machines . |
5. Homework ( process ) What are the scheduling algorithms of ?
- ** First come, first served (FCFS,First-Come-Frist-Served):** The principle of this algorithm is to arrive at the backup job queue according to the job ( Or the process enters the ready queue ) To select jobs in order of priority ( Or the process ).
- ** Short job preferred (SJF,Shortest Process Next):** This scheduling algorithm is mainly used for job scheduling , It selects the required running time from the job backup queue ( Estimated value ) The shortest job enters main memory and runs .
- ** Time slice rotation scheduling algorithm (RR,Round-Robin):** When the execution time slice of a process runs out , The scheduler stops the execution of the process , And send it to the end of the ready queue , Wait for the next time slice to be allocated before executing . The processor is then assigned to the new queue leader process in the ready queue , Also let it execute a time slice . This ensures that all processes in the ready queue , At a given time , Can obtain the execution time of the time slice processor .
- ** High response ratio first (HRRN,Highest Response Ratio Next):** According to the high response ratio (( Waiting time + Running time required )/ Running time required ) The principle of priority , Every time you select a job to run , The response of each job in the backup queue is calculated first RP Then select the job with the largest value and put it into operation .
- Priority (Priority) Scheduling algorithm : Schedule according to the priority of the process , The scheduling strategy that gives priority to high priority processes is called priority scheduling algorithm . Be careful : The more priorities , The lower the priority .
- ** Multilevel queue scheduling algorithm :** Multi queue scheduling is based on the nature and type of jobs , Divide the ready queue into several sub queues , All the homework ( Or the process ) According to its nature, it is put into the corresponding queue , Different ready queues adopt different scheduling algorithms .
6. What is a deadlock ? The cause of deadlock ? The necessary conditions for deadlock ? How to prevent deadlock ? How to avoid deadlock ? How to unlock ?
What is a deadlock : stay 2 In one or more concurrent processes , If each process holds a resource and waits for other processes to release the resources they currently hold , You can't move forward until you change that , Call this group of processes deadlock . informally , Namely 2 One or more processes are blocked indefinitely 、 A state of waiting for each other .
The cause of deadlock : Insufficient system resources ; The order of progress is illegal .
The necessary conditions for deadlock :( following 4 One of the conditions does not hold , There will be no deadlock )
- Mutually exclusive : A resource can only be accessed by one process at a time , That is, once the resource is allocated to a process , Other processes can no longer access , Until the end of the process visit .
- Inalienable : The resources obtained by a process are not used up , Cannot be forcibly deprived by other processes , It can only be released by the process resource that obtains the resource .
- To possess and wait for : A process itself already occupies some resources ( One or more ), But there are still resources that have not been met , Will wait for other processes to release the resource .
- Loop waiting for : There is a process chain , Make each process occupy at least one resource required by the next process .
How to prevent deadlock ( Static strategy ): Destroy one of the four necessary conditions for deadlock .
How to avoid deadlock ( Dynamic strategy ): It does not restrict the process's commands about applying for resources , Instead, each resource request command issued by the process is dynamically checked , And decide whether to allocate resources according to the inspection results . That is to say , In the process of resource allocation, if the possibility of deadlock is predicted , Avoid . The key of this method is to determine the security of resource allocation .
Common methods used :
- Security sequence . Security sequence {P1,P2,…,Pn} It's made up of : If for every process Pi, The additional resources it needs can be added by the resources currently available in the system plus all processes Pj The sum of current resources , be {P1,P2,…,Pn} For a safe sequence , At this time, the system is in a safe state , Will not enter the deadlock state .
- Banker Algorithm . Banker algorithm allows mutually exclusive conditions in the necessary conditions of deadlock 、 Inalienable 、 Occupy and wait for the existence of conditions . This method allows the process to dynamically request resources , Before the system allocates resources , First calculate the security of resource allocation . If this assignment will not cause the system to change from safe state to unsafe state , Resources can be allocated to the process ; Otherwise, resources will not be allocated , The process must be blocked waiting . So as to avoid deadlock .
How to unlock :
- A process that forcibly removes one or more deadlocks from the system to break the cyclic waiting chain , And recover all the resources allocated to the terminating process, and use the remaining process .
- Use an effective suspend and release mechanism to suspend some deadlocked processes , Its essence is to preempt resources from the suspended process to release the deadlock .
边栏推荐
- 【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.03 绘制方形螺旋
- 35岁真就成了职业危机?不,我的技术在积累,我还越吃越香了
- C language 005: common examples
- Reading notes 004: Wang Yangming's quotations
- 如何衡量产品是否“刚需、高频、痛点”
- Solutions to problems in sqlserver deleting data in tables
- STM32F1与STM32CubeIDE编程实例-旋转编码器驱动
- The difference between get and post
- 商品的设计等整个生命周期,都可以将其纳入到产业互联网的范畴内
- Gorm Association summary
猜你喜欢

Introduction to programming hardware
单机高并发模型设计
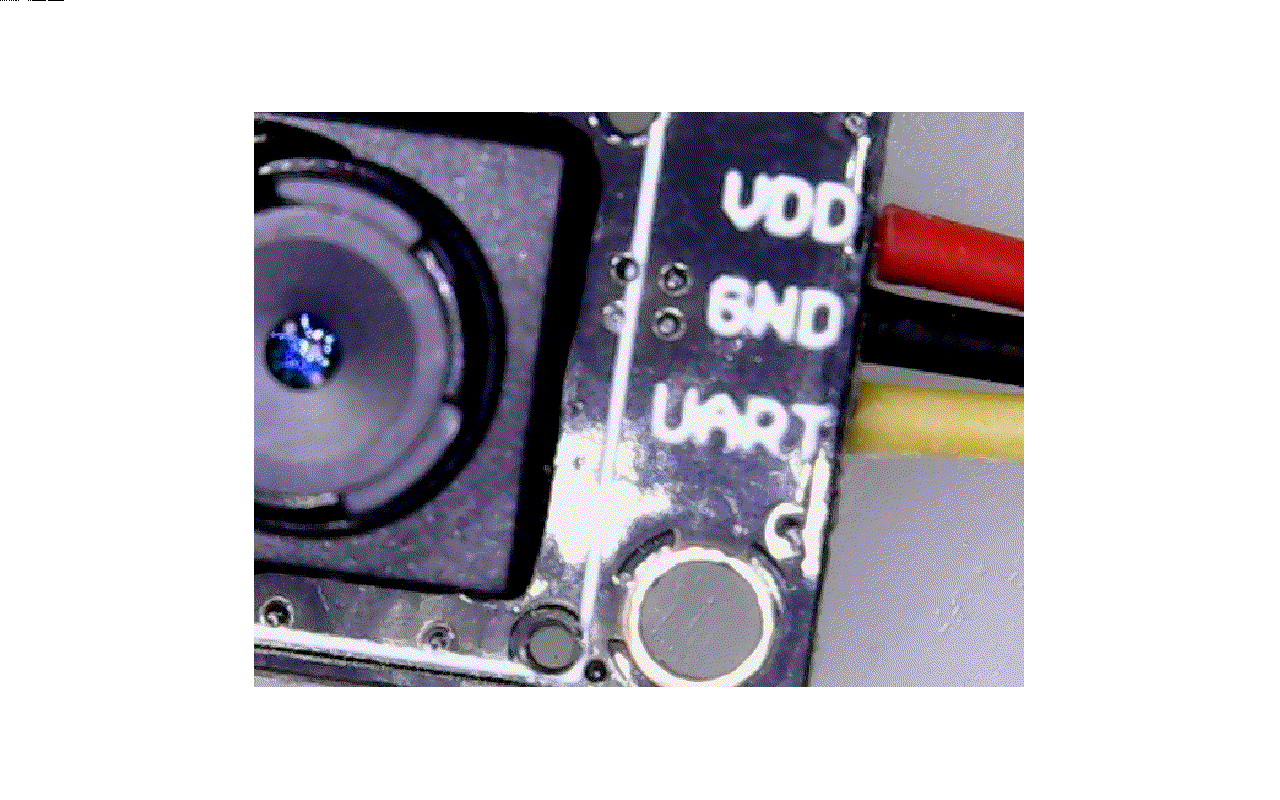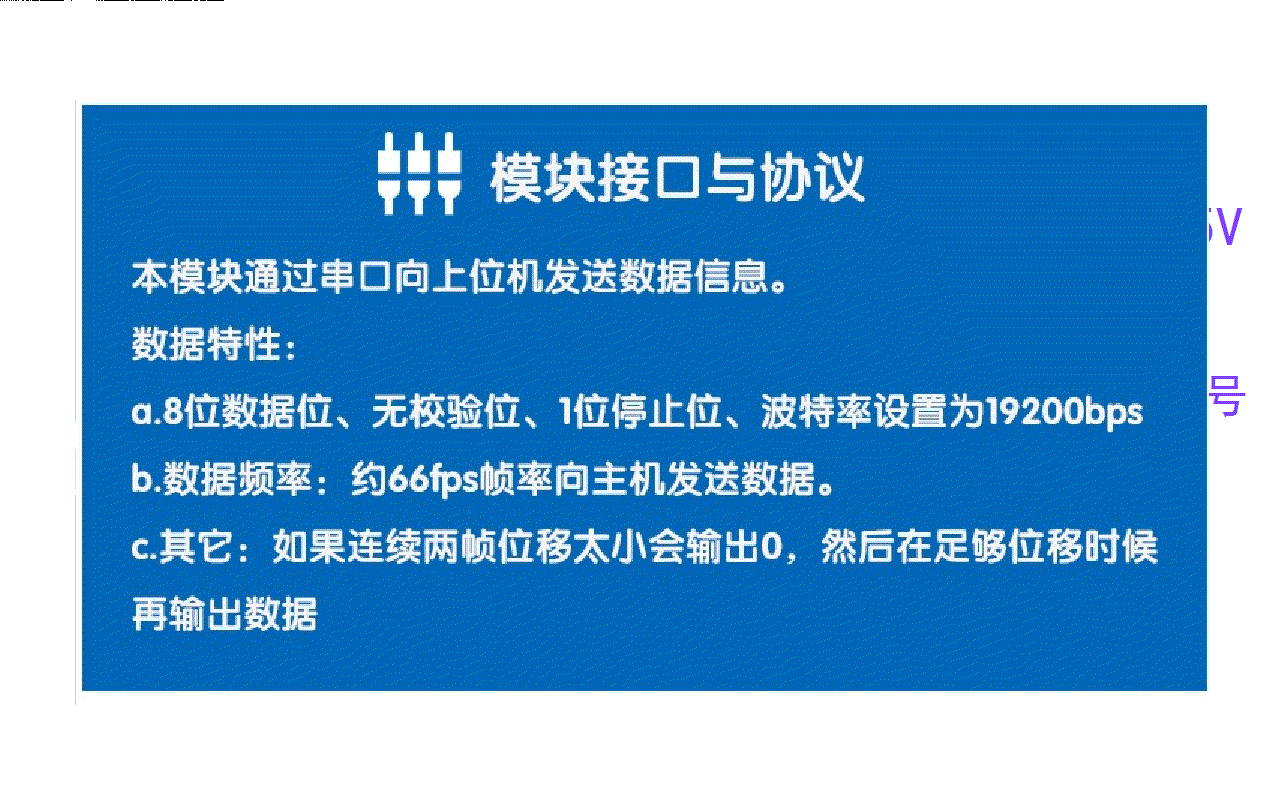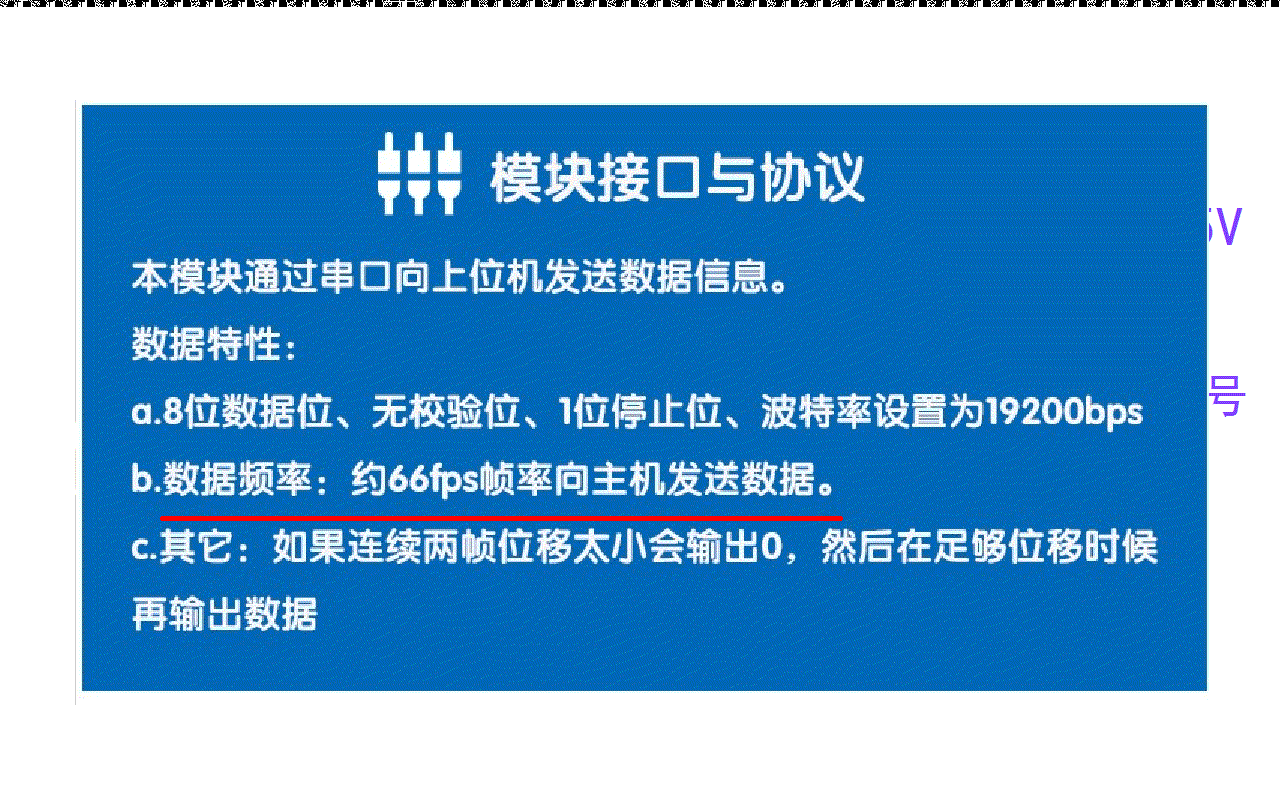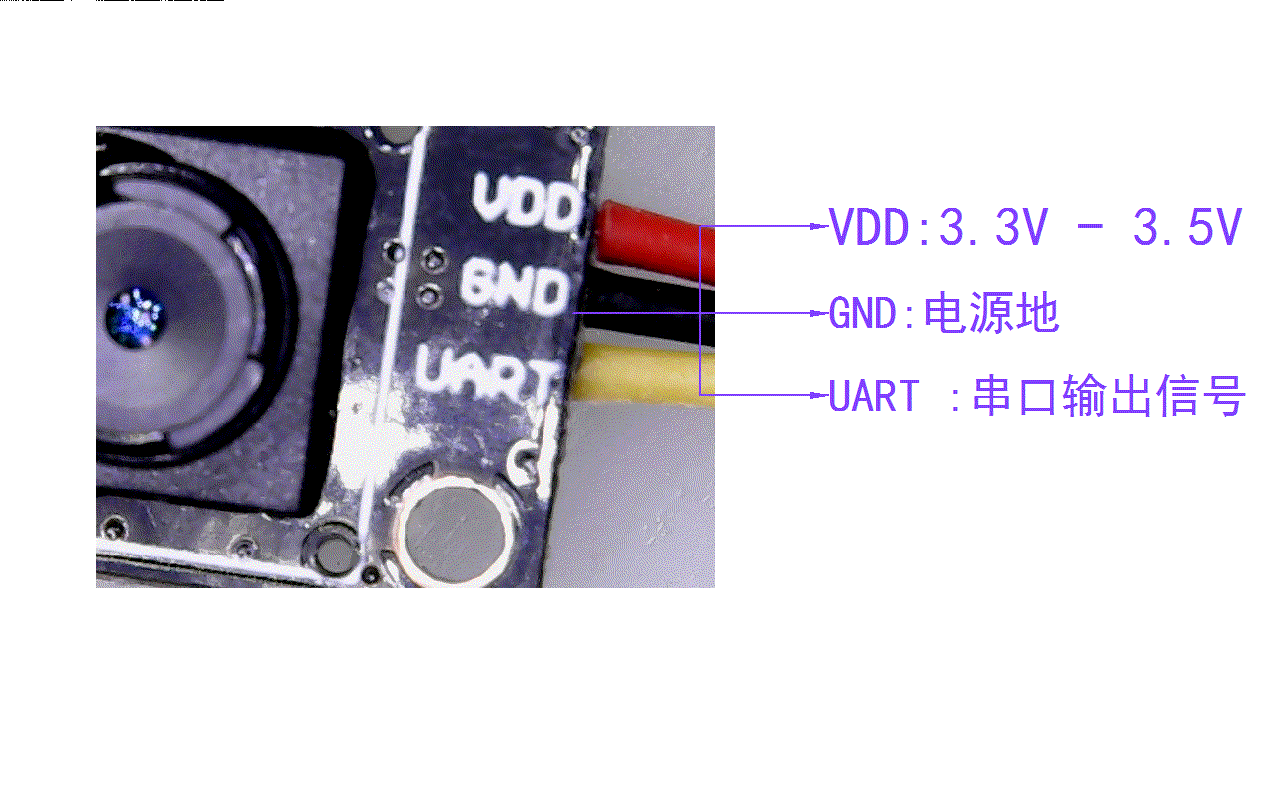
光流传感器初步测试:GL9306

35岁真就成了职业危机?不,我的技术在积累,我还越吃越香了

Uic564-2 Appendix 4 - flame retardant fire test: flame diffusion
Seven years' experience of a test engineer -- to you who walk alone all the way (don't give up)

How does starfish OS enable the value of SFO in the fourth phase of SFO destruction?
【史上最详细】信贷中逾期天数统计说明
![[the most detailed in history] statistical description of overdue days in credit](/img/f7/5c3cbfec5b010171376ac122c704b2.png)
[the most detailed in history] statistical description of overdue days in credit

STM32F1與STM32CubeIDE編程實例-旋轉編碼器驅動
随机推荐
At the age of 35, I made a decision to face unemployment
Tools for debugging makefiles - tool for debugging makefiles
Coindesk comments on the decentralization process of the wave field: let people see the future of the Internet
机器人(自动化)等专业课程创新的结果
52歲的周鴻禕,還年輕嗎?
35岁真就成了职业危机?不,我的技术在积累,我还越吃越香了
串联二极管,提高耐压
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 绘制雪花图案
Basic learning of SQL Server -- creating databases and tables with the mouse
When creating body middleware, express Is there any difference between setting extended to true and false in urlencoded?
Install sqlserver2019
Development of a horse tourism website (realization of login, registration and exit function)
Visual Studio Deployment Project - Create shortcut to deployed executable
Flask learning record 000: error summary
一鍵免費翻譯300多頁的pdf文檔
3年经验,面试测试岗20K都拿不到了吗?这么坑?
Single machine high concurrency model design
Archery installation test
[the most detailed in history] statistical description of overdue days in credit
Linkedblockingqueue source code analysis - add and delete