当前位置:网站首页>Logstash expressway entrance
Logstash expressway entrance
2022-07-06 19:48:00 【Full stack programmer webmaster】
Hello everyone , I meet you again , I'm the king of the whole stack , I've prepared for you today Idea Registration code .
Original address :http://logstash.net/docs/1.4.2/tutorials/getting-started-with-logstash
English is limited , If there are mistakes, please correct
Brief introduction
Logstash It's a reception , Handle , Tools for forwarding logs . Support system log ,webserver journal . Error log . Application log , In short, it includes all the log types that can be thrown out .
How about that? It sounds very powerful ? In a typical usage scenario (ELK): use Elasticsearch As the storage of background data ,kibana Used for front-end report display .
Logstash Act as a porter in the process , It stores data . Report query and log parsing create a powerful pipeline chain .
Logstash Provides a variety of input,filters,codecs and output Components , Let users easily realize powerful functions . OK, let's start
Depending on the conditions :JAVA
Logstash Execution only depends on java execution environment (jre). You can execute on the command line java -version command
Display similar results such as the following :
java -version
java version "1.7.0_45"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b18)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.45-b08, mixed mode)To ensure successful implementation Logstash It is recommended that you use the more recent jre Version number .
Can get the open source version number jre stay :http://openjdk.java.net
Or you can download it on the official website Oracle jdk Version number :http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/index.html
once jre It has been successfully installed in your system , We can continue
Start and execute Logstash Two command demonstration examples
The first step is to download Logstash
curl -O https://download.elasticsearch.org/logstash/logstash/logstash-1.4.2.tar.gzNow you should have a person named logstash-1.4.2.tar.gz The document of . Let's decompress it
tar zxvf logstash-1.4.2.tar.gzcd logstash-1.4.2Now let's implement :
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { stdout {} }'We can now enter some characters on the command line . And then we'll see logstash The output of :
hello world2013-11-21T01:22:14.405+0000 0.0.0.0 hello worldOk, That's interesting … We are implementing the above example logstash in , Defined a name ”stdin” Of input the other one ”stdout” Of output, No matter what characters we type .Logstash Will return the characters we entered in a certain format .
Here we use the command line -e Parameters , This parameter agrees Logstash Accept settings directly from the command line . This is especially fast to help us test whether the configuration is correct repeatedly without writing the configuration file .
Let's try a more interesting example . First, we use... On the command line CTRL-C Executed before command exit Logstash. Now we implement it again Logstash Use the following command :
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { stdout { codec => rubydebug } }'Let's type in some more characters , This time we input ”goodnight moon”:
goodnight moon{ "message" => "goodnight moon", "@timestamp" => "2013-11-20T23:48:05.335Z", "@version" => "1", "host" => "my-laptop"}The above demonstration example is called ”stdout” Of output( Joined the ”codec” Parameters ), We can change Logstash The output performance of . Similarly, we can add or change in your configuration file inputs、outputs、filters, It makes it possible to format log data arbitrarily , In order to customize a more reasonable storage format to facilitate the query .
Use Elasticsearch Store logs
Now , You might say :” It looks quite tall , Just manually input characters . And echo the characters from the console . The actual situation is not useful ”.
Well said. , So next we're going to build Elasticsearch To store input to Logstash Log data for . Suppose you haven't installed Elasticsearch. You can download RPM/DEB package Or download it manually tar package . By the following command :
curl -O https://download.elasticsearch.org/elasticsearch/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-1.1.1.tar.gz
tar zxvf elasticsearch-1.1.1.tar.gz
cd elasticsearch-1.1.1/
./bin/elasticsearchBe careful
This article uses Logstash 1.4.2 and Elasticsearch 1.1.1.
Different Logstash The version number has corresponding suggestions Elasticsearch Version number . Please confirm that you are using Logstash Version number !
Many other things about installation and setup Elasticsearch Information can be referred to Elasticsearch Official website . Because we mainly introduce Logstash To get started with ,Elasticsearch The default installation and configuration already meet our requirements .
It's just a matter of fact . Now Elasticsearch Has been executed and monitored 9200port 了 ( Everyone is done , Am I right? ?), With simple settings Logstash Can use Elasticsearch As its back end .
The default configuration is for Logstash and Elasticsearch Enough already , We ignore some extra options to set up elasticsearch As output:
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { elasticsearch { host => localhost } }'Input some characters arbitrarily .Logstash The log will be processed as before ( But this time we won't see any output , Because we didn't set up stdout As output Options )
you know, for logsWe can use curl Command to send a request to see ES Whether the data is received :
curl 'http://localhost:9200/_search?pretty'The returned content is as follows :
{ "took" : 2, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 5, "successful" : 5, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : 1, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "logstash-2013.11.21", "_type" : "logs", "_id" : "2ijaoKqARqGvbMgP3BspJA", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"message":"you know, for logs","@timestamp":"2013-11-21T18:45:09.862Z","@version":"1","host":"my-laptop"} } ] }}Congratulations , So far you have successfully used Elasticsearch and Logstash To collect log data .
Elasticsearch plug-in unit ( Digression )
Here's another example for querying your Logstash data (Elasticsearch Data in the ) A very useful tool is called Elasticsearch-kopf plug-in unit . For many other information, please see Elasticsearch plug-in unit .
install elasticsearch-kopf, Just before you install Elasticsearch Run the following command in the folder of :
bin/plugin -install lmenezes/elasticsearch-kopfNext visit http://localhost:9200/_plugin/kopf To save in browsing Elasticsearch Data in , Set and map !
Multiple outputs
As a simple example, set up multiple output , Let's set it at the same time stdout and elasticsearch As output Let's do it again Logstash. For example, the following :
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { elasticsearch { host => localhost } stdout { } }'When we type in some phrases . The input is echoed back to our terminal , At the same time, it will be saved to Elasticsearch!
( Able to use curl and kopf Plug in to verify ).
The default configuration – Index according to the daily date
You will find Logstash Can be smart enough in Elasticsearch Index on … The default format for each day is logstash-YYYY.MM.DD To index .
In the middle of the night (GMT),Logstash Take the initiative to update the index according to the timestamp . We can determine how much data to keep according to the data traced for how long . Of course, you can also migrate older data to other places ( Index again ) To facilitate the inquiry , In addition, suppose that we can simply delete data for a period of time Elasticsearch Curator.
Next
Next, let's start to understand many other advanced configuration items . In the following sections , We focus on logstash Some of the core features , And how to communicate with logstash Engine interaction .
The life cycle of events
Inputs,Outputs,Codecs,Filters Constitute the Logstash The core configuration item of .
Logstash By building a pipeline for event handling . Extract data from your log and save it to Elasticsearch in . Provide the basis for efficient query data .
In order to let you know at high speed Logstash A variety of options available , Let's first discuss some of the most commonly used configurations .
A lot of other information , Please refer to Logstash Event pipeline .
Inputs
input And input refers to log transmission data to Logstash in . Common configurations are as follows :
- file: Read a file from the file system , Very much like UNIX command “tail -0a”
- syslog: monitor 514port, according to RFC3164 Standard parsing log data
- redis: from redisserver Reading data . Support channel( Publish subscription ) and list Pattern . redis Generally in Logstash As ”broker” role , preservation events Queue total Logstash consumption .
- lumberjack: Use lumberjack Protocol to receive data , Now it has been changed to logstash-forwarder.
Filters
Fillters stay Logstash It acts as an intermediate processing component in the processing chain . They are often combined to achieve certain behaviors , Handle the flow of events that match specific rules . common filters For example, the following :
- grok: Parse irregular text and transform it into a structured format . Grok It is the best way to transform unstructured data into structured and searchable data . Yes 120 Multiple matching rules , There will be a way to meet your needs .
- mutate:mutate filter Agree to change the input document , You can name , Delete , Moving or changing fields in the process of handling events .
- drop: Discard some of it events No processing , such as :debug events.
- clone: Copy event. Fields can also be added or removed in this process .
- geoip: Add geographic information ( For the front desk kibana Graphical display uses )
Outputs
outputs yes logstash Deal with the end of the pipe . One event It can go through multiple outputs during processing , But once all outputs All operation ends , This event That's the end of the life cycle . Some are often used outputs contain :
- elasticsearch: Suppose you plan to save data efficiently , And it is convenient and simple to query …Elasticsearch It's a good way to . Yes , There is suspicion of advertising here , ha-ha .
- file: take event Save the data in a file .
- graphite: take event Data is sent to graphical components , A very popular open source storage graphical display component .http://graphite.wikidot.com/.
- statsd:statsd It's a statistical service , For example, technology and time statistics . adopt udp Communications , Aggregate one or more backend services , Suppose you have started using statsd, This option should be very practical for you .
Codecs
codecs It's a data stream based filter , It can be used as input.output Part of the configuration of .
Codecs It can help you easily cut the sent data that has been serialized . The popular codecs contain json,msgpack,plain(text).
- json: Use json Format encodes data / decode
- multiline: Aggregate data from multiple events into a single row . example :java Exception information and stack information
Get complete configuration information . Please refer to Logstash file in “plugin configuration” part .
Many other interesting Logstash Content
Use profile
Use -e Parameter specifying configuration on the command line is an unusual way , Just assume that you need to configure many other settings, which requires a very long content . In this case . First, let's create a simple configuration file , And specify logstash Use this profile . If we create a file named ”logstash-simple.conf” And saved in and Logstash In the same folder .
The content is as follows :
input { stdin { } }
output {
elasticsearch { host => localhost }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}Next , Run the command :
bin/logstash -f logstash-simple.confWe see logstash Execute the sample according to the configuration file you just created . This is more convenient . Be careful , We use -f Parameter to get from the file instead of using -e Parameters get the configuration from the command line . The above demonstration is very easy Example . Of course, let's continue to write some complex examples .
filter
filters It is a row processing mechanism to sort the provided formatted data into the data you need , Let's take a look at the following example , It's called grok filter Filter .
input { stdin { } }
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp" , "dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z" ]
}
}
output {
elasticsearch { host => localhost }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}function Logstash According to, for example, the following parameters :
bin/logstash -f logstash-filter.confNow paste the following line of information to your terminal ( Of course Logstash Will process the standard input ):
127.0.0.1 - - [11/Dec/2013:00:01:45 -0800] "GET /xampp/status.php HTTP/1.1" 200 3891 "http://cadenza/xampp/navi.php" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.9; rv:25.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/25.0"You will see feedback like the following :
{ "message" => "127.0.0.1 - - [11/Dec/2013:00:01:45 -0800] \"GET /xampp/status.php HTTP/1.1\" 200 3891 \"http://cadenza/xampp/navi.php\" \"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.9; rv:25.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/25.0\"", "@timestamp" => "2013-12-11T08:01:45.000Z", "@version" => "1", "host" => "cadenza", "clientip" => "127.0.0.1", "ident" => "-", "auth" => "-", "timestamp" => "11/Dec/2013:00:01:45 -0800", "verb" => "GET", "request" => "/xampp/status.php", "httpversion" => "1.1", "response" => "200", "bytes" => "3891", "referrer" => "\"http://cadenza/xampp/navi.php\"", "agent" => "\"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.9; rv:25.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/25.0\""}As you can see ,Logstash( Used grok filter ) One row of log data can be (Apache Of ”combined log” Format ) Cutting is set to different data fields . This is very useful for parsing and querying our own log data in the future . example :HTTP The return status code of .IP Address related and so on . It's very interesting easy. Very few matching rules are not grok Include , So suppose you are trying to parse some common log formats . Maybe someone has done this kind of work . Suppose you view specific matching rules . Refer to logstash grok patterns.
The other filter is date filter. This filter is responsible for parsing the timestamp in the log and assigning the value to timestame Field ( No matter when this data is collected logstash Of ).
You may notice in this example @timestamp The field is set to December 11, 2013, explain logstash Processing after a period of time after the log is generated . This field is added back to the data in the processing log , for instance … This value right here is logstash Handle event The timestamp .
Useful examples
Apache journal ( Get... From file )
Now , Let's use some useful configurations … apache2 Access log ! We will read the log file locally , And we can meet our needs by setting conditions event.
First . We create a file named logstash-apache.conf Configuration file for . The content is as follows ( You can change your file name and path according to the actual situation ):
input {
file {
path => "/tmp/access_log"
start_position => beginning
}
}
filter {
if [path] =~ "access" {
mutate { replace => { "type" => "apache_access" } }
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp" , "dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z" ]
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
host => localhost
}
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}Next . We create a file according to the above configuration ( In the example is ”/tmp/access.log”), The following log information can be used as file content ( You can also use your own webserver Generated log ):
71.141.244.242 - kurt [18/May/2011:01:48:10 -0700] "GET /admin HTTP/1.1" 301 566 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.9.2.3) Gecko/20100401 Firefox/3.6.3"
134.39.72.245 - - [18/May/2011:12:40:18 -0700] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 200 1189 "-" "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.0.4506.2152; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; InfoPath.2; .NET4.0C; .NET4.0E)"
98.83.179.51 - - [18/May/2011:19:35:08 -0700] "GET /css/main.css HTTP/1.1" 200 1837 "http://www.safesand.com/information.htm" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.0; WOW64; rv:2.0.1) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/4.0.1"Now use -f Parameter to run the above example :
bin/logstash -f logstash-apache.confYou can see apache The log data of has been imported into ES It's in . here logstash Will read according to your configuration , Process the specified file . No matter what is added to the file, the content will also be captured and finally saved to ES in .
Besides , In the data type The field value of is replaced with ”apache_access”( This function has been specified in the configuration ).
This configuration just makes Logstash Monitored apache access_log, However, in practice, it is often not enough and may need to be monitored error_log. Just changing one line in the above configuration can achieve . For example, the following :
input {
file {
path => "/tmp/*_log"
...Now you can see logstash Processed error Journal and access journal .
However , Suppose you check your data ( Maybe with elasticsearch-kopf), You will find access_log Logs are divided into different fields , But error_log There is no such thing . This is because we used “grok”filter And only configure matching combinedapachelog Log format , In this way, the logs that meet the conditions will be actively cut into different fields . We can parse the log according to its own format by controlling the log , Isn't it very good ? Right .
Besides , You may also find Logstash Will not repeatedly deal with what has been dealt with in the document events. because Logstash The location of file processing has been recorded . In this way, only the newly added lines in the file are processed . beautiful !
Conditional inference
Let's use the previous example to introduce the concept of conditional inference .
This concept should be generally accepted by most Logstash Users are familiar with .
You can use it like other ordinary programming languages if,else if and else sentence . Let's put each event The types of log files that depend on are marked (access_log,error_log Others are log Log file at the end ).
input {
file {
path => "/tmp/*_log"
}
}
filter {
if [path] =~ "access" {
mutate { replace => { type => "apache_access" } }
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp" , "dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z" ]
}
} else if [path] =~ "error" {
mutate { replace => { type => "apache_error" } }
} else {
mutate { replace => { type => "random_logs" } }
}
}
output {
elasticsearch { host => localhost }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}I think you've noticed , We use ”type” Field to mark each event, But we didn't actually analyze ”error” and ”random” Type of log … In reality, there may be many, many types of error logs , How to interpret is left as an exercise for readers . You can rely on existing logs .
Syslog
Ok, Now let's move on to a very useful example :syslog.Syslog about Logstash It is a very long-term configuration , And it has a very good performance ( The format of the agreement conforms to RFC3164).Syslog It's actually UNIX A weblog standard for , from client Send log data to local file or log server. In this example , You don't have to build it at all syslog example ; We can implement one through the command line syslog service , Through this example, you will see what happens .
First , Let's create a simple configuration file to implement logstash+syslog. File name is logstash-syslog.conf
input {
tcp {
port => 5000
type => syslog
}
udp {
port => 5000
type => syslog
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "syslog" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
}
syslog_pri { }
date {
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
}
}
}
output {
elasticsearch { host => localhost }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}function logstash:
bin/logstash -f logstash-syslog.confUsually . You need one client link to Logstashserver Upper 5000port Then send the log data . In this simple demonstration, we simply use telnet link to logstashserver Send log data ( Similar to the previous example in which we send log data in the command line standard input state ).
First, we open up a new shell forms , Then enter the following command :
telnet localhost 5000You can copy and paste the following example information ( Of course, other characters can also be used , It's just that this may be grok filter It can't be interpreted correctly ):
Dec 23 12:11:43 louis postfix/smtpd[31499]: connect from unknown[95.75.93.154]
Dec 23 14:42:56 louis named[16000]: client 199.48.164.7#64817: query (cache) 'amsterdamboothuren.com/MX/IN' denied
Dec 23 14:30:01 louis CRON[619]: (www-data) CMD (php /usr/share/cacti/site/poller.php >/dev/null 2>/var/log/cacti/poller-error.log)
Dec 22 18:28:06 louis rsyslogd: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="4.2.0" x-pid="2253" x-info="http://www.rsyslog.com"] rsyslogd was HUPed, type 'lightweight'.Then you can execute before you Logstash See the output result in the form of . Information is processed and parsed !
{ "message" => "Dec 23 14:30:01 louis CRON[619]: (www-data) CMD (php /usr/share/cacti/site/poller.php >/dev/null 2>/var/log/cacti/poller-error.log)", "@timestamp" => "2013-12-23T22:30:01.000Z", "@version" => "1", "type" => "syslog", "host" => "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:52617", "syslog_timestamp" => "Dec 23 14:30:01", "syslog_hostname" => "louis", "syslog_program" => "CRON", "syslog_pid" => "619", "syslog_message" => "(www-data) CMD (php /usr/share/cacti/site/poller.php >/dev/null 2>/var/log/cacti/poller-error.log)", "received_at" => "2013-12-23 22:49:22 UTC", "received_from" => "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:52617", "syslog_severity_code" => 5, "syslog_facility_code" => 1, "syslog_facility" => "user-level", "syslog_severity" => "notice"}Congratulations to all . See that you have become a close person Logstash Users of . You will be able to easily configure . perform Logstash, Can also send event to Logstash, But this process will have a lot of values used in this place to be dug .
Publisher : Full stack programmer stack length , Reprint please indicate the source :https://javaforall.cn/117154.html Link to the original text :https://javaforall.cn
边栏推荐
- 1805. Number of different integers in the string
- From spark csc. csr_ Matrix generate adjacency matrix
- Learn to explore - use pseudo elements to clear the high collapse caused by floating elements
- map的使用(列表的数据赋值到表单,json逗号隔开显示赋值)
- 精彩编码 【进制转换】
- 350. 两个数组的交集 II
- Live broadcast today | the 2022 Hongji ecological partnership conference of "Renji collaboration has come" is ready to go
- 部门树递归实现
- redisson bug分析
- ZABBIX proxy server and ZABBIX SNMP monitoring
猜你喜欢

MySQL information schema learning (II) -- InnoDB table
深入分析,Android面试真题解析火爆全网
《数字经济全景白皮书》保险数字化篇 重磅发布
接雨水问题解析
面试突击63:MySQL 中如何去重?
系统性详解Redis操作Hash类型数据(带源码分析及测试结果)

Systematic and detailed explanation of redis operation hash type data (with source code analysis and test results)
Zero foundation entry polardb-x: build a highly available system and link the big data screen

思维导图+源代码+笔记+项目,字节跳动+京东+360+网易面试题整理
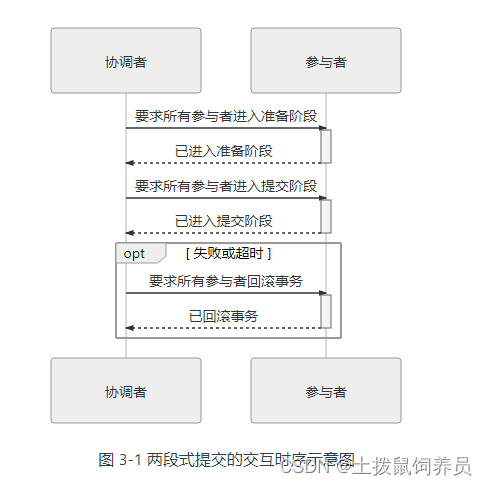
凤凰架构3——事务处理
随机推荐
如何自定义动漫头像?这6个免费精品在线卡通头像生成器,看一眼就怦然心动!
CPU负载很低,loadavg很高处理方法
凤凰架构2——访问远程服务
js实现力扣71题简化路径
Leetcode 30. Concatenate substrings of all words
Learning and Exploration - Seamless rotation map
企业精益管理体系介绍
[translation] supply chain security project in toto moved to CNCF incubator
接雨水问题解析
Swagger2 reports an error illegal DefaultValue null for parameter type integer
redisson bug分析
范式的数据库具体解释
A popular explanation will help you get started
A5000 vGPU显示模式切换
Documents to be used in IC design process
Social recruitment interview experience, 2022 latest Android high-frequency selected interview questions sharing
ZABBIX proxy server and ZABBIX SNMP monitoring
10 schemes to ensure interface data security
【pytorch】yolov5 训练自己的数据集
零基础入门PolarDB-X:搭建高可用系统并联动数据大屏
