当前位置:网站首页>Shangsilicon Valley JUC high concurrency programming learning notes (3) multi thread lock
Shangsilicon Valley JUC high concurrency programming learning notes (3) multi thread lock
2022-07-06 18:18:00 【exodus3】
One 、 Multithreaded locks
At some point , Only one thread can access these synchronized Method .
All static synchronization methods use the same lock —— Class object itself , These two locks are two different objects , So there is no race condition between static synchronization method and non static synchronization method . But once a static synchronization method gets the lock , Other static synchronization methods must wait for the method to release the lock before it can acquire the lock , Whether it's between static synchronization methods of the same instance object , Or between static synchronization methods of different instance objects , As long as they are instance objects of the same class .
synchronized The method of locking is , Object lock
The mechanism of locking the same object needs to wait , Different object lock mechanisms call the same one without waiting
added static Then for class Locks, not object locks

Analyze through specific examples
Two thread safe methods, a common method
class Phone {
public synchronized void sendSMS() throws Exception {
// Stop 4 second
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println("------sendSMS");
}
public synchronized void sendEmail() throws Exception {
System.out.println("------sendEmail");
}
public void getHello() {
System.out.println("------getHello");
}
}
public class Lock_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Phone phone = new Phone();
Phone phone2 = new Phone();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
phone.sendSMS();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "AA").start();
Thread.sleep(100);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// phone.sendEmail();
// phone.getHello();
phone2.sendEmail();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "BB").start();
}
}
The specific eight cases are
1 Standard access , Print SMS or email first
------sendSMS
------sendEmail
2 stop 4 Seconds in the SMS method , Print SMS or email first
------sendSMS
------sendEmail
3 Add common hello Method , Whether to text first or hello
------getHello
------sendSMS
4 Now there are two mobile phones , Print SMS or email first
------sendEmail
------sendSMS
5 Two static synchronization methods ,1 Mobile phone , Print SMS or email first
------sendSMS
------sendEmail
6 Two static synchronization methods ,2 Mobile phone , Print SMS or email first
------sendSMS
------sendEmail
7 1 Static synchronization methods ,1 A common synchronization method ,1 Mobile phone , Print SMS or email first
------sendEmail
------sendSMS
8 1 Static synchronization methods ,1 A common synchronization method ,2 Mobile phone , Print SMS or email first
------sendEmail
------sendSMS
summary :
1.- The same object accesses different synchronization locks , Is executed in order
The same object accesses synchronous and asynchronous locks , First, lock the execution asynchronously
Different objects access different synchronization locks , Execute in order
2.- The same object accesses different static synchronization locks , Execute in order
Different objects access different static synchronization locks , Execute in order
3.- The same object accesses a static synchronization lock , A synchronous lock , First execute the synchronization lock
Different objects access a static synchronization lock , A synchronous lock , First execute the synchronization lock
That is, first out synchronization lock before out static synchronization lock
Two 、 Fair and non-fair locks
Fair lock : Relatively inefficient
Not fair lock : Efficient , But threads starve easily
By looking at the source code , With parameters ReentrantLock(true) Lock for fairness ,ReentrantLock(false) Lock for unfairness
Mainly called NonfairSync() And FairSync()
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/** * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the * given fairness policy. * * @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy */
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
Specifically, the source code of its unfair lock and fair lock
View the source code of fair lock
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
/** * Acquires only if reentrant or queue is empty. */
final boolean initialTryLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedThreads() && compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
} else if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() == current) {
if (++c < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c);
return true;
}
return false;
}
Specific operations through code examples
In the front ticketing code , Continue to refer to the previous code
// First step Create a resource class , Define properties and operation methods
class LTicket {
// Number of tickets
private int number = 30;
// Create a reentrant lock
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// Ticket selling method
public void sale() {
// locked
lock.lock();
try {
// Judge whether there is a ticket
if(number > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : sell "+(number--)+" The remaining :"+number);
}
} finally {
// Unlock
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class LSaleTicket {
// The second step Create multiple threads , Call the operation method of the resource class
// Create three threads
public static void main(String[] args) {
LTicket ticket = new LTicket();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"CC").start();
}
}
Output results
AA : sell 30 The remaining :29
AA : sell 29 The remaining :28
AA : sell 28 The remaining :27
AA : sell 27 The remaining :26
AA : sell 26 The remaining :25
AA : sell 25 The remaining :24
AA : sell 24 The remaining :23
AA : sell 23 The remaining :22
AA : sell 22 The remaining :21
AA : sell 21 The remaining :20
AA : sell 20 The remaining :19
AA : sell 19 The remaining :18
AA : sell 18 The remaining :17
AA : sell 17 The remaining :16
AA : sell 16 The remaining :15
AA : sell 15 The remaining :14
AA : sell 14 The remaining :13
AA : sell 13 The remaining :12
AA : sell 12 The remaining :11
AA : sell 11 The remaining :10
AA : sell 10 The remaining :9
AA : sell 9 The remaining :8
AA : sell 8 The remaining :7
AA : sell 7 The remaining :6
AA : sell 6 The remaining :5
AA : sell 5 The remaining :4
AA : sell 4 The remaining :3
AA : sell 3 The remaining :2
AA : sell 2 The remaining :1
AA : sell 1 The remaining :0
Process finished with exit code 0
All are A Threads execute , and BC The thread didn't execute ( Or the probability of a thread appearing is very high , The probability of other threads is very small ), There is an unfair lock .
The setting can be changed through a parametric construction method in the reentrant lock
Change the code to private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
This is the Fair lock , Every thread has a chance to appear .
give the result as follows :
AA : sell 30 The remaining :29
AA : sell 29 The remaining :28
AA : sell 28 The remaining :27
AA : sell 27 The remaining :26
AA : sell 26 The remaining :25
AA : sell 25 The remaining :24
AA : sell 24 The remaining :23
AA : sell 23 The remaining :22
AA : sell 22 The remaining :21
AA : sell 21 The remaining :20
AA : sell 20 The remaining :19
AA : sell 19 The remaining :18
AA : sell 18 The remaining :17
AA : sell 17 The remaining :16
BB : sell 16 The remaining :15
AA : sell 15 The remaining :14
CC : sell 14 The remaining :13
BB : sell 13 The remaining :12
AA : sell 12 The remaining :11
CC : sell 11 The remaining :10
BB : sell 10 The remaining :9
AA : sell 9 The remaining :8
CC : sell 8 The remaining :7
BB : sell 7 The remaining :6
AA : sell 6 The remaining :5
CC : sell 5 The remaining :4
BB : sell 4 The remaining :3
AA : sell 3 The remaining :2
CC : sell 2 The remaining :1
BB : sell 1 The remaining :0
Process finished with exit code 0
3、 ... and 、 Reentrant lock
synchronized and lock Are reentrant locks
sychronized It's an implicit lock , No manual locking and unlocking , and lock To display the lock , Manual locking and unlocking are required .
Reentrant locks are also called recursive locks
And with the reentrant lock , After cracking the first one, you can go all the way to the inner structure .
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized(o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Outer layer ");
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Middle level ");
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Inner layer ");
}
}
}
},"t1").start();
result
t1 Outer layer
t1 Middle level
t1 Inner layer
Process finished with exit code 0
synchronized (o) Means to lock the current { } Code block inside
All of these are synchronized Locking mechanism
The following interpretation lock Locking mechanism
public class SyncLockDemo {
public synchronized void add() {
add();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lock Demonstrate reentrant locks
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// Create thread
new Thread(()->{
try {
// locked
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Outer layer ");
try {
// locked
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Inner layer ");
}finally {
// Release the lock
lock.unlock();
}
}finally {
// Release do
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1").start();
// Create a new thread
new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
System.out.println("aaaa");
lock.unlock();
},"aa").start();
}
}
result
t1 Outer layer
t1 Inner layer
aaaa
Process finished with exit code 0
Nested locks in the same lock , If the internal nested lock is not unlocked, it can still be output , But if you jump out of the thread , Executing another thread will cause deadlock .
Grasp the concept of locking and unlocking , All have to write .
Four 、 Deadlock
The phenomenon that two or more processes wait for resources because of competing for resources is called deadlock .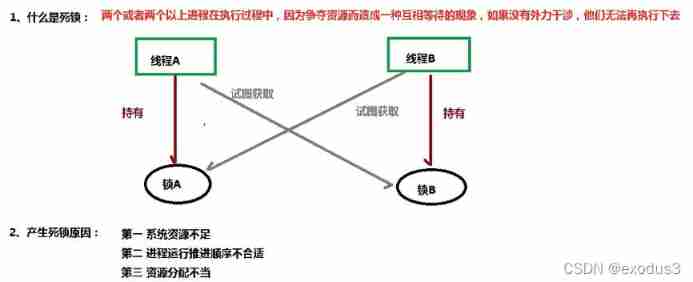
Cause of deadlock :
Insufficient system resources
Improper allocation of system resources
Improper running sequence of processes
Verify whether it is a deadlock
jps Be similar to linux Medium ps -ef View process number
jstack Built in stack trace tool
Deadlock verification process :
1、 Deadlock code :
public class DeadLock {
// Create two objects
static Object a = new Object();
static Object b = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (a) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Hold lock a, Trying to get lock b");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (b) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Get the lock b");
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (b) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Hold lock b, Trying to get lock a");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (a) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Get the lock a");
}
}
},"B").start();
}
}
The program didn't stop 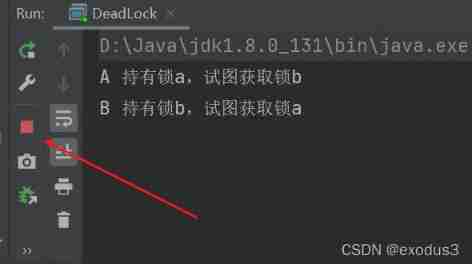
By using idea Self contained command line input jps -l
After checking the process number of its compiled code jstack Process number
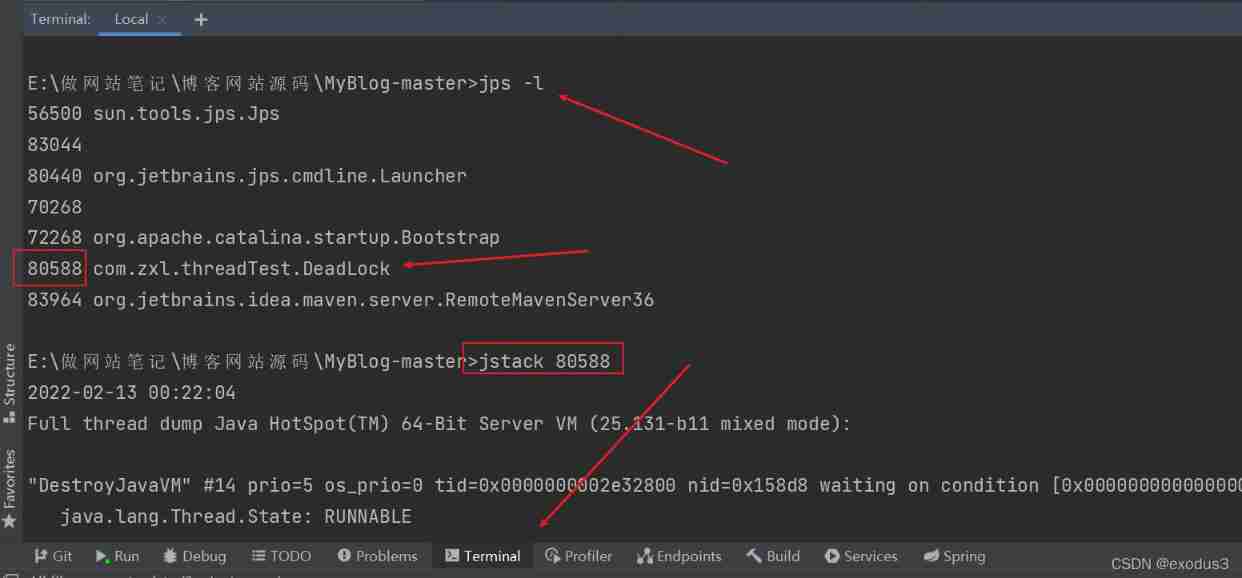
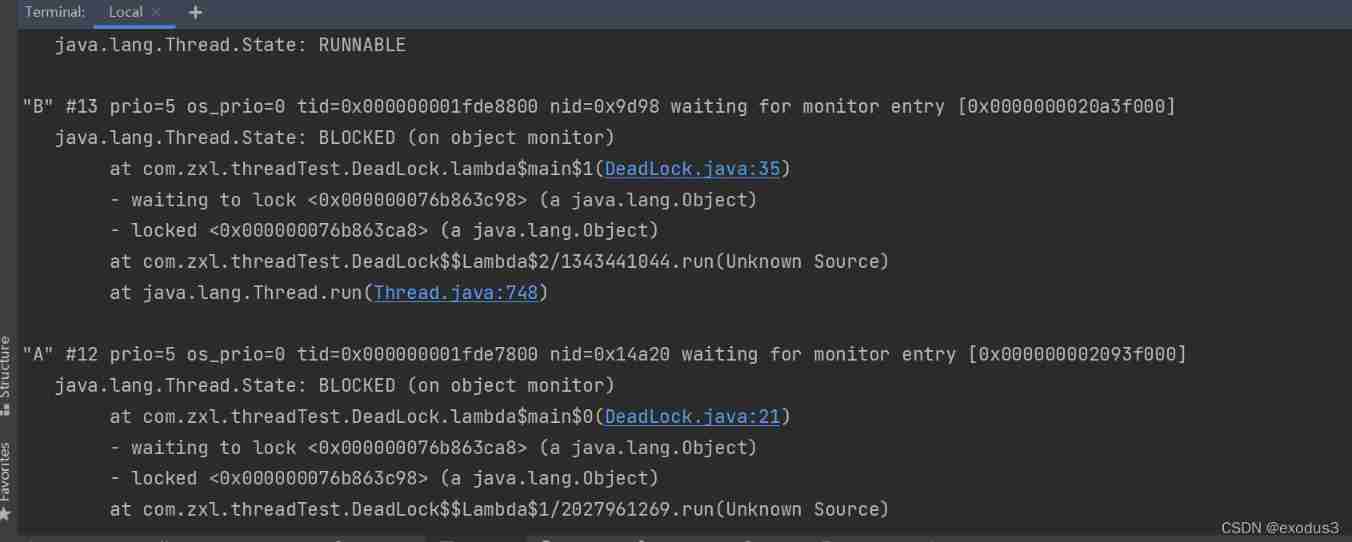
边栏推荐
- DOM简要
- 重磅硬核 | 一文聊透对象在 JVM 中的内存布局,以及内存对齐和压缩指针的原理及应用
- Grafana 9.0 is officially released! It's the strongest!
- MSF横向之MSF端口转发+路由表+SOCKS5+proxychains
- Maixll dock camera usage
- 287. 寻找重复数
- 递归的方式
- Jielizhi obtains the currently used dial information [chapter]
- Excel usage record
- Open source and safe "song of ice and fire"
猜你喜欢
Splay
![[.Net core] solution to error reporting due to too long request length](/img/62/6bdc43885f9be3fa4538276c0dc122.png)
[.Net core] solution to error reporting due to too long request length

J'aimerais dire quelques mots de plus sur ce problème de communication...
C language exchanges two numbers through pointers
Prophet模型的简介以及案例分析
MS-TCT:Inria&SBU提出用于动作检测的多尺度时间Transformer,效果SOTA!已开源!(CVPR2022)...
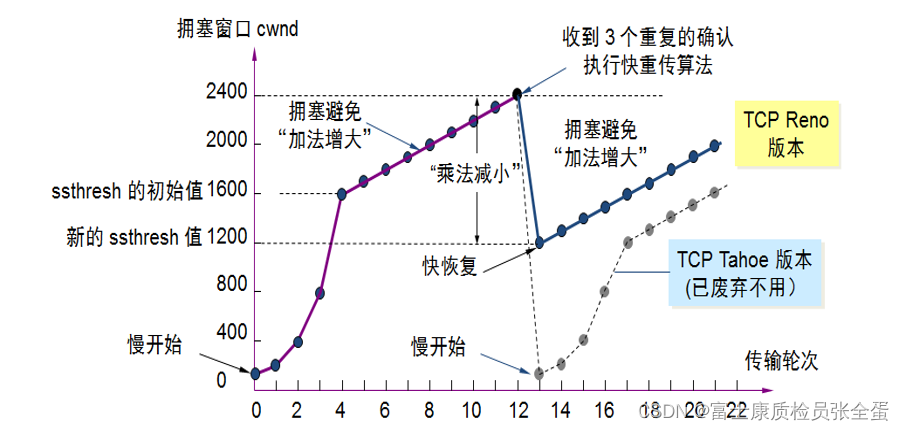
传输层 拥塞控制-慢开始和拥塞避免 快重传 快恢复
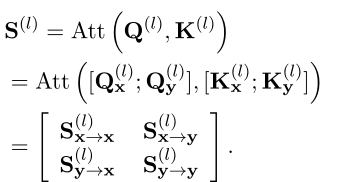
Distill knowledge from the interaction model! China University of science and Technology & meituan proposed virt, which combines the efficiency of the two tower model and the performance of the intera
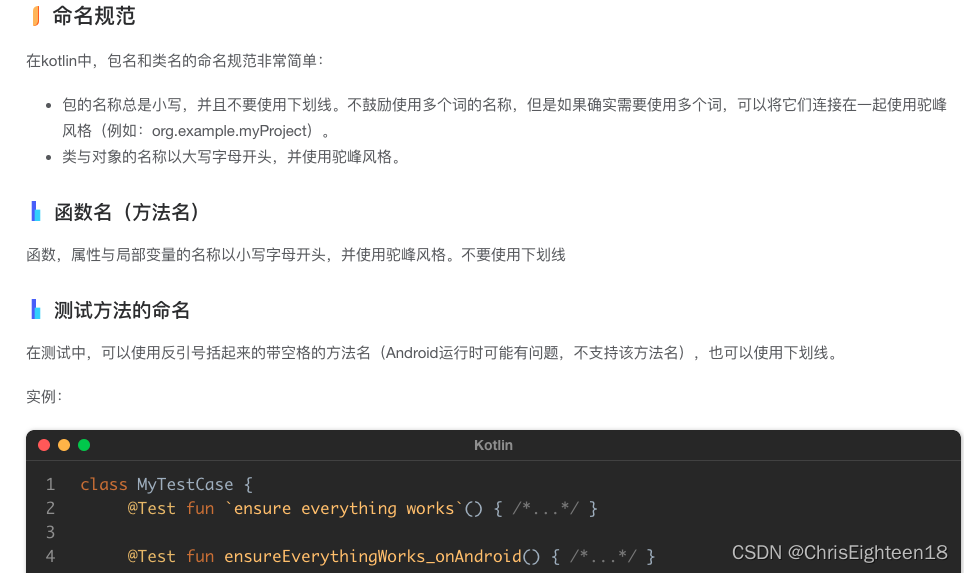
【Android】Kotlin代码编写规范化文档
Compilation Principle -- C language implementation of prediction table
随机推荐
Rb157-asemi rectifier bridge RB157
Introduction to the usage of model view delegate principal-agent mechanism in QT
STM32+HC05串口蓝牙设计简易的蓝牙音箱
Will openeuler last long
【LeetCode第 300 场周赛】
node の SQLite
DOM简要
Kivy tutorial: support Chinese in Kivy to build cross platform applications (tutorial includes source code)
atcoder它A Mountaineer
Running the service with systemctl in the container reports an error: failed to get D-Bus connection: operation not permitted (solution)
Windows连接Linux上安装的Redis
C language exchanges two numbers through pointers
1700C - Helping the Nature
d绑定函数
Recommend easy-to-use backstage management scaffolding, everyone open source
Codeforces Round #803 (Div. 2)
【剑指 Offer】 60. n个骰子的点数
F200 - UAV equipped with domestic open source flight control system based on Model Design
第三季百度网盘AI大赛盛夏来袭,寻找热爱AI的你!
30 minutes to understand PCA principal component analysis