当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree high frequency question type
Binary tree high frequency question type
2022-07-07 09:24:00 【Fly upward】
Catalog
1. The number of nodes in a complete binary tree
3. For the first K The number of layer nodes
4. The maximum depth of a binary tree
5. Find binary tree value Whether there is
6. Whether it is a complete binary tree
8. The subtree of another tree
11. Sequence traversal of binary tree
12. The nearest common ancestor of a binary search tree
13. Binary search tree Convert to a sorted two-way linked list
1. The number of nodes in a complete binary tree
Here's a tree for you Perfect binary tree The root node root , Find out the number of nodes of the tree .
Perfect binary tree Is defined as follows : In a complete binary tree , Except that the lowest node may not be full , The number of nodes in each layer reaches the maximum , And the nodes of the lowest layer are concentrated in the leftmost positions of the layer . If the bottom layer is No h layer , Then the layer contains 1~ 2h Nodes .
Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
link :https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes

class Solution {
//1. Traversal ideas
int count = 0;
public int countNodes1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
count++;
countNodes(root.left);
countNodes(root.right);
return count;
}
//2 Sub problem ideas
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}2. Number of leaf nodes
//1. Traversal ideas
int leafCount = 0;
int getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
leafCount++;
}
getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
return leafCount;
}
//2. Sub problem ideas
int getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
}
3. For the first K The number of layer nodes
/**
* For the first K The number of layer nodes
* Sub problem ideas
*/
int GetKLeveNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) {
return 1;
}
return GetKLeveNodeCount(root.left, k-1) + GetKLeveNodeCount(root.right, k-1);
}4. The maximum depth of a binary tree
Given a binary tree , Find out the maximum depth .
The depth of a binary tree is the number of nodes in the longest path from the root node to the farthest leaf node .
explain : A leaf node is a node that has no children .

Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth+1 : rightDepth+1;
}5. Find binary tree value Whether there is
TreeNode find(TreeNode root,char val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val == val) {
return root;
}
TreeNode ret = final (root.left, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
ret = final (root.right, val);
if (ret != null) {
return ret;
}
return null;
}6. Whether it is a complete binary tree
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList;
// In the queue
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur != null) {
queue.offer(left);
queue.offer(right);
}else {
break;
}
}
// Outgoing queue
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.peek();
if (top != null) {
return false;
}
queue.poll();
}
return true;
}7. Same tree
Here are the root nodes of two binary trees p and q , Write a function to check whether the two trees are the same .
If two trees are the same in structure , And the nodes have the same value , They are the same .
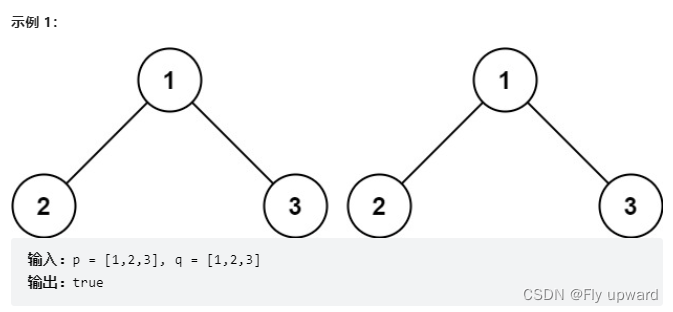
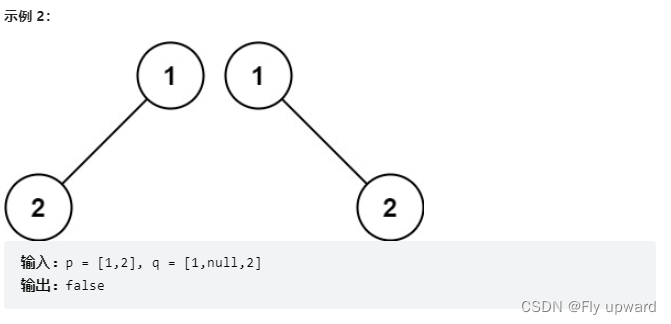
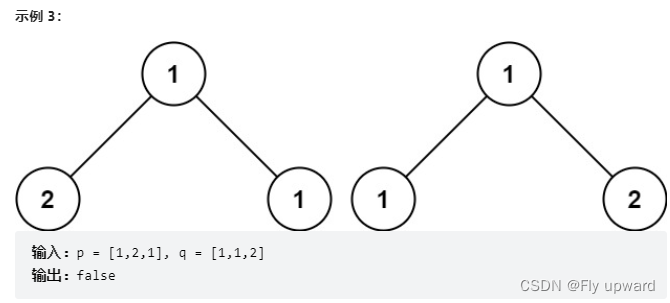
Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) {
return false;
}
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (q.val != p.val) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}8. The subtree of another tree
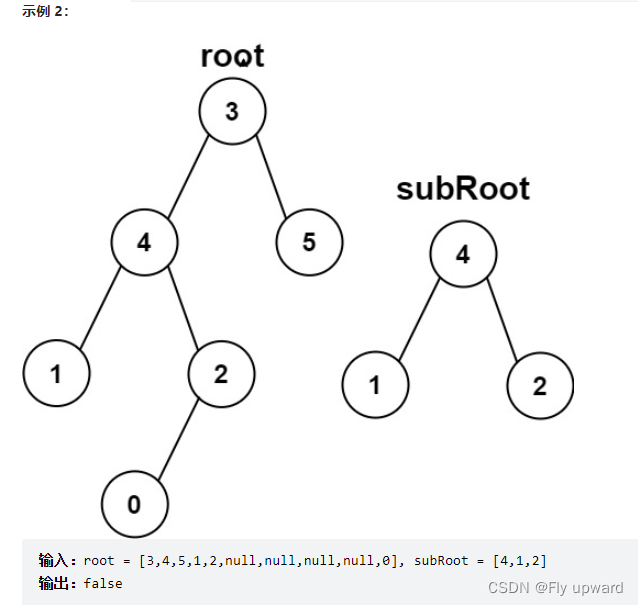
Here are two binary trees root and subRoot . test root Whether and subRoot Subtrees with the same structure and node values . If there is , return true ; otherwise , return false .
Binary tree tree A subtree of includes tree A node of and all descendants of this node .tree It can also be seen as a subtree of its own .
Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
link :https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree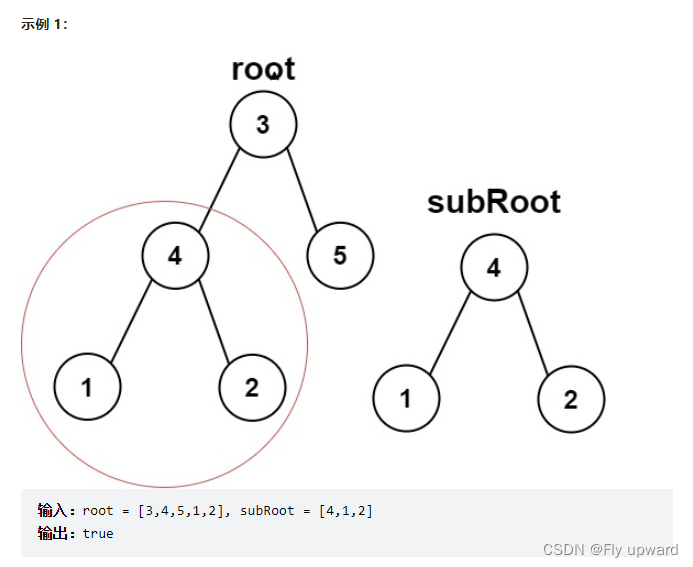
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root,TreeNode subRoot) {
if (root == null || subRoot == null) {
return false;
}
// Root node and subroot Are there two same trees
if (isSameTree(root,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
//subRoot Is it right? root The left subtree
if (isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
if (isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}9. Balanced binary trees
Given a binary tree , Determine if it's a highly balanced binary tree .
In this question , A height balanced binary tree is defined as :
A binary tree Every node The absolute value of the height difference between the left and right subtrees is not more than 1
Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
Solution 1
//1. First check the depth
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
return (leftHeight > rightHeight) ? (leftHeight + 1) : (rightHeight + 1);
}
//2. Check the depth difference between the left and right subtrees 1 Is balanced
public boolean isBalance(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
int left = height(root.left);
int right = height(root.right);
return Math.abs(left - right) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
Solution 2
public int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(root.left);
int rightHeight = height(root.right);
if (leftHeight >= 0 && rightHeight >= 0 && Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight) <= 1) {
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight) + 1;
}else {
// Explain the imbalance
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalance(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return height(root) >= 0;
}
10. Symmetric binary tree
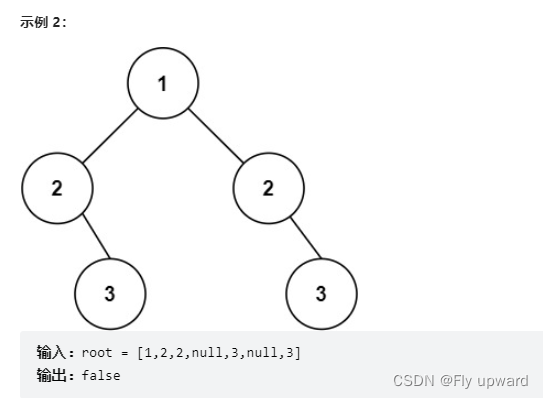
Give you the root node of a binary tree root , Check whether it is axisymmetric .

Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree, TreeNode rightTree) {
if (leftTree == null && rightTree != null) return false;
if (leftTree != null && rightTree == null) return false;
if (leftTree == null && rightTree == null) return true;
if (leftTree.val != rightTree.val) return false;
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right) &&
isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left ,root.right);
}
11. Sequence traversal of binary tree
Give you the root node of the binary tree root , Returns the Sequence traversal . ( That is, layer by layer , Access all nodes from left to right )
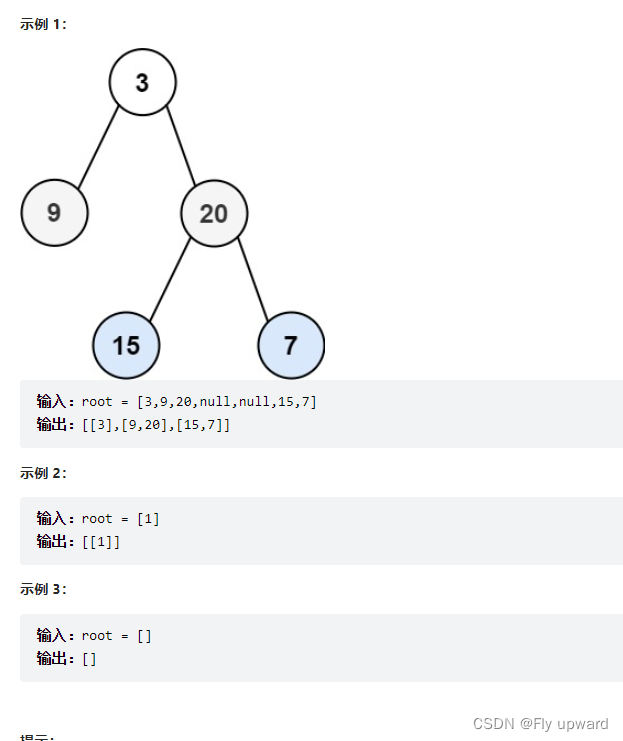
Title source : Power button (LeetCode)
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty) {
int size = queue.size();// How many nodes are there in the current layer
List<Integer> lst = new ArrayList<>();
while (size != 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
size--;
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}
12. The nearest common ancestor of a binary search tree
Given a binary tree , Find the nearest common ancestor of the two specified nodes in the tree .
In Baidu Encyclopedia, the most recent definition of public ancestor is :“ For a tree T Two nodes of p、q, Recently, the common ancestor is represented as a node x, Satisfy x yes p、q Our ancestors and x As deep as possible ( A node can also be its own ancestor ).
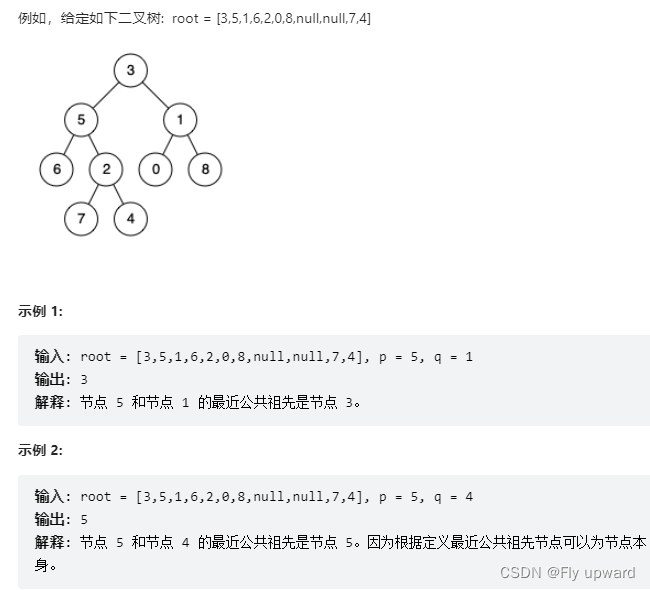
source : Power button (LeetCode)
link :https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-lcof
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (`root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftT = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightT = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if (leftT != null && rightT != null) {
return root;
}else if (leftT != null) {
return leftT;
}else {
return rightT;
}
}13. Binary search tree Convert to a sorted two-way linked list
TreeNode prev = null;
public void inorder(TreeNode pCur) {
if (pCur == null) {
return;
}
inorder(pCur.left);
pCur.left = prev;
if (prev != null) {
prev.right = pCur;
}
prev = pCur;
inorder(pCur.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if (pRootOfTree == null) {
return null;
}
inorder(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
while (head.left != null) {
head = head.left;
}
return head;
}边栏推荐
- Windows starts redis service
- Postman interface test (II. Set global variables \ sets)
- What are the suggestions for PMP candidates?
- JVM garbage collection detailed learning notes (II)
- H3C vxlan configuration
- 数据在内存中的存储
- 串口實驗——簡單數據收發
- DRF defines views and routes
- How to pass the PMP Exam in a short time?
- Kubernetes cluster capacity expansion to add node nodes
猜你喜欢
Connecting mobile phone with ADB
信息安全实验二 :使用X-SCANNER扫描工具
Netease Cloud Wechat applet
数据在内存中的存储
Data association between two interfaces of postman
Jmeters use
Detailed learning notes of JVM memory structure (I)
Where is the answer? action config/Interceptor/class/servlet

答案在哪里?action config/Interceptor/class/servlet
软件建模与分析
随机推荐
十二、排序
Mysql:select ... for update
PMP certificate preparation experience sharing
Locust performance test 3 (high concurrency, parameter correlation, assembly point)
JMeter JDBC batch references data as input parameters (the simplest method for the whole website)
Common short chain design methods
STM32 serial port register library function configuration method
Jmeters use
2021 year end summary
E-commerce campaign Guide
MySql数据库-索引-学习笔记
Connecting mobile phone with ADB
LeetCode每日一题(2316. Count Unreachable Pairs of Nodes in an Undirected Graph)
Mysql数据库-锁-学习笔记
flex弹性布局
Huawei HCIP - datacom - Core 03 jours
软件建模与分析
Selenium mouse sliding operation event
Skill review of test engineer before interview
Mysql database lock learning notes