当前位置:网站首页>QT and OpenGL: loading 3D models using the open asset import library (assimp) - Part 2
QT and OpenGL: loading 3D models using the open asset import library (assimp) - Part 2
2022-07-07 23:53:00 【Raring_ Ringtail】
Qt and OpenGL: Use Open Asset Import Library(ASSIMP) load 3D Model - The first 2 part
Translated from :https://www.ics.com/blog/qt-and-opengl-loading-3d-model-open-asset-import-library-assimp-part-2
By John Stone Wednesday, May 18, 2016
welcome back . This is based on Eric Stone The article “Qt and OpenGL: Use Open Asset Import Library(ASSIMP) load 3D Model ” Follow up article of . Last time we introduced how to use ASSIMP Load the model into our data structure , So that you can use OpenGL Rendering . This time, , We will show you how to write a program to actually render these models .
obviously , We will use Qt As a platform layer ( As the title of this blog says ), We will be in Kejiang OpenGL And Qt Choose from various methods of integration QOpenGLWindow. ( More about , See this webinar :http://www.ics.com/webinars/state-art-opengl-and-qt).
This is the list of our project skeleton :
#include <QtGui/QGuiApplication>
#include <QtGui/QKeyEvent>
#include <QtGui/QOpenGLWindow>
#include <QtGui/QOpenGLBuffer>
#include <QtGui/QOpenGLFunctions>
#include <QtGui/QOpenGLShaderProgram>
#include <QtGui/QOpenGLVertexArrayObject>
#include "modelloader.h"
static QString vertexShader =
"#version 330 core\n"
"\n"
"layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition;\n"
"layout(location = 1) in vec3 vertexNormal;\n"
"\n"
"out vec3 normal;\n"
"out vec3 position;\n"
"\n"
"uniform mat4 MV;\n"
"uniform mat3 N;\n"
"uniform mat4 MVP;\n"
" \n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" normal = normalize( N * vertexNormal );\n"
" position = vec3( MV * vec4( vertexPosition, 1.0 ) );\n"
" gl_Position = MVP * vec4( vertexPosition, 1.0 );\n"
"}\n"
;
static QString fragmentShader =
"#version 330 core\n"
"\n"
"in vec3 normal;\n"
"in vec3 position;\n"
"\n"
"layout (location = 0) out vec4 fragColor;\n"
"\n"
"struct Light\n"
"{\n"
" vec4 position;\n"
" vec3 intensity;\n"
"};\n"
"uniform Light light;\n"
"\n"
"struct Material {\n"
" vec3 Ka;\n"
" vec3 Kd;\n"
" vec3 Ks;\n"
" float shininess;\n"
"};\n"
"uniform Material material;\n"
"\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" vec3 n = normalize( normal);\n"
" vec3 s = normalize( light.position.xyz - position);\n"
" vec3 v = normalize( -position.xyz);\n"
" vec3 h = normalize( v + s);\n"
" float sdn = dot( s, n);\n"
" vec3 ambient = material.Ka;\n"
" vec3 diffuse = material.Kd * max( sdn, 0.0);\n"
" vec3 specular = material.Ks * mix( 0.0, pow( dot(h, n), material.shininess), step( 0.0, sdn));\n"
" fragColor = vec4(light.intensity * (ambient + diffuse + specular), 1);\n"
"}\n"
;
struct Window : QOpenGLWindow, QOpenGLFunctions
{
Window() :
m_vbo(QOpenGLBuffer::VertexBuffer),
m_nbo(QOpenGLBuffer::VertexBuffer),
m_ibo(QOpenGLBuffer::IndexBuffer)
{
}
void createShaderProgram()
{
if ( !m_pgm.addShaderFromSourceCode( QOpenGLShader::Vertex, vertexShader)) {
qDebug() << "Error in vertex shader:" << m_pgm.log();
exit(1);
}
if ( !m_pgm.addShaderFromSourceCode( QOpenGLShader::Fragment, fragmentShader)) {
qDebug() << "Error in fragment shader:" << m_pgm.log();
exit(1);
}
if ( !m_pgm.link() ) {
qDebug() << "Error linking shader program:" << m_pgm.log();
exit(1);
}
}
void createGeometry()
{
}
void initializeGL()
{
QOpenGLFunctions::initializeOpenGLFunctions();
createShaderProgram(); m_pgm.bind();
m_pgm.setUniformValue("light.position", QVector4D( -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f ));
m_pgm.setUniformValue("light.intensity", QVector3D( 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f ));
createGeometry();
m_view.setToIdentity();
m_view.lookAt(QVector3D(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.2f), // Camera Position
QVector3D(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), // Point camera looks towards
QVector3D(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f)); // Up vector
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glClearColor(.9f, .9f, .93f ,1.0f);
}
void resizeGL(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
m_projection.setToIdentity();
m_projection.perspective(60.0f, (float)w/h, .3f, 1000);
update();
}
void draw()
{
}
void paintGL()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
m_pgm.bind();
m_vao.bind();
draw();
m_vao.release();
update();
}
void keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent * ev)
{
if (ev->key() == Qt::Key_Escape) exit(0);
}
ModelLoader m_loader;
QMatrix4x4 m_projection, m_view;
QOpenGLShaderProgram m_pgm;
QOpenGLVertexArrayObject m_vao;
QOpenGLBuffer m_vbo, m_nbo;
QOpenGLBuffer m_ibo;
GLsizei m_cnt;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QGuiApplication a(argc,argv);
QSurfaceFormat f;
f.setMajorVersion( 3 );
f.setMinorVersion( 3 );
f.setProfile( QSurfaceFormat::CoreProfile );
Window w;
w.setFormat(f);
w.setWidth(800); w.setHeight(600);
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
Use this code , We can draw almost any geometry you can give us , So our task will become how to fill the empty createGeometry() Methods and empty draw() Method . Let's first solve the problem of creating geometry . If you remember, we ended our first blog post with the following code :
ModelLoader model;
if (!model.Load("head.3ds"))
{
m_error = true;
return;
}
QVector<float> *vertices;
QVector<float> *normals;
QVector<unsigned int=""> *indices;
model.getBufferData(&vertices, &normals, &indices);
m_rootNode = model.getNodeData();
We said :“ Here we are , You have used OpenGL Display all the data required by the model .” Let's see how to turn it into code .
void createGeometry()
{
if(!m_loader.Load("velociraptor_mesh_materials.dae", ModelLoader::RelativePath)) {
qDebug() << "ModelLoader failed to load model" << m_pgm.log();
exit(1);
}
// Get the loaded model data from the model-loader: (v)ertices, (n)ormals, and (i)ndices
QVector<glfloat> *v, *n; QVector<gluint> *i; m_loader.getBufferData(&v, &n, &i);
// Initialize and bind the VAO that's going to capture all this vertex state
m_vao.create();
m_vao.bind();
// Put all the vertex data in a FBO
m_vbo.create();
m_vbo.setUsagePattern( QOpenGLBuffer::StaticDraw );
m_vbo.bind();
m_vbo.allocate(&(*v)[0], v->size() * sizeof((*v)[0]));
// Configure the attribute stream
m_pgm.enableAttributeArray(0);
m_pgm.setAttributeBuffer(0, GL_FLOAT, 0, 3);
// Put all the normal data in a FBO
m_nbo.create();
m_nbo.setUsagePattern( QOpenGLBuffer::StaticDraw );
m_nbo.bind();
m_nbo.allocate(&(*n)[0], n->size() * sizeof((*n)[0]));
// Configure the attribute stream
m_pgm.enableAttributeArray(1);
m_pgm.setAttributeBuffer(1, GL_FLOAT, 0, 3);
// Put all the index data in a IBO
m_ibo.create();
m_ibo.setUsagePattern( QOpenGLBuffer::StaticDraw );
m_ibo.bind();
m_ibo.allocate(&(*i)[0], i->size() * sizeof((*i)[0]));
// Okay, we've finished setting up the vao
m_vao.release();
}
What we are doing is to use the ModelLoader object , Ask it to load a “ velociraptor” Model , Then the model is in QVector Object to provide us with model data . then , We get the model data , And create a separate Vertex-Buffer and Index-Buffer object , Then upload the model data to the graphics card . There? , We configure the attribute flow for vertex shader input , Because they point to these buffer objects , Then we are ready to render .
Now? , Let's do the actual rendering . Review the first article ,ModelLoader Object returns a grid data tree , Each mesh object contains a bunch of metadata about how to render it ( Including material color data ). What we need to do is create an algorithm , Traverse this “ Grid tree ”, Render the mesh in turn . Let's see how we do this in our code .
void drawNode(const QMatrix4x4& model, const Node *node, QMatrix4x4 parent)
{
// Prepare matrices
QMatrix4x4 local = parent * node->transformation;
QMatrix4x4 mv = m_view * model * local;
m_pgm.setUniformValue("MV", mv);
m_pgm.setUniformValue("N", mv.normalMatrix());
m_pgm.setUniformValue("MVP", m_projection * mv);
// Draw each mesh in this node
for(int i = 0; i<node->meshes.size(); ++i)
{
const Mesh& m = *node->meshes[i];
if (m.material->Name == QString("DefaultMaterial")) {
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Ka", QVector3D( 0.05f, 0.2f, 0.05f ));
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Kd", QVector3D( 0.3f, 0.5f, 0.3f ));
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Ks", QVector3D( 0.6f, 0.6f, 0.6f ));
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.shininess", 50.f);
} else {
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Ka", m.material->Ambient);
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Kd", m.material->Diffuse);
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.Ks", m.material->Specular);
m_pgm.setUniformValue("material.shininess", m.material->Shininess);
}
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, m.indexCount, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, (const GLvoid*)(m.indexOffset * sizeof(GLuint)));
}
// Recursively draw this nodes children nodes
for(int i = 0; i < node->nodes.size(); ++i)
drawNode(model, &node->nodes[i], local);
}
void draw()
{
QMatrix4x4 model;
model.translate(-0.2f, 0.0f, .5f);
model.rotate(55.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
drawNode(model, m_loader.getNodeData().data(), QMatrix4x4());
}
As you can see , We have built an elegant recursive algorithm to traverse the grid tree . Please note that , In each recursive step , How does the current local transformation matrix become the parent transformation matrix of the next level . in addition , Notice how we update the lighting parameters with the lighting metadata of each mesh object , In order to render the mesh object correctly .
this is it , We are using Qt,OpenGL and ASSIMP Render Raptor !
Thanks to the contributing author :Eric Stone,ICS Software Engineer of .
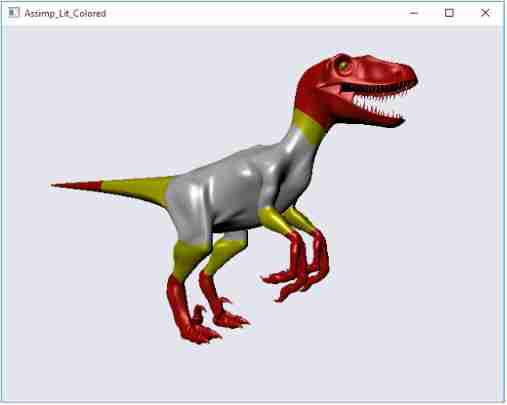
About author

John Stone
John Stone Is an experienced software developer , With a wide range of computer science education and entrepreneurial background , And in graphic visualization and virtual reality (VR) Have rich practical experience in . As the University of Texas at Austin VR Former technical director and researcher of the Laboratory , He spent many years honing his skills , use OpenGL Develop for scientific experiments and other projects based on VR Data acquisition system .
original text :https://www.ics.com/blog/qt-and-opengl-loading-3d-model-open-asset-import-library-assimp-part-2
Welcome to my official account. Notes on Jiangda
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![Balanced binary tree [AVL tree] - insert, delete](/img/1f/cd38b7c6f00f2b3e85d4560181a9d2.png)
Balanced binary tree [AVL tree] - insert, delete

95. (cesium chapter) cesium dynamic monomer-3d building (building)
archery安装测试
ping报错:未知的名称或服务
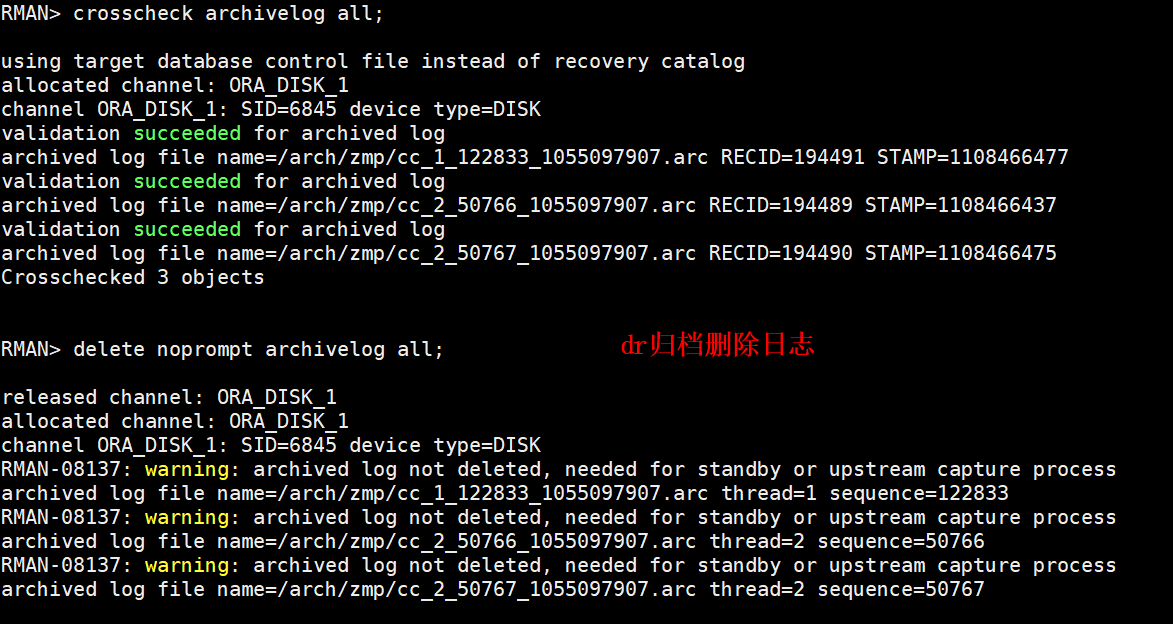
DataGuard active / standby cleanup archive settings

UIC564-2 附录4 –阻燃防火测试:火焰的扩散

Install sqlserver2019

Get started with mongodb
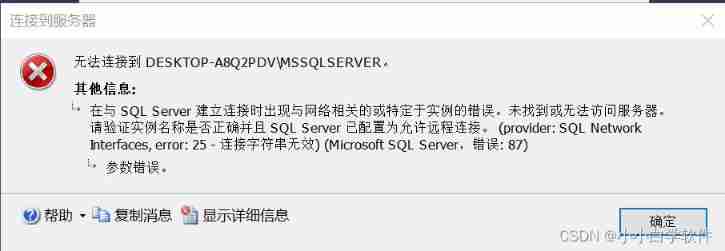
SQL connection problem after downloading (2)
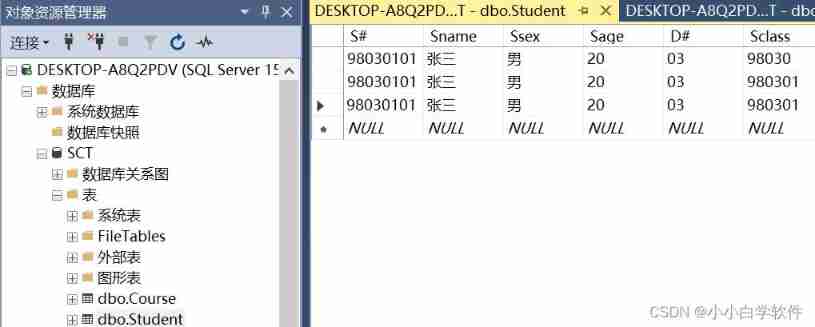
Basic learning of SQL Server -- creating databases and tables with code
随机推荐
Oracle string sorting
Resolve the URL of token
The file format and extension of XLS do not match
Take you hand in hand to build Eureka client with idea
MySQL Architecture
Chisel tutorial - 03 Combinatorial logic in chisel (chisel3 cheat sheet is attached at the end)
Flash download setup
c—线性表
P1067 [noip2009 popularity group] polynomial output (difficult, pit)
Get started with mongodb
数据湖(十五):Spark与Iceberg整合写操作
Laser slam learning (2d/3d, partial practice)
Take you hand in hand to build feign with idea
go time包常用函数
Go time package common functions
Possible SQL for Oracle table lookup information
postgres timestamp转人眼时间字符串或者毫秒值
DataGuard active / standby cleanup archive settings
Uic564-2 Appendix 4 - flame retardant fire test: flame diffusion
Archery installation test