当前位置:网站首页>opencv目标检测
opencv目标检测
2022-08-03 05:23:00 【纸鸢805】
目前常用的实用性目标检测与跟踪的方式方法有以下两种:
1. 帧差法
视频是由一帧帧的图片顺序播放组成, 通过对比前一帧的图像与现在这一帧对比,该方法对于运动目标过于敏感, 而且需要保障镜头必须保持固定,因此帧差法适用于行人稀少或者夜晚场景,能够有效的识别出移动目标出来。
1.1 帧差法函数
/*****************************************************************
* 函数名称: Mat video_run::moveCheck(Mat &frame1, Mat &teme1)
* 功能描述: 帧差法
* 参数说明: Mat &frame1 当前帧
* Mat &teme1 前一帧
* 返回值: 给动过的物体绘制矩形
* 修改记录:
* 日期: 2022-07-29 修改人: yida
* 描述:
* 日期: 2022-07-29 修改人: yida
* 描述:
******************************************************************/
Mat video_run::moveCheck(Mat &frame1, Mat &teme1)
{
Mat res, sres;
Mat frameGray, temeGray;
sres = frame1.clone();
//1、灰度处理目的:RGB三通道转灰度单通道,压缩到原图片三分之一大小
cvtColor(frame1, frameGray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(teme1, temeGray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
// 2. 帧差处理 找到两帧之间的差别、(正在运动的物体)
absdiff(frameGray, temeGray,res);
//imshow("res", res);
// 3. 二值化处理 把灰度图像转为黑白图像
threshold(res, res, 25, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
//imshow("threshold", res);
//4. 图像降噪 开运算 先腐蚀再膨胀 去除主要物体外部周边的白色
//闭运算 先膨胀再腐蚀 作用: 去除主要物体内部的黑色
// 4.1 腐蚀 , 减少白色区域
Mat element = cv::getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3));
erode(res, res, element);
//imshow("erode", res );
//4-2、膨胀目的:把白色区域变大
Mat element2 = cv::getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(20, 20));
dilate(res, res, element2);
//imshow("dilate", res);
//5 .提取关键点
// 寻找特征点
vector<vector<Point>> constours; //关键点
findContours(res, constours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0));
//
vector<vector<Point>> constours2(constours.size()); //关键点
vector<Rect> rect1(constours.size()); //矩形
int x, y , w, h;
int num = constours.size();
for(int i = 0; i < num ; ++i)
{
approxPolyDP(Mat(constours[i]), constours2[i], 3, true );
//多边拟合
rect1[i] = boundingRect(Mat(constours2[i]));
x = rect1[i].x;
y = rect1[i].y;
w = rect1[i].width;
h = rect1[i].height;
//绘制矩形
rectangle(sres, Point(x, y), Point(x+w, y + h), Scalar(0, 255, 120));
}
return sres;
}2. 级联分类器
帧差法能够有效的识别出运动的物体,但是并不能有效的挑出用户需要的物体,会把用户不需要的物体一起识别出来并且框选出来。
因此需要让程序学会识别出需要的目标以及不想识别到的目标。
2.1 操作步骤 (opencv 训练 级联分类器文件)
1. 正样本数据采集(需要检测的物体图片)
2. 负样本数据采集(非检测物的图片)
3. 调用opencv程序opencv_createsamples.exe程序实现样本数据采集
4. 调用opencv程序opencv_traincascade.exe样本训练程序进行训练
5. 生成级联分类器文件
2.2 级联分类器文件调用实现车辆检测 函数
/*****************************************************************
* 函数名称: void detectVarDaw(Mat &frame, CascadeClassifier &cascade, double scale)
* 功能描述: 通过级联分类器进行车辆识别
* 参数说明: Mat &frame 传入的一帧opencv mat图片
* CascadeClassifier &cascade 训练好的级联分类器文件
* double scale 压缩的倍数
* 返回值: 无
* 修改记录:
* 日期: 2022-08-01 修改人: yida
* 描述:
* 日期: 2022-08-01 修改人: yida
* 描述:
******************************************************************/
void detectVarDaw(Mat &frame, CascadeClassifier &cascade, double scale)
{
//灰度处理
Mat fgray;
cvtColor(frame, fgray, CV_RGB2GRAY);
//灰度压缩scale
Mat smalling(cvRound(frame.rows/scale), cvRound(frame.cols/scale), CV_8UC1); //定义一个接收resize 的容器
resize(fgray, smalling, smalling.size(), 0,0, INTER_LINEAR);
//直方图均值化, 让灰度图经过直方图函数处理, 黑白分明
equalizeHist(smalling, smalling);
vector<Rect>cars;
cascade.detectMultiScale(smalling, cars, 1.1, 2, 0|CV_HAAR_SCALE_IMAGE, Size(30, 30) ) ;
//绘制矩形
vector<Rect>::const_iterator iter;
for (iter=cars.begin() ;iter != cars.end( ) ;iter++){
rectangle(frame ,
CvPoint(cvRound(iter->x*scale) , cvRound(iter->y*scale) ),
CvPoint(cvRound((iter->x+iter->width)*scale) , cvRound((iter->y+iter->height)*scale)),Scalar(0,255,0),2,8);
}
imshow ( "frame" ,frame) ;
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Oracle 日历表详解(含节假日)
uni-app 滚动到顶部/指定位置
关于如何向FastAPI的依赖函数添加参数
ansible的安装和部署详细过程,配置清单基本操作
EIP-5058 能否防止NFT项目方提桶跑路?
Oracle 密码策略详解
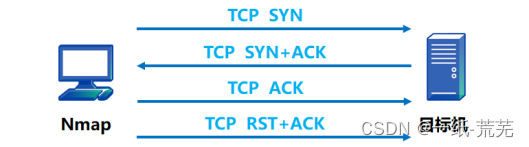
【 Nmap and Metasploit common commands 】
中国水煤浆行业“十四五”规划与运营模式分析报告2022~2028年
MySQL EXPLAIN 性能分析工具详解
Oracle count(1)、count(*)、count(列) 区别详解
中国水产养殖行业市场投资分析及未来风险预测报告2022~2028年
7.16(6)
处理异步事件的三种方式
MySQL 优化建议详解
【CSRF,SSRF,XXE,PHP反序列化,Burpsuite】
Django从入门到放弃三 -- cookie,session,cbv加装饰器,ajax,django中间件,redis缓存等
Flask,7
漫谈Map Reduce 参数优化
【IDEA】字体修改-护眼主题-文件注释头设置
微信小程序 自定义tabBar