当前位置:网站首页>How to read excel, PDF and JSON files in R language?
How to read excel, PDF and JSON files in R language?
2022-07-06 02:39:00 【ysds20211402】
from : Micro reading https://www.weidianyuedu.com
Reading guide : This article will discuss Excel、PDF And so on , And the parameter setting of the corresponding function .
If you need to reprint, please contact big data
The following figure summarizes the main packages , It is hoped that readers will encounter files in different formats in their daily practice and work , It can instantly reflect the package and corresponding function required to read the format .( Limited to space , This article does not include “ Flat document format ” Contents of this part , If you're interested , You can continue to pay attention to the follow-up articles of big data .)
▲ Data files in different formats are read with R package
01 readxl:Excel File read
readxl Microsoft's Excel Necessary for file reading R package , yes Hadley Wickham、Jennifer Bryan And other things 6 One of the classic packages completed by members .
It is worth mentioning that , One of the developers and actual maintainers of the package Jennifer Bryan( On the Internet, she is often called Jenny Bryan), It can be called with Hadley One of the few women with the same name R Language gods . Maybe it's because he's a university professor , Therefore, she can always use a very vivid and interesting way to simplify complex problems into easy to understand knowledge and transfer it to “ The small white ”, It is strongly recommended that readers with a basic knowledge of English can collect some of her keynote speeches or books .
Updated readxl Although there is still only 5 A function , However, the function is more powerful than the previous version . For the original version , The data will be read as common data.frame Format , And for the current version , The format of the read data set is tibble, It can be understood as an upgraded version of data.frame.
readxl Including two probing functions excel_format and excel_sheets, A function that references an example readxl_example, Newly added function to read specific cells cell-specification And most importantly read_excel function . This section will focus on read_excel Parameter setting and usage skills .
Data import function read_excel Main parameters and function comparison :
path
Data file path + file name , It can also be a url
sheet
Worksheet serial number or name , The default value is the first worksheet
range
Read the specified interval , You can restrict the function to read the original Excel Scope of documents , for example ,“A1:D100” All cells in this range will be read , Include blank cells .“ Worksheet 1!A1:D100” I can read it and call it “ Worksheet 1” The interval in . This parameter takes precedence over the parameter "skip"、"n_max"、"sheet"
col_names
This parameter has three choices , As follows .
1) It's true (TRUE), The first row of the raw data file is used as the column name , And not in the dataset .
2) For false (FALSE), The data column name is automatically assigned to X__1、X__2、X__3 etc. .
3) Custom string vector passed to parameter . At this point, the string vector will be used as the column name , The first column of the original data file will be saved to the first column of the dataset . If there is a default column name , A warning will be given , And automatically assigned to X1、X2、X3 etc. , But it will not affect the reading process . Duplicate column names also give warnings , In addition, a numerical sequence number will be added before the duplicate column name to distinguish
col_types
Column data type . There can be two forms of parameter transmission , As follows .
1)NULL, The default value is . The function will automatically resolve the type of each column of data .
2) Specify the variable type . The string reference is :"skip"、"guess"、"logical"、"numeric"、"date"、"text" or "list". It should be noted that , If only one data type is specified ( for example ,"numeric") Then all variables will be read as character data . If you specify a column as "skip", Then this column will not be read R In the to . Newly increased "list" Attribute will be very helpful in dealing with variable columns with longitude and latitude
na
Whether there are some characters in the original data file that need to be used na Instead of . Blank cells are used as the default
trim_ws
Whether the blank space before and after each data value is disposed , Take true or false
skip
Whether to skip a few lines to read the original data file , The default value is 0, Means not to skip ; You can pass any number
n_max
Maximum number of rows read
First, you need to load readxl package . Even though Hadley from 2017 Since, it has been promoting on the Internet that this package has belonged to tidyverse Part of , But users still have to manually load the package separately . load readxl The package code is as follows :
> library(readxl)
readxl The demonstration document is self-contained , Using functions readxl_example You can view the file name , And get the file path , The code is as follows :
> readxl_example()
[1] "clippy.xls" "clippy.xlsx" "datasets.xls" "datasets.xlsx"
[5] "deaths.xls" "deaths.xlsx" "geometry.xls" "geometry.xlsx"
[9] "type-me.xls" "type-me.xlsx"
Get the path of the sample file , You can copy readxl_example The result after the function runs , Then paste it into read_excel Functional path Parameters in .
The following code demonstrates the method of function nesting , This nested code writing method can simplify the code and reduce the frequency of naming intermediates to a certain extent . However, too much nesting will make readability worse , It is generally recommended to nest only two layers . Save the read data in iris in , perform str After the function, you will find that in addition to the classic data.frame outside , There are two other categories of data sets ,tbl_df and tbl. The example code of function nesting is as follows :
> iris <- read_excel(path = readxl_example(path = "datasets.xlsx"))
> str(iris)
## Classes "tbl_df", "tbl" and "data.frame": 150 obs. of 5 variables:
## $ Sepal.Length: num 5.1 4.9 4.7 4.6 5 5.4 4.6 5 4.4 4.9 ...
## $ Sepal.Width : num 3.5 3 3.2 3.1 3.6 3.9 3.4 3.4 2.9 3.1 ...
## $ Petal.Length: num 1.4 1.4 1.3 1.5 1.4 1.7 1.4 1.5 1.4 1.5 ...
## $ Petal.Width : num 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.1 ...
## $ Species : chr "setosa" "setosa" "setosa" "setosa" ...
It was named iris, Because of this example Excel The first worksheet in the file is the classic dataset . function excel_sheets It can be used to query the name of worksheet in the same file , In fact, the modern code is as follows :
> excel_sheets(path = readxl_example(path = "datasets.xlsx"))
## [1] "iris" "mtcars" "chickwts" "quakes"
stay datasets.xlsx Co existing in 4 Sheets , Which includes 4 The most classic R Language practice dataset . Here it is , I hope readers can browse these data sets by themselves , The format of the data set 、 Have a certain understanding of variable names and other situations .
Add parameters sheet or range You can read the data in the specified worksheet . What needs to be noted here is , The problem of parameter priority is mentioned above . For common exercise data sets ,sheet The worksheet specified by the parameter is sufficient . Readers just need to remember range Parameters can be used to handle special situations , in other words , When setting sheet If you are still dissatisfied with the read data, you can consider using it range.
The following code demonstrates sheet Two methods of parameter transmission : Location, serial number and name . The latter is recommended . It often happens that the position of the worksheet is changed due to accidental dragging , The data read after the unexpected location change will also be different , This increases the risk of code crashes . If you use a name , It will reduce the probability of errors . The sample code is as follows :
> mtcars <- read_excel(path = readxl_example(path = "datasets.xlsx"),sheet = 2)
> mtcars <- read_excel(path = readxl_example(path = "datasets.xlsx"),sheet = "mtcars")
For the following parameters , The reader can follow the above explanation , Add one parameter at a time , To gradually master the function of each parameter , No more details here .
02 DBI: Database data query 、 download
In the use of R Before the language interacts with the database , Readers need to clarify a question — Is it necessary to use R To process data . Simple data processing tasks , For example, data query 、 Filtering and simple operations , The corresponding database language should be better than R Language is a better choice .
But when you're not familiar with the database language , And they need R Language powerful statistical analysis and drawing environment to deal with the data in the database ,DBI The bag is definitely a shortcut . because Hadley The great God once again saved “ The small white ”.
With DBI package , There is no need to understand the tedious theoretical knowledge and skills in each link of database interaction , Just understand how to pass DBI Package to establish database connection 、 Query and read data . however , This bag is not a master key , Want to interact with the database without obstacles , following 6 Point is a necessary prerequisite .
The type of database is known , for example ,MySQL、PostgreSQL.
The corresponding database type has been installed R package .
Database server address .
Database name .
Access to the database 、 Account and password .
already installed dplyr The package is used to localize the data in the database .
Use R The general process of interacting with the database is : Establishing a connection → Send query request → Get relevant data . below , We use it PostgreSQL As a code example . First load three prerequisite packages , among ,DBI and PostgreSQL Will be used to establish a connection to the database and send requests .dplyr Is used to save the data in the database to the local database . The loading code is as follows :
> library(DBI)
> library(dplyr)
> library(RPostgreSQL)
Different types of databases may need to be adjusted dbConnect Parameters in , For specific adjustment methods, readers can refer to the help document . Database server address 、 name 、 Permission and other information need to be entered in single quotation marks , Please be sure to pay attention to whether the space symbol is accidentally copied or entered due to misoperation . If you're worried about password disclosure , You can use RStudio The built-in password pop-up function in .
dbListTables Function can be used to query the details in the database , And returns... In the form of a string vector , If there is no content in the database , Will return a null value . adjustment dbConnect The example code of the parameter is as follows :
> db_connect <- dbConnect(
RPostgreSQL::PostgreSQL(),
dbname = " Database name ",
host = " Server address ",
user = " user name ",
password = " password ")
> dbListTables(db_connect)
## [1] "MetaData" "Table1" "Table2"
The optimized tbl The function can directly call the specified data in the connected database , And save for tibble Data set in format . In the following code , The argument after the comma can also be “Table1” or “Table2” To express :
> tbl(src = db_connect, dbListTables(db_connect)[1])
The content of the book can be completely interactive , Here we only introduce the simplest basic usage , So that everyone can understand how to use R To query the database, I have the most basic impression .
03 pdftools:PDF file
Academic journals 、 Online magazines and e-books generally use PDF Format file rendering . Reading is rarely encountered in general metrological data analysis PDF File status , But in the process of text mining (Text Mining) And theme models (Topic Modelling) Forecasting ,pdftools The bag is absolutely necessary R Package one .
The package has only two generating functions , One for from PDF Extract data from ( The data here includes digital data and text data ), The other is used to render the file into PDF Format . In this section, we will only discuss the first generating function ——pdf_info.
pdf_info The following functions contain 6 Subfunctions , Different functions . however 6 The parameters of the sub functions are exactly the same , Namely pdf、opw and upw.
Data import function "pdf_info List of sub functions :
pdf_info: Read PDF Basic information of the document , for example , When to create 、 change , Version information , Whether there is a password , Pages, etc , See the code demonstration section for details
pdf_text: Extract all text or non text information in the file , Include page breaks 、 A newline
pdf_data: Extract digital data , The result of this extraction will be due to PDF File varies , Sometimes the data in the journal can be extracted completely , Sometimes because PDF Inconsistent separators are used in document creation, resulting in incomplete data extraction
pdf_fonts: Extract the font information of the document
pdf_attachments: Extract document attachments
pdf_toc: Extract document directory
Data import function "pdf_info Parameters, :
pdf:PDF File path , It can be a network link
opw:PDF The password of the file owner
upw:PDF The password of the file user
Due to limited space , The following code intercepts only part of the results for interpretation . What's used here is PDF The document is pdftools Help documentation for the package , Readers can come by themselves R Search and download on the official website . Help documentation is open PDF file , No password required . Read the document code as follows :
> library(pdftools)
> pdf_info(pdf = "./helpDocs/pdftools.pdf")
## $version
## [1] "1.5"
##
## $pages
## [1] 5
...
When using pdf_text When extracting document content , Everything is extracted as a string vector , The contents of each page are placed separately in a string . Help document PDF The format contains 5 page , So here you get a length of 5 The string vector of .
There are two ways to view the extracted text : The results can be displayed directly in console in ( Through execution print(text) Or run directly text), It can also be done through “[ ]” To specify the content of a page . The blank position will be displayed in the character format of space ,“\r\n” Represents a newline symbol . The code to extract the content of the document is as follows :
> text<- pdf_text("./helpDocs/pdftools.pdf")
> length(text)
## [1] 5
> class(text)
## [1] "character"
> text[1]
## [1] " Package ‘pdftools’\r\n May 27, 2018\r\nType Package\r\nTitle Text Extraction, Rendering and Converting of PDF Documents\r\nVersion 1.8\r\nDescription Utilities based on "libpoppler" for extracting text, fonts, attachments and\r\n
This document has no attachments , So an empty list will be displayed :
> pdf_attachments(pdf = "./helpDocs/pdftools.pdf")
## list()
The document contains a total of 6 Fonts ,pdf_fonts Will give the name of the font 、 type 、 Whether to embed these three types of information in the document , As follows :
> pdf_fonts(pdf = "./helpDocs/pdftools.pdf")
## name type embedded file
## 1 DSHWTW+NimbusRomNo9L-Medi type1 TRUE
## 2 UTHPMJ+NimbusRomNo9L-Regu type1 TRUE
## 3 DSQFGA+Inconsolata-zi4r type1 TRUE
## 4 LVIJIF+NimbusSanL-Regu type1 TRUE
## 5 DQRZJT+NimbusRomNo9L-Regu-Slant_167 type1 TRUE
## 6 YIECHJ+NimbusRomNo9L-ReguItal type1 TRUE
The sub function of directory reading will return the read content to a list , If the list is displayed directly in console It is likely to make people feel at a loss , Readers can practice by themselves . The best way is to use the read content jsonlite Package to json The format of the list is displayed , To help understand the architecture of the document .jsonlite Package to json The example code of the list is as follows :
> jsonlite::toJSON(x = pdf_toc(pdf = "./helpDocs/pdftools.pdf"), pretty = TRUE)
## {
## "title": "",
## "children": [
## {
## "title": "pdf_info",
## "children": []
## },
## {
## "title": "pdf_render_page",
## "children": []
## },
## {
## "title": "Index",
## "children": []
## }
## ]
## }
04 jsonlite:JSON file
JavaScript Object Notation(JSON) It is usually used as a document for exchanging information between different languages ,JSON Files not only save storage space , Its concise and clear form is also easy to understand .
jsonlite The package can complete JSON Format files are completely parsed and read to R From language , Any common R object (object) Output into JSON Format . this paper 03 In the festival ,toJSON Function can be used to convert PDF Convert document directory to JSON Format , In order to understand the relationship between all levels .
Read JSON Of documents fromJSON Function co inclusion 6 Parameters , Usually , In addition to specifying the file path , Other parameters can be set by default .
Data import function fromJSON Parameters, :
txt: It can be a paragraph JSON Format string , Network link or file path plus file name
simplifyVector: Forcibly transpose the original values in the ordered array into atomic vectors , It can be simply understood as retaining only data , There are true and false settings , Default to true , If set to false , The data will be read as a list , The list will contain sub lists , The variable name and corresponding data value will be listed in the sub list . See the code demonstration section for details
simplifyDataFrame: take JSON Cast records in an array to a dataset (data frame)
simplifyMatrix: take JSON A vector in an array is cast to a matrix or array
flatten: Automatically convert nested data sets to non nested flat data sets
…: Set the display method
First of all JSON Create a string vector in the form of a common array , Save as example. Brackets represent the beginning of the array , The double quotation marks represent the value , Values are separated by commas , Then use single quotation marks to save the array format into the string vector . because example The array in is according to JSON Format input , So use it directly fromJSON Function .
Under the default parameter setting , You can get one that contains 4 Of values R object — String vector . function fromJSON The two string vectors before and after , Although the name is the same , But the content is completely different , Interested readers can run alone example To compare the differences .formJSON The sample code is as follows :
> example <- "["a", "b", 0, "c"]"
> fromJSON(example)
## [1] "a" "b" "0" "c"
When parameters simplifyVector When specified as false , The returned result is a containing 4 A list of elements .4 Two elements represent common 4 It's worth , Each value is returned as a list .
When JSON When the original data file of format has multiple nesting , You can set parameters to view the data structure and read the data correctly . however , In general, readers are advised to use non nested data to practice and use R Language and JSON Interact with format data , Improve the difficulty after having a certain understanding . The results are as follows :
> fromJSON(example,simplifyVector = F)
## [[1]]
## [1] "a"
##
## [[2]]
## [1] "b"
##
## [[3]]
## [1] 0
##
## [[4]]
## [1] "c"
05 foreign package Statistical software data
All over the world , Open source data analysis tools are gradually replacing traditional data analysis software , for example SAS、SPSS. In the process ,foreign Package allows us to seamlessly connect data saved in traditional analysis software format . The package also integrates reading and writing .
Because of the irreversible rise of open source statistical analysis software all over the world , The use frequency of traditional analysis software is getting lower and lower , Its data format is also gradually marginalized , This section only lists the functions required to read the corresponding extension name in case of readers' need , Without further code demonstrations .
Data import package foreign List of data reading functions and corresponding reading files in :
.xpt:lookup.xport
ARFF files:read.arff
.dbf:read.dbf
Stata Binary Files:read.dta
.rec:read.epiinfo
.mtp:read.mtp
.sav:read.spss
.syd:read.systat
边栏推荐
- Redis delete policy
- How to improve the enthusiasm of consumers when the member points marketing system is operated?
- Network Security Learning - Web vulnerabilities (Part 1)
- GifCam v7.0 极简GIF动画录制工具中文单文件版
- 爬虫(9) - Scrapy框架(1) | Scrapy 异步网络爬虫框架
- 主数据管理(MDM)的成熟度
- Patch NTP server at the beginning of DDoS counterattack
- 如何精准识别主数据?
- Zero foundation self-study STM32 - Review 2 - encapsulating GPIO registers with structures
- Bigder:34/100 面试感觉挺好的,没有收到录取
猜你喜欢
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 21](/img/73/4050a592fdd99bf06e8fd853b157b6.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 21
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7](/img/44/1861f9016e959ed7c568721dd892db.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7
Qt发布exe软件及修改exe应用程序图标

Which ecology is better, such as Mi family, graffiti, hilink, zhiting, etc? Analysis of five mainstream smart brands
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16](/img/c3/f3746b161012acc3751b2bd0b8f663.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16
Referenceerror: primordials is not defined error resolution
Introduction to robotframework (III) Baidu search of webui automation

Pat grade a 1033 to fill or not to fill
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23](/img/72/a80ee7ee7b967b0afa6018070d03c9.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23
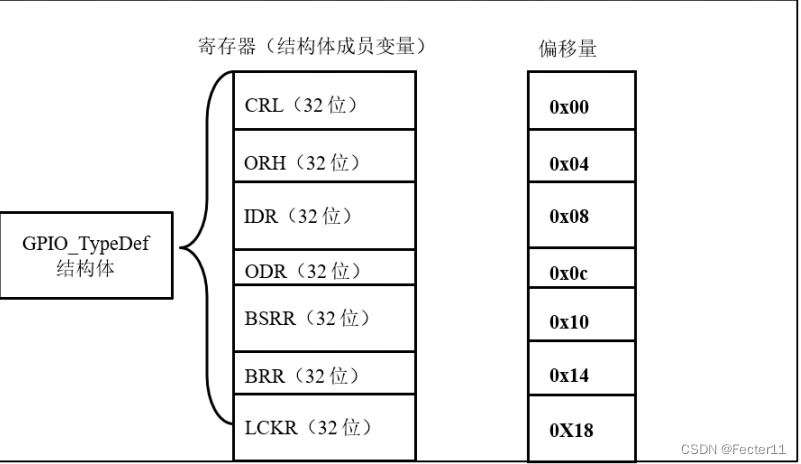
零基础自学STM32-复习篇2——使用结构体封装GPIO寄存器
随机推荐
Easy to use js script
纯Qt版中国象棋:实现双人对战、人机对战及网络对战
解决:AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘decode‘
How to accurately identify master data?
Introduction to robotframework (I) brief introduction and use
QT release exe software and modify exe application icon
LeetCode 103. Binary tree zigzag level order transverse - Binary Tree Series Question 5
Crawler (9) - scrape framework (1) | scrape asynchronous web crawler framework
我把驱动换成了5.1.35,但是还是一样的错误,我现在是能连成功,但是我每做一次sql操作都会报这个
2020.02.11
主数据管理理论与实践
DDoS "fire drill" service urges companies to be prepared
高数_向量代数_单位向量_向量与坐标轴的夹角
Yyds dry inventory comparison of several database storage engines
Six stone management: why should leaders ignore product quality
Force buckle 146 LRU cache
MySQL winter vacation self-study 2022 11 (5)
2022.02.13
怎么检查GBase 8c数据库中的锁信息?
球面透镜与柱面透镜