当前位置:网站首页>Skimage learning (2) -- RGB to grayscale, RGB to HSV, histogram matching
Skimage learning (2) -- RGB to grayscale, RGB to HSV, histogram matching
2022-07-07 17:02:00 【Original knowledge】
1、RGB Go gray
This example will have RGB The image of the channel is converted into an image with a single gray channel .
The value of each gray pixel is calculated as the corresponding red 、 Weighted sum of green and blue pixels :
Y = 0.2125 R + 0.7154 G + 0.0721 B
CRT Phosphors use these weights , Because they are more representative of human beings to red than the same weight 、 The perception of green and blue .
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
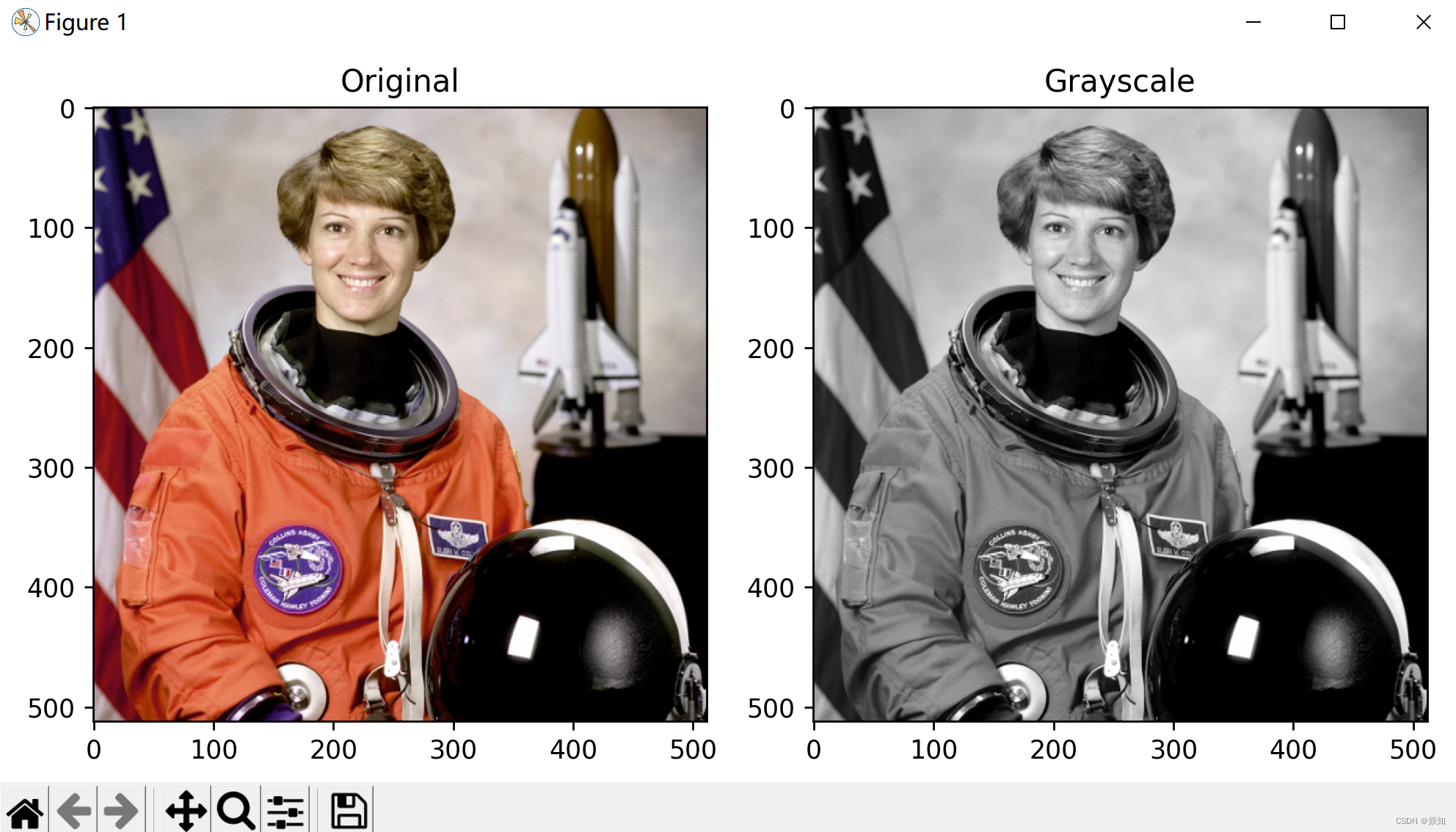
original = data.astronaut()
grayscale = rgb2gray(original)
#fig It's a variable name ,fig Represents the drawing window (Figure);ax Represents the coordinate system on this drawing window (axis), Will generally continue to ax To operate
# among figsize Used to set the size of the drawing ,a Is the width of the figure , b Is the height of the figure , In inches .
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
ax = axes.ravel()
ax[0].imshow(original)
ax[0].set_title("Original")
ax[1].imshow(grayscale, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_title("Grayscale")
fig.tight_layout()#ight_layout The subgraph parameters will be automatically adjusted , Make it fill the entire image area . This is an experimental feature , May not work in some cases . It just checks the axis labels 、 Scale label and title section .
plt.show()
2、RGB turn HSV
hsv Detailed explanation :https://blog.csdn.net/bamboocan/article/details/70627137
This example shows how RGB To HSV( tonal , saturation , brightness ) Transformation can be used to facilitate the segmentation process .
Usually , The objects in the image have different colors ( tonal ) And brightness , So these features can be used to separate different areas of the image .
stay RGB In the middle , Hue and brightness are expressed as R、G、B Linear combination of channels , And they correspond to HSV Single channel of image ( Hue and value channels ).
A simple segmentation image , Then, threshold only HSV passageway .
For example, picture dyeing homogenization , We often use rgb2hsv To solve the problem , It can effectively protect the texture 、 Distribution and other characteristics .
Here we look at an example of chromosome color separation :
Be careful , The example here is HED Color space ,HSV Space is the same effect .
from skimage import io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage.color import rgb2hsv
# First load RGB Image and extract Hue and Value passageway :
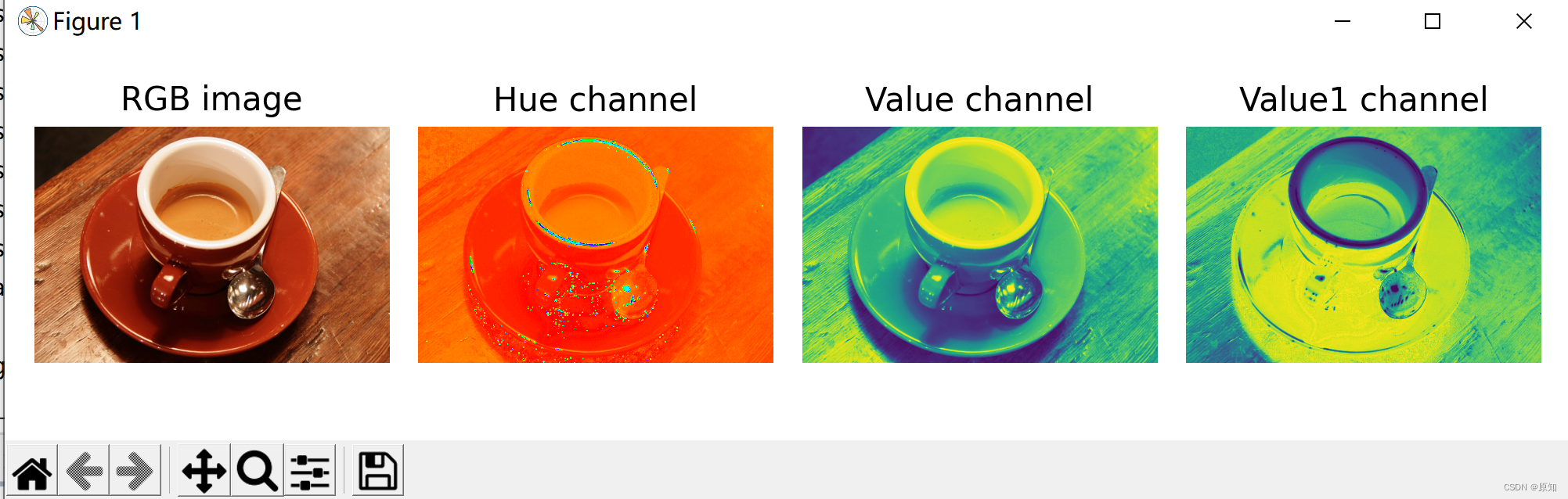
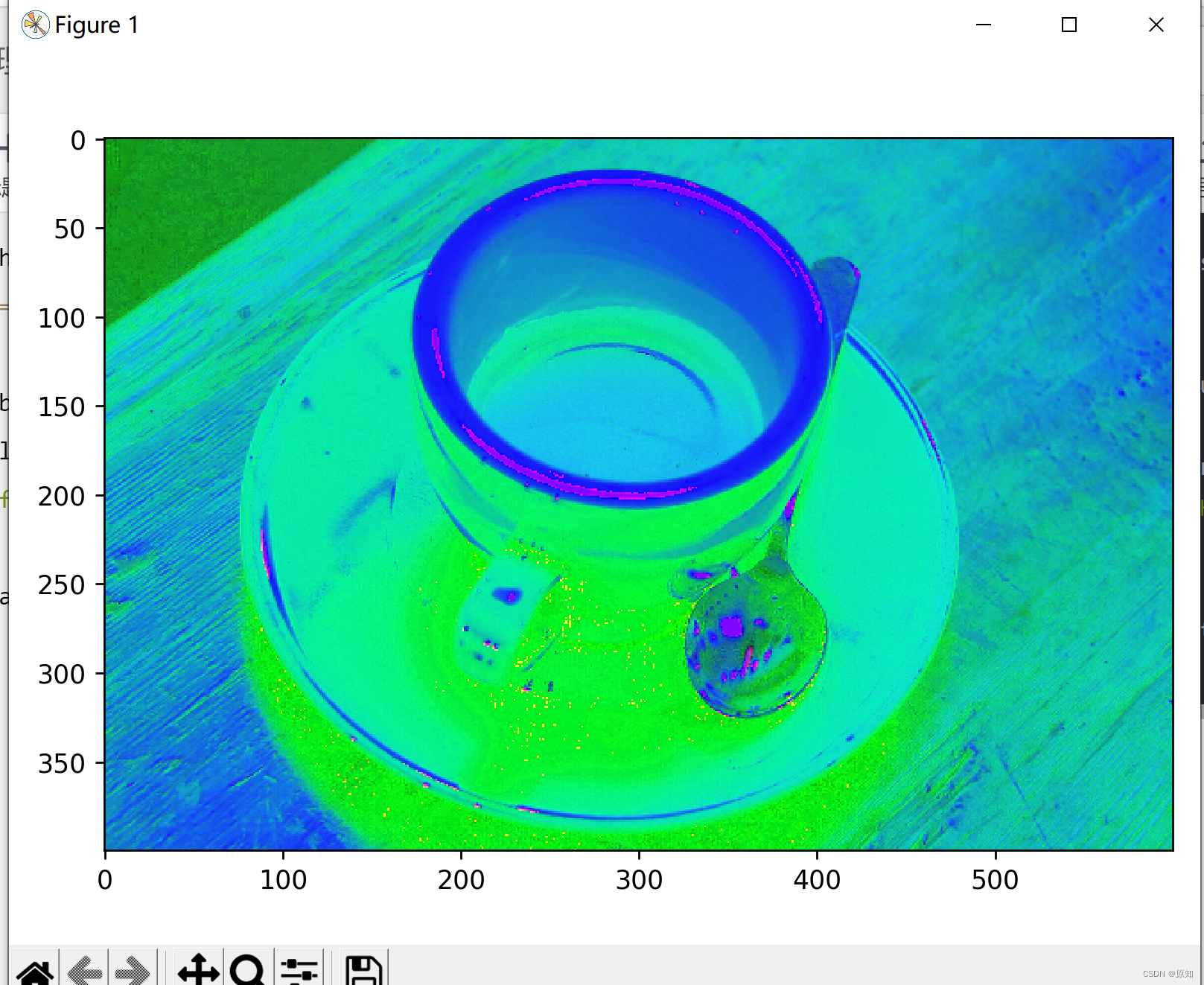
rgb_img = data.coffee()
hsv_img = rgb2hsv(rgb_img)
io.imshow(hsv_img)
plt.show()
hue_img = hsv_img[:, :, 0]# It is a way to process multidimensional data , It represents the first two dimensions , Take all of them 0 Index number .
value_img = hsv_img[:, :, 2]
value1_img = hsv_img[:, :, 1]
fig, (ax0, ax1, ax2,ax3) = plt.subplots(ncols=4, figsize=(8, 2))
ax0.imshow(rgb_img)
ax0.set_title("RGB image")
ax0.axis('off')
ax1.imshow(hue_img, cmap='hsv')
ax1.set_title("Hue channel")
ax1.axis('off')
ax2.imshow(value_img)
ax2.set_title("Value channel")
ax2.axis('off')
ax3.imshow(value1_img)
ax3.set_title("Value1 channel")
ax3.axis('off')
fig.tight_layout()
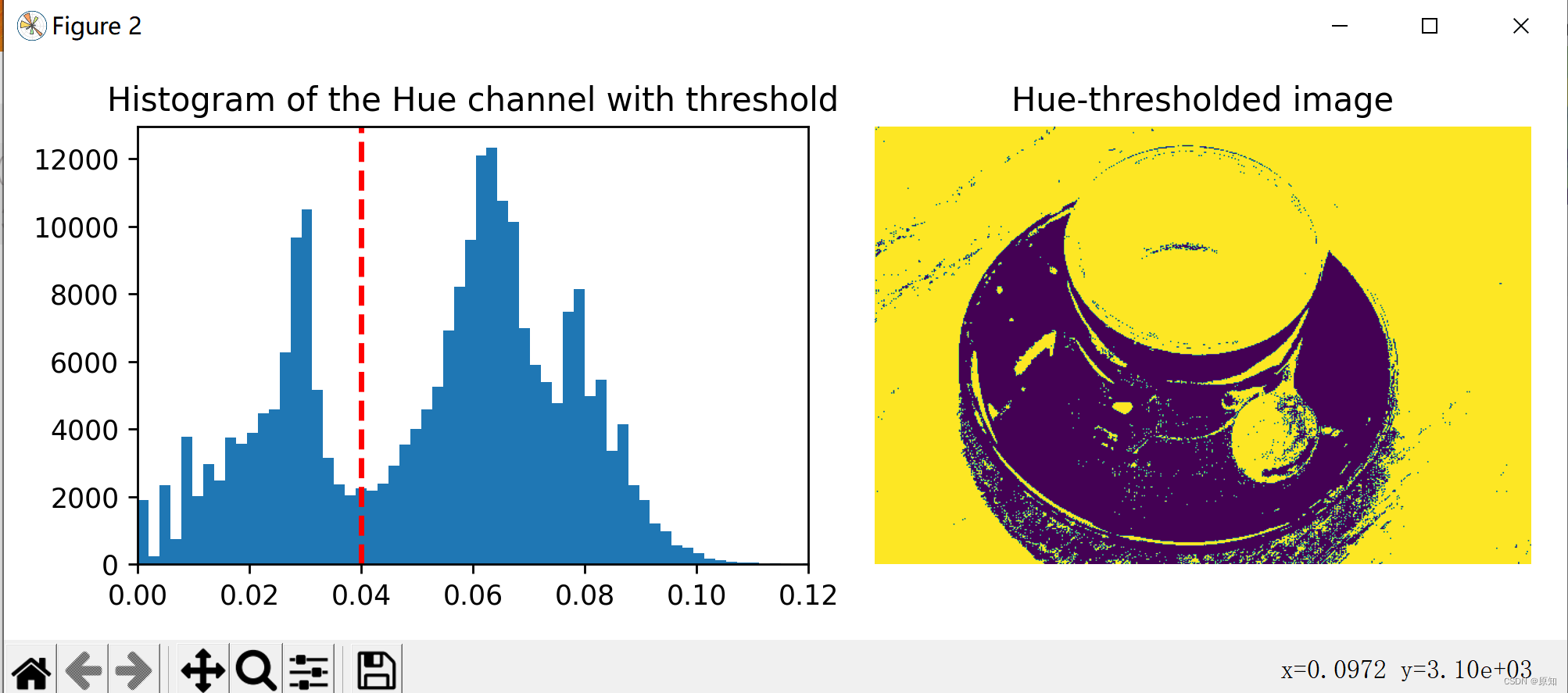
# stay Hue Set a threshold on the channel , Separate the cup from the background :
hue_threshold = 0.04# Why is this passage 0.04
binary_img = hue_img > hue_threshold
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(8, 3))
''' plt.hist Function is used to draw histogram . The function prototype : plt.hist(x, bins=None) Parameters x It's a one-dimensional array ,bins It can be understood as the number of rectangles , The default is 10. '''
ax0.hist(hue_img.ravel(), 512)#512 Is the number of histogram bars Set by yourself
ax0.set_title("Histogram of the Hue channel with threshold")#Hue Channel histogram with threshold
#matplotlib Library axiss Module Axes.axvline() The function is used to add a vertical line on the axis .
ax0.axvline(x=hue_threshold, color='r', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2)
#matplotlib Library axiss Module Axes.set_xbound() Function to set x The upper and lower numerical boundaries of the axis .
ax0.set_xbound(0, 0.12)
ax1.imshow(binary_img)
ax1.set_title("Hue-thresholded image")
ax1.axis('off')
fig.tight_layout()
# stay Value Perform an additional threshold on the channel , Partially remove the shadow of the cup :
fig, ax0 = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 3))
value_threshold = 0.10
binary_img = (hue_img > hue_threshold) | (value_img < value_threshold)
ax0.imshow(binary_img)
ax0.set_title("Hue and value thresholded image")
ax0.axis('off')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()

3、 Histogram matching
This example shows the characteristics of histogram matching . It manipulates the pixels of the input image , Match its histogram with the histogram of the reference image .
If the image has more than one channel , As long as the number of channels in the input image and the reference image is equal , Then match each channel independently .
Histogram matching can be used as a lightweight normalization in image processing , For example, feature matching , Especially in images from different sources or different conditions ( Namely light ) In the case of shooting .
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage import exposure
from skimage.exposure import match_histograms
reference = data.coffee()
image = data.chelsea()
matched = match_histograms(image, reference, channel_axis=-1)
''' '''
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 3),
sharex=True, sharey=True)
for aa in (ax1, ax2, ax3):
aa.set_axis_off()
ax1.imshow(image)
ax1.set_title('Source')
ax2.imshow(reference)
ax2.set_title('Reference')
ax3.imshow(matched)
ax3.set_title('Matched')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
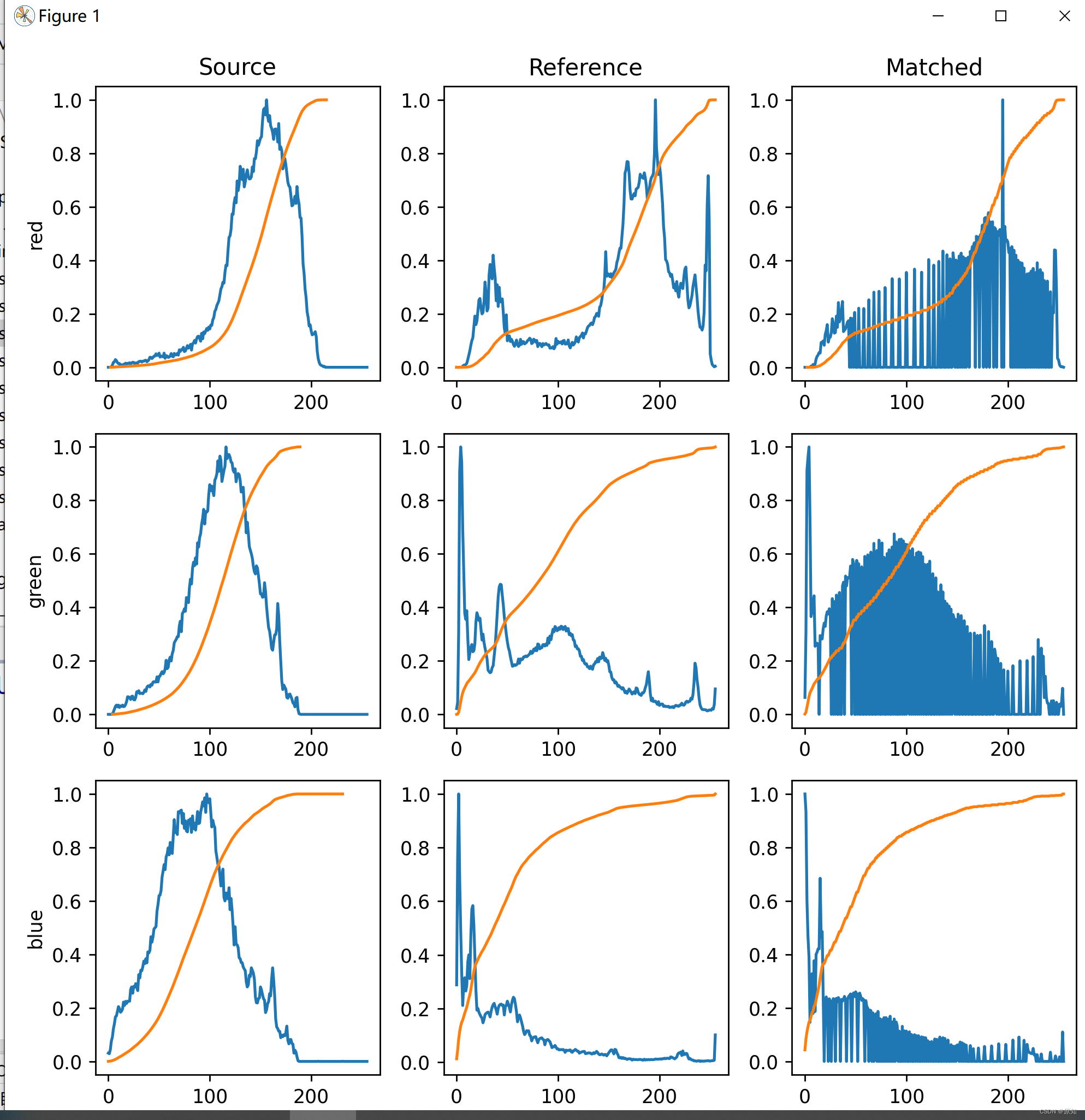
# To illustrate the effect of histogram matching , We draw each RGB Histogram and cumulative histogram of channels .
# Obviously , The matching image of each channel has the same cumulative histogram as the reference image .
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 8))
#enumerate This adds an index , At the same time, it can read the elements
for i, img in enumerate((image, reference, matched)):
for c, c_color in enumerate(('red', 'green', 'blue')):
img_hist, bins = exposure.histogram(img[..., c], source_range='dtype')
# The largest value of each group of data divided by the data is normalization . The maximum value after processing is 1, Other values are less than 1 Number of numbers .
# In the histogram bin The meaning of : To calculate the color histogram, we need to divide the color space into several small color intervals , That is, histogram bin, The color histogram is obtained by calculating the inner pixels of color in each cell ,bin The more , The stronger the resolution of histogram to color , But it increases the burden of computers . namely ( As shown in the figure above 10 Vertical bar area , Each vertical bar area is called a bin)
axes[c, i].plot(bin, img_hist / img_hist.max())
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(img[..., c])
axes[c, i].plot(bins, img_cdf)
axes[c, 0].set_ylabel(c_color)
print(c,i)
axes[0, 0].set_title('Source')
axes[0, 1].set_title('Reference')
axes[0, 2].set_title('Matched')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
annotation :
1、 Returns the histogram of the image
cucim.skimage.exposure.histogram(image, nbins=256, source_range='image', normalize=False)
Returns the histogram of the image , And numpy.histogram Different , This function returns bin Center of , And will not recombine integer arrays .
For integer arrays , Each integer value has its own bin, This improves speed and intensity-resolution.
Calculate histogram on flattened image : For color images , This function should be used separately on each channel to obtain the histogram of each color channel .
Parameters :
image: Array , The input image .
nbins: Integers , Optional , Used to calculate the histogram bin Number . For integer arrays , This value will be ignored .
source_range: character string , Optional ,‘image’( Default ) Determine the range of the input image . ‘dtype’ Determine the expected range of the data type image .
normalize: Boolean type , Optional , If True, The histogram is normalized by the sum of its values .
Return value :
hist: Array , Histogram value .
bin_centers: Array ,bin The value of the center .
2、 Returns the cumulative distribution function of a given image (cdf).
cucim.skimage.exposure.cumulative_distribution(image, nbins=256)
Parameters :
image: Array , Image array .
nbins: Integers , Optional , Image histogram of bin Number .
return :
img_cdf: Array , The value of the cumulative distribution function .
bin_centers: Array , The center of the box .
3、 Histogram matching (histogram matching)
meaning : Make the cumulative histogram of the source image consistent with the target image
from skimage.exposure import match_histograms
Parameters 1: The source image ; Parameters 2: Target image ; Parameters 3: Multi channel matching
matched = match_histograms(image, reference, multichannel=True)

边栏推荐
- 【Seaborn】组合图表:PairPlot和JointPlot
- Sort out several important Android knowledge and advanced Android development interview questions
- 正在准备面试,分享面经
- Personal notes of graphics (4)
- 如何在软件研发阶段落地安全实践
- 面向接口编程
- 应用在温度检测仪中的温度传感芯片
- Blue Bridge Cup final XOR conversion 100 points
- LeetCode 1031. Maximum sum of two non overlapping subarrays
- QT video transmission
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
As an Android Developer programmer, Android advanced interview
Talk about the realization of authority control and transaction record function of SAP system
time标准库
网关Gateway的介绍与使用
如何在软件研发阶段落地安全实践
LeetCode 213. 打家劫舍 II 每日一题
在哪个期货公司开期货户最安全?
Binary search tree (features)
Sort out several important Android knowledge and advanced Android development interview questions
直接上干货,100%好评
skimage学习(2)——RGB转灰度、RGB 转 HSV、直方图匹配
Personal notes of graphics (2)
【图像传感器】相关双采样CDS
C语言进阶——函数指针
LeetCode 1986. The minimum working time to complete the task is one question per day
Module VI
AutoLISP series (1): function function 1
typescript ts 基础知识之类型声明
LeetCode 312. Poke balloon daily
SqlServer2014+: 创建表的同时创建索引