当前位置:网站首页>1.C语言初阶练习题(1)
1.C语言初阶练习题(1)
2022-07-06 09:20:00 【是王久久阿】
目录
TEXT 1(函数与三目操作符)
写一个函数,输入两个不同的整数,求较大的那一个。
int max(int x, int y)//需要返回值,所以设置成int,如果不需要返回值,可以设置void
{
return (x > y ? x:y);//三目操作符(条件操作符)
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("较大的那个数是%d\n", max(a, b));
return 0;
}介绍一下三目操作符:
- 三目操作符的格式(表达式1?表达式2:表达式3)
- 表达式1为真,执行表达式2;若表达式1为假,执行表达式3。
- (x > y ? x:y)的意思为:若是x>y为真,则返回x;若是x<y为假,则返回y。
当函数需要返回值时,将函数类型设置为int,再return一个整型即可。如果函数不需要返回值,将函数类型设置为void即可。
因为a、b都是整型变量,所以将a、b的参数传给max函数时,max函数也需要用整型去接收,这里a和b是实参,x和y是形参,形参是实参的临时拷贝,改变形参并不会改变实参,如何通过形参改变实参呢?看TEXT 2。
TEXT 2(传参)
写一个函数,交换两个变量的数值。
void change(int* px, int* py)//因为穿的是地址,所以要用指针接收,px、py为指针变量
{
int i = 0;
i = *px; //通过地址找到a、b的值,间接改变a、b
*px = *py;
*py = i;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
printf("交换前:a=%d,b=%d\n", a, b);
change(&a, &b);//用取地址符号,将a、b的地址传给函数
printf("交换后:a=%d,b=%d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}通过地址可以实现改变实参,这里我们通过取地址符号将a、b的地址传给px、py,因为传的参数是整型,这里用整型指针int*接收,px、py就是指针变量,存放着a、b的地址。
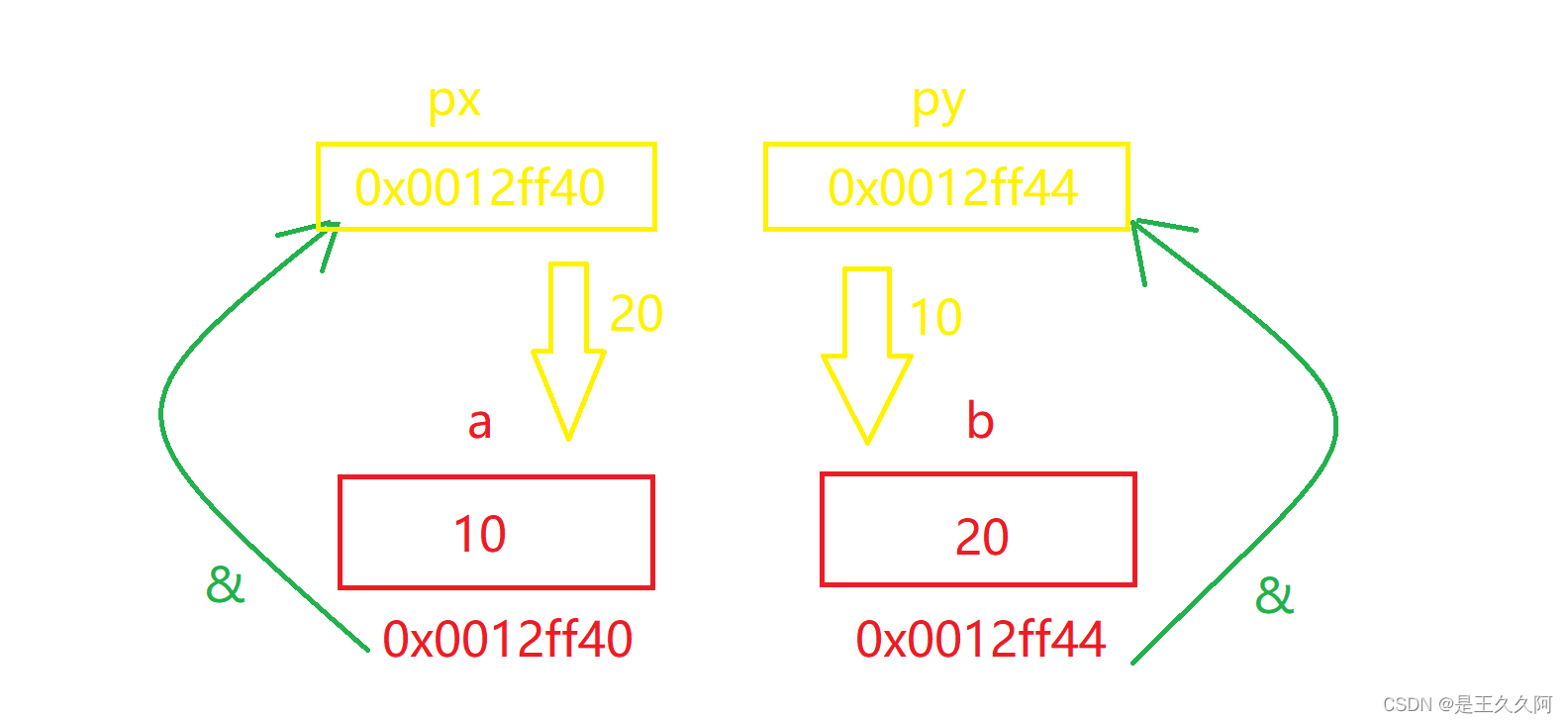
假设a的地址为0x0012ff40,b的地址为0x0012ff44,当我们通过取地址符号将a、b的地址传给px、py后,px、py里面存放的就是a和b的地址,通过改变地址里存放的数据,进而间接改变a、b的值。数组传参时,传的是首元素的地址。
TEXT 3(return)
已知一个函数y=f(x),当x < 0时,y = 10;当x = 0时,y = 0;当x > 0时,y = -10
输入一个整数x(-10000<x<10000),求其输出的值y。
#include<stdio.h>
int fun(int x)
{
if (x > 0)
return -10;
else if (x < 0)
return 10;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("当x=%d时,y=%d", x, fun(x));
return 0;
}在定义的函数中,如果包含多层嵌套,可以用return跳出函数,直接返回。
TEXT 4(取商和取模)
给定两个整数a和b (0 < a,b < 10,000),计算a除以b的整数商和余数。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("a/b=%d,a%%b=%d\n", a / b, a % b);//想要打印%需要%%
return 0;
}%%为转义字符,作用是显示%。
TEXT 5(ASCII码)
字符常量或字符变量表示的字符在内存中以ASCII码形式存储。转换以下ASCII码为对应字符并输出他们。73, 32, 99, 97, 110, 32, 100, 111, 32, 105, 116 , 33
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[13] = { 73, 32, 99, 97, 110, 32, 100, 111, 32, 105, 116 , 33 };
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}putchar也可以用ASCII码输出对应的字符,但是putchar每次只能输出一个字符,想要输出字符串比较麻烦。
TEXT 6(设置域宽)
输入一个人的出生日期(包括年月日),年月日之间的数字没有分隔符,将该生日中的年、月、日分别输出。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0;
scanf("%4d%2d%2d", &year, &month, &day);//通过设置域宽截取数据
printf("year=%d\nmonth=%d\nday=%d\n", year, month, day);
return 0;
}通过设置域宽让scanf截取数据,例如%4d的意思是:域宽为4,在其中的数据会存放到year里。
TEXT 7(转义字符)
在屏幕上打印
printf("Hello world!\n");
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("printf\(\"Hello world!\\n\"\)\;\n");
printf("cout << \"Hello world!\" << endl;\n");
return 0;
}当想打印的内容与转义字符混淆时,在其面前加入一个\即可,例如想打印一个“\n”,只需要“\\n”即可。
TEXT 8(for循环)
打印1-100之间所有3的倍数的数字
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
for (num = 1; num <= 100; num++)
{
if (num % 3 == 0)
{
printf("%d ", num);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
改代码还可以写成:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
for (num = 3; num <= 100; num+=3)
{
printf("%d ", num);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}基于我们对数学的了解,可以直接设置每次打印3的倍数,省略判断的部分。
TEXT 9(找最大数)
获得4名同学的成绩,编程找到最高分。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
int max = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
if (arr[i] > max)
{
max = arr[i];
}
}
printf("最高的成绩为%d\n", max);
return 0;
}因为成绩不可能是负数,所以假设最高分为0分,每次输入成绩时都判断一下,如果比当前最高分高,则更新最高分。(该方法的好处是每次输入数据之后都会判断,当输入完成后结果也判断出来,非常简便迅速)
TEXT 10(冒泡排序)
写代码将给定的5个整数数按从小到大输出。
#include<stdio.h>
void change(int* px, int* py)//交换两个数
{
int i = 0;
i = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = i;
}
int main()
{
int arr[6] = {7,8,1,2,6};
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5-1-i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
change(&arr[j], &arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[j]);
}
return 0;
}冒泡排序的核心思想为相邻两个数比大小,大的往后站。第一轮排序可以找到最大值,第二轮排序可以找到第二大的值,当排序进行到第n-1轮时,顺序已然排好了。

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

TYUT太原理工大学2022“mao gai”必背

Smart classroom solution and mobile teaching concept description

There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
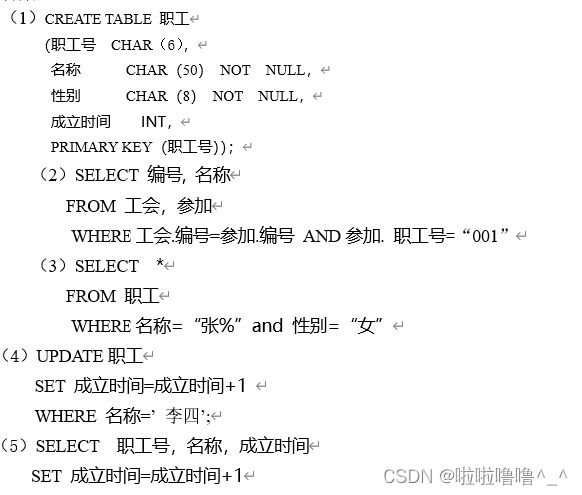
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之数据库操作
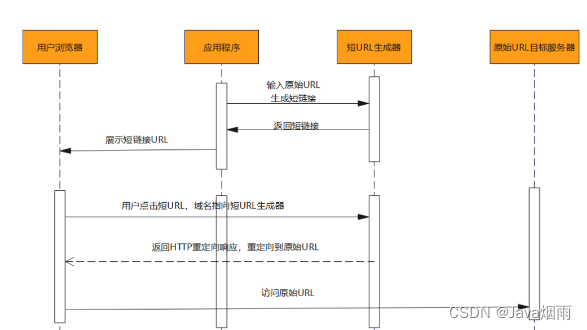
How do architects draw system architecture blueprints?
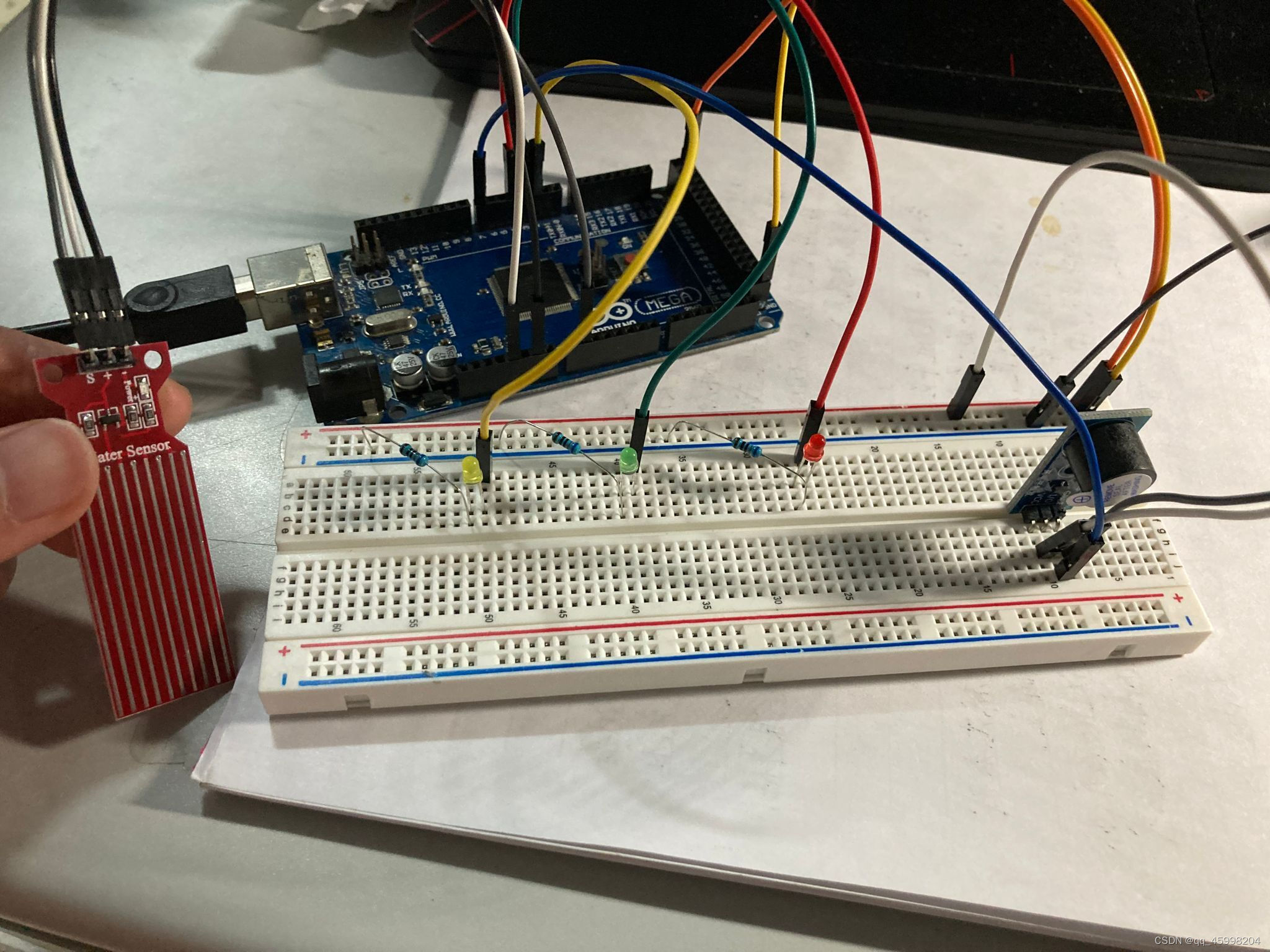
arduino+水位传感器+led显示+蜂鸣器报警
4.二分查找
阿里云一面:并发场景下的底层细节 - 伪共享问题
系统设计学习(一)Design Pastebin.com (or Bit.ly)
Iterable、Collection、List 的常见方法签名以及含义
随机推荐
Exception: ioexception:stream closed
Comparison between FileInputStream and bufferedinputstream
Voir ui plus version 1.3.1 pour améliorer l'expérience Typescript
4.30动态内存分配笔记
MySQL Database Constraints
Introduction and use of redis
Arduino+ water level sensor +led display + buzzer alarm
Interview Essentials: talk about the various implementations of distributed locks!
Differences and application scenarios between MySQL index clock B-tree, b+tree and hash indexes
7.数组、指针和数组的关系
2年经验总结,告诉你如何做好项目管理
初识C语言(上)
MySQL 30000 word essence summary + 100 interview questions, hanging the interviewer is more than enough (Collection Series
系统设计学习(二)Design a key-value cache to save the results of the most recent web server queries
Record: Navicat premium can't connect to MySQL for the first time
阿里云微服务(一)服务注册中心Nacos以及REST Template和Feign Client
Redis介绍与使用
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库之关系代数小题
(超详细onenet TCP协议接入)arduino+esp8266-01s接入物联网平台,上传实时采集数据/TCP透传(以及lua脚本如何获取和编写)
String类