当前位置:网站首页>tensorflow包tf.keras模块构建和训练深度学习模型
tensorflow包tf.keras模块构建和训练深度学习模型
2022-07-27 08:45:00 【qq_27390023】
1. 读入数据
以mnist数据为例,手写数字(0-9)的分类问题,有监督学习。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
### 1. 读入数据
# mnist数据集作为演示数据
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
assert x_train.shape == (60000, 28, 28)
assert x_test.shape == (10000, 28, 28)
assert y_train.shape == (60000,)
assert y_test.shape == (10000,)
# print(x_train[1]) # 第一个图片数据
#print(y_train)
#增加一个维度: 图片数,行,列,图层
x_train=np.expand_dims(x_train,axis = 3)
x_test=np.expand_dims(x_test,axis = 3)
input_shape = x_train.shape[1:] # 去掉最高维!!!
print(input_shape)
#input_shape = tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28,28))
# 数据re-scale 到 0~1.0之间
x_train = x_train/255.
x_test = x_test/255.
# print(x_train[1])
# y值转化为one-hot编码
def one_hot(labels):
onehot_labels=np.zeros(shape=[len(labels),10])
for i in range(len(labels)):
index=labels[i]
onehot_labels[i][index]=1
return onehot_labels
y_train = one_hot(y_train)
y_test = one_hot(y_test)
print(y_train[0])2.通过计算过程搭建模型
### 2.通过计算过程搭建模型
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=input_shape) # Returns a placeholder tensor
x = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(inputs)
# A layer instance is callable on a tensor, and returns a tensor.
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(x)
predictions = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
# Instantiate the model given inputs and outputs.
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=predictions)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=['accuracy'])
print("model fit")
model.fit(x=x_train,y=y_train,batch_size=128, epochs=10)
print("model prediction")
test_loss,test_acc=model.evaluate(x=x_test,y=y_test)
print("Test Accuracy %.2f"%test_acc)3. 通过Sequential模型
### 3. 通过Sequential模型
## 超参数设置
#FILTERS_1 = 32
#KERNEL_SIZE_1 = 5
#STRIDES_1 = (1,1)
#FILTERS_2 = 64
#KERNEL_SIZE_2 = 4
#STRIDES_2 = (2,2)
#POOL_SIZE = (2,2)
#DROPOUT_RATE = 0.25
#DENSE_UNIT_NUM_1 = 128
#DENSE_UNIT_NUM_2 = 10
#BATCH_SIZE = 128
#EPOCHS_NUM=100
## 全连接
def mnist_net(input_shape):
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=input_shape)) #输出层
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation=tf.nn.relu)) #隐含层
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10, activation=tf.nn.softmax)) #输出层
return model
## 卷积神经网络
def mnist_cnn(input_shape):
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=32,kernel_size = 5,strides = (1,1),
padding = 'same',activation = tf.nn.relu,input_shape = input_shape))
# kernel_size = (5,5)
model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2), padding = 'valid'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=64,kernel_size = 3,strides = (1,1),padding = 'same',activation = tf.nn.relu))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2), padding = 'valid'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128,activation = tf.nn.relu))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10,activation = tf.nn.softmax))
return model
#模型训练与预测
my_model = mnist_net(input_shape)
#my_model = mnist_cnn(input_shape)
my_model.compile(optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=['accuracy'])
print("model fit")
my_model.fit(x=x_train,y=y_train,batch_size=64, epochs=10)
print("model prediction")
test_loss,test_acc=my_model.evaluate(x=x_test,y=y_test)
print("Test Accuracy %.2f"%test_acc)4. 自定义模型类
### 4.通过模型类
## 定义模型类,重写__init__和call函数
class My_model(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self,
input_shape,
l1=True,
l2=False,
kernel_size_1=5,
coefficient=0.01,
drop_rate=0.1,
hidden_dim=128,
feature_dim=10):
super(My_model, self).__init__()
tf.keras.backend.set_floatx('float64')
self.l1 = tf.keras.regularizers.l1(l=coefficient)
self.l2 = tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=coefficient)
self.l1l2 = tf.keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=coefficient, l2=coefficient)
if l1 and l2:
self.reg = self.l1l2
else:
if l1:
self.reg = self.l1
elif l2:
self.reg = self.l2
else:
self.reg = None
self.conv2D_1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=32,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = (1,1),
padding = 'same',
activation = tf.nn.relu,
input_shape = input_shape)
self.maxPool2D_1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),
strides = (2,2),
padding = 'valid')
self.conv2D_2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=64,
kernel_size = 3,
strides = (1,1),
padding = 'same',
activation = tf.nn.relu,
input_shape = input_shape)
self.maxPool2D_2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),
strides = (2,2),
padding = 'valid')
self.dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(drop_rate)
self.flatten = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()
self.dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(hidden_dim,
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_regularizer=self.reg)
self.final_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10,activation = tf.nn.softmax)
def call(self,x_input):
# 第一次特征提取
x = self.conv2D_1(x_input)
x = self.maxPool2D_1(x)
# 第一次特征提取
x = self.conv2D_2(x)
x = self.maxPool2D_2(x)
# dropout提高模型的泛化
x = self.dropout(x)
# 两层全连接
features1 = self.flatten(x)
features2 = self.dense(features1)
model_output = self.final_output(features2)
# return model_output,features1,features2 # 返回多个值,无法用model.fit
return model_output
my_model = My_model(input_shape,
l1=True,
l2=False,
kernel_size_1=5,
coefficient=0.01,
drop_rate=0.1,
hidden_dim=128,
feature_dim=10)
my_model.compile(optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss="categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=['accuracy'])
print(y_train.shape)
print("model fit")
my_model.fit(x=x_train,y=y_train,batch_size=512, epochs=3)
print("model prediction")
test_loss,test_acc=my_model.evaluate(x=x_test,y=y_test)
print("Test Accuracy %.2f"%test_acc)
## 定义模型训练函数(对于复杂模型,需要手动定义损失函数和模型训练方法)
import math
## 定义损失函数
# 当损失函数比较复杂时,该函数很有必要
def get_loss(y_pre,y_input):
cce = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy()
all_loss = cce(y_pre,y_input)
return all_loss
## 定义梯度计算函数
def get_grad(model, x_input, y_input):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
model_output = model(x_input)
all_loss = get_loss(model_output,y_input) # 调用get_loss函数
grads = tape.gradient([all_loss],model.trainable_variables)
return all_loss, grads
## 定义训练函数
def train_model(model,
x_train,
y_train,
batch_size=512,
optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
num_epochs=5):
# 确定stop条件
for epoch in range(1,num_epochs+1):
print("Epoch {}/{}".format(epoch,num_epochs))
step = 0
step_num = math.ceil(len(x_train)/batch_size)
for x in range(0, len(x_train), batch_size):
step += 1
x_inp = x_train[x: min(len(x_train),x + batch_size)]
y_inp = y_train[x: min(len(x_train),x + batch_size)]
all_loss, grads = get_grad(model, x_inp, y_inp)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
print("\r", end="")
print ("{}/{}".format(step,step_num),end=" ")
print("loss:", all_loss.numpy())
# 打印进度条
#print("\r", end="")
#print("{}/{} [".format(step,step_num),"=" * (step//2), end="")
return model
my_model = My_model(input_shape,
l1=True,
l2=False,
kernel_size_1=5,
coefficient=0.01,
drop_rate=0.1,
hidden_dim=128,
feature_dim=10)
trained_model = train_model(my_model,x_train,y_train,num_epochs=3)
print("training is over.")
# 模型在测试集上的表现
y_test_pre = trained_model(x_test)
test_loss = get_loss(y_test_pre,y_test) # 调用get_loss函
print("Test Loss %.2f"%test_loss)
test_acc=tf.keras.metrics.CategoricalAccuracy()(y_test_pre,y_test)
print("Test Accuracy %.2f"%test_acc)参考:
边栏推荐
- 4275. Dijkstra序列
- Vertical align cannot align the picture and text vertically
- Hundreds of people participated. What are these people talking about in the opengauss open source community?
- JS basic exercises
- 【nonebot2】几个简单的机器人模块(一言+彩虹屁+每日60s)
- 第2章 前台数据展现
- Using ecological power, opengauss breaks through the performance bottleneck
- Cenos7 update MariaDB
- 691. 立方体IV
- Matlab数据导入--importdata和load函数
猜你喜欢

Create a project to realize login and registration, generate JWT, and send verification code

4274. 后缀表达式
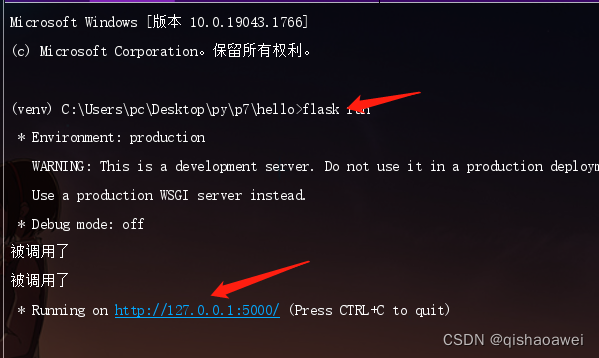
P7 Day1 get to know the flask framework

4276. 擅长C

redis 网络IO

Initial summary of flask framework creation project
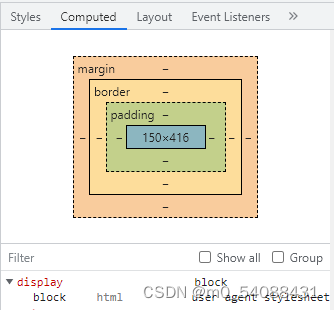
Element display mode: block level, inline, inline block, nesting specification, display mode conversion

Redis network IO
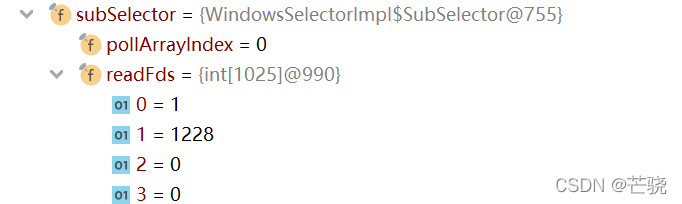
NIO总结文——一篇读懂NIO整个流程

Flink1.15源码阅读flink-clients客户端执行流程(阅读较枯燥)
随机推荐
Background image related applications - full, adaptive
四个开源的人脸识别项目分享
Flask one to many database creation, basic addition, deletion, modification and query
How to view instances of software objects in QSIM?
Hangzhou E-Commerce Research Institute released an explanation of the new term "digital existence"
低成本、低门槛、易部署,4800+万户中小企业数字化转型新选择
JS rotation chart
Digital intelligence innovation
VS Code中#include报错(新建的头文件)
Horse walking oblique sun (backtracking method)
redis 网络IO
3311. Longest arithmetic
杭州电子商务研究院发布“数字化存在”新名词解释
Flask project configuration
无法获取下列许可SOLIDWORKS Standard,无法找到使用许可文件。(-1,359,2)。
arguments
数智革新
It's better to be full than delicious; It's better to be drunk than drunk
Redis network IO
Arm system call exception assembly