当前位置:网站首页>Summary of all knowledge points of C language
Summary of all knowledge points of C language
2022-06-26 16:39:00 【Woody heart】
C Language
Catalog
- C Language
- One 、 Basic knowledge of
- Two 、 data type
- 3、 ... and 、 String and format input and output
- (1) Single character literal and string literal
- (2) Format input and output functions `scanf\fscanf\sscanf\printf\fprintf\sprintf`
- (3) String output function
- (4) String input function
- (5) String function `strcpy\strcmp\strlen\strcat\strchr`
- (6) Character conversion function `atoi\atof\atol`
- (7) Memory manipulation function
- Four 、 Process control ( loop )
- 5、 ... and 、 Process control ( Select and branch )
- 6、 ... and 、 Character input / Output and input verification
- 7、 ... and 、 function
- 8、 ... and 、 Array
- Nine 、 The pointer
- (1) Definition of pointer
- (2) Unary operator `&` and `*`
- (3) When to use the pointer ?
- (4) Basic operations of pointer variables
- (5)`const` Modify a pointer
- (6) The secondary pointer
- (7) Pointer array ( An array of pointers )
- (8) Array pointer ( Pointer to array )
- (9) A function pointer
- (10) Function pointer array
- Ten 、 Storage class 、 Link and memory management
- 11、 ... and 、 File with the IO
- Twelve 、 Other data types
- 13、 ... and 、 Data storage format
- fourteen 、C The preprocessor
- 15、 ... and 、C library
- Reference
One 、 Basic knowledge of
(1)C Language keywords

auto break case char const continue default do double else enum extern float for goto if int long register return short signed sizeof static switch typedef union unsigned void volatile while
- auto—— automatic , All local variables are auto Embellished , These variables are automatically created and automatically destroyed .
- extern—— External , Used to declare external variables
- register—— Register key
- typedef—— Type renaming
- inline—— Inline function specifier
- _Noreturn—— Function specifiers , Indicates that the calling function will not return after the function completes the call
- _Static_assert—— Assert keywords , If there is a problem with the assertion, it will not be compiled , Print error messages
include and define None of them are keywords , They are preprocessing instructions .
(2)C The main part of the program
C A preprocessor is a preprocessor instruction ( With # Symbol start ) Find the source code program , And deal with them before you start compiling programs .
# define SOME 1 //C The preprocessor , Constant definition
# include <stdio.h> //C The preprocessor , Import header file
void function(void); // Function declaration
int main() //c Program entry
{
int n;
printf("Hello World!");
function();
return 0;
}
void function(void)
{
printf("Other function");
return 0;
}
(3) Escape sequences escape sequence

(4) Basic operators
Common basic operators include , Monocular operator :

Relational operators in binocular operators :

1. Assignment operator =
C The language allows multiple assignments
int a, b, c;
a = b = c = 98;
The value of the assignment expression is the value of the operand to the left of the assignment operator . for example :
while((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
ch = getchar() The value of this assignment expression is ch Value , Then judge ch != '\n', For flow control .
2. Arithmetic operator +、-、*、/
C The decimal part of the integer division result in the language will be directly discarded , Rather than rounding , This process is called truncation .
printf("integer division 5/4 is %d", 5/4); // The result is 1
3. The comma operator ,
The comma operator has two properties , First , It ensures that the expressions separated by it are evaluated from left to right ( In other words , A comma is a sequence point , So all the side effects of the items on the left side of the comma occur before the program executes the items on the right side of the comma ). secondly , The value of the entire comma expression is the value of the right item .
x = (y = 3, (z=++y+2) + 5) // Final x The value of is 11
Commas can also be used as separators , This is its most common use .
char ch, date;
4. Logical operators &&、||、!

C99 The standard adds spelling that can replace logical operators , They are defined in iso646.h Header file , If the header file is included in the program , You can use and replace &&, use or replace ||, use not replace !, This is the sum of python Logical operators of are consistent .
# include <iso646.h>
and == &&;
or == ||;
not == !;
Logical expressions are evaluated from left to right . Once you find a factor that makes the whole expression false , Immediately stop the evaluation of the rest .
5. Conditional operator ?( Ternary operator ):
Conditional operator ( Ternary operator ) yes C The only ternary operator in the language . The general form of conditional expression is as follows :
expression1 ? expression2 : expression3
If expression1 It's true , Then the value of the entire conditional expression is the same as expression2 The value of is the same ; If expression1 For false , Then the sum of the values of the entire conditional expression expression3 identical .
(5 > 3) ? 1 : 0; // The output value is 1
And python The ternary expression of is similar to .
6. An operator <<、>>、^、~、&、|:
Move left <<, Move right >>, Bitwise XOR ^, Press ( Binary system ) Bit inversion ~,& Bitwise AND ,| Press bit or .
The specific operation of moving left is to discard the left , Zero on the right , The specific operation of moving right is to discard the right , For unsigned numbers, fill the left with zero , For signed numbers, the left side is supplemented with sign bits .
int a, b =2;
a = b << 1;
a = b >> 1;
a = ~b;
7. Other operators
7.1sizeof Operators and size_t type
sizeof Operator returns the size of the operands in bytes ,C Language policy ,sizeof return size_t Type value , This is an unsigned type , But it is not a new type .sizeof The following parentheses can be omitted , This means that sizeof Is an operator ( Operator ) Not a function , But when sizeof When the byte size of the type needs to be taken , Brackets cannot be omitted .sizeof Operator can calculate the byte size of a variable or type , But we need to pay attention sizeof The contained expression is not involved in the calculation .
int n = 0;
size_t intsize;
intsize = sizeof(int);
7.2 Modulo operators %
Modulo operators can only be used for integers, not floating-point numbers .
7.3 Increment operator ++
++ Have prefix mode and suffix mode , The difference between prefix mode and suffix mode is :

The increment operator can facilitate process control
int num = 0;
while (num++ < 10) // Facilitate process control control num stay (1~10)
{
printf("curretn num is %d", num);
}
7.4 Decrement operator --
-- The use of and ++ Agreement , Both increasing and decreasing operations have high priority , Only () The priority of is higher than them .
7.5 Other assignment operators +=、-=、*=、/=、%= and &=、|=、^=、>>=、<<=

7.6 Subscript reference [], Function call (), Structural members . and -> Operator :
struct Stu
{
char name[30];
int age;
double float;
};
struct Stu s = {
" Zhang San ", 22, 99.9};
s.name, s.age, s.score // visit s Structure member variables for
(5) Compound statement compound statement
A compound statement is one or more statements enclosed in curly braces , Compound statements are also called blocks (Block).C Language and Python Different , stay C Indentation in the language does not work for the compiler , The compiler passes curly braces {} To identify blocks , Parsing instructions . The purpose of using indentation is to develop a good code style , Easy to read .
(6) Empty statement
A single one ; Will be treated as an empty statement that does nothing null statement.
Two 、 data type
(1) Integer types
Basic integer types include :
int
char
Characters are actually stored as integers .ASCII code .
_Bool
_BoolVariables of type can only store 1( really )0( false ). If you assign other non-zero values to_BoolType variable , This variable will be set to 1.C99 Provides stdbool.h The header file , This header file makes bool be called _Bool Another name for , And also put true and false They are defined as 1 and 0 Symbolic Constant of . After including the header file , The code can be written with C++ compatible , because C++ hold bool、true and false Defined as keyword .# include <stdio.h> # include <stdbool.h> int main(void) { printf("true is %d, false is %d", true, false) return 0; } // Output : true is 1, false is 0
**a. ** stay int On the basis of :
- int signed int
- unsigned int Unsigned integer
- short int (short) Short
- unsigned short int (unsigned short) Unsigned short
- long int (long) Long integer
- unsigned long int (unsigned long)
- long long int (long long) Longer integer
b. stay char On the basis of :
(2) Floating point type
(3) Byte size of type
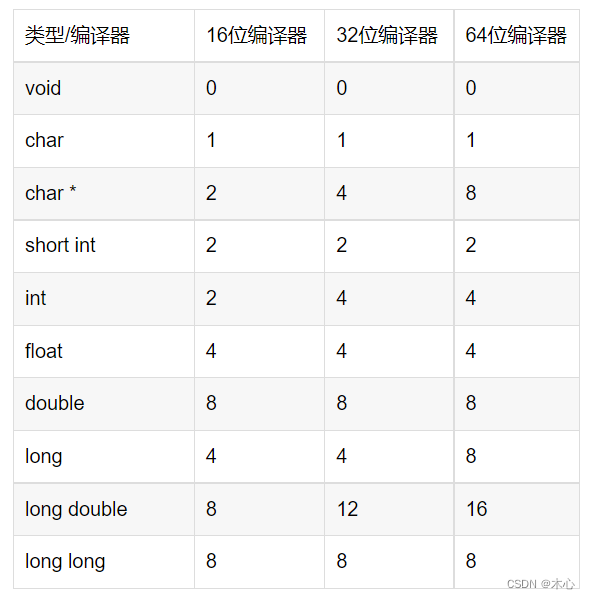
(4) Type conversion
C The language has a mechanism for automatic type conversion , But automatic type conversion is often error prone , This error can be avoided by using cast . A cast character is a parenthesis placed before a quantity () Enclosed type name , The type name is the target type you want to convert to . parentheses () The type enclosed with it constitutes Cast operators . The general form is (type)
mice = 1.6 + 1.7;
mice = (int)1.6 + (int)1.7;
In addition to regular type conversions ,C The language also has implicit type conversions , Be commonly called ( Improve the overall shape ).

** How to improve the integer ? Signed integers are promoted according to the sign bits of the data , If it is positive, then it can be complemented 0 To promote , If it's negative, then it's through complement 1 To promote . Unsigned integers are raised all through complement 0 To promote .** Let's take an example :
int main(void)
{
char a = 3;
char b = 127;
char c = a + b;
printf("%d\n",c); // Print -126
return 0;
}
This is because char Type takes up one byte in total 8 position , The value is -127~127 Between ,127+3 The binary result of is 1000010, If it is converted to an integer, it is -126.
3、 ... and 、 String and format input and output
(1) Single character literal and string literal
C A single character literal in a language is stored in char Type in the , however C The language does not have a data format specifically for storing strings , Usually use char Array of To store strings , The single character literal is '' Single quotation marks are used to indicate , The literal value of a string is "" Use double quotation marks to indicate :
char bit = 'a';
char bit8[8] = "abcdefgh";

The characters in double quotes and the compiler automatically add the ending \0 character , Are stored in memory as strings , If there is no interval between string literals , Or separated by white space characters ,C It is treated as a concatenated string literal . for example :
char greeting[50] = "Hello, and" " how are you" " today!";
char greeting[50] = "Hello, and how are you totday!"; // The two are equivalent
String constants belong to the static storage category (static storage class), This shows that if you use a string constant in a function , The string will only be stored once , Even if the function is called more than once , And exist throughout the life cycle of the program . The contents enclosed in double quotation marks are treated as pointers to the storage location of the string . for example :
"space of string"; // This string , It's actually an array , The array itself is the address pointing to the first element of the array
printf("%c", *"space of string"); // The printed result should be the first element --s
You can also use Pointer representation 、 Array notation creates a string , for example :
const char *ptr1 = "Something is pointing at me."; // Pointer representation
const char ar1[] = "Something is pointing at me."; // Array representation , The two declarations are almost the same
All in all , Initializing an array copies the string of the static storage area into the array , The initialization pointer only copies the address of the string to the pointer . The array name created by the array representation is a constant , Pointer notation creates pointers that are variables . Both can be represented by arrays , You can modify the array ( because , The elements of the array are variables , But the array name is not a variable ), And you can add and subtract pointers , But only pointer variables created using pointer notation can be incremented and decremented . An array is a copy of a variable in memory ( copy ), A pointer is a reference to a variable in memory .
(2) Format input and output functions scanf\fscanf\sscanf\printf\fprintf\sprintf
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Print character output | putchar | stdio.h | Output single character , Character usage '' |
| Get character input | getchar | stdio.h | Get single character input , Character usage '' |
| Print string output | puts | stdio.h | Output single line characters , Until I met \0 And automatically add a newline character at the end \n. |
| Get string input | gets | stdio.h | Get the entire line of input , It reads the entire line of input , Until the line break , Then discard the newline , Store other characters , And add a null character at the end of these characters to make it a string . |
| Format input | scanf | stdio.h | Formatted input function for standard input –stdin |
| Format input | fscanf | stdio.h | Formatted input statements for all streams –stdin/ file |
| Format input | sscanf | stdio.h | Read formatted input data from a string |
| Format output | printf | stdio.h | Formatted output function for standard output –stdout |
| Format output | fprintf | stdio.h | Formatted output statements for all streams –stdout/ file |
| Format output | sprintf | stdio.h | Convert a formatted data into a string |
1、 Use printf()
printf and scanf From the header file <stdio.h>
printf and scanf The parameters of include , Format strings and parameters ,printf Function has a return value , The return value is the printed character length .

Modifier of conversion description
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-b43SathP-1655802386019)(D:\Study_Data\Markdown_Note\figure\image-20220424151445735.png)]
printf The tag , And python The format control of is very similar to

2、 Use scanf()
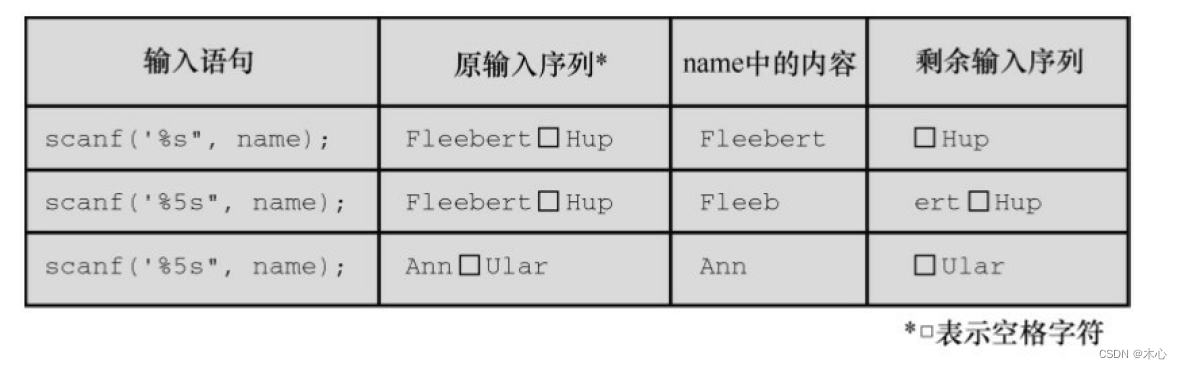
scanf() Read the value of the basic variable type , You need to add a before the variable name &,& It is called the address operator .scanf() Read a string into a character array , No need to use &.scanf() The function uses white space ( A newline 、 Tabs and spaces ) Divide the input into multiple fields . Skip whitespace when matching the conversion description to the fields in turn . The only exception is %c Conversion description , according to %c,scanf() Will read every character , Including blanks .scanf() Conversion instructions and printf() Almost the same .scanf There are two ways to determine the end of the input , The first one is , If you use %s Conversion instructions , The following is a blank character ( Blank line 、 Space 、 Tabs and line breaks ) As the end of a character .** The second kind , If field width is specified , Such as %10s that scanf() Will read 10 Characters or stop reading to the first blank character ( The condition that is satisfied first is the condition that the input ends ).** If you use... With multiple conversion instructions scanf(),C Specify to stop reading at the first wrong position .scanf Function has a return value ,scanf The return value of is the number of items successfully read .
3、* Usage of
printf() Medium * Can be used instead of , Character assignment in format control , for example :
printf("%*.*f", width, precision, 3.14159); //width Specify the character length ,precision Specify the precision to be retained after the decimal point
scanf() Medium * Put in % And conversion characters , You can make scanf() Skip the corresponding output item , for example :
int n;
printf("Please enter three integers:\n");
scanf("%*d %*d %d\n", &n); // Skipped the first two entries
printf("The last integer is %d\n", n);
4、 Use getchar()
getchar() and putchar() The functions are all from the header file <stdio.h>,getchar() The function takes no arguments , It returns the next character from the input queue . for example , The following statement reads the input of the next character , And assign the value of this character to the variable ch:
ch = getchar();
// And the following scanf The effect is the same
scanf("%c", &ch);
5、 Use putchar()
putchar() Function prints its arguments , For example, the following statement assigns the previous value to ch The value of is printed as a character :
putchar(ch);
// With the following printf The effect is the same
printf("%c", ch);
Be careful getchar() and putchar() No conversion instructions are required , Because they can only handle a single character .
(3) String output function
| function | Function name | The header file | purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Character input function | fgetc | stdio.h | All input streams |
| Text line input function | fgets | stdio.h | All input streams |
| Format input function | fscanf | stdio.h | All input streams |
| Binary input function | fwrite | stdio.h | file |
| Character output function | fputc | stdio.h | All output streams |
| Text line output function | fputs | stdio.h | All output streams |
| Format output function | fprintf | stdio.h | All output streams |
| Binary output function | fread | stdio.h | file |
puts() Output single line characters , Until I met \0 And automatically add a newline character at the end \n.

fputs() This function is used to process file output , Be similar to fprintf

(4) String input function
gets() Get the entire line of input , It reads the entire line of input , Until the line break , Then discard the newline , Store other characters , And add a null character at the end of these characters to make it a string .
fgets() This function is specifically designed to handle file input , Be similar to fscanf

(5) String function strcpy\strcmp\strlen\strcat\strchr
String functions are contained in the header file string.h in
| function | Function name | Function details |
|---|---|---|
| Calculate string length | strlen | Encountered... While calculating string length \0 Stop length calculation |
| String splicing | strcat | The source string must be in \0 ending , And the character space must be large enough |
| String splicing | strncat | You can specify the number of characters to be spliced |
| String comparison | strcmp | Compare two strings character by character , according to ASCII Table for size comparison , Same back 0, The former is greater than the latter 1, The latter is greater than the former -1.strcmp Compare strings instead of Should use the "" instead of '' |
| String comparison | strncmp | You can specify the length of the comparison string , The length is calculated from the position of the first element of the string |
| String copy | strcpy | Copy the data from the source string to the destination string , And returns a pointer to the target string , And source The string pointer does not have to point to the beginning of the array , This property can copy part of the array ,strcpy Can copy \0 |
| String copy | strncpy | You can specify the length of the copy string , The length is calculated from the position of the first element of the string |
| Character lookup function | strchr | Find the target character in the source string , And return the address where the target character is first searched |
| String lookup function | strstr | Find the destination string in the source string , And return the address where the target string is first searched |
More character test functions isupper\islower\toupper\tolower See header file for details ctype.h
(6) Character conversion function atoi\atof\atol
atoi\atof\atol Convert the string to integer respectively , floating-point , Long integer value . The header file is included in stdlib.h in .
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convert a string to an integer value | atoi | stdlib.h | Returns the converted value , If no conversion is performed, it returns 0, The string should start with a number |
| Convert a string to a floating point type | atof | stdlib.h | Returns the converted value , If no conversion is performed, it returns 0, The string should start with a number |
| Converts a string to a long integer | atol | stdlib.h | Returns the converted value , If no conversion is performed, it returns 0, The string should start with a number |
| String by base Binary conversion to long integer | strtol | string.h | Returns the converted value , And save the unconverted character address to end Pointer |
| String by base Binary to unsigned long | strtoul | string.h | Returns the converted value , And save the unconverted character address to end Pointer |
| String by base Binary conversion to double precision floating point type | strtod | string.h | Returns the converted value , And save the unconverted character address to end Pointer |
(7) Memory manipulation function
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copy the contents of one block of memory to another | memcpy | string.h | memcpy It is assumed that there is no overlap between two pieces of memory , You need to specify the number of bytes of memory , Return to destination address |
| Copy the contents of one block of memory to another | memmove | string.h | memmove Do not assume that there is no overlap , You need to specify the number of bytes of copy memory to return to the destination address |
| according to ASCII Table compares the elements in two memory blocks one by one | memcmp | string.h | You need to specify the number of bytes to compare , Return value return -1、0、1 One of them |
| Set a block of memory to the specified content | memset | string.h | You need to specify the set number of bytes , Return the copy address of the target memory |
Four 、 Process control ( loop )
(1)while loop
while The loop consists of three parts , First of all while keyword , And then there was () Test conditions in , And finally {} Circulation body in . If there is only one statement in the loop body, you may not use {} Cover up .
while (expression)
statement
statement It can be a simple statement or a compound statement . Typical while The loop pseudocode is as follows
Get initial value
while ( The value meets the test conditions )
{
Process the value
Get the next value
}
(2) for loop
for The loop consists of three parts , First of all for keyword , And then there was () Control expression in , And finally {} Circulation body in . If there is only one statement in the loop body, you can omit {}. The control expression consists of three parts , Use two... Respectively ; separate , The first expression is initialization , Only in for Execute once at the beginning of the loop . The second expression is the test condition , Evaluate the expression before executing the loop , If the expression is false , The loop ends . The third expression performs parameter updates , Evaluate at the end of each cycle .
for (initialize; test; update)
stetement
statement It can be a simple statement or a compound statement . Typical for The loop pseudocode is as follows
for ( Get initial value ; The value meets the test conditions ; Get the next value )
{
Process the value
}
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int x;
int y = 55;
for (x = 1; y <= 75; y = (++x * 5) + 50)
printf("%10d %10d\n", x, y);
return 0;
}
// Output
1 55
2 60
3 65
4 70
5 75
Use this example to illustrate , The third expression performs parameter update at the end of each loop .
for loop One or more expressions can be omitted from the control expression of ( But don't omit ;), Just include a statement that can be ended in the loop .
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int ans, n;
ans = 2;
for (n = 3; ans <= 25; )
{
ans = ans * n;
printf("n = %d; ans = %d.\n", n, ans);
}
printf("n = %d; ans = %d.\n", n, ans);
return 0;
}
n = 3; ans = 6.
n = 3; ans = 18.
n = 3; ans = 54.
n = 3; ans = 54.
But one thing to note is that , Omitting the second expression is considered true , The cycle goes on all the time .
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
for (; ;)
printf("This is a bad loop\n");
return 0;
}
Will always print This is a bad loop.
The first expression doesn't have to be an initial value for a variable , You can also use printf(), Just remember , The first expression is executed only once at the beginning of the loop . The last expression does not have to update the parameters of the variable , You can also use sacnf(), Just remember , The last expression is executed after each loop .
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int num = 0;
for (printf("Keep entering numbers!\n"); num != 6; scanf("%d", &num));
printf("That's the one I want!\n");
return 0;
}
(3)do while loop
while and for Cycles are all Entry condition loop , That is, check the test conditions before each iteration of the loop , All the contents in the loop body may not be executed .do while It is Export condition cycle , That is, the test conditions are not checked until after each iteration of the loop , The loop body is guaranteed to be executed at least once .
do
statement
while (expression);
statement It can be a simple statement or a compound statement . A typical do while The pseudocode is as follows
Get initial value
do
{
Process the value
Get next value
} while( The value meets the test conditions );
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
const int secret_code = 13;
int code_entered;
do
{
printf("To enter the triskaidekaphobia therapy club.\n");
printf("please enter the secret code number: ");
scanf("%d", &code_entered);
} while (code_entered != secret_code);
printf("Congratulation! You are cured.\n");
return 0;
}
(4) Loop control statement :continue and break
countinue Statement will skip the rest of this iteration , And start the next iteration . If continue Statement in nested loop , Only the inner loop containing the statement will be affected .
The execution of a program into a loop break When the sentence is , Will terminate the loop that contains it , And move on to the next phase . If break Statement is inside a nested loop , It only affects the current loop containing it .

(5) Flow control statement :goto
goto Statement causes program control to jump to the corresponding label statement . Colons are used to separate labels from label statements . Label statements follow variable naming rules . Label statements can appear in goto In front of or behind . Form the following :
goto label;
label: statement
goto Use as few statements as possible ,C Programmers can accept a kind of goto Usage of — Jump out of a set of nested loops when a problem occurs ( One break Statement can only jump out of the current loop ).
5、 ... and 、 Process control ( Select and branch )
(1)if sentence
if A statement usually consists of three parts , First of all if keyword , And then there was () Selection conditions in , And finally {} Selectors in , If there is only one statement in the selection body, you may not use {} Cover up . When the selection condition is true , execute {} Select statement in .if The general form of the statement is as follows :
if (expression)
statement
(2)if else sentence
if else A statement usually consists of four parts , First of all if else keyword , And then there was () Selection conditions in , And finally {} Selectors in . When the selection condition is true , perform if Select the statement after the condition , When the selection condition is false , perform else The following sentence .if else The general form of the statement is as follows :
if (expression)
statment1
else
statement2
(3)if -else if -else sentence
if - else if - else A statement usually consists of five parts , First of all if、else if and else keyword , And then there was () Selection conditions in , And finally {} Selectors in . The general form is as follows :
if (expression1)
statement1
else if (expression2)
statement2
else
statement3
Special attention should be paid here else and if The matching problem of , The matching rule is , If there are no curly braces {},else With the nearest if matching , Unless the latest if By {} Cover up .
(4)switch break Multiple choice
switch In parentheses () The value of the test expression in should be an integer value ( Include char type ).case The label must be of type integer ( Include char type ) Constant or integer constant expression ( namely , The expression contains only integer constants ). Variables cannot be used as case label .swtich Its structure is as follows :
switch( Integer expression )
{
case Constant 1:
sentence <- Optional
case Constant 2:
sentence <- Optional
default:
sentence <- Optional
}
switch(expression)
{
case label1: statement1 // Use break Jump out of swtich
case label2: statement2
default: statement3
}
break Let the program go switch sentence , Jump to switch The next statement after the statement starts execution . without break sentence , It starts with matching tags and goes to swtich At the end of .

6、 ... and 、 Character input / Output and input verification
(1) buffer
Unbuffered input , It means that the waiting program can immediately use the characters entered by the user ( No need to press enter key ). Buffered input means , The characters entered by the user are collected in the temporary storage area of a buffer , Press down enter Post key , The program can use the characters entered by the user . There are two types of buffers : Full buffer and line buffer , Full buffering means that the buffer is not flushed until the buffer is full . Line buffering is when line breaks occur \n Refresh the buffer . Keyboard input is usually line buffered input , So press enter Key before refreshing the row buffer .
Usually , The system uses line buffered input , That is, when the user presses enter Key before the input is transmitted to the program . Press down enter The key also passes a newline character , Pay attention to handling this newline character when programming .
while (getchar() != '\n') // Skip all characters and one line break , Can be used to clean up the input buffer
continue;
(2) Files and streams
A file is an area of memory where information is stored , Usually files are stored in some kind of permanent storage . Conceptually ,C Programs deal with streams rather than directly with files . flow (stream) Is an idealized data flow of actual input or output mapping , This means different attributes and different kinds of input , Represented by a more uniform flow of attributes . therefore , The process of opening a file is to associate the stream with the file , And reading and writing are done through streams .
The end of the document , stay C In language , use getchar() A special value will be returned when the end of the file is detected , namely EOF(end of file Abbreviation ).scanf() The function also returns... When it detects the end of the file EOF. Usually ,EOF It's defined in stdio.h Header file .
# define EOF (-1)
EOF It's a value , Marks the end of the file detected , Not a value that can be found in a file . In most operating systems , One way to detect the end of a file is , Place a special character at the end of the file to mark the end of the file . stay DOS Embedded... Is used in the system **Ctrl + Z Character to mark the end of the file , stay UNIX Embedded... Is used in the system Ctrl + D Character to mark the end of the file .Windows Put the... At the beginning of a line Ctrl + Z** Recognized as the end of the file .
C Three standard streams built into the language ,C As long as the language program runs, three streams are opened by default , Include stdout、stdin、stderror They are standard output streams 、 Dimension input stream 、 Standard error output stream .

7、 ... and 、 function
(1) The function prototype ( Function declaration )
A custom function must have a function declaration , This is because the return type of the function is unknown when the function is first encountered in the program , So it must be declared in advance (forward declaration) Specify the return type of the function in advance . But if you put the definition of a function in the main function main Before , You can omit the pre declaration , Because the compiler is running until main All the information about this function has been instructed before . But it's not compound C Standard style of ,main Only the framework of the whole program is provided , It's better to main In front of all function definitions ( Or you can put the function declaration in main Inside the variable declaration ), in addition , Usually put functions in other files , So pre declaration is essential .( This sum python It's a different style ,python Allow functions to appear anywhere in the same source file , And it can be called arbitrarily without pre declaration , If the function appears in another file , Then you need to import the file module .)
(2) Functions with parameters
ANSI C The function type is required to be declared before each variable , In other words, you cannot use the same type of variable list as ordinary function variables .
void dibs(int x, y, z); // Invalid function declaration
void dibs(int x, int y, int z); // Valid function declarations
When a function accepts arguments , The function prototype uses a comma separated list to indicate the number and type of arguments . According to personal preference , The formal parameter variable name can also be omitted . as follows :
void dibs(int, int, int); // Omit variable names
void interchange(int*, int*); // Omit pointer variable name
among void Represents the return value type of a function , This function has no return value, so it is void type ,dibs Represents the function name ,(int x, int y, int z) Indicates that the function consists of three formal parameters . If the function has no formal arguments, you can use the void To indicate that there is no parameter list , as follows :
void pirnt_name(void);
Examples of how a function containing a pointer should be declared :
int digit(double, int); // digit Accept one double Parameters of type and a int Parameters of type , Return to one int Variable of type
double* which(double*, double*) // which Takes two double The address of a type variable , Return to one double The address of a type variable
(3) The return value of the function
Use return A function of a statement is , Terminate the function and return control to the next statement of the calling function . When declaring a function, you must declare the type of the function , Function type with return value should be the same as its return value type , Functions that do not return a value should be declared as void type . The type of function refers to the type of return value of function , Is not a type of function formal parameter .
If the type of the return value of the function does not match the declared return type , The return value will be converted to the return type of the function declaration .
8、 ... and 、 Array
(1) Definition of array
An array is a series of values of the same type stored in sequence , The entire array has an array name , Accessing individual items or elements in an array through integer subscripts .C There is a potential pitfall in language , Considering the impact on execution speed ,C The compiler does not check whether the array subscript is correct , Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the index of the array does not exceed all indexes of the array .
char name[40]; // Initializes a with a length of 40 Of char Type array
square brackets [] Indicates that a file named name Array of ,** The number in square brackets indicates the number of elements in the array , stay C99 Before adding a variable length array , The size of the array must be an integer constant .** Arrays can be accessed by index , The starting index is 0. Numbers in square brackets can also be omitted , Let the compiler automatically match the size of the array and the number of items in the initialization list . Constant expressions should be used in the creation of arrays , Instead of using variables . One dimensional arrays are stored continuously in memory , The array name stores the address of the first element of the array , The address of each element in the array increases from low to high .
(2) Initialize array
1、 Use curly braces {} Initialize the array one by one , Example :
int power[8] = {
1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 16, 32, 64};
When the number of values in the initialization list is less than the number of array elements , The compiler initializes the remaining elements to 0. in other words , If you don't initialize the array , Array elements are the same as uninitialized ordinary variables , All stored in it are garbage values , however , If the array is partially initialized , The remaining elements are initialized to 0.
2、 Specify initializer , The initializer can be used to initialize the specified array elements . You can use the bracketed subscript in the initialization list to indicate the element to be initialized , for example :
int arr[6] = {
[5] = 212}; // hold arr[5] Initialize to 212, The other elements are 0
Give an example to illustrate two important features of the initializer .
int days[12] = {
31, 28, [4] = 31, 30, 31, [1] = 29 };
// result :[31, 29, 0, 0, 31, 30, 31, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Initializers have two important features , First of all , If there are more values after the specified initializer , Such as the initialization list fragment in this example :[4] = 31, 30, 31, Then the following values will be used to initialize the values after the specified element . second , If the specified element is initialized here , Then the final initialization will replace the previous initialization .
(3) The assignment of an array
C It is not allowed to assign an array as a unit to another array , Curly braces are not allowed except for initialization {} Assignment in list form . for example :
int oxen[5] = {
5, 3, 2, 8}; // Initialization is correct
int yaks[5];
yaks = oxen; // Don't allow
yaks[5] = {
5, 3, 2, 8}; // Not initialization , So use {} Is an invalid assignment
(4) Specify array size
When you declare an array , Integer constant expressions can only be used in square brackets . The so-called integer constant expression , Is an expression made up of integer constants . And the size of the array must be greater than 0.
(5) Multidimensional arrays
Create a multidimensional array example :
float rain[5][12]; // Created a 5 x 12 Two dimensional array of
rain contain 5 Elements ,5 Each of the elements is a connotation 12 individual float Array of type elements .
Initialization of multidimensional array , Initialization can also omit the internal curly brackets , Keep only the outermost pair of curly braces . As long as the number of initializations is correct , Initialization has the same effect , But if the initialization value is not enough , Then initialize line by line in order , Until all values are used up , Elements that are not initialized later are uniformly initialized to 0.

When creating a multidimensional array , The parameters of the first dimension can be omitted , Parameters of other dimensions cannot be omitted , Because multidimensional arrays can be initialized according to the number of parameters passed in during initialization , Automatically determine the value of the first dimension .
(6) Arrays and pointers
Yes C In terms of language , You cannot pass an entire array as a parameter to a function , But you can pass the address of the array . The array name is the address of the first element of the array , In other words, directly using the array name can represent the address of the first element of the array , If flizny Is an array , Then the following statement holds :
flizny == &flizny[0]; // The array name is the address of the first element of the array
Take advantage of this feature , You can access arrays in another way :
flizny + 2 == &flizny[2] // Same address
flizny[2] == *(flizny + 2) // The same value
You want an array as a formal parameter , So how to define it ? remember , The array name is the address of the first element of the array , All actual parameters are pointers to the address of the first element of the array , It should be assigned to a pointer form parameter , That is, the parameter points to a pointer .
int sum(int ar); // Such a function declaration is wrong
int sum(int* ar); // Correct function declaration
int sum(int ar[]); // Another correct function declaration
int sum(int* ); // Omit the parameter name
int sum(int []); // Omit the parameter name
Only in the function prototype or function definition header , It can be used int ar[] Instead of int* ar. Another thing to be aware of , If the intent of the function is not to modify the data content in the array , Then you should use keywords when declaring formal parameters in function prototypes and function definitions const. Generally speaking , If you write a function that needs to modify the array , When you declare an array parameter, you do not use const; If you write a function without modifying the array , It is better to use... When declaring array parameters const. for example :
int sum(const int ar[], int n); // The array needs to be modified
int sum(int ar[], int n); // There is no need to modify the array
int sum(const int [], int); // Omit the parameter name
int sum(int [], int); // Omit the parameter name
What are the similarities and differences between arrays and pointer initialization strings ?
All in all , Initializing an array copies the string of the static storage area into the array , The initialization pointer only copies the address of the string to the pointer . The main difference between the two is : Array names are constants , A pointer is a variable , This is reflected in the fact that array names cannot use unary operators ++,-- etc. .
(7) Variable length array
C99 Added variable length array (variable-length array, VLA), Allows the use of variables to express the dimensions of an array . Variable length arrays have some limitations . Variable length array must be an autostore class , This means that whether declared in a function or as a function formal parameter , No use static or extern Store class specifiers . Note that variable length arrays cannot be resized , In a variable length array ” change “ It doesn't mean that you can modify the size of the created array , Once the variable length array is created , Its size remains the same , there ” change “ refer to , When creating an array , You can use variables to specify the dimensions of an array . for example :
int sum2d(int rows, int cols, int ar[rows][cols]); //ar It's a variable length array VLA
int sum2d(int, int, int [*][*]); //ar It's a variable length array , The dimension parameter name is omitted
If the dimension parameter name is omitted , Then you must use an asterisk * To replace the omitted dimension .
(8) Compound literal
To give functions with array parameters , Pass equivalent array constants ,C99 New compound literal quantity (compound literal). A literal quantity is a constant other than a symbolic constant .** For arrays , Compound literal quantity is similar to array initialization list , Type names preceded by parentheses .** for example :
int diva[2] = {
10, 20}; // Declared a normal array
(int [2]){
10, 20}; // Declared an array compound literal , But no variable name was specified for this character literal , Therefore... Cannot be called .
int *pt1;
pt1 = (int [2]){
10, 20}; // Assign an array compound literal to pt1 The pointer , And diva Exactly the same
remember , Compound literals are a means of providing temporary required values , A compound literal quantity has a block scope , Once you leave the block that defines the compound literal , The program will not guarantee that the literal still exists .
Nine 、 The pointer
(1) Definition of pointer
Fundamentally , A pointer is a variable whose value is a memory address ( Or data objects ). The value of the pointer variable is the address . To create a pointer variable , First declare the type of the pointer variable .
Pointer declaration , When declaring a pointer , You must specify the type of variable the pointer points to , Because different types of variables occupy different storage space , Some pointer operations require that you know the size of the object . in addition , The program must know the type of data stored in the specified location . Pointer declaration example :
int *pi; //pi It's pointing int Pointer to type variable
char *pc; //pc It's pointing char Pointer to type variable
float *pf, *pg; //pf、pg Is directed float Pointer to type variable
The type specifier indicates the type of the object the pointer points to , asterisk * Indicates that the declared variable is a pointer .* And pointer name , Usually , Programmers use spaces when declaring , Omit spaces when dereferencing variables . The type of pointer determines the number of bytes added or subtracted during pointer operation .
(2) Unary operator & and *
Find the address :& Operator
Unary operator & Give the storage address of the variable . If epoch Is a variable name. , that &epoch Is the address of the variable .
Indirect operators :*
Use indirect operators * Can retrieve the value that exists at the specified pointer position , This operator is sometimes referred to as the dereference operator . How to use it is as follows :
val = *ptr; // find ptr The value of the point
prt = &bah;
val = *ptr; // amount to val = bah
(3) When to use the pointer ?
generally speaking , Two types of information about variables can be passed to functions , There are two forms of invocation :
function1(x); // Pass on x Value
function2(&x); // Pass on x The address of
The first form requires that the formal parameter in the function definition must be an and x Variables of the same type , The second form requires that the formal parameter in the function definition must be a pointer to a variable of the correct type . If you want to calculate or process values , Then use the first form of function call ; If you want to change the variable of the calling function in the called function , The second form of function call is used . Only when the program needs to change the value of a variable in a function , Will pass the pointer . For arrays , There is no choice but to pass the pointer , Because it's more efficient .
(4) Basic operations of pointer variables
| Operation name | Operation precautions |
|---|---|
| assignment | You can assign an address to a pointer |
| Quoting | * Operator gives a pointer to the value stored on the address |
| address-of | Like all variables , Pointer variables also have their own addresses , You can use another pointer to represent the address of a pointer variable . |
| Add and subtract pointers and integers | Whether it's Canada 、 reduce 、 Increasing or decreasing , The integer will match the size of the type the pointer points to ( In bytes ) Multiply , Then add the result to the address . hypothesis ptr1 Point to urn The first element of , therefore ptr1 + 4 And &urn[4] Equivalent . Pointer plus an integer or increasing pointer , The value pointed to by the pointer does not change in units of the size of the object pointed to . |
| Compare | Using relational operators, you can compare the values of two pointers , If both pointers point to the same type of object . |
| The pointer - The pointer | The result of subtraction between pointers of the same type is the number of elements between the two pointers |
(5)const Modify a pointer
Although the use of # define Directive can create symbolic constants with similar functions , however const It is more flexible to use , You can create const Array ,const Pointers and points const The pointer to .
Point to
constThe pointer to , Cannot be used to modify values :double rates[5] = { 88.99, 100.12, 59.45, 183.11, 340.5}; const double *pd = rates; //pd Point to the first element of the array *pd = 29.89; // It is not allowed to modify the value , because pd It's pointing const The pointer to rates[0] = 29.89; // allow , because rates Not by const limit pd++; // allow , There is no problem changing the pointer positionPoint to
constA pointer to a function usually exists in a function parameter , Indicates that the function does not use pointers to change data .- 1、 Point to
constThe pointer to can point toconstData or notconstdata ;2、 Normal pointer can only point to nonconstdata :
double rates[5] = { 88.99, 100.12, 59.45, 183.11, 340.5}; const double locked[4] = { 0.08, 0.075, 0.0725, 0.07}; const double *pc; double *pnc; pc = rates; // It works pc = locked; // It works pnc = rates; // It works pnc = locked; // Invalid This rule is very reasonable , otherwise , Can be modified by pointer
constThe values in the array . therefore , Use of formal parameters of functionsconstNot only to protect data , It also allows functions to handleconstArray .- 1、 Point to
Declare a pointer that cannot point elsewhere , Be careful
constWhere to use :double rates[5] = { 88.99, 100.12, 59.45, 183.11, 340.5}; double * const pc = rates; //pc Point to the beginning of the array pc = &rates[2]; // Don't allow , Because the pointer cannot point elsewhere *pc = 99.99; // You can change the value that the pointer points toWhen creating a pointer , Can be used twice
const, This pointer can neither change the address it points to , Nor can you change the value on the pointing address :double rates[5] = { 88.99, 100.12, 59.45, 183.11, 340.5}; const double * const pc = rates; //pc Point to the beginning of the array pc = &rates[2]; // It is not allowed to modify the address pointed to *pc = 99.99; // It is not allowed to modify the value pointed toIn short , hold
constPut it in*Anywhere on the left , The data pointed to by the limited pointer cannot be changed ;constPut it in*On the right side , Defines that the pointer itself cannot be changed .
(6) The secondary pointer
Pointer variable is also a variable , It also takes up storage space , You can also use & Get its address ,C Language does not limit the number of pointers , When defining pointer variables, you have to add one * Number , Similarly, when dereferencing, it must be determined according to the series of the pointer * The number of . Example :
int a = 100;
int* p = &a; // First level pointer
int** pp = &p; // The secondary pointer
printf("%d\n", *p); // Dereference level 1 pointer
printf("%d\n", **pp); // Dereference second level pointer
The first level is often used in the actual development process 、 Secondary pointers but advanced pointers are rarely used .
(7) Pointer array ( An array of pointers )
How to declare a pointer variable pointing to a two-dimensional array , Such as ,zippo:
int(* pz)[2]; //pz Point to one connotation and two int An array of types , Array pointer
int * pax[2]; //pax Is an array containing two pointer elements , Each element points to int The pointer to , First level pointer array
parentheses () Priority is higher than *, therefore * The first and pz combination , So a pointer array is declared ( There are two connotations int Type value ) The pointer to .
because [] High priority , With the first pax combination , therefore pax Make an array of two elements , then * Express pax The array contains two pointers .
hypothesis junk It's a 3X4 Array of , To declare a pointing array ( contains 4 individual int Type values ) The pointer to , You can declare the parameters of a function like this .
void somefunction(int (*pt)[4]);
in addition , If and only if pz Is a formal parameter of another function , You can declare that :
void somefunction(int pt[][4]);
generally speaking , Declare a point to N Pointer to dimension group , Only values in the left square brackets can be omitted .

What is the type of pointer array ?
int* arr1[10]; // The type of each element in the pointer array is int*
char** arr2[4]; // The type of each element in the pointer array is char**
char*** arr3[5]; // The type of each element in the pointer array is char***
(8) Array pointer ( Pointer to array )
An array pointer is a kind of pointer , Is a pointer to an array , Point to the address of the array ( Note that it does not point to the address of the first element of the array , The two need to be distinguished ), How to define an array pointer ?
Definition of array pointer , because * The priority of is less than [], Then you need to use () contain *, Put it on the back [] It means that this is an array , Together, it represents an array pointer . Examples are as follows :
int arr[10] = {
0 };
int (*pd)[10] = &arr; // It defines pointing to arr The array type is int The pointer to
double* ch[5]; // A type is defined as double* Of ch Array
double* (*pc)[5] = &ch; // It defines pointing to ch The array type is double* The pointer to
The difference between the array pointer and the address of the first element of the array :&arr Represents the address of the first element of the array , and arr Represents the address of the array , Address of array +1 Will skip the size of the entire array .
The use of array pointers , Array pointer refers to the entire array , Dereferencing the array pointer is equivalent to obtaining the array name , Then you can traverse the array , Example :
int arr[10] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int (*pa)[10] = &arr;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", *((*pa) + i)); // Yes pa To dereference , It is equivalent to obtaining the array name arr
printf("%d\n", (*pa)[i]);
}
Array pointers are mostly used to handle two-dimensional arrays , For two-dimensional arrays , The array name is the address of the first element of the array , The first element is a one-dimensional array , For this one-dimensional array , The address of the first element is the address of one element of the array , So the two-dimensional array name is the address of the first one-dimensional array , It is also the address of the first element of the array .

int arr[10] = {
0 };
int (*ptr)[10] = &arr; //ptr The type of pointer should be int (*)[10]
(9) A function pointer
A function pointer is a pointer to a function address ,& Function name Get the address of the function , Pay attention to two points :& Function name == Function name ,& Array name != Array name . The function name stores the address of the function ,& The function name is also the address of the function . The array name stores the address of the first element of the array , Pay attention to differences .
Definition of function pointer , To define a function pointer, you need to specify the parameter type of the function and the return value type of the function , Definition is similar to array pointer , because * No. 1 has low priority , So we need to () Cover up . Example :
int Add(int x, int y);
int (*ptr)(int, int) = &Add; // It defines pointing to Add Pointer to function .
ptr = Add; // Directly use the function name to assign values , It's also equivalent
If omitted * Ahead () Then the situation will be completely different
int * ptr(int, int); // This is the declaration of a function , Both parameter lists are int, The return value is int*
Dereference of function pointer , Dereference the function pointer to get the function name , Then you can use () Make function calls . actually , There is no need to dereference function pointers , Function pointers and function names are actually equivalent , Because the function name itself is a pointer .
printf("%d\n", Add(1, 3)); // Call the function name directly , Print 4
printf("%d\n", (*ptr)(1, 3)); // Dereference function pointer to get function name , Then it makes a call , Print 4
printf("%d\n", ptr(1, 3)); // Function pointer and function name are equivalent , Call directly , Print 4
(10) Function pointer array
Function pointer array is an array of function pointers , Function pointers of the same type can be stored in the function pointer array . Definition of function pointer array :
int ADD(int x, int y) // Define the addition function
{
return x + y;
}
int SUB(int x, int y) // Define subtraction function
{
return x - y;
}
int (*pfArr[2])(int, int) = {
ADD, SUB }; // Define an array of function pointers
The function pointer array is used as Transfer table , It is convenient to call multiple similar functions .
Ten 、 Storage class 、 Link and memory management
(1) Scope
C The scope of the language includes : Block scope 、 Function scope 、 Function prototype scope 、 File scope .
- Block scope , Variables declared in the block scope , Can only be used in block scope , How to distinguish a block ? A block is a pair
{}Enclosed code area . - Function scope , Function scope only applies to goto The label of the statement .
- Function prototype scope , The scope of the function prototype is from the definition of the function parameter to the end of the prototype declaration .
- File scope , Variable with file scope , It can be seen from its definition to the end of the file where the definition is located , File scope variables are also called global variables .
(2) link
C Language variables have three connection properties : External links 、 Internal links and no connections .
Has block scope 、 Variables of the function scope or function prototype scope are connectionless properties , This means that these variables belong to the block that defines them 、 Function or prototype private . Variables with file scope can be external links or internal links . Externally linked variables can be used in multi file programs , Internally linked variables can only be used in one file .
(3) Storage period
C Objects have four storage periods : Static storage period 、 Thread storage period 、 Automatic storage period 、 Dynamically allocate storage periods .
The file scope variable has a static storage period , Block scoped variables have automatic storage periods . Introduce five different storage categories :

1、 Store category keywords auto\register\static\extern
atuo Is used to declare that the storage category of a variable is an automatic storage category . Automatic variables belong to the automatic storage category , With automatic storage period 、 Block scoped and connectionless . The variable exists when the program enters the block where the variable is declared , Variables are destroyed when the program exits the block . By default , Any variable declared in a block or function header belongs to the automatic storage category . In order to express the intention more clearly ( for example , To indicate that an externally defined variable is intentionally overridden , Or emphasize that you should not change this variable to another storage category ), Can display the use of keywords auto.
register The function of is to declare that the storage category of a variable is register storage .
static Is used to declare a static variable , Static means that the variable does not move in memory , It's not that its value stays the same .
extern To indicate that the function uses an external variable , You can add... Before this variable extern Statement , External variables can only be initialized once , And can only be done when defining the variable . If an external variable or function used by a source code file is defined in another source code file , Must be used extern Declare the variable in this file .
2、 Store category keywords _Thread_local\typedef
(4) Random valued function rand\srand\time
How to use random functions correctly rand,rand You need to set the random number seed before using , adopt srand Set the random number seed to time Current time , Then the sequence of random numbers is different each time , The real random .
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generate random number | rand | stdlib.h | Returns a random number , The scope is 0~RAND_MAX Between |
| Set random number seed | srand | stdlib.h | Set random number seed , Seed of incoming settings |
| Get the current time | time | time.h | Pass in a pointer to save the result , You can also pass in a null pointer , Return to the current time |
(5) Dynamic memory allocation function malloc\calloc\realloc\free
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open up memory space | malloc | stdlib.h | Parameter accepts the number of bytes to open up space , Returns the pointer to the open space , The type is void*, You can pass Change the pointer type by casting , If space creation fails, it returns NULL The pointer |
| Open up memory space | calloc | stdlib.h | The parameter accepts the number of elements to open up the space and the number of bytes of each element , Open up memory space and all Part is initialized to 0, Returns the pointer to the open space , Open up failure return NULL |
| Reclaim memory space | realloc | stdlib.h | Parameter accepts a pointer that has been opened up , The byte size of the re opened space , The return type is void*, If the development fails, it returns NULL |
| Release space | free | stdlib.h | Parameter accepts a pointer to the opened space , And free the memory space pointed to by the pointer .free Letters used The number pointer does not have to be associated with malloc Pointer variables of are consistent , But both pointers must point to the same memory space . |
Memory leak (memory leak) It means that the allocated memory space is not released , But lost the pointer to the space , The memory cannot be accessed again , This is a memory leak .
(6) Qualified type keywords const\volatile\restrict\_Atomic
const The role of is , The attribute of a qualified variable is read-only , Can't be changed , Can only be initialized .
volatile The role of is , The attributes of a qualifying variable can be changed , The limited data processing can be modified by other processes besides the current program , It is mainly used to process variables in threads , Mainly used for concurrent programming .
restrict The role of is , Qualifying pointers are the only and initial way to access data objects , Can only be used to decorate pointer objects . Easy compiler optimization .
11、 ... and 、 File with the IO
(1) file
C Language provides two file modes : Text mode and binary mode . All files are stored in binary form , however , If the file originally uses binary encoded characters ( Such as Unicode) For text , This file is a text file . If the binary in the file represents the machine language code or numerical value or picture or music code , Then the file is a binary file , It contains binary content . If you need to save or restore data without losing accuracy , Please use binary mode and fread() and fwrite() function .


(2)IO function
The key concept in buffered file systems is file pointers FILE*, Used to point to a file object structure , It contains operation files IO The location of the buffer used by the function , Operate on the file pointer , You can read and write files .FILE* The pointer is defined in stdio.h In the library .
| function | function | library | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open the file object | fopen | stdio.h | Open file return file pointer , If the opening fails, return NULL |
| Close file object | fclose | stdio.h | Close the file object pointed to by the file pointer , If it is closed successfully, it returns 0, Otherwise return to EOF, When closing a file, the new buffer of the file will be flushed |
| Character input function | fgetc / getc | stdio.h | Returns the characters obtained from the file object , Characters returned successfully , Failure to return EOF |
| Character output function | fputc / putc | stdio.h | Write characters to file objects , Characters successfully written , Failure to return EOF |
| String input function | fgets | stdio.h | Get string from stream object , You need to specify the length of the string , And will automatically add... After the string \0So it can only store the specified length -1 Length string , Get failed return NULL, Successfully returns str The pointer to |
| String output function | fputs | stdio.h | Output string to stream object , |
| Format input function | fscanf | stdio.h | Get formatted input from stream object , If the reception is successful, it returns 1, Failure returns 0 |
| Format output function | fprintf | stdio.h | Write formatted output to stream object , If the output is successful, the number of characters ( contain \0),If it fails, it returns a negative number |
| Binary input function | fread | stdio.h | Only for documents , Returns the number of items successfully read |
| Binary output function | fwrite | stdio.h | Only for documents , Returns the number of items successfully written |

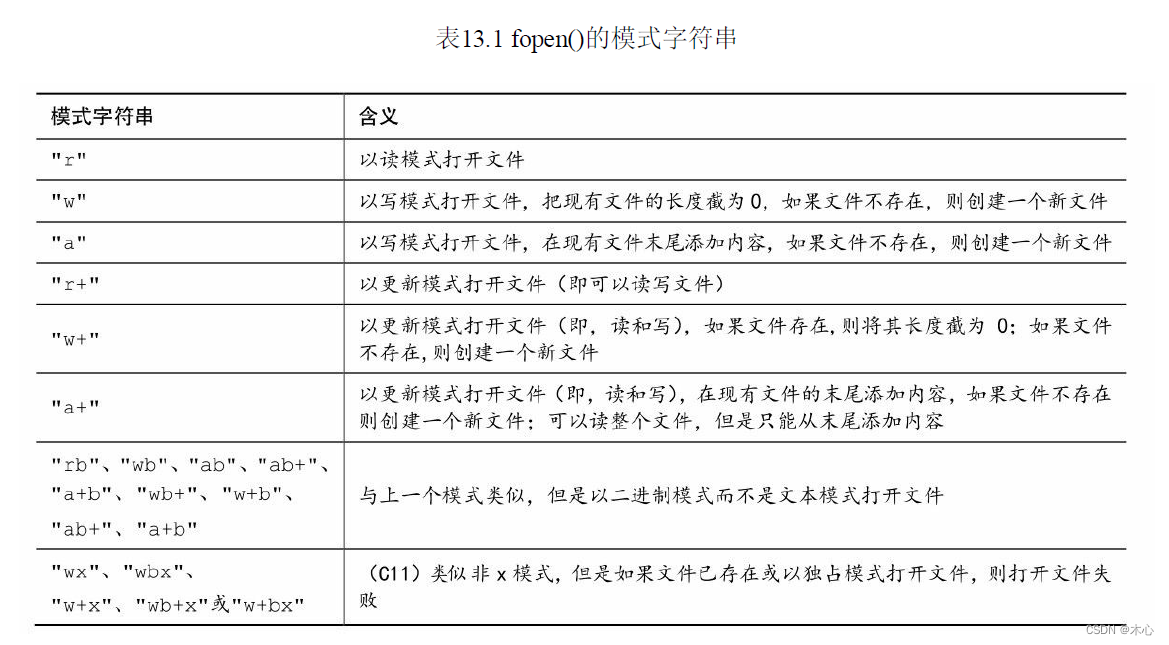
fopen The open mode is as follows :
(3) File pointer operation function
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| The file pointer returns the beginning of the file | rewind | stdio.h | Reset the position of the file pointer |
| Specify the location of the pointer to the file | fseek | stdio.h | By offset and start , Get the location of the file pointer , If the normal return value is 0, When an error occurs, the return value is 0, The offset should be a long The type is data , such as 0L,1L |
| Returns the position of the file pointer | ftell | stdio.h | Returns the position of the file pointer |
| Get the location of the file pointer | fgetpos | stdio.h | |
| Set the position of the file pointer | fsetpof | stdio.h |
fseek You can use the starting amount of three file locations

(4) Detect file error function
| function | function | The header file | Function details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Determine whether it is because of the end of the file EOF Lead to | feof | stdio.h | If because of EOF Cause error , Then return a non-zero value , Otherwise return to 0 |
| Determine whether it is caused by read / write errors | ferror | stdio.h | If... Is caused by a read / write error , Then return a non-zero value , Otherwise return to 0 |
Twelve 、 Other data types
(1) Structure struct
Declaration of a structure , The declaration and definition of structure variables can be combined into one step .
struct tag
{
member-list;
} variable-list;
Initialization of structure , have access to {} To initialize the structure , for example :
struct tag a ={
initial-list}; // Create a structure variable a, And initialize it
Struct has a specified initializer , Its syntax is similar to the specified initializer of an array , however , The specified initializer of the struct uses the dot operator and the member name ( Instead of square brackets and subscripts ) Identify specific elements . for example , Initialization only book Structure of the value member . in addition , The last assignment to a particular member is the value it actually gets .
struct book b = {
.value = 10.99};
Structure access , There are two ways , First use . Access structure members through structure variables , Second use ->, Access to members through structure pointers .
(2) Some characteristics of the structure
We need to pay attention to , You have to use & Operator to get the address of the structure . Different from the array name , The structure name is not an alias for its address name .
When you need to transfer parameters from a structure , Pass the address of the structure as much as possible , Instead of passing structure variables directly , Because passing structure variables directly will copy a structure , Cause a lot of memory consumption .
C Language allows one structure to be assigned directly to another structure , But arrays can't do that , That is to say if n_data and o_data Is the same type of structure , So you can do that :
n_data = o_data; // Assign a structure to another structure
Structure compound literal , The structure compound literal can be passed to the corresponding structure , As the value of the structure , Assign a value to the structure . The syntax is to put the type name in parentheses () in , Followed by a curly bracket {} An enclosed initialization list . for example :
struct book = {
char title[30];
char author[30];
float price;
}
struct book ABook;
ABook = (struct book){
"The Idiot", "Fyodor Dostoyevsky", 6.99}; // Use the struct literal to pass to the corresponding struct
(3) Consortium union
A consortium is a data type , It can store different data types in the same memory space ( Not stored at the same time ). A declared union can only store values of one of these types , This is different from the structure . The typical use of a consortium is , Design a table to store both irregular , Also do not know the mixed type of order in advance . Use the array of the Union , The consortia are all of the same size , Each consortium can store various data types .
Consortium initialization , There are three ways :1、 Initialize a union to another union of the same type .2、 The first element of the union is initialized by default .3、 Use the specified initializer to initialize . Example :
union hold{
// Declare a consortium
int digit;
double bigft;
char letter;
};
union hold valA;
valA.letter = 'R';
union hold valB = valA; // Initialize with another union
union hold valC = {
88}; // Initialize the federated digit member , Initialize the first member by default
union hold valD = {
.bigft=118.2};// Specify the initializer to initialize
Visit of the consortium , There are two ways , First use . Access structure members through union variables , Second use ->, Access to members through union pointers .
(4) enumeration enum
Actually enumerating enum Constant is int type , therefore , As long as it can be used int Enum types can be used where they are . The purpose of enumerating types is to improve the readability of programs . Its syntax is similar to the structure . Constants in enumerated types are called enumerators
Enumeration
enum spectrum{
red,
orange,
yellow,
};
enum spectrum color; // Defines an enumeration constant color
Enumeration constant assignment , In the declaration of enumeration , You can specify integer values for enumeration constants . If you assign a value to only one enumeration constant , There is no assignment to the following enumeration constant , Then the following constants will be given subsequent values .
(5)typedef
typedef Keywords can be used to create C Alias or abbreviation of standard type .
utilize typedef You can customize the name for a type .typedef Run by compiler , Not a preprocessing statement .typedef The scope of the defined variable depends on typedef The position of the statement , If defined inside a function , It has local scope , Limited by the function where the definition is located . If defined outside the function , Has a file scope . for instance :
typedef unsigned char BYTE; // Define new data types
BYTE x, y[10], *z; // have access to BYTE To define variables
Can also be typedef For structure , for example :
typedef struct complex{
float real;
float imag;
} COMPLEX; // The structure complex Redefine as COMPLEX type
Use typedef To name a structure , The label of the structure can also be omitted
typedef struct {
double x;
double y;
} rect; // Directly name the structure as rect, Omitted structure labels
Use typedef Need to remember when ,typedef No new types have been created , It just adds a convenient label to an existing type .
typedef It can also be used for function pointers , for example :
typedef void(* V_FP_CHARP)(char* ); // A new function pointer type is defined V_FP_CHARP, The return value type of the function is void, The argument list of the function is char*
How to use custom function pointer types ? for example :
V_FP_CHARP fp; // Created a fp Function pointer of
void(*fp)(char* ); // Similar to creating function pointers like this
(6) Some complicated statements

The key is to understand *、()、[] The priority of the . Remember the three rules :
1、()、[] Has a higher priority than *.
2、()、[] Same priority for .
3、()、[] From left to right .
13、 ... and 、 Data storage format
On the question of Radix :
Each octal (octal) Bit for 3 Binary bits , Each hex (hex) Bit correspondence 4 Binary bits .
(1) Integer storage format
Data is stored in binary sequences , A byte byte Yes 8 bits bit, each bit Can store a binary number . for example int Four bytes are required to store , So one int The bytes occupied by variables of type are 4*8=32 position . Unsigned integers all bit Are used to store binary numbers .
Signed integers , The highest bit is used to store symbol bits 1 It means a negative number ,0 It means it's a positive number , Negative numbers are stored in memory in the form of The form of binary complement (two’s complement), The specific method is to reverse every bit except the sign bit , And then again +1. If you need to obtain the original code from the complement, you should do the same .
//1 Stored in memory as 32 position bit
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
//-1 Store... In memory in the form of complement
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 // Original code
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 // Take the opposite
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 //+1 Get the complement
(2) Floating point storage
see C Language details .md
(3) Bit operation and mask
Bitwise and operations are often used to mask mask, The so-called mask refers to some settings (1) Or off (0) Bit combination of .

(4) Bit fields
Bit fields bit field Declare through a structure , This structure declares that each field provides a label , And determine the width of the field .

C Languages have two ways to access bits , The first is through the bitwise operator , Another way is to create a bit field in the structure .
fourteen 、C The preprocessor
The preprocessing instruction starts from # Began to run , Until the next line break . in other words , The preprocessed instruction length is limited to one line .
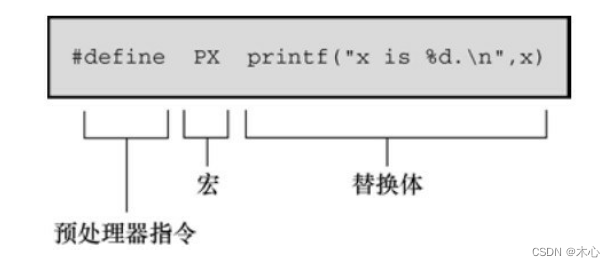
(1) Symbolic constant #define
#define Like other preprocessing instructions , With # As the beginning of a line . Directives can appear anywhere in the source file , Its definition is valid from where the instruction appears to the end of the file .
Each row #define It's all made up of three parts , The first part is #define The instruction itself . The second part is the selected abbreviation , Has become a macro . Spaces are not allowed in the name of a macro , And it must be observed C Naming rules for languages : Only characters can be used 、 Numbers and underscores _, And the first character cannot be a number . The third part is the substitution . Once the preprocessor finds an instance of the macro in the program , The macro is replaced with a substitute . The process of changing from a macro to the final alternative text is called macro expansion . In the pretreatment stage , The preprocessor does not do calculations , Don't evaluate expressions , It's just a macro replacement .
(2) stay #define Parameters used in
stay #define You can create function like macro with shape and function similar to function .

The macro completes the replacement work in the preprocessing stage , So use enough parentheses if necessary () To ensure the correct sequence of operations and combinations . And should avoid using ++x And so on , Because these behaviors are undefined , generally speaking , Do not use increment or decrement operators in macros .
Create a string with a macro :# Operator ,C The language allows macro parameters to be included in a string , In the replacement body of a class function macro ,# As a preprocessing operator , You can convert tokens into strings . for example , If x Is a macro parameter , that #x Is to convert bit strings "x" The formal parameter name of , This process is called stringing . Example :
#define PSQR(x) printf("The square of "#x" is %d.\n", ((x)*(x)))
Preprocessor adhesive :## Operator ,## Operator can be used in the replacement part of class function macro .## The function of is to combine two marks into one mark .
#include <stdio.h>
#define XNAME(n) x##n
#define PRINT_XN(n) printf("x"#n"=%d\n", x##n) //PRINT_XN() Macro use # Operator combination string ,## Strings combine tokens into a new identifier
int main(void)
{
int XNAME(1) = 14;
int XNAME(2) = 20;
int x3 = 30;
PRINT_XN(1); // Print x1=14
PRINT_XN(2); // Print x2=20
PRINT_XN(3); // Print x3=30
return 0;
}
Variable parameter macro :... and __VA_ARGS__, By placing the macro parameter in the list Last parameter Write it as an ellipsis ... To realize the function of changing parameters ,__VA_ARGS__ Can be used in the replacement section , Indicates what the ellipsis stands for . for example :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PR(X,...) printf("Message"#X":"__VA_ARGS__)
int main(void)
{
double x = 48;
double y;
y = sqrt(x);
PR(1, "x=%g\n", x); // Print Message1:x=48
PR(2, "x=%.2f, y=%.4f\n", x, y); // Print Message2:x=48.00, y=6.9282
return 0;
}
(3) File contains #include
When the preprocessor finds #include When the command , The following file name will be checked and the contents of the file will be included in the current file , That is, replace the... In the file #include Instructions . Doing so is equivalent to inputting the entire contents of the included file into the source file #include Where the command is located .#include There are two forms :
#include <stdio.h> // The file name is in angle brackets
#include "mystuff.h" // The file name is in double quotation marks
stay UNIX In the system , Angle brackets <> Tell the preprocessor to look for the file in the standard system directory . So use <> Generally, it contains the header file of the system . Double quotes "" Tell the preprocessor to first in the current project directory ( Or other directory specified in the file name ) Find the file , If it is not found, go to the standard system directory to find it . for example :
#include <stdio.h> // Look in the system directory stdio.h
#include "hot.h" // Find... Under the current path hot.h
#include "/usr/bin/cold.h" // In the catalog /usr/bin Search for cold.h
(4) Use header file
C It is customary in language to use .h Suffix indicates header file , These files contain information that needs to be placed at the top of the program . Header files often contain preprocessing instructions . Some header files ( Such as stdio.h) Provided by the system , Of course, you can also create your own header file . In most cases , The contents of the header file are the information that the compiler needs to generate the final code , Instead of adding material to the final code .
The most common forms of header files are as follows : Include symbolic constants 、 Macro functions 、 Function declaration 、 Structure template definition 、 The type definition .


(5) Other precompiled instructions
#undef Used to cancel the defined #define Instructions
#define LIMIT 400 // Set a symbolic constant LIMIT
#undef LIMIT // The symbol constant LIMIT The definition of
Remove the above definition , Now we can put LIMIT Redefine as a new value . Even if there was no definition LIMIT, Cancel LIMIT The definition of is still valid . If you want to use a name , There is uncertainty as to whether it has been defined before , For safety reasons, you can use #undef The command undefines the symbol . We need to pay attention to ,#define The scope of a macro begins with its declaration in the file , Until you use #undef The instruction cancels the macro definition , Extend to the end of the file .
#defined Used to determine whether the identifier is #define Defined , If it is defined, it returns 1, Otherwise return to 0. This new method is often associated with #elif Use it together .
(6) Conditional compilation
1、#ifdef、#else、#endif
#ifdef、#else、#endif Logic and if、else Sentences are very similar , It's just #ifdef need #endif To mark the end of the preprocessing statement .
#ifdef MAVIS
#include "horse.h" // If it has been used #define Defined MAVIS, Then execute the following instructions
#define STABLES 5
#else // If it doesn't work #define Definition MAVIS, Then execute the following instructions
#include "cow.h"
#define STABLES 15
#endif // end #ifdef sentence
2、#ifndef、#else、#endif
#ifndef Command and #ifdef The use of instructions is similar to , Can also be combined with #else、#endif Use it together , But their logic is the opposite .#ifndef You can determine whether the following identifier is undefined , It is often used to define identifier constants that have not been defined before .
#ifndef SIZE
#define SIZE 100 // Define a previously undefined identifier constant
#endif
#ifndef It can also be used to prevent the same file from being included more than once , For example, in things.h Header file :
#ifndef THINGS_H_
#define THINGS_H_ // Put the contents of the header file in a #ifndef、#endif In the block , In this way, the contents of the header file are included only once
...
#endif
It can also be used to prevent multiple inclusion of header files **#pragma once** sentence , Add this statement on the first line of the header file , You can make the header file contain only once .
#pragma once // Use this statement at the beginning of the header file so that the header file is included only once
3、#if、#elif
#if The instructions are very similar C In language if,#if Followed by an integer constant expression , If the expression is non-zero , Then the expression is true . Can be used in instructions C Relational and logical operators . for example :
#if SYS==1
#include "horse.h"
#elif SYS==2
#include "cat.h"
#else
#include "dog.h"
#endif
#if、#elif and #defined Use it together , You can achieve #ifdef The effect of , for example :
#if defined(IBMPC)
#include "ibmpc.h" // If you define IBMPC So it includes ibmpc.h The header file
#elif defined(VAX)
#inlcude "vax.h" // If you define VAX So it includes vax.h The header file
#else
#include "genreal.h" // Default includes general.h The header file
#endif
(7) Predefined macros and __func__

C99 The standard provides a name for __func__ Predefined identifier for , It expands into a string representing the function name ( The function contains the identifier ). that __func__ Must have function scope , And in essence, macros have file scope . therefore ,**__func__ yes C Predefined identifiers for languages instead of predefined macros .** Simply speaking ,__func__ The predefined identifier represents a string of function names ,__func__ When called inside different functions , The string that represents the name of the function under this scope .
(8) Generic selection _Generic
_Generic yes C11 Key words of ._Generic The following parentheses contain multiple items separated by commas . The first term is an expression , The following items are all composed of a type 、 A colon and a value make up , for example float:1. Which tag does the type of the first item match , The value of the entire expression is the value after the tag . for example :
_Generic(x, int:0, float:1, double:2, default:3)
Suppose that in the above expression x yes int Variable of type ,x Type match int:0 The label of , Then the value of the entire expression is 0. If there is no tag matching the type , Then the value of the entire expression is the default value default:3. Generic selection statements and switch Statements like , Only the former uses the type of expression to match the label , The latter matches the tag with the value of the expression .
15、 ... and 、C library
The header file contains the declarations of all the functions in this series , This directly includes the header file , You can omit the complex work of including the function prototype declaration every time you use the function . for example
(1)ctype.h

(2)math.h

(3)stdio.h
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-FPSUB3Pn-1655802386023)(D:\Study_Data\Markdown_Note\figure\image-20220621143125665.png)]
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-CVZo8FYS-1655802386024)(D:\Study_Data\Markdown_Note\figure\image-20220621143249782.png)]
(4)stdlib.h


(5)stdlib.h Medium exit() and atexit()
1、atexit() Function usage
This function uses a function pointer . To use atexit() function , Order passes the address of the function to be called when exiting to atexit() that will do . then ,atexit() Register the functions in the function list , When calling eixt() These functions are executed when ( The order of execution is opposite to the order of the functions in the list , That is, the last added function executes first ). One thing to note is that even if the call is not shown exit() function , The program will still execute on exit ateixt() Registered functions , This is because main() When it ends, it implicitly calls exit().
2、exit() Function usage
exit() After execution atexit() After the specified function , Will finish some cleaning work : Refresh all output streams 、 Close all open streams and close by standard I/O Function to create a zero time file . then exit() Return control to the host environment .UNIX Program usage 0 Indicates successful termination , use 1 Indicates that the termination failed .C Defines a name EXIT_FAILURE and EXIT_SUCCESS Indicates termination failure and successful termination .

however ,exit() The function also accepts 0 Indicates successful termination , Accept 1 Indicates that the termination failed . In non recursive main() Use in a function exit() Function is equivalent to using return. For all that , stay main() Functions other than exit() It will also terminate the entire program .
(6)assert.h

assert() Macro accepts an integer expression as an argument , If the expression evaluates to false ,assert() The macro is in the standard error stream (stderr) Write an error message to the , And call abort() Function termination program (abort() The prototype of the function is stdlib.h Header file ).
assert() Have a mechanism that can be turned on or off without changing the code . If you think the program has been ruled out BUG, You can write the following macro definition in the include assert.h In front of :
#define NDEBUG
And recompile the program , In this way, the compiler will disable all assert() sentence . If the program goes wrong again , Then you can remove this statement , Recompile the program so that it is enabled again assert() sentence .
And assert Similar assertion keywords include _Stattic_assert. The difference between the two is assert Can cause a running program to abort , and _Stattic_assert Can cause the program to fail to compile , And print an error message .
Reference
边栏推荐
- 我把它当副业月入3万多,新手月入过万的干货分享!
- Which position does Anxin securities rank? Is it safe to open an account?
- 108. simple chat room 11: realize client group chat
- 【力扣刷题】11.盛最多水的容器//42.接雨水
- 100+ data science interview questions and answers Summary - basic knowledge and data analysis
- MS | Xie Liwei group found that mixed probiotics and their metabolites could alleviate colitis
- stm32h7b0替代h750程序导致单片机挂掉无法烧录程序问题
- R language uses cor function to calculate the correlation matrix for correlation analysis, uses corrgram package to visualize the correlation matrix, reorders rows and columns using principal componen
- Gui+sqlserver examination system
- 无需人工先验!港大&同济&LunarAI&旷视提出基于语义分组的自监督视觉表征学习,显著提升目标检测、实例分割和语义分割任务!...
猜你喜欢

IAR工程适配GD32芯片

Ideal path problem

TCP congestion control details | 1 summary
JUnit unit test

Vibrating liquid quantity detecting device

pybullet机器人仿真环境搭建 5.机器人位姿可视化
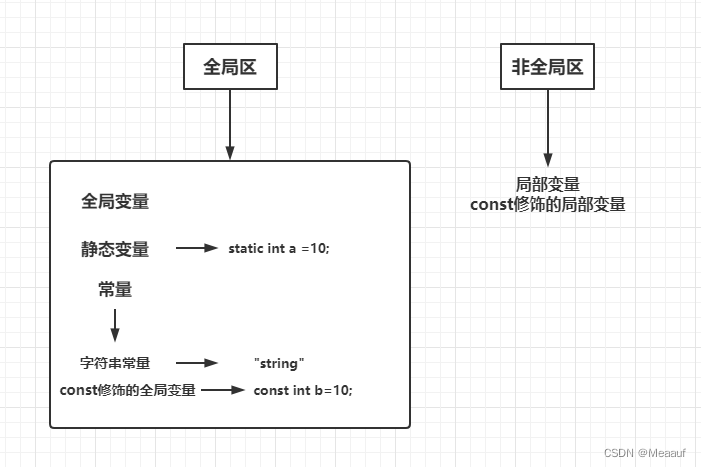
内存分区模型

Arduino UNO + DS1302简单获取时间并串口打印

Structure the graduation project of actual combat camp
JS教程之使用 ElectronJS、VueJS、SQLite 和 Sequelize ORM 从 A 到 Z 创建多对多 CRUD 应用程序
随机推荐
LeetCode Algorithm 24. Exchange the nodes in the linked list in pairs
内存分区模型
[机缘参悟-31]:鬼谷子-抵巇[xī]篇-危机是危险与机会并存
基于Kubebuilder开发Operator(入门使用)
神经网络“炼丹炉”内部构造长啥样?牛津大学博士小姐姐用论文解读
Notes on key review of software engineering at the end of the term
This year, the AI score of college entrance examination English is 134. The research of Fudan Wuda alumni is interesting
电路中缓存的几种形式
5g is not flat and 6G is restarted. China leads wireless communication. What is the biggest advantage of 6G?
长安链交易防重之布谷鸟过滤器
108. 简易聊天室11:实现客户端群聊
Redis 迁移(操作流程建议)1
[207] several possible causes of Apache crash
JS教程之 使用 Electron.JS 构建原生桌面应用程序乒乓游戏
GUI+SQLServer考试系统
Research on natural transition dubbing processing scheme based on MATLAB
Detailed explanation of cookies and sessions
[learn FPGA programming from scratch -46]: Vision - development and technological progress of integrated circuits
Redis的ACID
【207】Apache崩溃的几个很可能的原因,apache崩溃几个