当前位置:网站首页>Understand chisel language thoroughly 05. Chisel Foundation (II) -- combinational circuits and operators
Understand chisel language thoroughly 05. Chisel Foundation (II) -- combinational circuits and operators
2022-07-04 14:08:00 【github-3rr0r】
Chisel Basics ( Two )—— Combinational circuits and operators
Combinational logic circuits are mathematically speaking , It is a digital logic circuit described by the operators of Boolean algebra , That is, the combination of a series of Boolean algebraic operators .Chisel in , These Boolean algebra operators follow C、Java、Scala And other programming languages are similar , such as ,& yes Bitwise AND The operator ,| yes Press bit or The operator . This part will introduce in detail Chisel Basic bitwise operators in 、 Arithmetic operator 、 Logical operators 、 Comparison operators, etc , as well as Chisel A high-order combinational circuit operator in —— Multiplexer .
An example of a simple combinational logic circuit
The next line of code , A combinational circuit is defined , It uses a signal connected to the door a and b, Then put the output and signal of this and gate c Connected by or doors :
val logic = (a & b) | c
The circuit diagram corresponding to this expression is as follows :
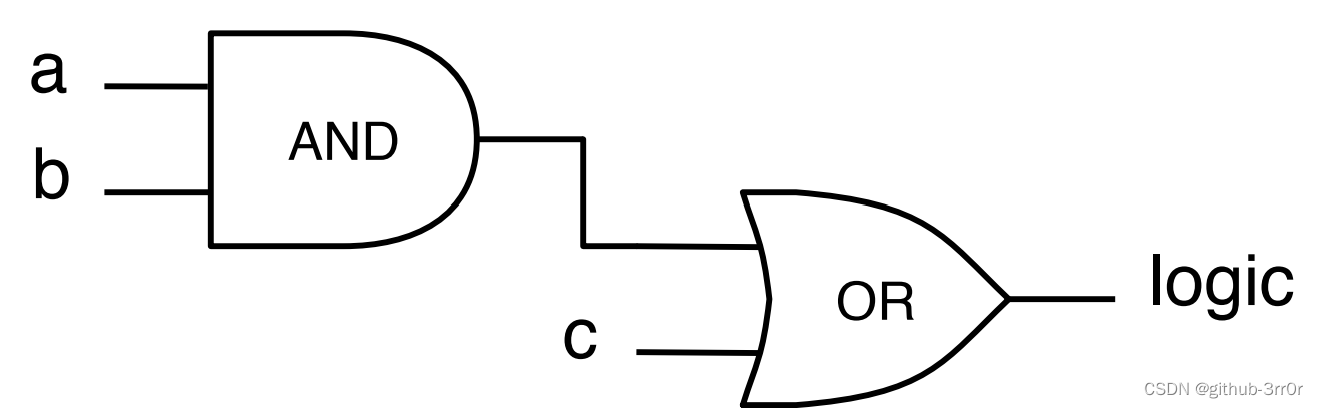
You can see that the basic grammar is very simple , It should be noted that , In this circuit And gate and Or gate The input signal of can be a single bit , It can also be a bit vector .
Chisel Bit operators in
The following examples demonstrate four basic bit operations , It's using Scala Standard operators in , Their operands can be UInt、SInt and Bool:
val and = a & b // Bitwise AND
val or = a | b // Press bit or
val xor = a ^ b // Bitwise XOR
val not = ~a // According to the not
These basic bit operations are very basic , There are also two shift operations , Their operands can be UInt or SInt:
val shiftleft = a << b
val shiftright = a >> b
It should be noted that , about SInt Operands of type , Moving to the right may expand the symbol , Arithmetic shift right .
summary Chisel Medium An operator as follows :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
& | Bitwise AND | UInt、SInt、Bool |
| ` | ` | Press bit or |
^ | Bitwise XOR | UInt、SInt、Bool |
~ | According to the not | UInt、SInt、Bool |
<< | Move left | UInt、SInt |
>> | about UInt Logical shift right , about SInt It's arithmetic shift right | UInt、SInt |
Chisel The arithmetic operator in
Here is Chisel Use in Scala Arithmetic operations performed by standard operators , Their operands can be UInt or SInt:
val add = a + b // Add
val sub = a - b // Subtraction
val neg = -a // Take the opposite number
val mul = a * b // Multiplication
val div = a / b // division
val mod = a % b // Remainder
Note the bit width inference here :
- For addition and subtraction , The resulting width is the widest of the operands ;
- For multiplication , The result width is the sum of the widths of the operands ;
- For division and remainder , The width of the result is usually the width of the dividend ;
in addition , For addition and subtraction , You can also specify whether to extend the bit width and reserve the carry , stay + or - Add after % Just don't expand the bit width , add & Just don't keep carry , The default is not to expand the bit width .
summary Chisel Medium Arithmetic operator as follows :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
+ or +% | Add ( Do not retain carry ) | UInt、SInt |
+& | Add ( Carry reservation ) | UInt、SInt |
- or -% | reduce ( Do not retain carry ) | UInt、SInt |
-& | reduce ( Carry reservation ) | UInt、SInt |
* | ride | UInt、SInt |
/ | except | UInt、SInt |
% | Remainder | UInt、SInt |
Chisel Logical operators in
Logical operators are for Bool The value of type , Yes Logic and 、 Logic or and Logic is not These three , and Scala And other programming languages are similar :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
&& | Logic and | Bool |
| ` | ` | |
! | Logic is not | Bool |
Chisel Comparison operators in
For less than 、 Less than or equal to 、 Greater than and greater than or equal to ,Chisel and Scala It's consistent , But it means different in equal and unequal . The operand of the comparison operator is UInt or SInt, Summarized below :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
> | Greater than | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
>= | Greater than or equal to | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
< | Less than | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
<= | Less than or equal to | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
=== | be equal to | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
=/= | It's not equal to | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
Although here === and =/= It looks strange , But don't make a mistake , The designer said that this is to make Scala Original == and != Still available .
Chisel Specification operators in
This is a Chisel Easy to use operators in , The operands are SInt or UInt, Perform a conventional operation on each bit of the operand , The return value is Bool type , The three specification operators are as follows :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
.andR | And the statute | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
.orR | Or statute | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
.xorR | XOR Protocol | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
Usage is as follows :
val allSet = x.andR // And the statute
val anySet = x.orR // Or statute
val parity = x.xorR // XOR Protocol
Chisel Bit field operators in
We mentioned earlier UInt and SInt Are bit vectors , Therefore, there should be some operators that operate on the bit fields of vectors , The specification operators in the previous part belong to this class .Chisel There are other bit field operators in :
For example, extracting a single bit from a bit vector , The operator is (n), Means to extract the n position , Least significant bit LSB The index for 0:
val xLSB = x(0) // extract x The lowest point of
You can also extract a bit segment , The operator is (end, start), Means to extract the start Position to the first end Fields between bits , This start and end Is included , The return value is UInt:
val xTopNibble = x(15, 12) // hypothesis x yes 16 Bit , extract x The height of 4 position
You can also copy a bit vector many times , The operator is Fill(n, x),n Is the number of copies ,x For the copied bit vector , It can only be or UInt, The return value is also UInt:
val usDebt = Fill(3, "hA".U) // "hAAA".U
Finally, we can splice multiple bit vectors , The operator is ## or Cat, and Verilog Medium {} similar , Examples are as follows :
val float = Cat(sign, exponent, mantissa) // Splice three vectors , perhaps
val float = sign ## exponent ## mantissa
But here's the thing , The type of operand on both sides of the splicing operation must be the same , And the return value is UInt, therefore , If used on multiple operands ## Attention should be paid to when splicing , For example, for three SInt Splicing will report an error , And for two SInt And a UInt There will be no error when splicing , While using Cat There will be no such problem .
Another thing to note is , although ## and Cat The function is similar , But generated Verilog It will be different , such as :
a := -1.S ## -2.S
Will generate :
assign a = {1'sh1,2'sh2};
and :
a := Cat(-1.S, -2.S)
Will generate :
assign a = 3'h6;
Generally speaking, use Cat Splicing is better .
Summarized below :
| The operator | describe | data type |
|---|---|---|
x(n) | To extract the first n position | UInt、SInt, return Bool |
x(end, start) | To extract the first start To the first end position | UInt、SInt, return UInt |
Fill(n, x) | Bit vector x Copy n Time | UInt, return UInt |
a ## b | Bit vector splicing | UInt、SInt, return UInt |
Cat(a, b, ...) | Bit vector splicing | UInt、SInt, return UInt |
About Chisel The priority of the operator
Chisel The priority of the operator does not act Chisel Part of the language is directly defined , It depends on the order of assignment of the circuit , Follow naturally Scala Operator priority of . If you are really unsure , It would be Use parentheses To express the priority of operation .
Digression ,Chisel and Scala Operator priority and Java/C Similar but different , and Verilog and C It's the same , however VHDL There is no such feature directly . stay VHDL Inside , All operators have the same priority , Calculate from left to right .
Chisel Medium 2-1 Multiplexer
Multiplexer (multiplexer) It is a combinational circuit that selects one of multiple inputs as the output , Its most basic form is 2-1 Multiplexer , That is, one of two . Here is a 2-1 Multiplexer , Or for short Mux:
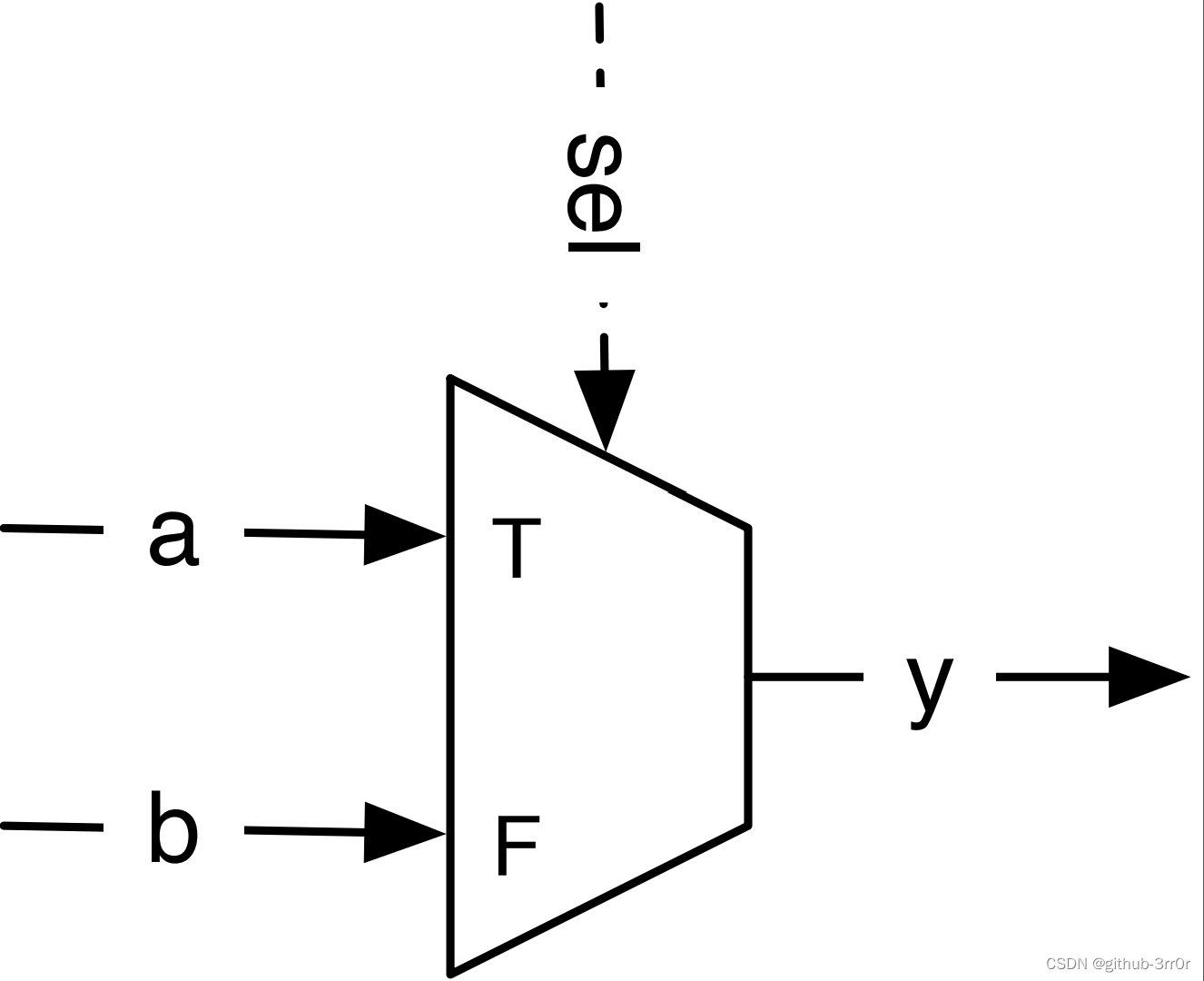
According to the selection signal sel Value , Output y Will indicate the input signal a or b. Of course , We can also achieve this with logic gates Mux Of , however Chisel The standard library provides Mux As a standard operator , Examples are as follows :
val y = Mux(sel, a, b)
When sel It's a Chisel Medium Bool Type values , by true When selecting output a, Otherwise, select output b. here a and b It can be arbitrary Chisel Basic type or aggregate class ( such as bundle or vector, I'll tell you more later ), As long as they are of the same type .
Conclusion
With the above basic arithmetic 、 Logic operation and multiplexer here , Then we can describe all combinational circuits . however , It is obviously not elegant to use these to describe , For example, I want to achieve a 3-8 Decoder , I can't use 8 individual Mux Well ? The readability of the code is too poor ! and Chisel It also provides more component and control abstractions , It can make us more elegant when describing a combinational circuit , The relevant content will be detailed later !
边栏推荐
- unity不识别rider的其中一种解决方法
- 苹果5G芯片研发失败:继续依赖高通,还要担心被起诉?
- The Secretary of Homeland Security warned immigrants "not to embark on a dangerous journey"
- 源码编译安装MySQL
- OPPO Find N2产品形态首曝:补齐各项短板
- 自主工业软件的创新与发展
- 吃透Chisel语言.06.Chisel基础(三)——寄存器和计数器
- Install Trinity and solve error reporting
- One of the solutions for unity not recognizing riders
- 小程序直播 + 电商,想做新零售电商就用它吧!
猜你喜欢
Unity Shader学习(三)试着绘制一个圆
![[antd step pit] antd form cooperates with input Form The height occupied by item is incorrect](/img/96/379d1692f9d3c05a7af2e938cbc5d7.png)
[antd step pit] antd form cooperates with input Form The height occupied by item is incorrect
Redis —— How To Install Redis And Configuration(如何快速在 Ubuntu18.04 与 CentOS7.6 Linux 系统上安装 Redis)

2022g3 boiler water treatment examination question simulation examination question bank and simulation examination
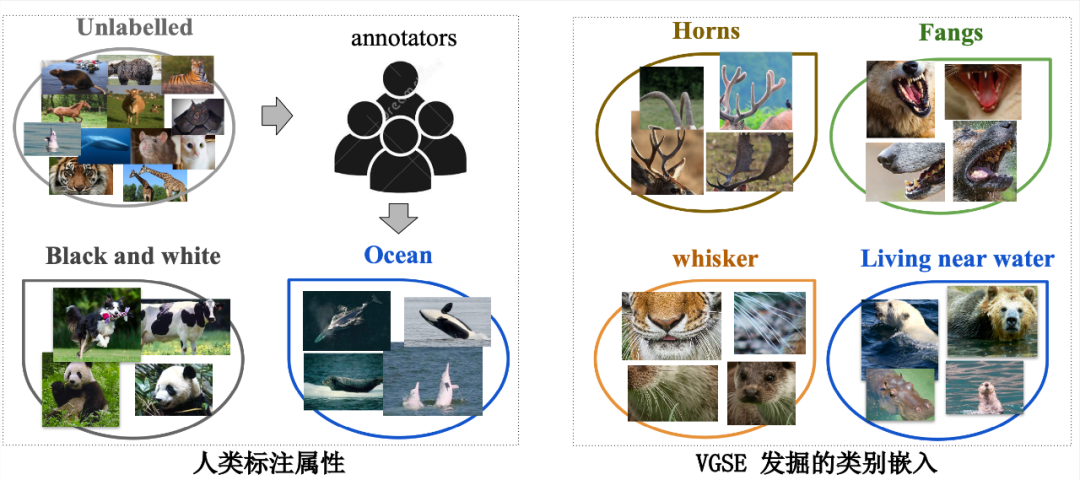
CVPR 2022 | 大幅减少零样本学习所需的人工标注,提出富含视觉信息的类别语义嵌入(源代码下载)...
嵌入式编程中五个必探的“潜在错误”

中邮科技冲刺科创板:年营收20.58亿 邮政集团是大股东
2022 Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination question bank and online simulation examination
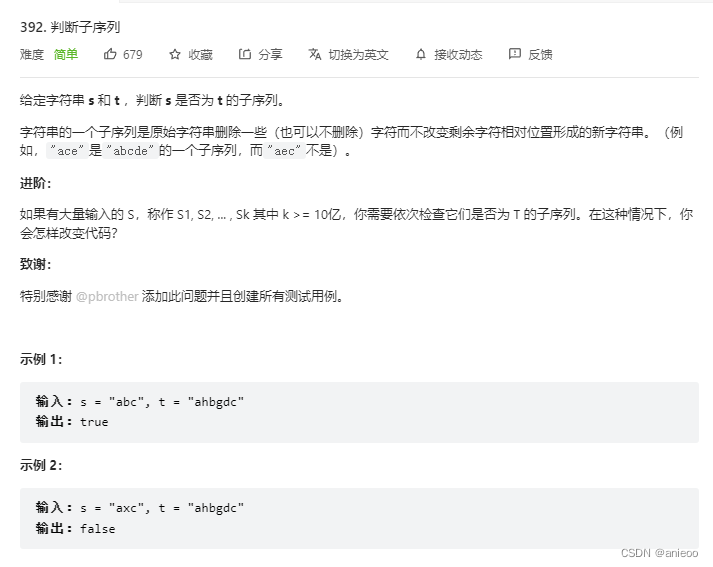
392. 判断子序列
面试拆解:系统上线后Cpu使用率飙升如何排查?
随机推荐
.Net之延迟队列
Animation and transition effects
Fs4056 800mA charging IC domestic fast charging power IC
WS2811 M是三通道LED驱动控制专用电路彩灯带方案开发
Haobo medical sprint technology innovation board: annual revenue of 260million Yonggang and Shen Zhiqun are the actual controllers
华昊中天冲刺科创板:年亏2.8亿拟募资15亿 贝达药业是股东
吃透Chisel语言.10.Chisel项目构建、运行和测试(二)——Chisel中生成Verilog代码&Chisel开发流程
Fs7867s is a voltage detection chip used for power supply voltage monitoring of digital system
吃透Chisel语言.03.写给Verilog转Chisel的开发者(没有Verilog基础也可以看看)
程序员转方向
2022 hoisting machinery command examination simulation 100 questions simulation examination platform operation
Qt如何实现打包,实现EXE分享
Applet live + e-commerce, if you want to be a new retail e-commerce, use it!
392. 判断子序列
使用默认路由作为指向Internet的路由
JVM memory layout detailed, illustrated, well written!
Hardware Basics - diode Basics
Variable promotion and function promotion in JS
中邮科技冲刺科创板:年营收20.58亿 邮政集团是大股东
【C 题集】of Ⅶ