当前位置:网站首页>Prepare for the autumn face-to-face test questions
Prepare for the autumn face-to-face test questions
2022-07-06 02:07:00 【#HashMap#】
1. The difference between object-oriented and process oriented ?
Process oriented : Process oriented performance is better than object-oriented , Because the instantiation and invocation of object-oriented classes require a lot of overhead , If you consider the cost , Process oriented application and single chip microcomputer , Embedded development environment .
object-oriented : Object oriented has the advantage of easy maintenance , extensible , Easy to reuse , With encapsulation , Inherit , Polymorphism , Be able to design a low coupling and flexible system
2.Java Characteristics of language ?
1) object-oriented , With encapsulation , Inherit , Polymorphism
2) Cross platform
3) Multithreading support
4) Support network programming
5) Compilation and interpretation coexist
3.JVM,JDK,JRE The relationship between
JVM:Java virtual machine , Usually compiled .class The file will be interpreted in the virtual machine , Into binary machine code
JDK: contain Java compiler (javac),Java Compiler tools (( Such as javadoc and jdb)
JRE: contain Java The core library ,Java command ,JVM
summary :JDK contain JRE and JVM,JRE contain JVM
4.Java and C++ The difference between
1) Both are object-oriented languages , With encapsulation , Inherit , Polymorphism
2)Java Pointer access to memory is not supported , Program memory is more secure
3)Java Only inheritance ,C++ You can inherit more , however Java Multiple inheritance can be realized through the interface
4)Java Can automatically manage memory , No need for programmers to release memory manually
5) stay C language ⾔ in , String or character array will end with ⼀ Extra characters ‘\0’ To indicate the end . however ,Java language ⾔ There is no terminator in this ⼀ Concept .
5. The difference between character type constant and string constant
1) Character constants are in the form of single quotation marks , Each character represents ASCLL code , It can be calculated ;
2) String constants are in double quotation marks , Each string represents the memory address
3) Character constants account for 2 Bytes , String constant takes several bytes
Java data type :

6. The difference between overloading and rewriting ?
heavy load : Occurs in the same category , Many methods execute different logic according to different parameter transfer methods .
Conditions of use : Same method name , Return value , Parameter type , Number of parameters , The order of parameters can be different
rewrite : Occurs in inheritance , It is often the extension of subclasses to parent methods .
Conditions of use :“ Two are the same, two are small and one is big ”. Both refer to : The method name is the same as the parameter list . Two little fingers are : The return value type of the subclass must be less than or equal to the parent class ; The exception thrown by the subclass is less than or equal to the parent class . One refers to : The access permission of the subclass must be greater than or equal to that of the parent class .
About “ The return value type of the subclass must be smaller than the understanding of the parent class ”
If the return value type of the method of the parent class is void Or basic data type , The subclass cannot be modified when overridden , If it is a reference data type, the subclass must be less than or equal to the parent class .
public class Hero {
public String name() {
return " Superhero Movie ";
}
}
public class SuperMan extends Hero{
@Override
public String name() {
return " super ⼈";
}
public Hero hero() {
return new Hero();
}
}
public class SuperSuperMan extends SuperMan {
public String name() {
return " Superheroes ";
}
@Override
public SuperMan hero() {
return new SuperMan();
}
}
7. Can constructors be rewritten ?
Constructors cannot be rewritten , But it can be overloaded , A typical example is often seen with the and with theout parameter constructors .
8. encapsulation , Inherit , polymorphic
encapsulation : Privatize the properties of an object , Only one interface is provided to access the properties of the object
Inherit : Function extension based on the original class , After the child class inherits the parent class , New functions can be added to method rewriting .
A child class has all the properties and methods of the parent class , But not accessible .
Whether the subclass must override the method of the parent class ?
There are two situations :1. If the method is abstract , You must rewrite 2. If the method is ordinary , You can not rewrite .
polymorphic : Which class instance object does a reference variable point to , The method of which class is called by the reference variable is uncertain during programming , It can only be determined at run time .
There are two ways to achieve polymorphism :1. Inherit ( Override multiple methods of the same subclass ) 2. Interface ( Implement the interface and cover the same method )
9.String StringBuilder StringBuffer difference
1) variability
String Class is an immutable long string , because String Class source code contains private final char[] value modification , and StringBuilder and StringBuffer Inherited from AbstractStringBuilder class , Also use char[] value Realization , But no final modification .
2) Thread safety
String Class is immutable , It can be understood as a constant , Thread safety .StringBuilder and StringBuffer There are public methods , however StringBuffer Add synchronization lock to the method , So thread safety .
3) performance
String Is immutable , So only through new new String object , and StringBuilder and StringBuffer Is to operate on the object itself , Better performance , And in the same case StringBuilder Than StringBuffer High performance 10%-15%
For the three, make ⽤ Summary of : 1. Operate on a small amount of data : optimum ⽤ String 2. Single thread operation string buffer operation ⼤ Quantity data : optimum ⽤ StringBuilder 3. Multithreading operation string buffer operation ⼤ Quantity data : optimum ⽤ StringBuffer
10. Is it illegal to call non static members in a static method ?
It's illegal. , According to many interviews, the answer to this question is : Because static methods belong to classes , You can call... Directly through the class , The non static member belongs to the instance object , You need to call... Through an object , Hearing this, I was confused with many people . In fact, this should be understood from JVM Class loading mechanism of .

We just need to focus on the connection and initialization phases , In the preparation phase of the connection , Static variables will be assigned , That is initialization , Non static variables are not assigned ; In the initialization phase, the static method initializes , Non static methods do not initialize , Then non static members ( Methods and variables ) When to initialize ? The answer is after instantiating the object , That is to say new After object . Now you can answer this question clearly , During class loading, static methods are initialized first , At this time, non static members are still sleeping , It's not initialized yet , Then the static method calls non static members, of course, will make mistakes !
11.Java Why should we use parameterless construction in ?
Because subclasses need to use super() Call a specific constructor in the parent class , If the subclass does not super(), Then we will call the parameterless construction of the parent class , At this time, there will be errors if there is no nonparametric structure . So the parent class needs to add a parameterless constructor .
12. The difference between interface and abstract class ?
Interface :1.8 The previous method must be public, Interfaces can only be constant variables or abstract methods ;1.8 The time method can be public perhaps default, There can be default methods and static methods ;1.9 Time can be private, There can be private static methods and private methods
2. There can only be static and final Modifying variables
3. A class can implement multiple interfaces , But only one abstract class can be implemented
abstract class :1.8 The default used to be prodected;1.9 The default is default
13. The difference between member variable and local variable ?
1. In terms of grammatical form : Member variables belong to classes ,⽽ Local variables are in ⽅ A variable defined in the law or ⽅ Parameters of the method ; Member variables can be public , private , static Decorated by modifiers such as ,⽽ Local variables cannot be modified by access control Fuji static Modified ; however , Both member variables and local variables can be final Modified .
2. From the storage of variables in memory ⽅ type Look at : If the member variable is such that ⽤ static Embellished , So this member variable belongs to In the class of , If you don't make ⽤ static modification , This member variable belongs to the instance . Object in heap memory , If the Bureau Part variable type is basic data type , So it's stored in stack memory , If it's a guide ⽤ data type , That store points to the heap A reference to a memory object ⽤ Or point to the address in the constant pool .
3. From variable in memory ⽣ Save time Look up : Member variables are objects ⼀ part , It follows the creation of the object ⽽ There is ,⽽ Local variables follow ⽅ The tone of law ⽤⽽⾃ The motion disappears .
4. If a member variable is not given an initial value : will ⾃ Move to the default value of the type ⽽ assignment (⼀ There are two exceptions : By final modification Member variables must also be explicitly assigned ),⽽ Local variables don't ⾃ Dynamic assignment .
14. establish ⼀ What operator does an object use ? How object entities differ from object references ?
new Operator ,new Create an object instance ( Object instance in heap memory ), Object citation ⽤ Point to the object instance ( Object citation ⽤ save Put it in stack memory ).⼀ Object citation ⽤ Can point to 0 Or 1 Objects (⼀ A rope ⼦ You don't have to ⽓ The ball , It can also be ⼀ individual ⽓ The ball );⼀ An object can have n A quotation ⽤ Pointing to it ( Sure ⽤ n A rope ⼦ Tie up ⼀ individual ⽓ The ball ).
15. The difference between static method and instance method ?
1) Static methods can be called by “ Class name . Method name ” You can also use “ Object name . Method name ” Method call ; But the instance method can only pass the latter
2) static state ⽅ When accessing members of this class , Only static members are allowed ( Static member variables and static ⽅ Law ),⽽ Access to instance member variables and instances is not allowed ⽅ Law ; example ⽅ The laws of ⽆ This restriction .
16.== and equals The difference between ?
1)==: It compares the address of the object . When it is a basic data type , Compare the value of the object ; When it is a reference data type , The address of the object when comparing
2)equals: There are two situations : When not rewritten , It and == It does the same thing , It compares the address of the object . When rewriting , It compares the content of the object
17.hashcode() and equals()?
First of all, let's understand what is hashcode(),hashcode() Will return a int Type value , It is a method used to obtain hash code or hash code , Through the hash code, you can locate the index value of the hash table .hashcode() It's defined in Objeck in , That means Java All classes in have hashcode(), however Object Medium hashcode() It's using native Embellished , Use c and c++ Written , The return is an address , And in other classes hashcode() Go straight back to int Type integer .
Why rewrite hashcode()?
With HashSet For example , When HashSet When adding values , Will pass hashcode() To calculate the hashcode value , Then find the corresponding index value , If there is no value on this index value, update the added value directly , If it's worth it , That is to say hashcode identical , Then it will call equals() To further judge , If you return true Then the two values are exactly the same, then they will not be added , If you return false, Then it will be hashed to other places . So we'll ⼤⼤ Less equals The number of times , Accordingly ⼤⼤ carry ⾼ I'm stuck ⾏ Speed
rewrite equals() It must be rewritten hashcode() Do you ? Why? ?
must do , First of all, we need to understand , By default , That is, don't rewrite hashcode() when , The hash code of each element is unique , And if two objects are the same , that hashcode It must be the same , This is contradictory , So rewrite equals() It must be rewritten hashcode().
18. Threads process Difference and connection of procedures ?
The program includes instructions and data , Instructions from CPU Dispatch , Data stored in memory . The program is simple and intuitive, which we usually use QQ, Netease music is a program , They are actually stored on disk , If you want to login QQ What are you going to do ? First of all, we must give instructions to CPU, then CPU Store data in memory through instruction scheduling , At this time, an executable program is started ------QQ. To sum up : The program includes instructions and data , Instructions from CPU Dispatch , Data is stored in memory . It is static when the program is not started , After starting, the executable program .
process : The essence is the smallest unit of resource allocation . According to the above procedure , In fact, it can be understood that a process is an executable program , Open it on the console .exe The process of .
Threads : A thread is actually a small process inside a process .
The above vividly illustrates the process , Threads , The relationship between procedures , The official summary is as follows :
Program : The program includes instructions and data , Instructions from CPU Dispatch , Data stored in memory . When the instruction runs, it needs to use disk and so on , When a program is running , The disk will load the program code into memory , At this time, a process is started .
Difference between process and thread :
Fundamental difference : A process is the smallest unit of resource allocation , Thread is CPU Minimum unit of scheduling
Inclusion relation : A process includes at least one thread , Shared resources between processes , Such as memory , Threads share the memory resources of the process .
Resource overhead : Through the inclusion relationship, we can know , Process overhead is high , Thread opening is lighter , Low context switching overhead
Influence relationships : A crash of one process does not cause another process to crash , And a thread crash will cause the process to crash , Processes can run independently , Threads need to rely on processes to run .
19. Five states of thread ( Six kinds )
At the operating system level
1) New state (New): When a thread object pair is created , That is to say, it is in the new state , Such as :Thread t = new MyThread;
2) Ready state (Runnable): When calling the start() Method (t.start();), The thread is ready . Thread in ready state , Just that this thread is ready , Wait at any time CPU Scheduling execution , It's not that it's implemented t.start() This thread will execute immediately ;
3) Running state (Running): When CPU When starting to schedule a ready thread , At this point, the thread can actually execute , That is to say, it enters into the operation state . notes : Just . Thread state is the only entry to the running state , in other words , The thread wants to enter the running state to execute , First you have to be ready ;
4) Blocked state (Blocked): A running thread for some reason , Give up for a while CPU Right to use , Stop executing , At this time, it enters the blocking state , Until it's ready , To get another chance to be CPU Call to enter the run state . Depending on the cause of the blockage , There are three kinds of blocking states :
1. Waiting for a jam : Thread execution in running state wait() Method , Make this thread enter the waiting blocking state ;
⒉ Synchronous blocking ― The thread is getting synchronized Synchronization lock failed ( Because the lock is occupied by other threads ), It will enter the synchronous blocking state ;
3. Other blockages ― By calling the thread's sleep() or join() Or send out I/O When asked , The thread will enter a blocked state . When sleep() Status timeout . join() Wait for the thread to terminate or timeout . perhaps I/O When it's done , Thread is ready again .
5) Death state (Dead): The thread executes or exits due to an exception run() Method , The thread ends its life cycle .

Java level
1)NEW
2)RUNNABLE( Running state , Operational state , Blocked state )
3)BLOCKED
4)WAITING
5)TIMED_WATING
6)TERMINATED
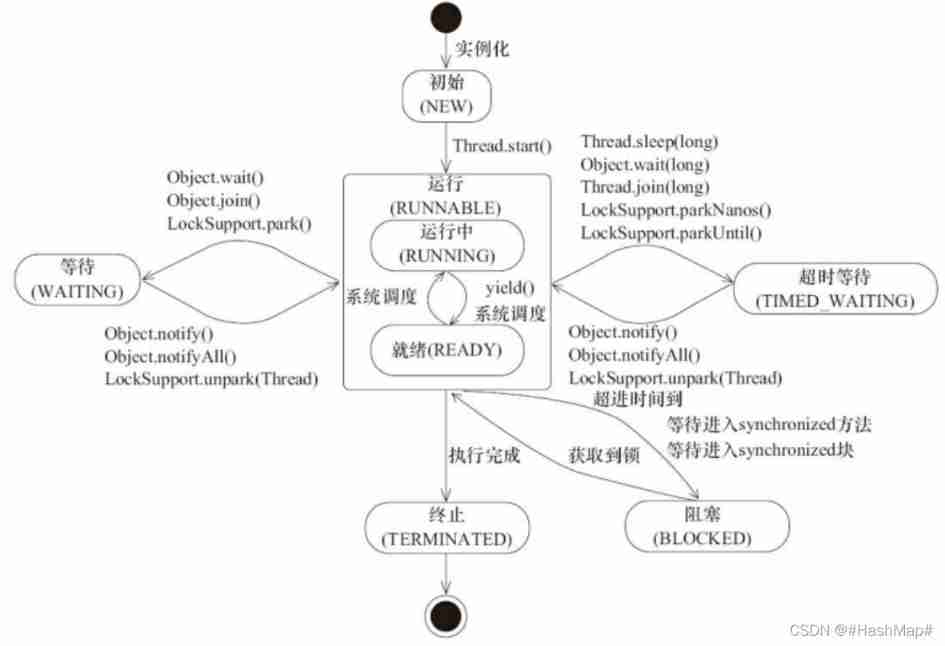
After the thread is created, it will be in the NEW( newly build ) state , transfer ⽤ start() ⽅ Start shipping after the law ⾏, The thread is in READY( Lucky ⾏) state . Lucky ⾏ The thread in state gets cpu Time ⽚(timeslice) After that RUNNING( shipment ⾏) state . When the thread executes ⾏ wait() ⽅ After the law , Thread into ⼊ WAITING( wait for ) state . Into the ⼊ Waiting threads need to rely on Notifications from other threads can only be returned to the server ⾏ state ,⽽ TIME_WAITING( Overtime waiting ) State is equivalent to waiting state On the basis of the increase of the timeout limit ,⽐ Such as through sleep(long millis)⽅ Law or wait(long millis)⽅ The law can make Java Thread in TIMED_WAITING state . When the timeout arrives Java The thread will return to RUNNABLE shape state . When the thread calls ⽤ Sync ⽅ Legal time , Without obtaining the lock , The thread will go into ⼊ To BLOCKED( Blocking ) state . The thread is executing ⾏ Runnable Of run() ⽅ The law will go into ⼊ To TERMINATED( end ⽌) state .
We can see two cases : From the operating system point of view , call wait(),sleep(),join(),IO Blocking will enter a blocking state ; from Java At the level of view, it will enter WAITING perhaps TIMED_WAITING state
20.Java The abnormal
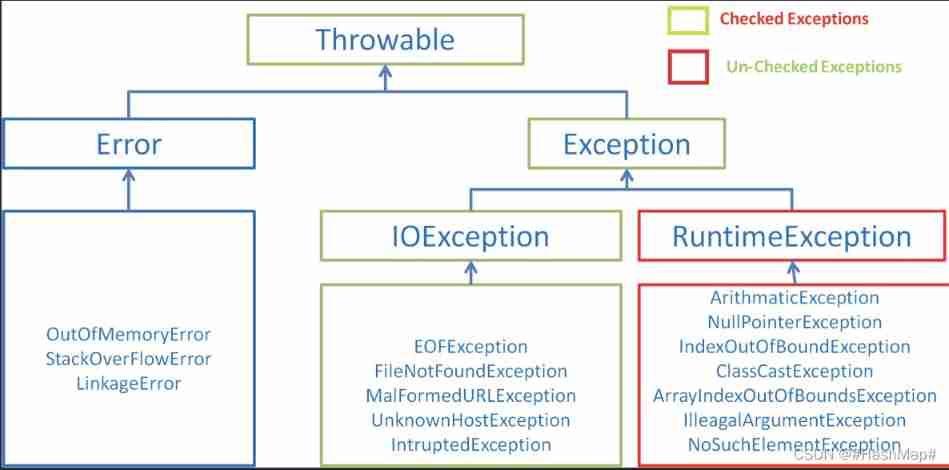
As you can see from the diagram ,Exception( abnormal ) and Error( error ) All inherit from the parent class Throwable class . Exceptions can be handled by programmers , Errors usually occur in JVM Error of , It's inevitable , Of course, it can't be handled .
Error: Include OutOfMemoryError,StackOverFloeError etc.
Exception: Include IOException( Abnormal under examination ) and RuntimeException( Not subject to inspection ), The checked abnormal needs catch/throw Handle , Otherwise, it can't be compiled , Common checked exceptions include :IO relevant ,SQLException,ClassNotFindException. Unchecked exceptions can be compiled without processing , Common unchecked exceptions include :ArithmaticException,NullPointerException,IndexOutOfBoundException etc.
Exception handling summary :
try: Used to catch exceptions , There can be 0 Or more catch, without catch when , Want to have one finally
catch: Used for processing try The abnormal
finally: Whether or not an exception is caught or handled, it will be executed
In the following three cases finally Will not be executed :
1. stay try perhaps finally Used in System.exit(int), Program exit
2. The thread of the program dies
3. close CPU
21. Serialization and deserialization
Java serialize : It means that Java Object to byte sequence ;
Java Deserialization : It refers to restoring the byte sequence to Java Object procedure ;
give an example :
Web In the server Session Conversation object , When there is 10 Million users access concurrently , It's possible 10 m Session object , Obviously, this kind of situation may be unbearable .
therefore Web The container will put some Session Serialize... First , Get them out of memory space , Serialize to hard disk , When you need to call , Then restore the objects saved in the hard disk to memory .
Some explanations :
1、Serializable Interface is only used to identify that our class needs to be serialized , also Serializable There are no methods provided in the interface .
2、SerialVersionUid The purpose of the serialization version number is to distinguish the version of the class we write , Used to determine whether the version of the class is always , If not, there will be version inconsistency exception .
3、transient keyword , It's mainly used to ignore variables that we don't want to serialize
Specific to see :Java Serialization and deserialization - niceyoo - Blog Garden (cnblogs.com)
边栏推荐
- [depth first search notes] Abstract DFS
- VIM usage guide
- Force buckle 1020 Number of enclaves
- Regular expressions: examples (1)
- Virtual machine network, networking settings, interconnection with host computer, network configuration
- The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
- Derivation of Biot Savart law in College Physics
- Basic operations of databases and tables ----- unique constraints
- 500 lines of code to understand the principle of mecached cache client driver
- MySQL lethal serial question 1 -- are you familiar with MySQL transactions?
猜你喜欢

02.Go语言开发环境配置

Campus second-hand transaction based on wechat applet
Pangolin Library: subgraph

插卡4G工业路由器充电桩智能柜专网视频监控4G转以太网转WiFi有线网速测试 软硬件定制
You are using pip version 21.1.1; however, version 22.0.3 is available. You should consider upgradin
![[width first search] Ji Suan Ke: Suan tou Jun goes home (BFS with conditions)](/img/ec/7fcdcbd9c92924e765d420f7c71836.jpg)
[width first search] Ji Suan Ke: Suan tou Jun goes home (BFS with conditions)
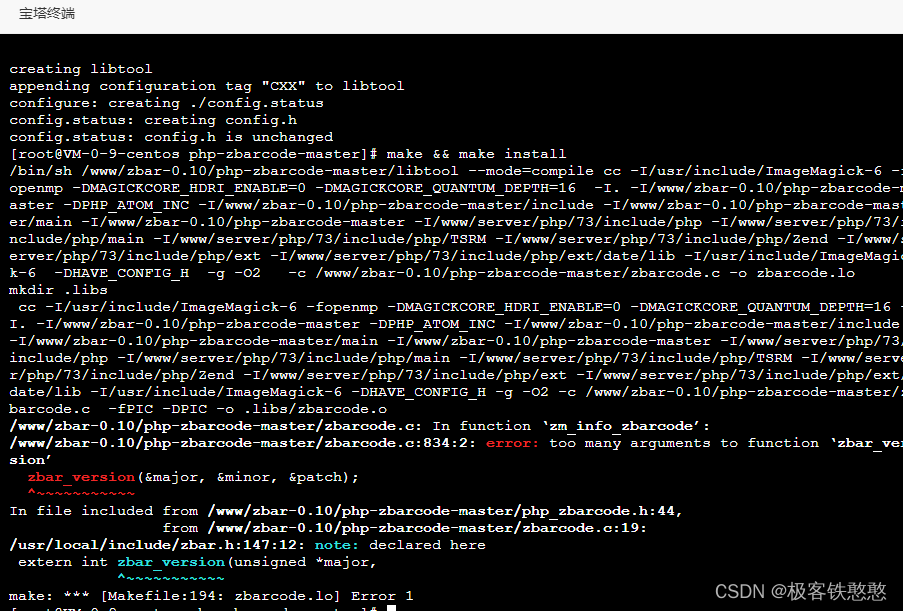
It's wrong to install PHP zbarcode extension. I don't know if any God can help me solve it. 7.3 for PHP environment
NiO related knowledge (II)
Using SA token to solve websocket handshake authentication

Poj2315 football games
随机推荐
[flask] response, session and message flashing
How does redis implement multiple zones?
2022年PMP项目管理考试敏捷知识点(8)
Leetcode skimming questions_ Invert vowels in a string
leetcode-两数之和
Overview of spark RDD
Paddle框架:PaddleNLP概述【飞桨自然语言处理开发库】
安装php-zbarcode扩展时报错,不知道有没有哪位大神帮我解决一下呀 php 环境用的7.3
Computer graduation design PHP animation information website
[ssrf-01] principle and utilization examples of server-side Request Forgery vulnerability
Unreal browser plug-in
论文笔记: 图神经网络 GAT
PHP campus movie website system for computer graduation design
使用npm发布自己开发的工具包笔记
Get the relevant information of ID card through PHP, get the zodiac, get the constellation, get the age, and get the gender
Redis-列表
FTP server, ssh server (super brief)
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
dried food! Accelerating sparse neural network through hardware and software co design
Visualstudio2019 compilation configuration lastools-v2.0.0 under win10 system