当前位置:网站首页>CAS mechanism
CAS mechanism
2022-07-07 10:31:00 【HGW689】
List of articles
1、 What is? CAS?
CAS The full name is Compare And Swap( Compare and exchange , To be exact, it is called : Compare and exchange the same )
It's modern CPU A widely supported special instruction that operates on shared data in memory .CAS The role of is :CAS Comparison and exchange can be converted into atomic operations , This atomic operation is performed directly by the processor CPU Guarantee .
( It can be seen as a lightweight synchronized, It can guarantee the atomic operation of variable modification )
CAS Instruction requires three operands , Namely :
- Memory location ( stay Java Can be simply understood as the memory address of the variable , use V Express )
- Old pre value ( use A Express )
- Ready to set the new value ( use B Express )
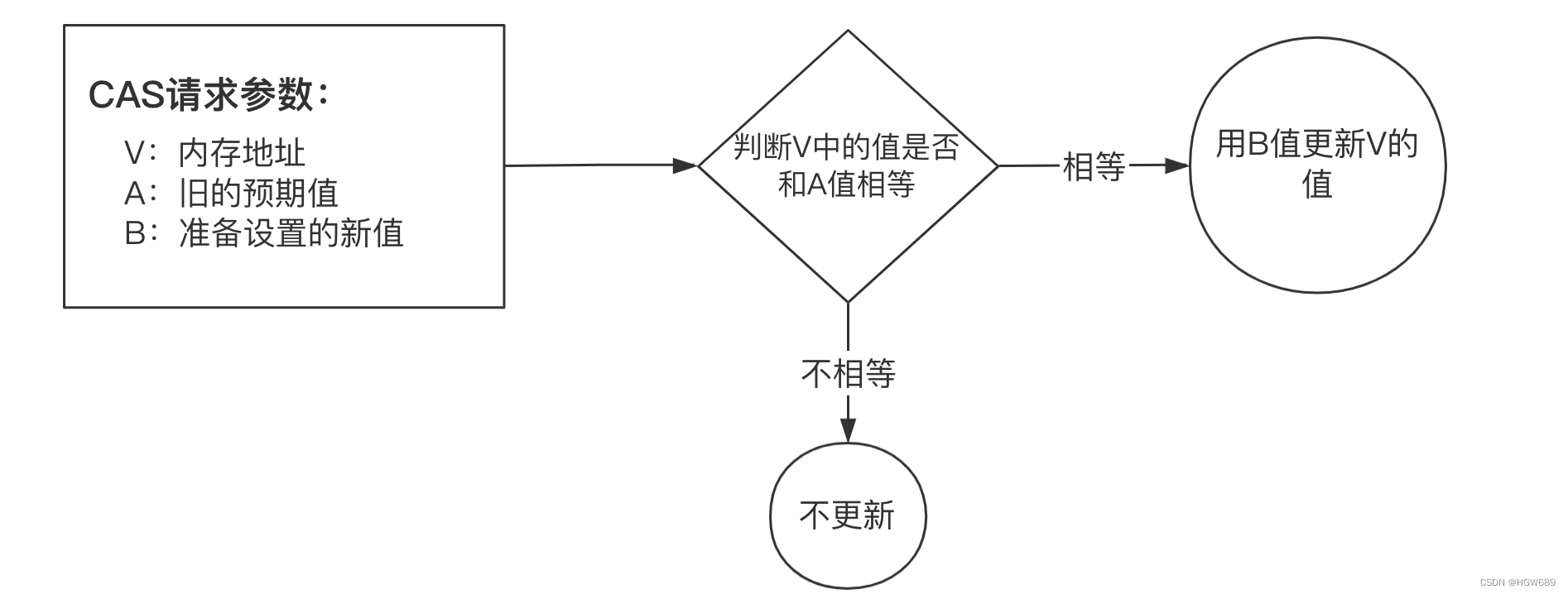
CAS Instruction execution , If and only if V accord with A when , The processor will use B to update V Value , Otherwise it doesn't perform updates or again ( When he tries again, this behavior is called —— The spin ). But whether it is updated or not V Value , Will return to V The old value . This process is an atomic operation , It will not be interrupted by other threads during execution .
It is a kind of CPU Concurrent primitives , Primitives belong to the category of operating system terms , Is composed of several instructions , A process used to accomplish a function , And the execution of primitives must be continuous , No interruption is allowed during execution , in other words CAS It's a piece. CPU Atomic instructions for , Will not cause so-called data inconsistency .
So many principles have been said , Roll it Demo Well ~ By implementing classes AtomicInteger Let's demonstrate CAS:
public class CASDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(6);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(6, 2022) + "\t" + atomicInteger.get());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(6, 2022) + "\t" + atomicInteger.get());
}
}

for the first time C The value is equal to the A, Therefore, the C Change it to B. The second time C The value obtained is not equal to A, Therefore, it is not modified .
2、CAS The realization of atomic operation 3 Big problem ?
ABA problem 、 Long cycle time and large resource consumption 、 There's only one guarantee Atomic operation of shared variables .
Long cycle time and large resource consumption
For example, the source code getAndAddInt Method execution , There is one do while. If CAS Failure , It's going to keep trying . If CAS It's been a long time without success , May give CPU High cost .
ABA problem
If a variable V The first time I read it is A value , And check that it's still A value , Does that mean that its value has not been changed by other threads ?
It's impossible , because If its value has been changed to B, It was later changed back to A, that CAS The operation will be wrong. It has never been changed . This loophole is called CAS Operation of the “ABA problem ”. Next Demo~
public class ABADemo {
static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(100);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,200);
// Pause 10 millisecond
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(200,100);
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
// Pause 200 millisecond
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,500) + "\t" + atomicInteger.get());
}
},"tw").start();
}
}
In the code t1 The thread changes the value to 200, But again t2 The thread is modified to 100. but t1 Thread doesn't know , It will be wrong for people. It has never been changed .
So how to solve ABA The problem? ? have access to java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference<V> Class to solve
public class ABADemo {
static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(100);
static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> stampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(100,1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = stampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+" First version number :"+stamp);
// Pause 500 millisecond , Guaranteed behind t2 The version number obtained by thread initialization and t1 equally
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
stampedReference.compareAndSet(100, 200, stampedReference.getStamp(), stampedReference.getStamp()+1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"2 Sub version number :"+stampedReference.getStamp());
stampedReference.compareAndSet(200,100,stampedReference.getStamp(), stampedReference.getStamp()+1);
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = stampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+" First version number :"+stamp);
// Pause 1000 millisecond , Guarantee t2 The version number obtained by thread initialization and t1 equally
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean b = stampedReference.compareAndSet(100, 500, stamp, stampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println(b + "\t" + stampedReference.getReference() + "\t" + stampedReference.getStamp());
},"t2").start();
}
}
3、Unsafe class
from JDK5 after ,Java It's only in class libraries that CAS operation , This operation is performed by sun.misc.Unsafe The inside of the class compareAndSwapXXX() The underlying implementation of the method package is CPU Instructions cmpxchg.
perform cmpxchg At the time of instruction , Will determine whether the current system is a multi-core system , Lock the bus if it is , Only one thread will lock the bus successfully , The successful locking will execute CAS operation , in other words CAS The atomicity of CPU Achieve exclusive .
Unsafe Class explanation
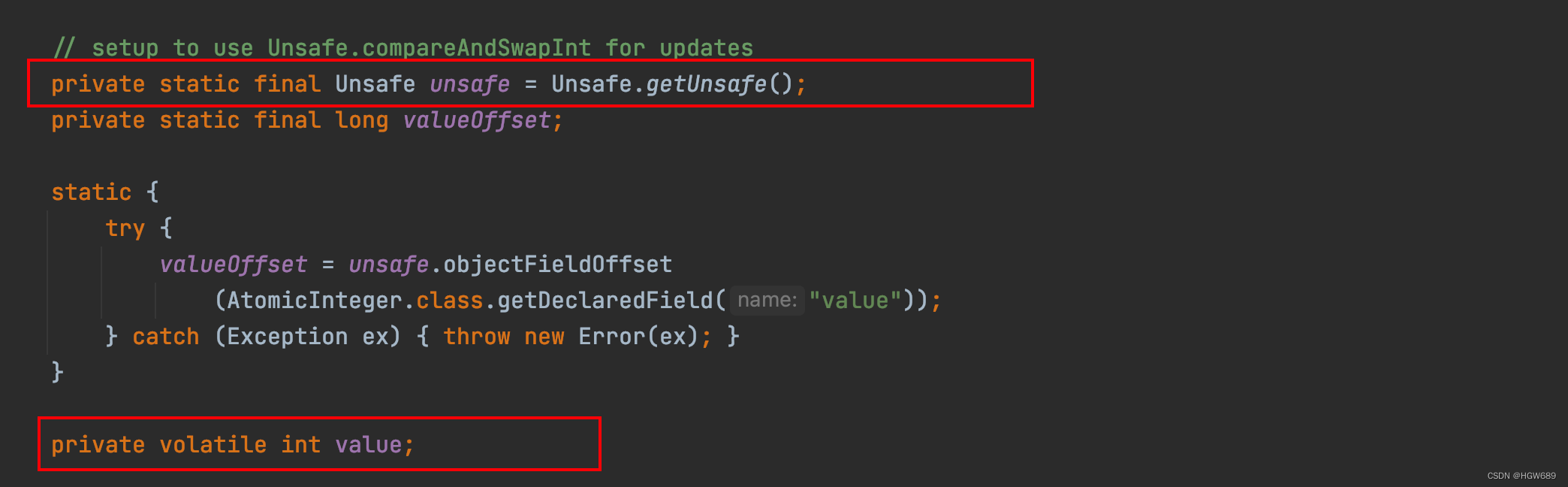
1、Unsafe
yes CAS The core of the class , because Java Method cannot directly access the underlying system , Need to go through the local (native) Method to access ,Unsafe It's like a back door , Based on this class, you can directly operate the data of specific memory .Unsafe Class exists in sun.misc In bag , Its internal method operation can be like C Direct operation of memory as a pointer to , because Java in CAS Operation execution depends on Unsafe Class method .
Be careful :Unsafe All methods in the class are native Embellished , in other words Unsafe The methods in the class directly call the underlying resources of the operating system to perform corresponding tasks .
2、 Variable valueOffset, Indicates the offset address of the variable value in memory , because Unsafe Is to get the data according to the memory offset address .
3、 Variable value use volatile modification , Ensures memory visibility between multiple threads .
Source code interpretation
Next, let's analyze the source code :
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
Click through compareAndSet() Source code for method , It is found that it calls unsafe.compareAndSwapInt() Method , stay unsafe Class , There are three main methods :
public final native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object var1, long var2, Object var4, Object var5);
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
public final native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object var1, long var2, long var4, long var6);
The above three methods are similar , Mainly for 4 One parameter for explanation :
- var1: Represents the object to operate on
- var2: Represents the address of the attribute in the object to be manipulated Offset
- var4: Indicates the expected value of the data that needs to be modified
- var5/var6: Indicates the new value to be modified to
Here is an explanation of the offset , There is a saying in the University compilation ~this Equivalent to the first address of the current object , We need to find the corresponding value Storage location in memory , At this point, you need an offset , namely : Receiving address + Offset = The location of the value in memory
We know i++ It is not safe in the case of multithreading , that atomicInteger.getAndIncrement() Methods? ?
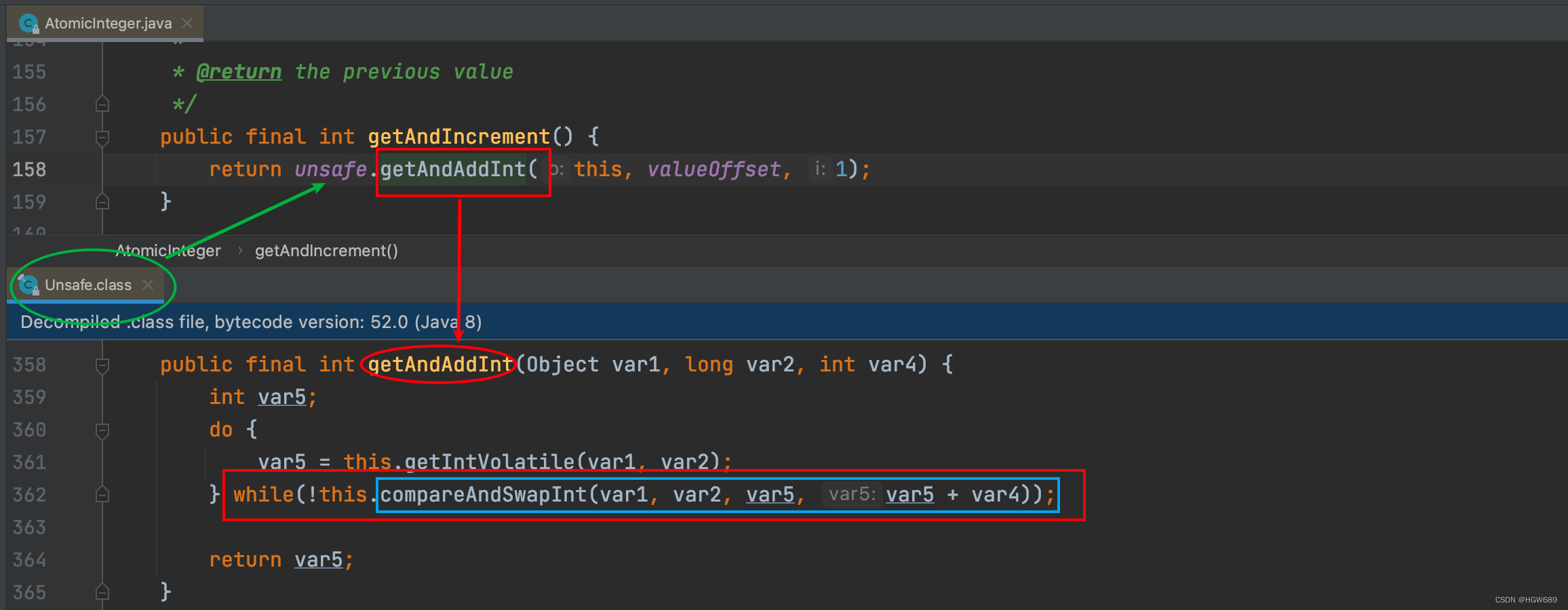
Assuming that thread A And site B Two threads execute at the same time getAndIncrement() Method ( Run in different places CPU On ):
- Suppose main memory value The original value is 3, according to JMM Model , Threads A and Threads B Each holds a share with a value of 3 Of value Copies of the are to their respective working memory .
- Threads A adopt getIntVolatile(var1, var2) Get value value 3, Suppose that the thread A suspended .
- Threads B Also through getIntVolatile(var1, var2) Get value value 3, The thread B Not suspended and executed compareAndSwapInt Method , The comparison memory value is also 3, Then the memory value is successfully modified to 4, Threads B completion of enforcement .
- The thread A Awakened , perform compareAndSwapInt Methods to compare , It is found that the value in main memory is inconsistent with the old expected value , This indicates that the value has been updated by other threads , The thread A This modification failed , Spin again .
- Threads A Recapture value value , Because of the variable value By volatile modification , So other threads modify it , Threads A Is visible , Threads A Carry on compareAndSwapInt Compare and replace , Until we succeed .
Unsafe Class compareAndSwapInt, Corresponding to local methods , The implementation of this method is located in unsafe.cpp, Let's find out ~
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-xilwh0X8-1656433185456)(JUC Concurrent programming .assets/image-20220628234302944.png)]](/img/2b/fb6b2b8273a0c564ef4d69c039254b.png)
4、AtomicReference<V>
AtomicReference and AtomicInteger Very similar , The difference is AtomicInteger It's the encapsulation of integers , and AtomicReference It corresponds to the common object reference . In other words, it can ensure the thread safety when you modify the object reference .
AtomicReference It's the effect, it's the right ” object ” Perform atomic operations . It provides an object reference variable whose reading and writing are atomic . Atom means that multiple threads try to change the same AtomicReference( For example, compare and exchange operations ) Will not make AtomicReference In a state of inconsistency .
namely Object references that can be updated atomically .
First write a User class :
class User{
String username;
int age;
// Omit the full parameter construction method 、setter、getter、toString
}
adopt AtomicReference Class implementation for ”User object ” Perform atomic operations .
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicReference<User> userAtomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
User hgw = new User("hgw", 22);
User hly = new User("hly", 22);
userAtomicReference.set(hly);
System.out.println(userAtomicReference.compareAndSet(hly, hgw) +"\t,"+ userAtomicReference.get());
System.out.println(userAtomicReference.compareAndSet(hly, hgw) +"\t,"+ userAtomicReference.get());
}
}
5、CAS—— spinlocks
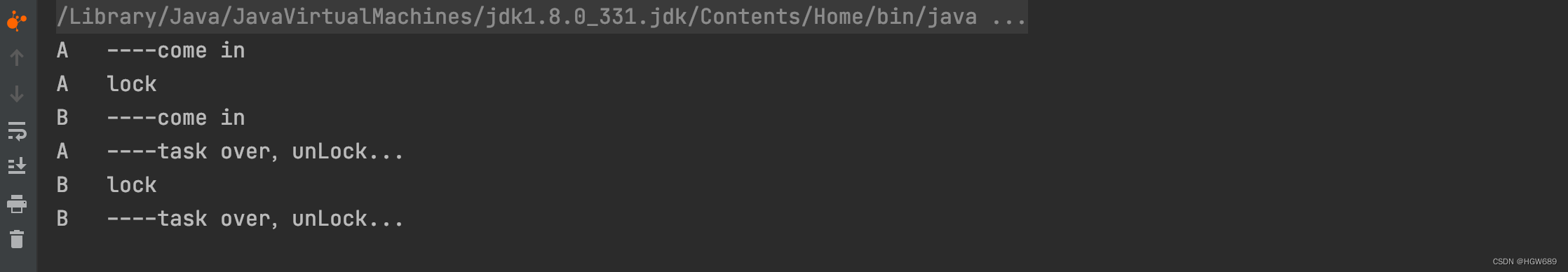
To talk about CAS Of course, we need to talk about spin lock , Write a spin lock here to show you ~
public class SpinLockDemo {
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
public void lock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"----come in");
while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"lock");
}
public void unLock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread,null);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"----task over,unLock...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo();
new Thread(()->{
spinLockDemo.lock();
// Pause the thread for a few seconds
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
spinLockDemo.unLock();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
spinLockDemo.lock();
spinLockDemo.unLock();
},"B").start();
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
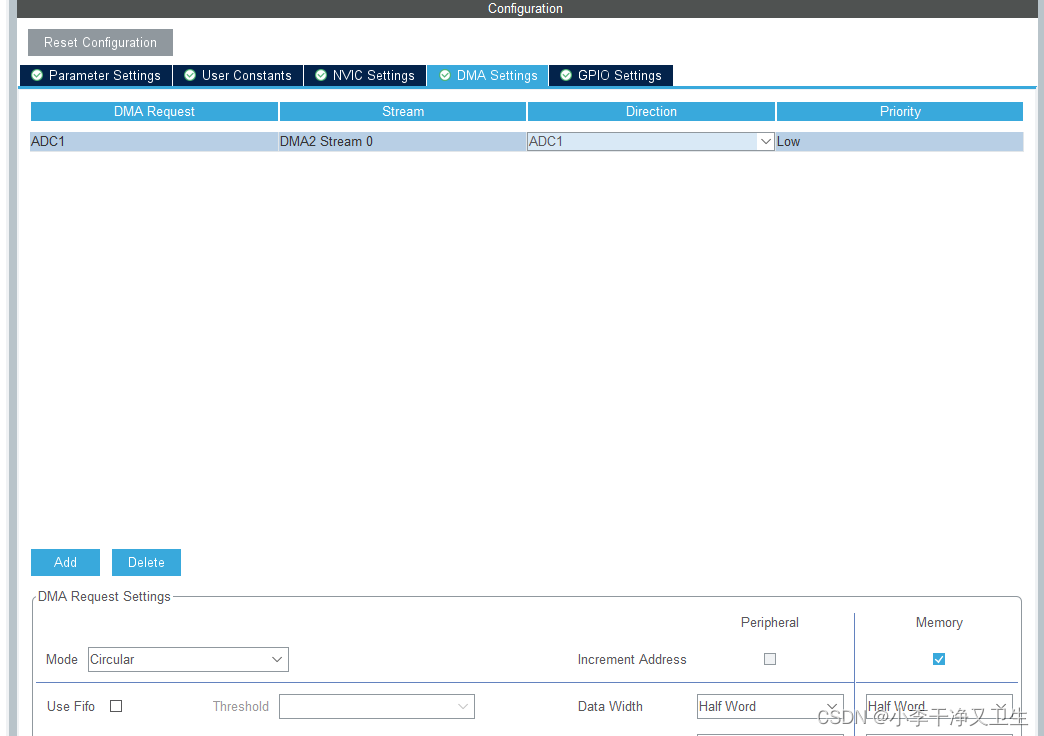
HAL库配置通用定时器TIM触发ADC采样,然后DMA搬运到内存空间。

Pre knowledge reserve of TS type gymnastics to become an excellent TS gymnastics master

OpenGL glLightfv 函数的应用以及光源的相关知识
![P1031 [NOIP2002 提高组] 均分纸牌](/img/ba/6303f54d652fa7aa89440e314f8718.png)
P1031 [NOIP2002 提高组] 均分纸牌

JMeter installation

Elegant controller layer code

Weekly recommended short videos: what are the functions of L2 that we often use in daily life?
php \n 换行无法输出
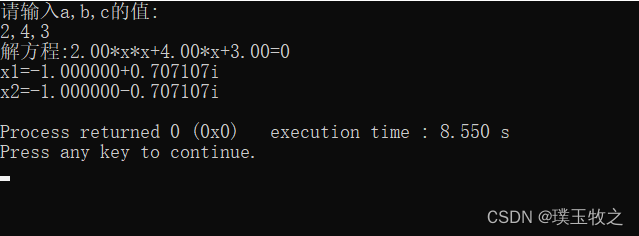
求方程ax^2+bx+c=0的根(C语言)
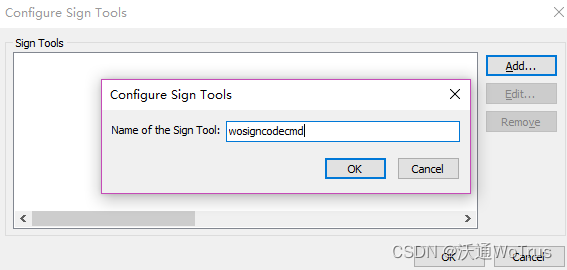
Inno setup packaging and signing Guide
随机推荐
Leetcode-303: region and retrieval - array immutable
施努卡:机器人视觉抓取工作原理 机器视觉抓取
.NET配置系统
MySQL insert data create trigger fill UUID field value
XML configuration file parsing and modeling
P1223 排队接水/1319:【例6.1】排队接水
Talking about the return format in the log, encapsulation format handling, exception handling
Hdu-2196 tree DP learning notes
CSAPP Bomb Lab 解析
MCU is the most popular science (ten thousand words summary, worth collecting)
Jump to the mobile terminal page or PC terminal page according to the device information
[sword finger offer] 42 Stack push in and pop-up sequence
【STM32】STM32烧录程序后SWD无法识别器件的问题解决方法
The width of table is 4PX larger than that of tbody
[second on] [jeecgboot] modify paging parameters
深入分析ERC-4907协议的主要内容,思考此协议对NFT市场流动性意义!
Kotlin realizes wechat interface switching (fragment exercise)
反射效率为什么低?
【华为机试真题详解】高矮个子排队
Why is the reflection efficiency low?