当前位置:网站首页>Nmap user manual learning records
Nmap user manual learning records
2022-07-05 03:38:00 【paidx0】
Catalog
Take a brief note of nmap Some of the basic instructions , Don't ask , There are too many orders , I am tired of turning English documents ,nmap Its scanning function and concealment are very powerful , It is necessary to have a look more
Description of objectives
-iL <inputname> ( Enter from a list or file )
-iR <hostnum> ( Randomly select the number of generation targets )
--exclude <host1,host2> ( Excluded host network )
The host found
-sL ( List scan )
-sP (Ping scanning , Can and in addition -P0 Any way of discovery )
-P0 ( nothing Ping, All hosts are considered online , Skip host discovery )
-PS <portlist> (TCP SYN Ping)
-PA <portlist> (TCP ACK Ping, What is actually sent is SYN message , instead of ACK message . Stateless firewall , Stateful unexpected firewall , Designated -PS And specify the -PA, namely SYS and ACK)
-PU <portlist> (UDP Ping, through TCP A firewall )
-PE;-PP;-PM (ICMP Ping)
-PR (ARP Ping , be based on ARP Bi Ji Yu IP Faster and more reliable , By default, when the target host is on the same LAN , Even if you specify ping The type of , You can also use ARP. Don't want to ARP,--send-ip)
-n ( Never reverse domain name resolution )
-R ( All target reverse domain name resolution )
--system-dns ( Use the system domain name resolver , Unless nmap Of DNS Only when there is a problem , Because thieves are slow )
Port scanning
nmap Of 6 Two port States
1、open( Open )
2、closed ( closed )
3、filtered( Filtered )
4、unfiltered( Unfiltered ,ACK Scanning will classify this state , Other types of scan confirmation )
5、open|filtered( Open or filtered )
6、closed|filtered( Closed or filtered )
-sS (SYN, Default ,TCP Half connection is not easy to find , Return explicit port status )
-sT (TCP)
-sU (UDP)
-sN;-sF;-sX (TCP Null,FIN,Xmas, Except that the detection flag bit is different , Completely consistent in behavior , You can avoid some stateless firewalls , Even better than SYN More secret , Disadvantages: the port status cannot be marked correctly )
-sA (ACK, Unable to determine the port status , Used to discover firewall rules )
-sW (TCP window , inaccurate )
-sM (Maimon, and Null,FIN,Xmas Exactly the same as , Except that the message is FIN/ACK)
--scanflags ( custom TCP scanning , Set flag bit or scan type )
-sl <zombie host:probeport> (TCP Port blind scan , There is no message from your truth ip Address to destination , Extreme concealment , Default without ports 80)
-sO (IP Protocol scan )
-b <ftp host> (FTP Bounce scan , agent ftp Connect , Format <username>:<password>@<server>:<port>,server It is fragile. FTP Server name ip)
Port specification
-p <port range> ( Scan only the specified port )
-F ( Quick scan , about 1200 Common ports )
-r ( Sequential scanning , For efficiency , Default random scan , Move forward according to the common port )
Service and version detection
-sV ( Version detection ,-A Open the operating system and version detection at the same time )
--allports ( Do not exclude any ports for version probe , Skip by default 9100 port , Print data like some simple printers )
--version-intensity <intensity> ( Set version scan strength 1-9, Default 7)
--version-light (version-intensity2 Another name for , Lightweight and faster , The identification service is weak )
--version-all ( Try all the probes ,version-intensity9 Another name for , Detection of each port )
--version-trace ( Track version scan activity , Print detailed information about the scanning and debugging in progress )
-sR (RPC,-sV Version detection includes it and is more comprehensive , all -sR Rarely need )
Operating system detection
-O ( Enable operating system detection ,-A)
--osscan-limit ( Detect the specified target operating system , Use only -O or -A Operating system detection works )
--osscan-guess;--fuzzy ( Extrapolate the operating system test results , Try to match when you can't be sure , Default match )
Time and performance
--min-hostgroup <milliseconds>;--max-hostgroup <milliseconds> ( Adjust the size range of the parallel scanning group )
--min-parallelism <milliseconds>;--max-parallelism <milliseconds> ( Adjust the parallelism of the detection message , Usually max Set to 1,min Set to 10)
--min-rtt-timeout <milliseconds>;--max-rtt-timeout <milliseconds>;--initial-rtt-timeout <milliseconds> ( Adjust detection message timeout )
--host-timeout <milliseconds> ( Give up the low speed target host )
--scan-delay <milliseconds>;--max-scan-delay <milliseconds> ( Adjust the time interval of detection message , Avoid threshold based intrusion detection and prevention systems )
-T <Paranoid|Sneaky|Polite|Normal|Aggressive|Insane> ( Set time template 0-5, The first two are used for IDS avoid ,Polite Reduce scanning speed to use less bandwidth and target resources , Default Normal,Aggressive Speed up scanning ,Insane Faster speed sacrifices accuracy )
A firewall /IDS avoid
-f ( Segmented message );--mtu ( Use specified MTU, You can customize the offset size , Do not use -f, The offset must be 8 Multiple )
-D <decoy1,decoy2,decoy3.....,me....> ( Use decoys to conceal scanning , The first 6 Use at or later positions me, The port scan detector will not report this true ip, If not used nmap Will be true ip Put it in a random position )
-S <IP_address> ( Source address spoof , Constant cooperation -e or -P0 Use )
-e <interface> ( Use the specified interface )
--source-port <portnumber>; -g <portnumber> ( Source port spoof ,nmap Send data from the specified port )
--data-length <number> ( When sending a message , Additional random data )
--ttl <value> ( Set up IP time-to-live Domain )
--randomize-hosts ( The order of the target hosts is random )
--spoof-mac <mac address,prefix,or vendor name> (MAC Address hoax )
Output
-oN <filespec> ( The standard output is written directly to the specified file )
-oX <filespec> (XML Output is written directly to the specified file )
-oS <filespec> ( Interactive output )
-oG <filespec> (Grep Output , Not recommended ,XML Very powerful )
-oA <basename> ( Scan results in standard format 、XML、Grep One time output , Store separately <basename>.nmap,<basename>.xml and <basename>.gnmap In file )
-v ( Detailed output )
-d [level] ( Set debug level 0-9, Than -v More information , Mainly developers use this )
--packet-trace ( Track messages sent and received , Print the message summary sent and received , For debugging )
--iflist ( List interfaces and routes , Output the detected interface list and system route , Debugging route and device description error )
--append-output ( Append... To the output file , Because the default is overwritten )
--resume <filename> ( Continue interrupted scan ,-oN or -oG When the log is retained ,nmap Append the new result to the file , I won't support it XML)
The other options
-A ( Intense scanning mode , Operating system included -O And version scanning -sV)
--interactive ( Start in interactive mode , This option contains a ! The operator , Used to perform shell command , Can be used to claim , This is also not installed Nmap setuid root One of many reasons )
--send-eth ( Use the original Ethernet frame to send , The original socket word (IP layer ) yes UNIX The most effective way to host , And Ethernet frames are the best Windows operation System , because Microsoft The original socket support is disabled )
--send-ip ( In the original IP Layer send , requirement Nmap Through the original IP Socket send message , Instead of the lower ones Too net frame )
example
nmap -v scanme.nmap.org
Scan the host for all reservations TCP port ,-v For more details
nmap -sS -O scanme.nmap.org/24
Secret SYN scanning , Detect the operating system version , Same as host C Segment machine
nmap -sV -p 22,53,110,143,4564 198.116.0-255.1-127
Host enumeration ,TCP scanning , The object is B class 188.116 In segment 255 individual 8 Seat net . Used to determine whether the system is running sshd、DNS、imapd or 4564 port
nmap -v -iR 1000 -P0 -p 80
Random 1000 Host scanning web Whether the service is on
nmap -P0 -p80 -oX logs/pb-port80scan.xml -oG logs/pb-port80scan.gnmap 216.163.128.20/20
scanning 4096 individual IP Address , lookup Web The server ( No ping), Put the result in Grep and XML Format preservation .
host -l company.com | cut -d -f 4 | nmap -v -iL
Conduct DNS Area transmission , To discover company.com Host in , And then IP Address to Nmap. be used for GNU/Linux, Other systems have different commands for area transmission .
边栏推荐
- Single box check box
- How to make the listbox scroll automatically when adding a new item- How can I have a ListBox auto-scroll when a new item is added?
- Jd.com 2: how to prevent oversold in the deduction process of commodity inventory?
- Six stone programming: advantages of automated testing
- [deep learning] deep learning reference materials
- SQL performance optimization skills
- 【web审计-源码泄露】获取源码方法,利用工具
- Quick start of UI component development of phantom engine [umg/slate]
- Learning notes of raspberry pie 4B - IO communication (I2C)
- Pat grade a 1119 pre- and post order traversals (30 points)
猜你喜欢
![[groovy] string (string injection function | asBoolean | execute | minus)](/img/ea/bf1e6aa713cf54e29653e35b164560.jpg)
[groovy] string (string injection function | asBoolean | execute | minus)
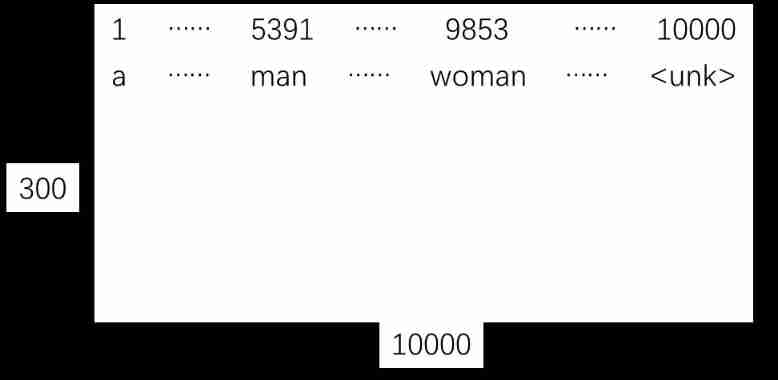
Yyds dry goods inventory embedded matrix
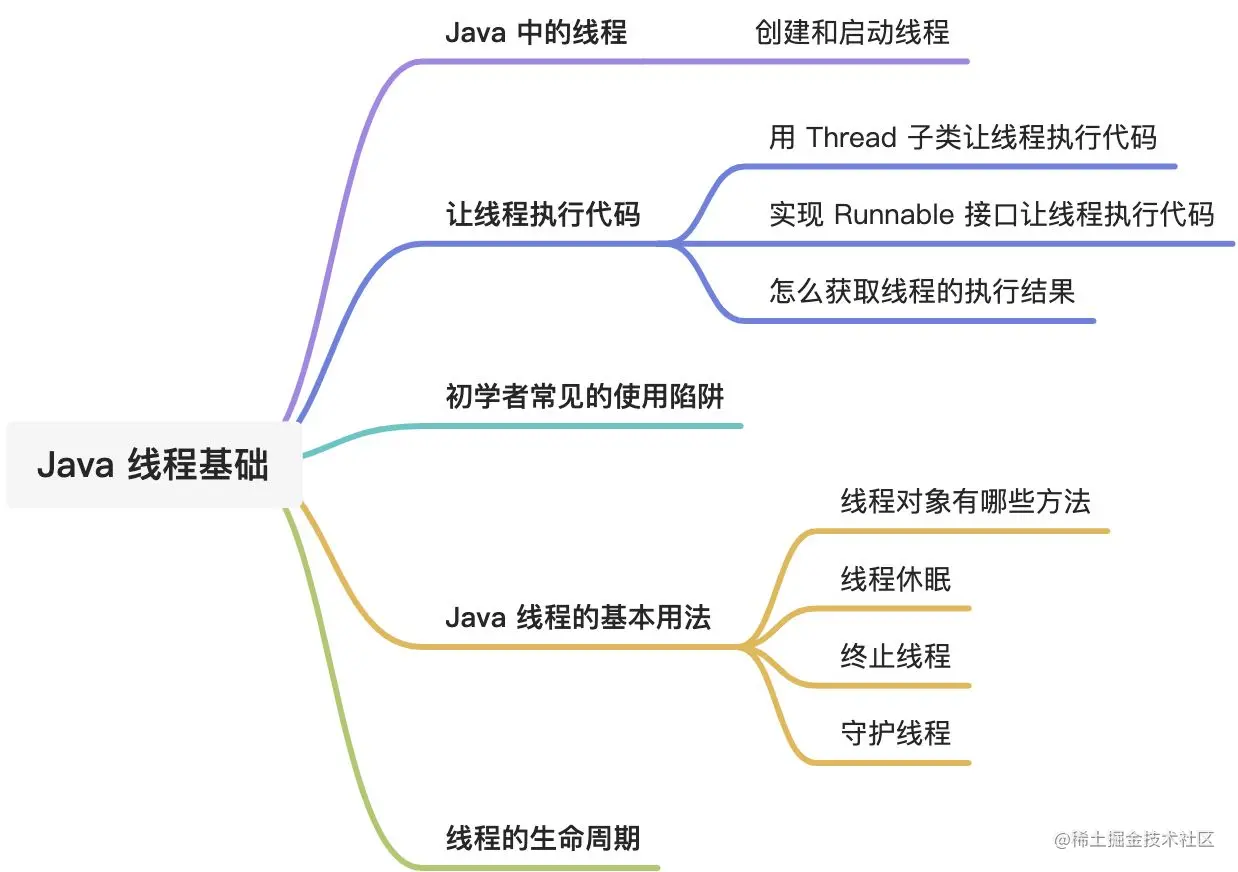
线程基础知识

Why are there fewer and fewer good products produced by big Internet companies such as Tencent and Alibaba?
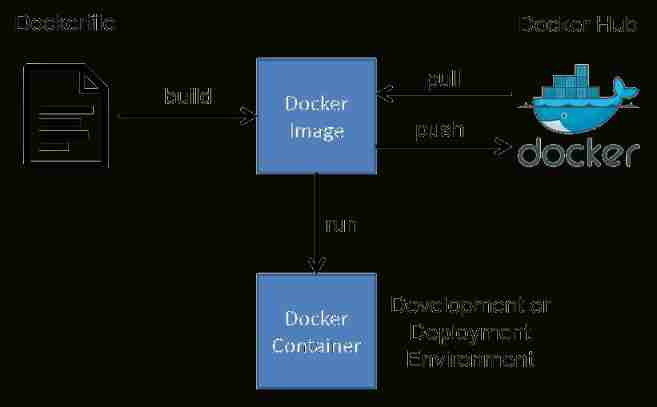
Bumblebee: build, deliver, and run ebpf programs smoothly like silk
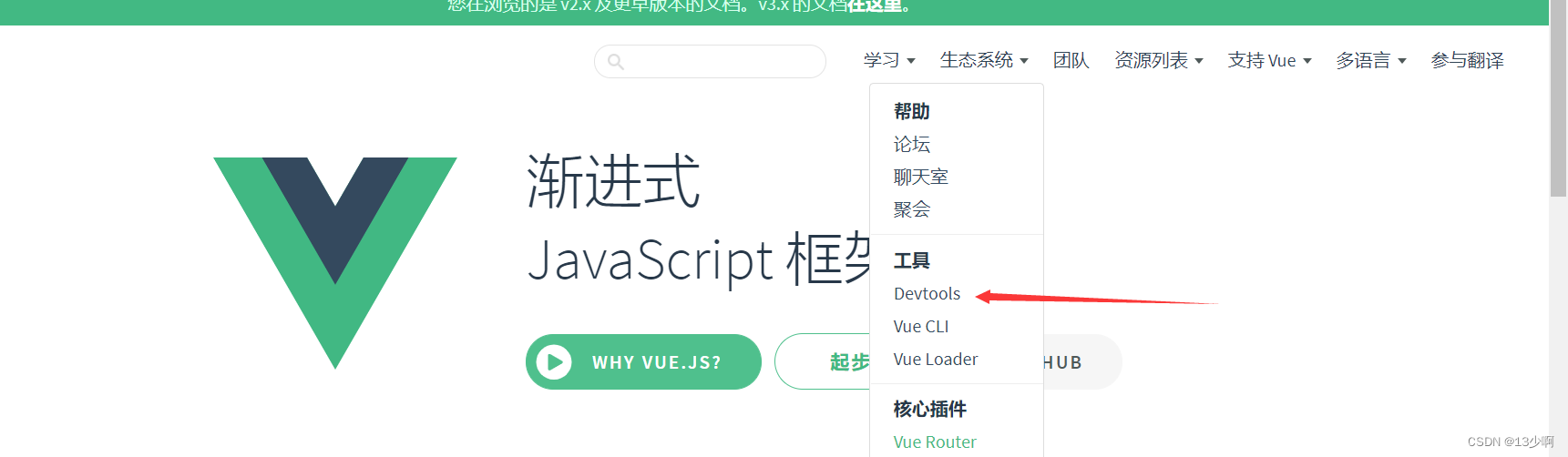
Utilisation simple de devtools
New interesting test applet source code_ Test available
Redis6-01nosql database
Multi person online anonymous chat room / private chat room source code / support the creation of multiple chat rooms at the same time
The latest blind box mall, which has been repaired very popular these days, has complete open source operation source code
随机推荐
C file in keil cannot be compiled
The perfect car for successful people: BMW X7! Superior performance, excellent comfort and safety
Azkaban actual combat
Pytest (4) - test case execution sequence
Pdf things
【做题打卡】集成每日5题分享(第三期)
[web source code code code audit method] audit skills and tools
Kbp206-asemi rectifier bridge kbp206
Usage scenarios and solutions of ledger sharing
Anchor free series network yolox source code line by line explanation Part 2 (a total of 10, ensure to explain line by line, after reading, you can change the network at will, not just as a participan
Yyds dry goods inventory embedded matrix
[wp]bmzclub几道题的writeup
Basic knowledge of tuples
[learning notes] month end operation -gr/ir reorganization
NPM introduction link symbolic link
[Chongqing Guangdong education] 2777t green space planning reference questions of National Open University in autumn 2018
v-if VS v-show 2.0
程序员的视力怎么样? | 每日趣闻
单项框 复选框
MySQL winter vacation self-study 2022 11 (9)