当前位置:网站首页>Matplotlib drawing interface settings
Matplotlib drawing interface settings
2022-07-07 21:43:00 【En^_^ Joy】
List of articles
Coordinate limits and titles
| Code | meaning | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| plt.xlim() | Definition x Axis coordinate limit | Leftmost value , The rightmost value |
| plt.ylim() | Definition y Axis coordinate limit | The lowest value , The top value |
| plt.axis() | Set coordinate limits | [xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax] |
plt.axis('tight') | Tighten the axis , Leave no blank | |
plt.axis('equal') | Set the resolution of the graphics displayed on the screen ( Ratio of unit length of two axes ) | |
| plt.title() | Graphic title | |
| plt.xlabel() | x Axis title | |
| plt.ylabel() | y Axis title | |
| plt.style.use() | Table style | |
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') | Hide the axis top boundary | |
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') | Hide the right boundary of the coordinate axis | |
| ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(2)) | Definition x The scale unit of the coordinate axis | Need to be from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator |
| ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(0.1)) | Definition y The scale unit of the coordinate axis | Need to be from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator |
| plt.xticks() | Change the scale | coordinates , Substitute data ([0.2, 0.4, 0.6], ['A', 'B', 'C']) |
Table style
Use plt.style.available You can see all the styles
| Solarize_Light2 | _classic_test_patch | bmh | classic | dark_background |
| fast | fivethirtyeight | ggplot | grayscale | seaborn |
| seaborn-bright | seaborn-colorblind | seaborn-dark | seaborn-dark-palette | seaborn-darkgrid |
| seaborn-deep | seaborn-muted | seaborn-notebook | seaborn-paper | seaborn-pastel |
| seaborn-poster | seaborn-talk | seaborn-ticks | seaborn-white | seaborn-whitegrid |
| tableau-colorblind10 |
How to use style sheets
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
This will change the style of all tables , if necessary , You can use the style context manager to temporarily change to another style :
with plt.style.context('fivethirtyeight'):
plt.plot([1,2,3], [3,1,2])
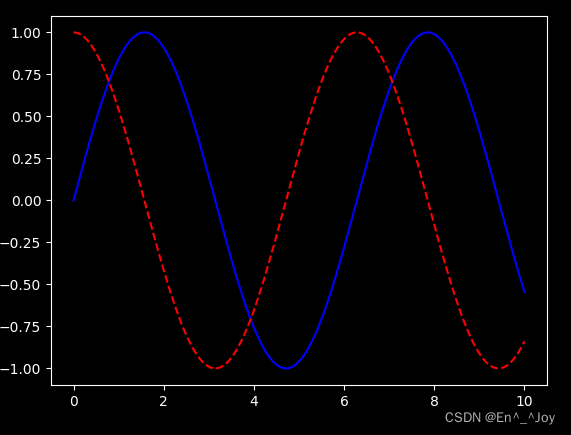
dark_background style
plt.style.use('dark_background')
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x),'-b')
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x), '--r')
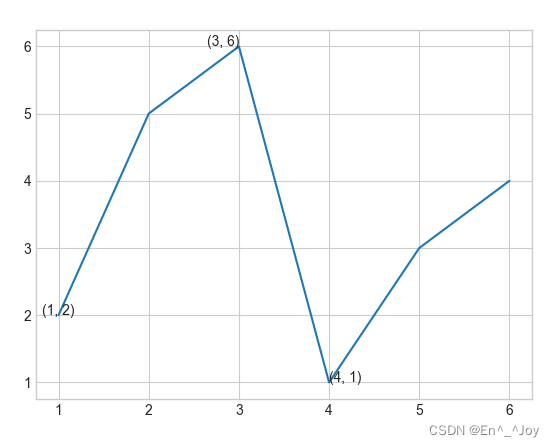
Words and notes
plt.text(): Add notes ( be equal to ax.text())
This method requires x Axis position 、y Axis position 、 character string 、 And some optional parameters , Such as the color of the text 、 Font size 、 style 、 Alignment, etc
plt.plot([1,2,3,4,5,6], [2,5,6,1,3,4])
# Add text to the diagram
ax.text(1,2,(1,2), ha='center')
ax.text(3,6,'(3, 6)', ha='right')
ax.text(4,1,str((4,1)))
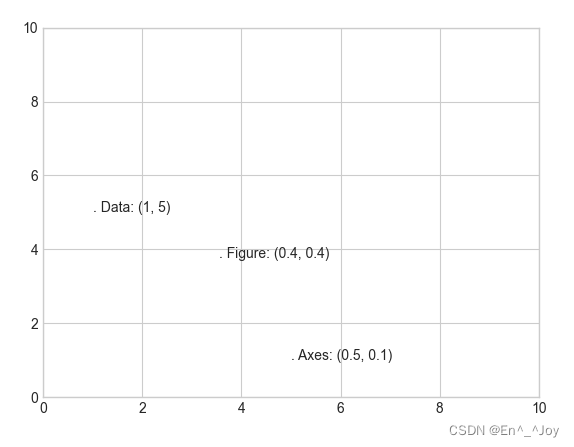
transform Parameters : Coordinate transformation and text position
ax.transData: Coordinate transformation based on data ( Axis )ax.transAxes: Coordinate transformation based on coordinate axis ( In axis dimensions )( Coordinate system scale )fig.transFigure: Coordinate transformation based on graphics ( In drawing dimensions )( Figure scale )
ax.set_xlim(0,10)
ax.set_ylim(0,10)
# Add text to the diagram
ax.text(1, 5, ". Data: (1, 5)", transform=ax.transData)
ax.text(0.5, 0.1, ". Axes: (0.5, 0.1)", transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(0.4, 0.4, ". Figure: (0.4, 0.4)", transform=fig.transFigure)
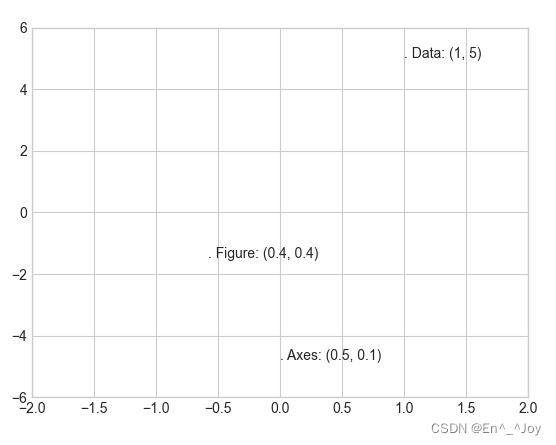
When changing the coordinate axis , Only ax.transData Your point will change
ax.set_xlim(-2,2)
ax.set_ylim(-6,6)
Arrows and notes
plt.annotate(): Draw arrows and notes
ax.set_xlim(-2,5)
ax.set_ylim(-6,6)
ax.annotate('A', xy=(3, 1), xytext=(4, 4), arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
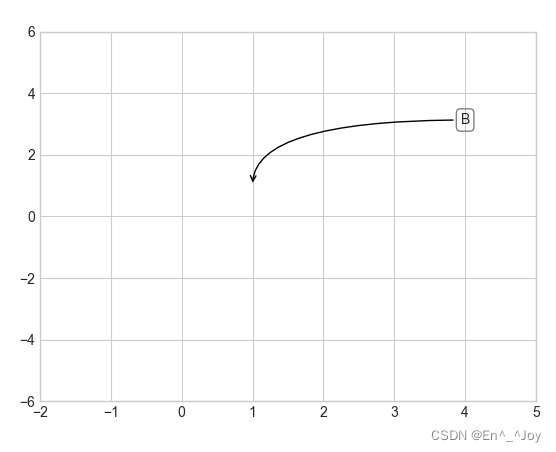
ax.annotate('B', xy=(1, 1), xytext=(4, 3), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="angle3,angleA=0,angleB=-90"))
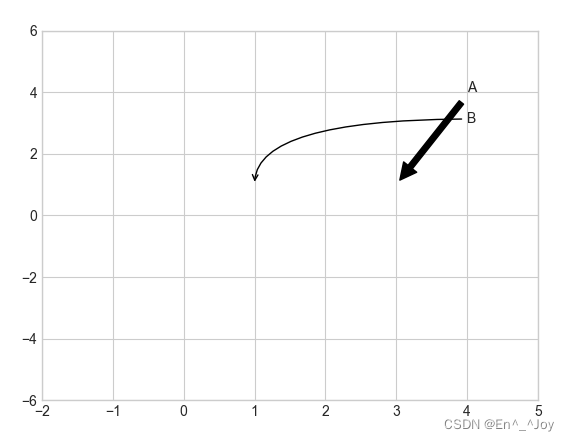
ax.annotate('B', xy=(1, 1), bbox=dict(boxstyle="round",fc="none",ec="gray"), xytext=(4, 3),
ha='center',arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="angle3,angleA=0,angleB=-90"))
Custom coordinate scale
Define the scale unit of the coordinate axis
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(0.2))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(0.3))
Hide the upper boundary right boundary
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
Change the scale
plt.xticks([0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8], ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
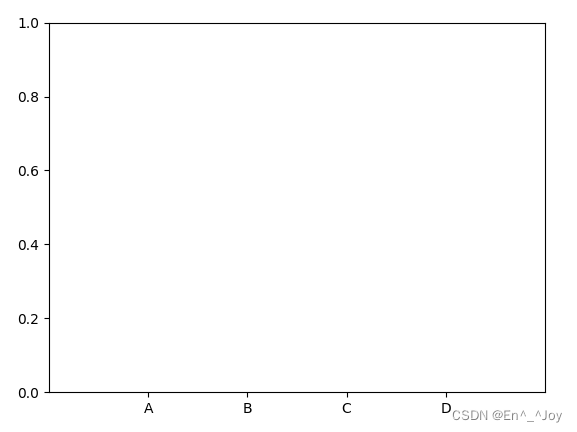
Major and minor scales
The main scale tends to be larger , Secondary scales tend to be smaller , For example, logarithmic graph
# Create graphics
fig = plt.figure()
# Axis
ax = plt.axes(xscale='log', yscale='log')
ax.set_xlim(10**0,10**5)
ax.set_ylim(10**0,10**5)
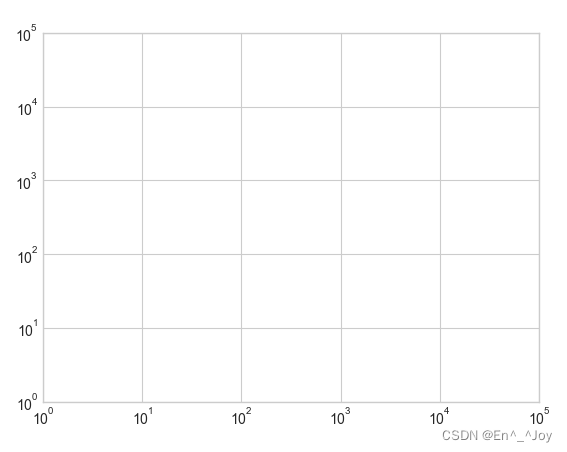
Set the formatter and locator Custom scale properties
Hide scales and labels
Hidden scales and labels are usually used plt.NullLocator() And plt.NullFormatter() Realization
Below we remove X Axis labels ( But the tick marks are preserved / Gridlines ),Y Axis scale ( The label is also removed )
# Create graphics
fig = plt.figure()
# Axis
ax = plt.axes()
ax.set_xlim(0,5)
ax.set_ylim(0, 5)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
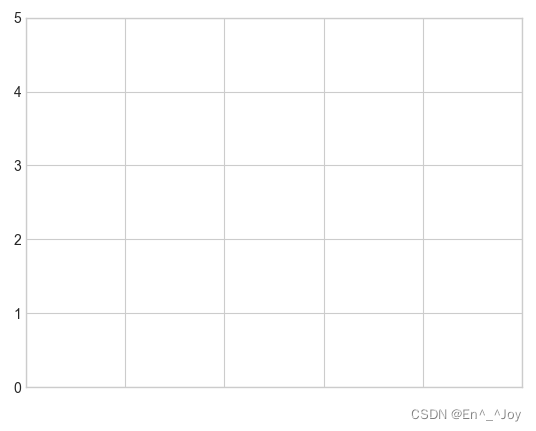
Increase or decrease the number of scales
adopt plt.MaxNLocator() Set the maximum number of scales displayed
fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 4, sharex=True, sharey=True)
for axi in ax.flat:
axi.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MaxNLocator(5))
axi.yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MaxNLocator(5))
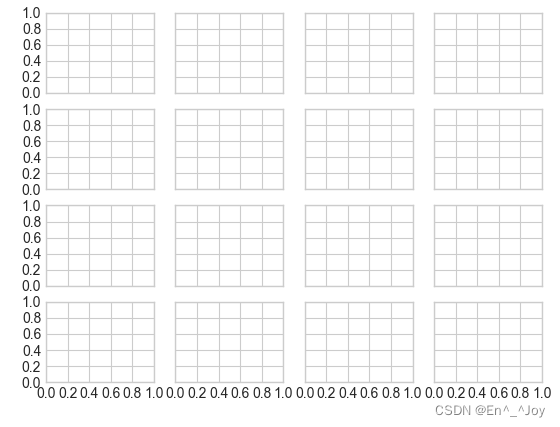
Summary of format generator and locator
| Locator class | describe |
|---|---|
| NullLocator | No scale |
| FixedLocator | The scale position is fixed |
| IndexLocator | Use index as locator ( Such as x=range(len(y)) |
| LinearLocator | from min To max Command the scale evenly |
| LogLocator | from min To max Scale by logarithmic distribution |
| MultipleLocator | Scale and range are cardinal numbers (base) Multiple |
| MaxNLocator | Find the best position for the maximum scale |
| AutoLocator | ( Default ) With MaxNLocator Simple configuration |
| AutoMinorLocator | Locator for minor scale |
| Format generator class | describe |
|---|---|
| NullFormatter | There is no label on the scale |
| IndexFormatter | Set a set of labels as a string |
| FixedFormatter | Manually label the scale |
| FuncFormatter | Set labels with custom functions |
| FormatStrFormatter | Set the string format for each scale value |
| ScalarFormatter | ( Default ) Set the label for the label value |
| LogFormatter | Default format generator for logarithmic axes |
Explanation of the meaning of the figure and line ( legend )
| function | Parameters | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ax.legend() | There can be no parameters , You can also have the following parameters | Create line meaning |
loc='upper left' | The drawing line shows the position | |
frameon=False | Cancel the legend outline | |
ncol=2 | Number of legend label columns | |
fancybox=True | Legend rounded border | |
framealpha=0.5 | Border transparency | |
borderpad=1 | Text spacing | |
shadow=True | Add shadow |
plt.legend(): Create a legend containing each graphic element
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x),'-b', label='Sin')
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x), '--r', label='Cos')
leg = ax.legend(loc='upper left', frameon=True, ncol=2, fancybox=True, framealpha=0.5, borderpad=1, shadow=True)
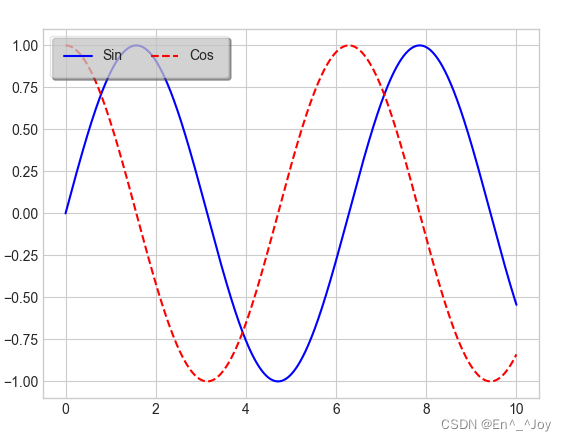
Select the element shown in the legend
By means of plt.plot() Use or not use label Parameter to determine whether the icon is displayed
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
plt.plot(x, [2,5,6,4,2,3], label='1')
plt.plot(x, [3,4,1,6,2,5], label='2')
plt.plot(x, [5,8,4,6,2,9])
plt.plot(x, [2,4,5,8,1,6], label='4')
plt.plot(x, [9,6,4,2,8,3])
# Show icons
plt.legend()
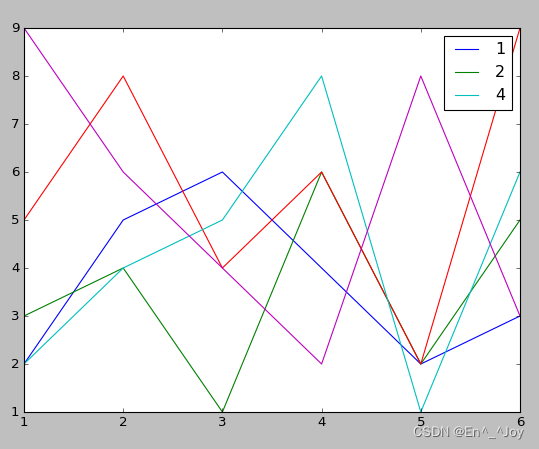
Show points of different sizes in the legend
la = np.random.uniform(0,10,100) # Abscissa
lo = np.random.uniform(0,10,100) # Ordinate
po = np.random.randint(0,100,100) # Color
ar = np.random.randint(0,1000,100) # size
# drawing
plt.scatter(lo, la, label=None, c=po, cmap='viridis', s=ar,linewidth=0, alpha=0.5)
# Draw a legend
for ar in [100,200,300]:
plt.scatter([],[],c='k',alpha=0.3, s=ar,label=str(ar))
# Show icons
plt.legend(scatterpoints=1, frameon=False, labelspacing=1)
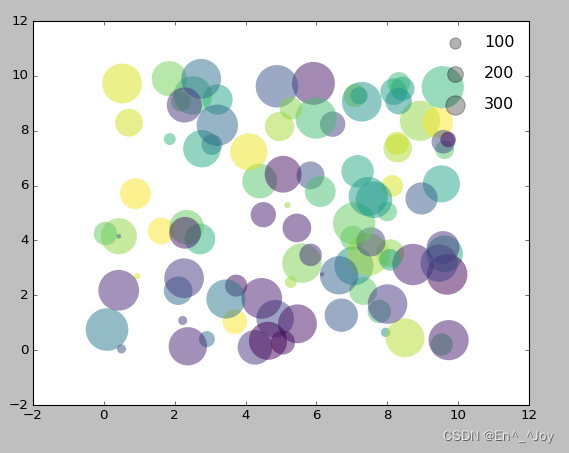
Configure color bar
Add a title to the color bar
cd = plt.colorbar()
cb.set_label('label')
adopt plt.colorbat Function to create a color bar
# drawing
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
I = np.sin(x)*np.cos(x[:,np.newaxis])
plt.imshow(I)
plt.colorbar()
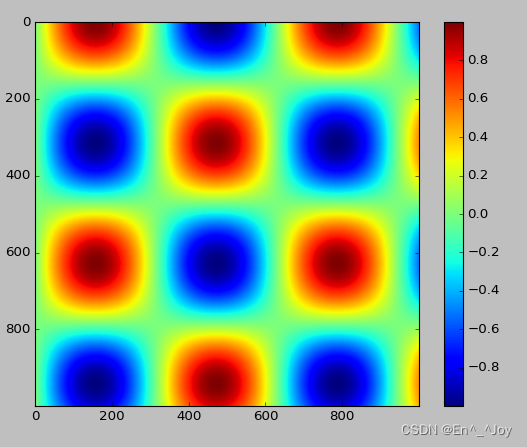
Configure color bar
cmap Parameters : Set the color scheme of the color bar
plt.imshow(I, cmap='gray')
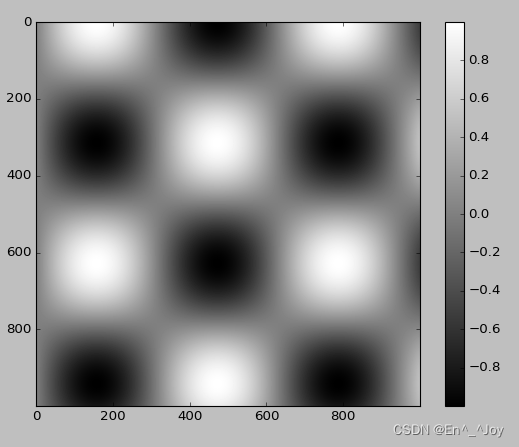
Sequential color scheme : A color scheme consisting of a continuous set of colors ( for example binary or viridis) Reciprocal color scheme : It consists of two complementary colors , Indicates two meanings ( for example RdBu or PuOr) Qualitative color schemes : A set of colors in random order ( for example rainbow or jet)
plt.imshow(I,cmap='jet')
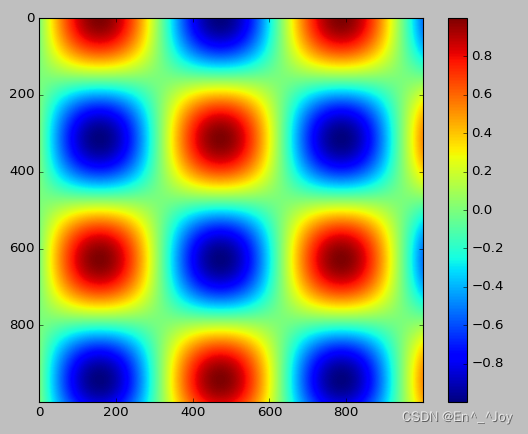
Limitation of color bar scale and setting of extended function
It can shorten the upper and lower limits of color values , For data beyond the upper and lower limits , adopt extend Parameters use triangle arrows to represent numbers larger or smaller than the upper limit
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
I = np.sin(x)*np.cos(x[:,np.newaxis])
# Set... For the image 1% noise
speckles = (np.random.random(I.shape)<0.01)
I[speckles] = np.random.normal(0,3,np.count_nonzero(speckles))
plt.figure(figsize=(10,3.5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.imshow(I, cmap='RdBu')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.imshow(I, cmap='RdBu')
plt.colorbar(extend='both')
plt.clim(-1,1)
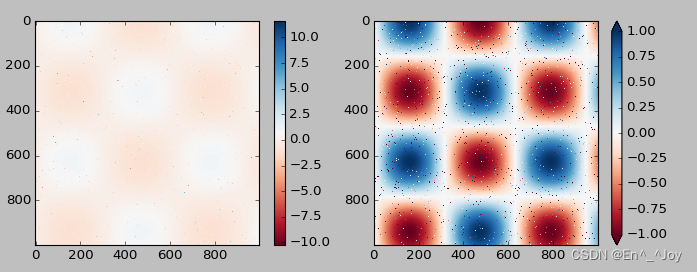
Discrete color bar
Sometimes it is necessary to represent discrete data , have access to plt.cm.get_cmap() Parameters
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
I = np.sin(x)*np.cos(x[:,np.newaxis])
plt.imshow(I, cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('Blues', 6))
plt.colorbar()
plt.clim(-1,1)
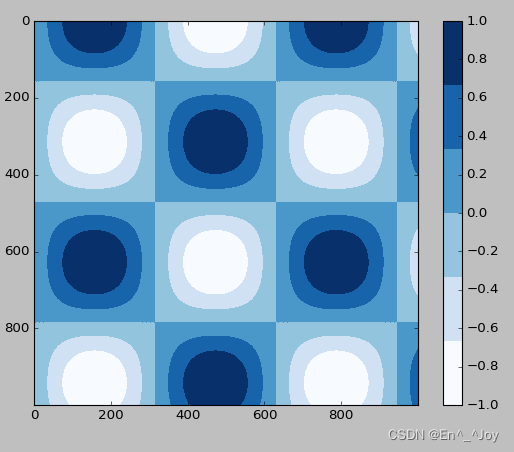
Manually configure the drawing
# With a gray background
ax = plt.axes(fc='#E6E6E6')
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
# Draw a white grid line
plt.grid(color='w', linestyle='solid')
# Hide the lines of the axis
for spine in ax.spines.values():
spine.set_visible(False)
# Hide the upper and right scales
ax.xaxis.tick_bottom()
ax.yaxis.tick_left()
# Weaken scale and label
ax.tick_params(colors='gray', direction='out')
for tick in ax.get_xticklabels():
tick.set_color('gray')
for tick in ax.get_yticklabels():
tick.set_color('gray')
# Set the frequency histogram contour setting and fill color
ax.hist(x, edgecolor='#E6E6E6', color='#EE6666')
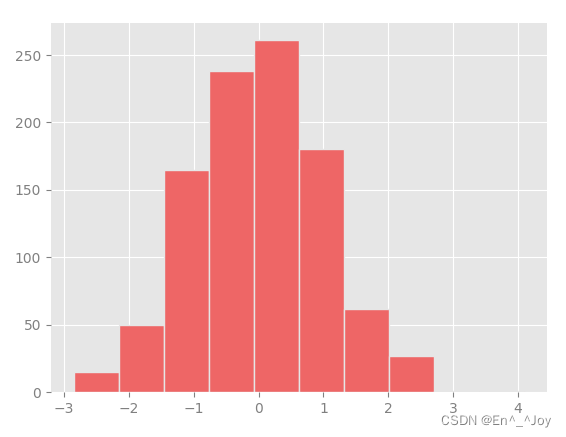
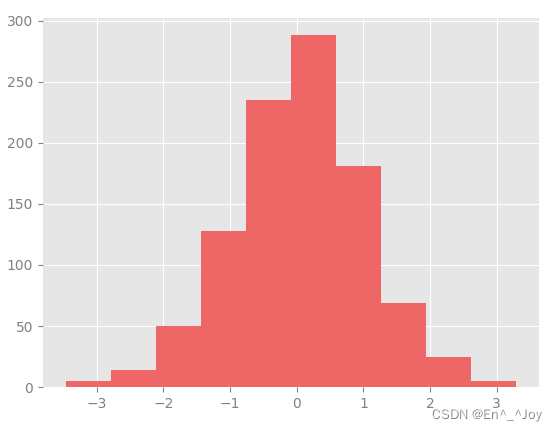
This method is very troublesome to configure , The following method only needs to be configured once and can be used on all graphics
Modify default configuration :rcParams
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import cycler
#fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Copy the current rcParams Dictionaries , Change enough to restore
Ipython_default = plt.rcParams.copy()
# use plt.rc Function to modify configuration parameters
colors = cycler('color', ['#EE6666', '#3388BB', '#9988DD', '#EECC55', '#88BB44', '#FFBBBB'])
plt.rc('axes', facecolor='#E6E6E6', edgecolor='none', axisbelow=True, grid=True, prop_cycle=colors)
plt.rc('grid', color='w', linestyle='solid')
plt.rc('xtick', direction='out', color='gray')
plt.rc('ytick', direction='out', color='gray')
plt.rc('patch', edgecolor='#E6E6E6')
plt.rc('lines', linewidth=2)
x = np.random.randn(1000)
plt.hist(x)
# display picture
plt.show()
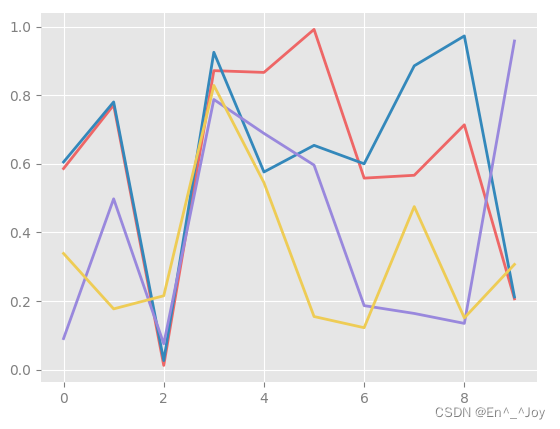
Draw some line drawings to see rc Parameter effect
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import cycler
#fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Copy the current rcParams Dictionaries , Change enough to restore
Ipython_default = plt.rcParams.copy()
# use plt.rc Function to modify configuration parameters
colors = cycler('color', ['#EE6666', '#3388BB', '#9988DD', '#EECC55', '#88BB44', '#FFBBBB'])
plt.rc('axes', facecolor='#E6E6E6', edgecolor='none', axisbelow=True, grid=True, prop_cycle=colors)
plt.rc('grid', color='w', linestyle='solid')
plt.rc('xtick', direction='out', color='gray')
plt.rc('ytick', direction='out', color='gray')
plt.rc('patch', edgecolor='#E6E6E6')
plt.rc('lines', linewidth=2)
for i in range(4):
plt.plot(np.random.rand(10))
# display picture
plt.show()
stay Matplotlib file There is more information in it
Visual exception handling
The accepted range of certain data is 70±5, I measured that it was 75±10, Is my data consistent with accepted values
In the result of graphic visualization, the error is displayed by graphics , Can provide sufficient information
Basic error line (errorbar)
fmt Parameters : Control the appearance of lines and points
x = np.linspace(0,10,50)
dy = 0.8
y = np.sin(x)+dy*np.random.randn(50)
plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=dy,fmt='.k')
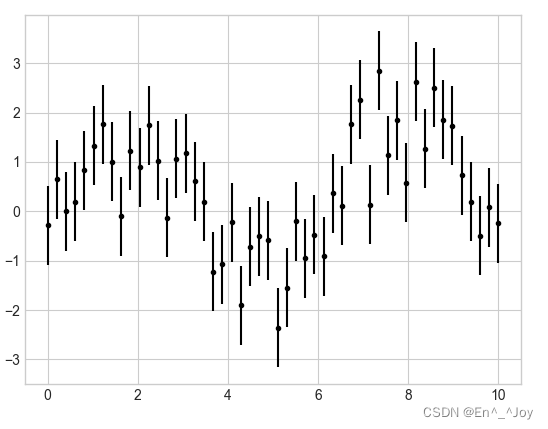
errorbar You can define the style of error line graphics
x = np.linspace(0,10,50)
dy = 0.8
y = np.sin(x)+dy*np.random.randn(50)
plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=dy,fmt='o',color='black',ecolor='lightgray',elinewidth=3,capsize=0)
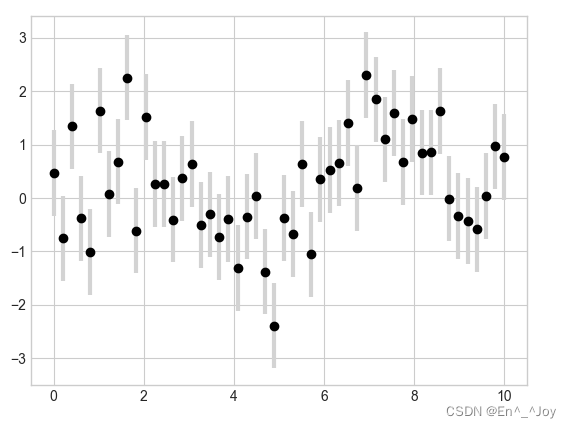
You can also set the horizontal error (xerr)、 Unilateral error (one-sidederrorbar)、 And other forms of error
边栏推荐
- HDU4876ZCC loves cards(多校题)
- 【JDBC Part 1】概述、获取连接、CRUD
- Problems encountered in installing mysql8 for Ubuntu and the detailed installation process
- Demon daddy C
- Take the intersection of two sets
- Restore backup data on persistent volumes
- The cyberspace office announced the measures for data exit security assessment, which will come into force on September 1
- [C language] advanced pointer --- do you really understand pointer?
- Unity3d 4.3.4f1执行项目
- Addition, deletion, modification and query of sqlhelper
猜你喜欢

Using enumeration to realize English to braille
Usage of MySQL subquery keywords (exists)
![Jerry's manual matching method [chapter]](/img/92/74281c29565581ecb761230fbfd0f3.png)
Jerry's manual matching method [chapter]
L2:ZK-Rollup的现状,前景和痛点

Magic weapon - sensitive file discovery tool
建立自己的网站(18)
![Restapi version control strategy [eolink translation]](/img/65/decbc158f467ab8c8923c5947af535.png)
Restapi version control strategy [eolink translation]
【JDBC Part 1】概述、获取连接、CRUD
Qt编写物联网管理平台39-报警联动
L'enregistreur de disque dur NVR est connecté à easycvr par le Protocole GB 28181. Quelle est la raison pour laquelle l'information sur le canal de l'appareil n'est pas affichée?
随机推荐
Feature generation
Why can't win11 display seconds? How to solve the problem that win11 time does not display seconds?
Can Huatai Securities achieve Commission in case of any accident? Is it safe to open an account
Static test tool
Hdu4876zcc love cards (multi check questions)
QT compile IOT management platform 39 alarm linkage
Demon daddy B3 read extensively in a small amount, and completed 20000 vocabulary+
Tupu digital twin coal mining system to create "hard power" of coal mining
[200 opencv routines] 223 Polygon fitting for feature extraction (cv.approxpolydp)
Ant destination multiple selection
私募基金在中國合法嗎?安全嗎?
Differences and connections between MinGW, mingw-w64, tdm-gcc and other tool chains "suggestions collection"
Redis - basic use (key, string, list, set, Zset, hash, geo, bitmap, hyperloglog, transaction)
国家正规的股票交易app有哪些?使用安不安全
Magic weapon - sensitive file discovery tool
UVA 11080 – place the guards
Ten thousand word summary data storage, three knowledge points
Default constraint and zero fill constraint of MySQL constraint
Do you have to make money in the account to open an account? Is the fund safe?
POJ 3140 Contestants Division「建议收藏」
