当前位置:网站首页>[brush questions] BFS topic selection
[brush questions] BFS topic selection
2022-07-05 03:54:00 【People in the shadow LX】
List of articles
1.BFS Use scenarios
Hierarchical traversal
Traverse a graph layer by layer 、 Count 、 matrix
The shortest path of a simple graph
Connected block problem
Find all other connected points through one point of the graph
Find a non recursive implementation of all solution problems
A topological sort
Time complexity :
N A little bit ,M side , On the drawing BFS Time complexity = O(N + M), be supposed to O(M) It's not a big problem , because M Generally than N Big .
M The biggest is O(N^2) The level of ( There is an edge between any two points ), So the worst case may be O(N^2)
1.1. On the shortest path algorithm
1.1.1dijkstra Algorithm
Also called single source shortest path algorithm , Solve the shortest path from one point to the vertices of the other points
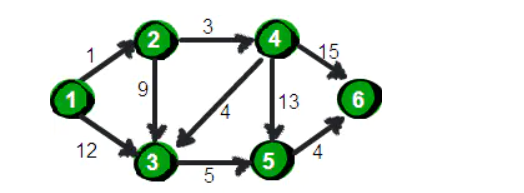
First, write the adjacency matrix

Use dis Array stores source vertices (1 Vertex number ) The distance to the other vertices
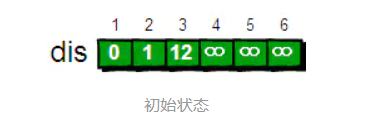
Specific ideas
From the beginning dis The minimum value found in the array is 2, that 1->2 The shortest path of the vertex becomes the definite value , The value is 1.
From the top 2 Start off , The vertex that can be reached is 2->3,2->4; If the middle vertex 2 Conduct " transit ", that 1->2->3 The path of is 1(1->2 Shortest path )+9(2->3 The path of ) by 10, Less than 1->3 Distance of 12, So will dis Array 1->3 The value of a 10; Yes 2->4 Do the same 1->4 The shortest path of is updated to 4.
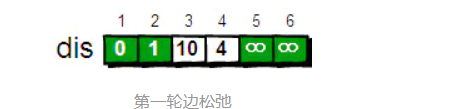
In the present dis Array , The determined vertices are 2; After the first relaxation, it is removed to the vertex 2 The shortest path is 1->4( The path length is 4), The vertices 4 To determine the value . from 4 Start off
- The vertices that can be reached are 3,5,6; Put the vertex 4 As " transit " Carry out the second round of relaxation
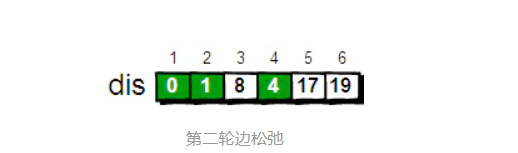
Now the determined vertex is 2,4; The shortest path of the remaining vertices is 1->3, The vertices 3 Is the shortest path , Change to a certain value ;
Go to the next round of relaxation

The final relaxation result is :
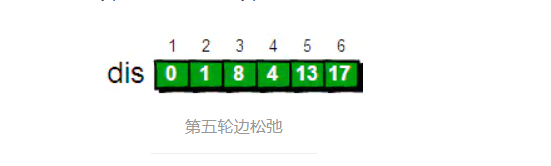
dis The shortest path to each vertex is stored in the array
// Code implementation
const int INF=INT_MAX;// Maximum
const int Maxsize=INT_MAX;// Maximum number of vertices
int e[Maxsize][Maxsize];// Adjacency matrix
int flag[Maxsize];// Tag array , Record whether the vertex is
int dis[Maxsize];// Distance table
int n,m;//n Representation node ,m edge
// initialization dis Array
void dijkstra(){
// In adjacency matrix 0 There is no number of positions , For convenience, start according to the node
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dis[i]=e[1][i]
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
flag[i]=0;
}
book[i]=1;
// Yes dis Relax
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
// about n Nodes need to be n-1 Secondary relaxation treatment
// Record the shortest distance of this round of relaxation
int min_num=INT_MAX;
// Record the determined nodes of this round of relaxation
int min_index=0;
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
if(flag[k]==0&&dis[k]<min_num)// If the node is not determined
{
min_num=dis[k];
min_index=k;
}
}
// Determine the node
flag[min_index]=1;
// Relaxation treatment
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(flag[j]==0&&e[min_index][j]<INT_MAX)// If there is a path between two nodes
{
dis[j]=min(dis[j],dis[min_index]+e[min_index][j]);
}
}
}
}
dijkstra Optimization of algorithm
c edge
{
int d,v;// d: distance ;v: node ( Arc head )
edge(){
}
edge(int a,int b)// initialization d and v
{
d=a,v=b;
}
// heavy load "<" Operator , In order to change the collation of the priority queue
// according to " Shortest distance "d To sort
bool operator < (const edge&x)const
{
if(d==x.d)return v<x.v;
else return d>x.d;
}
};
vector<edge>G[Maxsize];// chart G
int dis[Maxsize];// Distance table
int n,m;// n: Number of vertices m: Number of edges
int v1,v2,w;// v1->v2,weight==w
// Dijkstra Algorithm , The source point is s
void dijkstra(int s)
{
// initialization dis Array
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)dis[i]=INF;
dis[s]=0;
priority_queue<edge>que;// Priority queue
que.push(edge(dis[s],s));// Press the starting point into the queue
// The queue is not empty
while(!que.empty())
{
// get the min_index
edge temp=que.top();
que.pop();
int v=temp.v;// The vertices
if(dis[v]<temp.d)continue;//
// Traversal vertex v All connected edges
for(int i=0;i<G[v].size();i++)
{
edge e=G[v][i];
if(dis[e.v]>dis[v]+e.d)
{
dis[e.v]=dis[v]+e.d;
que.push(edge(dis[e.v],e.v));
}
}
}
}
1.1.2Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
The core of Freud's algorithm is through the introduction of the third k Vertices are transferred , It only needs sentence e[ i ] [ 1 ]+e[ 1 ] [ j ] Will it be better than e[ i ] [ j ] Small that will do .
// The core of Freudian algorithm is only a few lines of code , among e Denotes the adjacency matrix
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
// There may be more than one intermediary
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// Traverse all nodes
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
e[i][j]=min(e[i][j],e[i][k]+e[j][j];)
}
}
}
The advantage of Freudian algorithm is that it can deal with negative weight problems
2. subject
subject 1:
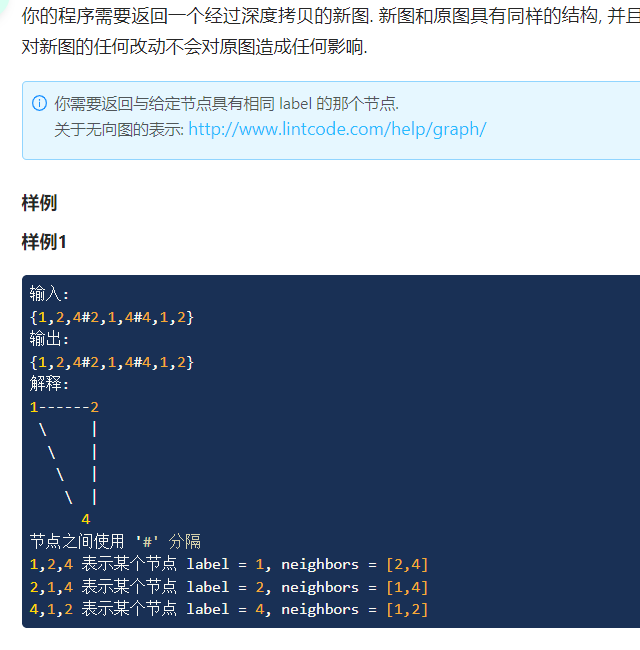
Method 1 : Divide and conquer
class Solution {
public:
UndirectedGraphNode *clone(UndirectedGraphNode*node,map<int,UndirectedGraphNode *>&table){
if(node==NULL){
return NULL;
}
// If the current node has been copied
if(table.find(node->label)!=table.end()){
return table[node->label];
}
// If the current node is not copied
// Call constructor
UndirectedGraphNode *newcode=new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label);
table[node->label]=newcode;
for(int i=0;i<(node->neighbors).size();i++){
UndirectedGraphNode *code=clone((node->neighbors)[i],table);
(newcode->neighbors).push_back(code);
}
return newcode;
}
UndirectedGraphNode* cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) {
map<int,UndirectedGraphNode *>visittable;
return clone(node,visittable);
}
};
Method 2 :BFS
// The idea is divided into three steps
// First step : Get all non repeating points
// The second step : Map points to copied points
// The third step : Copy edge
class Solution {
public:
UndirectedGraphNode* cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode *node) {
if(node==nullptr){
return node;
}
// First step : Get all the points
vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>nodes=getnodes(node);
// The second step : Map the obtained points to the copied points
unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode*,UndirectedGraphNode*>mapping=clonenodes(nodes);
// The third step : Connecting edge
connectnodes(mapping,nodes);
return mapping[node];
}
vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>getnodes(UndirectedGraphNode *node){
queue<UndirectedGraphNode *>q;
// Not repeated Set
unordered_set<UndirectedGraphNode *>s;
vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>nodes;
q.push(node);
s.insert(node);
nodes.push_back(node);
while(!q.empty()){
UndirectedGraphNode*tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto neighbor:tmp->neighbors){
// If in s Find , If it means it has been put in, skip
if(s.find(neighbor)!=s.end()){
continue;
}
q.push(neighbor);
s.insert(neighbor);
nodes.push_back(neighbor);
}
}
return nodes;
}
unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>clonenodes(vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>nodes){
unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>mapping;
for(auto node:nodes){
mapping.insert(make_pair(node,new UndirectedGraphNode(node->label)));
}
return mapping;
}
// Connect the copied edges
void connectnodes(unordered_map<UndirectedGraphNode *,UndirectedGraphNode *>mapping,vector<UndirectedGraphNode *>nodes){
for(auto node:nodes){
for(auto neighbor:node->neighbors){
UndirectedGraphNode*newnode=mapping[node];
UndirectedGraphNode*newneighbor=mapping[neighbor];
newnode->neighbors.push_back(newneighbor);
}
}
}
};
( subject 2)
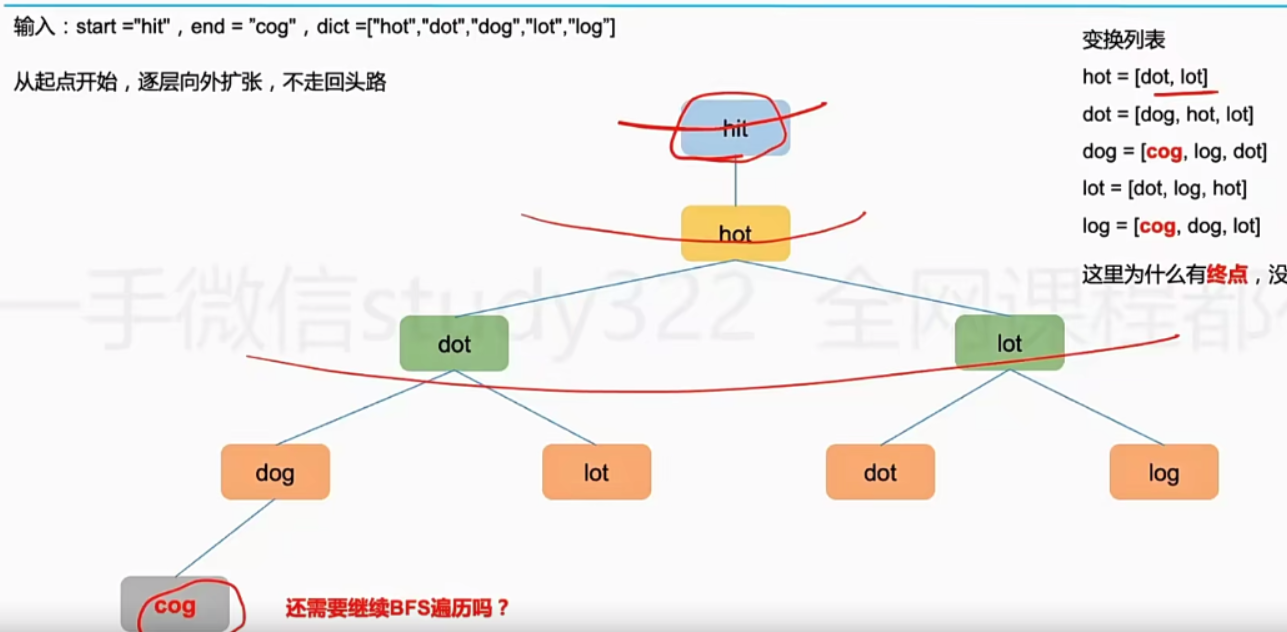
[120 · The word chain - LintCode]
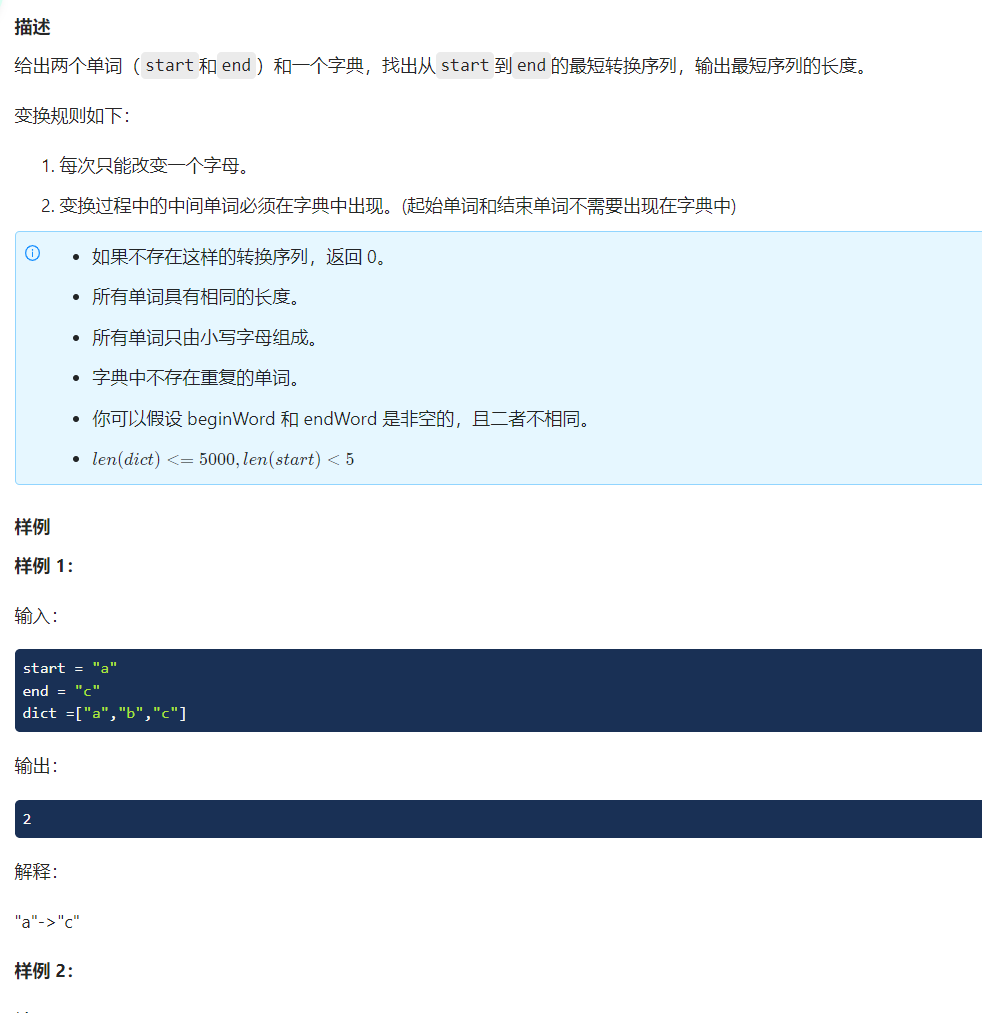
Ideas :
Each word that can be converted forms a tree , So you can use BFS Get the results
// version LintCode
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string &start, string &end, unordered_set<string> &dict) {
int n=start.size();
if(start==end){
return 1;
}
if(n<1||n!=end.size()){
return -1;
}
queue<string>q;
q.push(start);
dict.erase(start);
int step=2;
while(!q.empty()){
// Record the number of words on this level
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
string tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
// Replace letters
for(int j=0;j<tmp.size();j++){
char ch=tmp[j];
for(char c='a';c<='z';c++){
if(ch==c){
continue;
}
tmp[j]=c;
if(tmp==end){
return step;
}
else if(dict.find(tmp)!=dict.end()){
q.push(tmp);
dict.erase(tmp);
}
tmp[j]=ch;
}
}
}
// After each traversal, you need to add 1
step++;
}
return 0;
}
};
( subject 3: Connected block problem )
[433 · The number of Islands - LintCode]
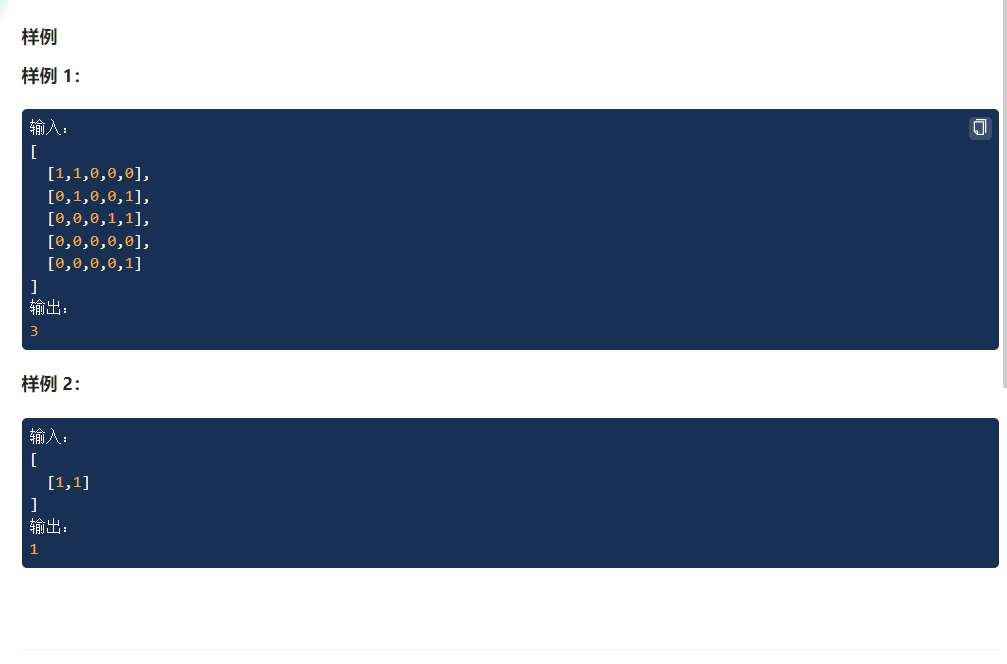

class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<bool>> &grid) {
if(grid.size()==0||grid[0].size()==0){
return 0;
}
int m=grid.size(),n=grid[0].size(),num=0;
// Tag array
vector<vector<bool>>flag(m,vector<bool>(n,false));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]&&!flag[i][j]){
dfs(grid,flag,i,j,m,n);
num++;
}
}
}
return num;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<bool>>&grid,vector<vector<bool>>&flag,int i,int j,int m,int n){
if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||!grid[i][j]||flag[i][j]){
return ;
}
flag[i][j]=true;
dfs(grid,flag,i+1,j,m,n);
dfs(grid,flag,i-1,j,m,n);
dfs(grid,flag,i,j+1,m,n);
dfs(grid,flag,i,j-1,m,n);
}
};
( subject 5)
[611 · The shortest route for a knight - LintCode]
Method :BFS
BFS Convert the reached point into a tree according to the path , Simulate the sequence traversal of the tree .
// simple BFS
class Solution {
public:
int shortestPath(vector<vector<bool>> &grid, Point source, Point destination) {
int m=grid.size(),n=grid[0].size();
if(m==0||n==0){
return -1;
}
queue<Point>q;
q.push(source);
int ans=0;
vector<vector<int>>direct={
{
1,2},{
1,-2},{
-1,2},{
-1,-2},{
2,1},{
2,-1},{
-2,1},{
-2,-1}};
while(!q.empty()){
// Record the number of this layer
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
Point tmp=q.front();q.pop();
if(tmp.x==destination.x&&tmp.y==destination.y){
return ans;
}
for(int k=0;k<8;k++){
Point node;
node.x=tmp.x+direct[k][0];
node.y=tmp.y+direct[k][1];
if(node.x>=0&&node.x<m&&node.y>=0&&node.y<n){
if(!grid[node.x][node.y]){
q.push(node);
}
grid[node.x][node.y]=true;
}
}
}
ans++;
}
return -1;
}
};
( subject 6)
[618 · Search for nodes in the graph - LintCode]
// simple bfs
class Solution {
public:
UndirectedGraphNode* searchNode(vector<UndirectedGraphNode*>& graph,
map<UndirectedGraphNode*, int>& values,
UndirectedGraphNode* node,
int target) {
queue<UndirectedGraphNode*>q;
q.push(node);
set<UndirectedGraphNode*>se;
se.insert(node);
while(!q.empty()){
UndirectedGraphNode* tmp=q.front();q.pop();
if(values[tmp]==target)
{
return tmp;
}
for(auto it=tmp->neighbors.begin();it!=tmp->neighbors.end();it++){
if(se.find(*it)==se.end()){
se.insert(*it);
q.push(*it);
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
( subject 7)
[431 · Find the connected block of undirected graph - LintCode]
// Inspection point : Union checking set
// use map Record parent node
map<int,int>f;
// Find the root node
int find(int x){
return f[x]==x?x:f[x]=find(f[x]);
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> connectedSet(vector<UndirectedGraphNode*> nodes) {
if(nodes.empty()){
return {
};
}
// initialization
for(int i=0;i<nodes.size();i++){
f[nodes[i]->label]=nodes[i]->label;
}
for(auto e:nodes){
// Those who are neighbors are the same
for(auto i:e->neighbors){
if(find(e->label)!=find(i->label)){
f[find(i->label)]=f[find(e->label)];
}
}
}
map<int,vector<int>>tmpres;
for(auto e:nodes){
// Put the same parent node in the same vector in
tmpres[find(e->label)].push_back(e->label);
}
vector<vector<int>>res;
for(auto i:tmpres){
// Insert map Medium vector<int> part
res.push_back(i.second);
}
return res;
}
};
On the matrix bfs
( subject 8)
[598 · Zombie matrix - LintCode ]
class point{
public:
int x,y;
point(int _x,int _y)
:x(_x),y(_y)
{
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int zombie(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
int cnt=0,n=grid.size();
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
int m=grid[0].size();
if(m==0){
return 0;
}
queue<point>q;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
q.push(point(i,j));
}
}
}
int day[4][2]={
{
1,0},{
-1,0},{
0,-1},{
0,1}};
while(!q.empty()){
int size=q.size();
cnt++;
// Infect the upper, lower, left and right points
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
point head=q.front();q.pop();
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=head.x+day[k][0];
int y=head.y+day[k][1];
if(x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m&&grid[x][y]==0){
grid[x][y]=1;
q.push(point(x,y));
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
// If there is 0 It means there are survivors
if(grid[i][j]==0){
return -1;
}
}
}
// It needs to be reduced by one , I added one more time when I first entered the queue
return cnt-1;
}
};
( subject 9)
[573 · The establishment of the post office II - LintCode]
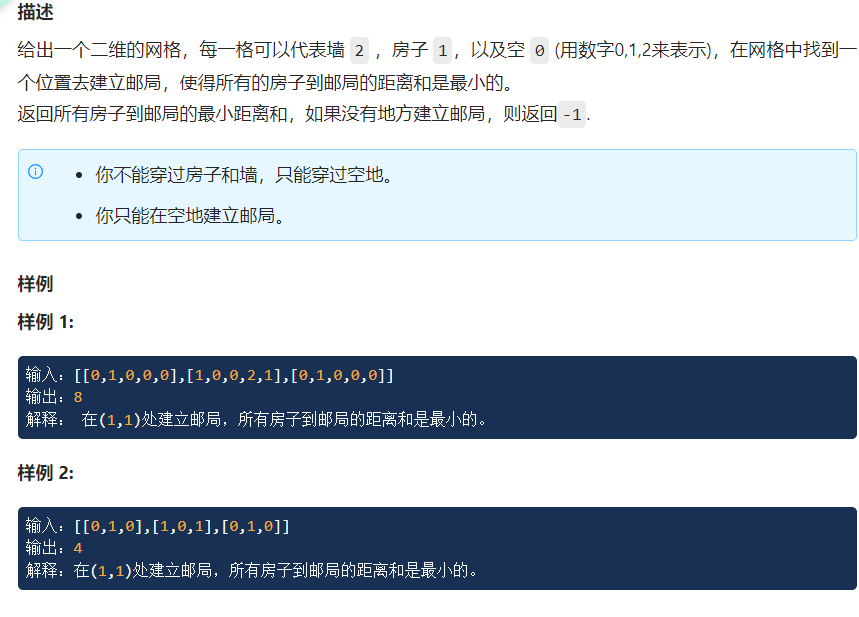
The solution of this problem is similar to map analysis .
( Map analysis )[573 · The establishment of the post office II - LintCode]
/* Direct thinking : 1. Traverse all empty locations 2. Use it for each open space bfs To all house Distance of 3. Find the shortest distance by fighting in the arena */
class Solution {
public:
#define WALL 2
#define HOUSE 1
#define EMPT 0
const vector<vector<int>> direct= {
{
1,0}, {
0,1}, {
-1,0}, {
0,-1}};
int minDis;
int numHouse;
class Coord {
public:
int x, y;
Coord(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {
};
};
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
// write your code here
if (grid.size() == 0) {
return -1;
}
minDis = -1;
numOfHouse(grid);
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == EMPT) {
Coord pos(i, j);
findDis(pos, grid);
}
}
}
return minDis;
}
void numOfHouse(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == HOUSE) {
numHouse++;
}
}
}
}
bool isInBound(vector<vector<int>> &grid, int x, int y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.size() || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].size()) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
void findDis(Coord &pos, vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size()));
queue<Coord> q;
q.push(pos);
visited[pos.x][pos.y] = 1;
int dis = 0;
int visitedHouse = 0;
int step = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int qsize = q.size();
step++;
for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++) {
Coord cd = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < direct.size(); j++) {
int x = cd.x + direct[j][0];
int y = cd.y + direct[j][1];
if (isInBound(grid, x, y) && visited[x][y] == 0) {
if (grid[x][y] == HOUSE) {
dis += step;
if (minDis != -1 && dis >= minDis) {
return;
}
visitedHouse++;
if (visitedHouse == numHouse) {
minDis = dis;
return;
}
}
if (grid[x][y] == EMPT) {
q.push(Coord(x, y));
}
visited[x][y] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
};
class point{
public:
int x,y;
point(int _x,int _y)
:x(_x),y(_y)
{
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int dir[4][2]={
{
1,0},{
-1,0},{
0,1},{
0,-1}};
// Record the number of houses
int mindis=INT_MAX,numhouse=0;
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
int n=grid.size(),m=grid[0].size();
if(n==0||m==0){
return -1;
}
numofhouse(grid);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
// If it's a vacant lot , Just look for all his distances
if(grid[i][j]==0){
point pos(i,j);
finddis(pos,grid);
}
}
}
return mindis;
}
void numofhouse(vector<vector<int>>&grid){
for(int i=0;i<grid.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
numhouse++;
}
}
}
}
bool isinfound(int x,int y,vector<vector<int>>&grid){
if(x<0||x>=grid.size()||y<0||y>=grid[0].size()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
void finddis(point&p,vector<vector<int>>&grid){
// Record whether the point is traversed
vector<vector<bool>>visit(grid.size(),vector<bool>(grid[0].size()));
queue<point>q;
q.push(p);
//visit Record the number of houses visited ,distance Record the distance
visit[p.x][p.y]=1;
int visithouse=0,step=0,distance=0;
while(!q.empty()){
step++;
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
point head=q.front();q.pop();
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=head.x+dir[k][0];
int y=head.y+dir[k][1];
if(isinfound(x,y,grid)&&visit[x][y]==0)
{
if(grid[x][y]==1){
distance+=step;
visithouse++;
if(visithouse==numhouse){
mindis=min(distance,mindis);
return ;
}
}
// If it is an empty point that has not been accessed , Just join the queue
if(grid[x][y]==0){
q.push(point(x,y));
}
visit[x][y]==1;
}
}
}
}
}
};
边栏推荐
- De debugging (set the main thread as hidden debugging to destroy the debugging Channel & debugger detection)
- 汇编-入门
- ActiveReportsJS 3.1 VS ActiveReportsJS 3.0
- Subversive cognition: what does SRE do?
- DMX parameter exploration of grandma2 onpc 3.1.2.5
- English essential vocabulary 3400
- 【软件逆向-基础知识】分析方法、汇编指令体系结构
- 【刷题】BFS题目精选
- Easy processing of ten-year futures and stock market data -- Application of tdengine in Tongxinyuan fund
- IronXL for . NET 2022.6
猜你喜欢
![[wp][introduction] brush weak type questions](/img/d0/9eb3ade701057837d98e4a20082a10.png)
[wp][introduction] brush weak type questions
Use of vscode software
IPv6 experiment
De debugging (set the main thread as hidden debugging to destroy the debugging Channel & debugger detection)
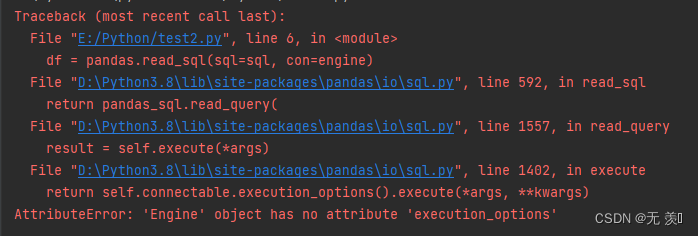
已解决(sqlalchemy+pandas.read_sql)AttributeError: ‘Engine‘ object has no attribute ‘execution_options‘

The new project Galaxy token just announced by coinlist is gal
面试字节,过关斩将直接干到 3 面,结果找了个架构师来吊打我?
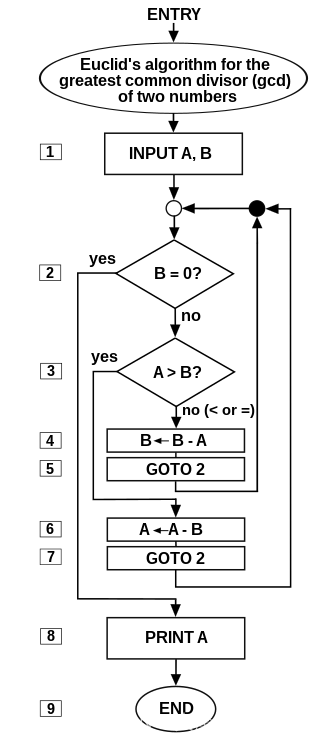
An elegant program for Euclid‘s algorithm
![[C language] address book - dynamic and static implementation](/img/eb/07e7a32a172e5ae41457cf8a49c130.jpg)
[C language] address book - dynamic and static implementation
ActiveReportsJS 3.1 VS ActiveReportsJS 3.0
随机推荐
25K 入职腾讯的那天,我特么哭了
[positioning in JS]
IronXL for .NET 2022.6
Clickhouse同步mysql(基于物化引擎)
Analysis of glibc strlen implementation mode
[vérification sur le Web - divulgation du code source] obtenir la méthode du code source et utiliser des outils
Official announcement! The third cloud native programming challenge is officially launched!
UE4 DMX和grandMA2 onPC 3.1.2.5的操作流程
特殊版:SpreadJS v15.1 VS SpreadJS v15.0
speed or tempo in classical music
NEW:Devart dotConnect ADO. NET
ABP vNext microservice architecture detailed tutorial - distributed permission framework (Part 1)
输入的查询SQL语句,是如何执行的?
程序员的视力怎么样? | 每日趣闻
NEW:Devart dotConnect ADO.NET
speed or tempo in classical music
Clickhouse物化视图
Delphi read / write JSON format
Deflocculant aminoiodotide eye drops
一文带你了解BI的前世今身与企业数字化转型的关系