当前位置:网站首页>[ibdfe] matlab simulation of frequency domain equalization based on ibdfe
[ibdfe] matlab simulation of frequency domain equalization based on ibdfe
2022-07-02 03:42:00 【FPGA and MATLAB】
1. Software version
matlab2015b
2.IBDFE Frequency domain equalization scheme
What we have now IBDFE The structure is as follows :

From the structure ,IBDFE It is composed of feedforward filter and feedback filter , among C and B Represents the coefficients of feedforward filter and feedback filter . From the existing literature and data , At present, the structure is in the calculation process , Each iteration requires the estimation of coefficients , Thus, the complexity of system implementation is increased . Aiming at problems , At present, the main research results are as follows LC-IBDFE etc. , It separates the error in the decision signal from the expected signal , This reduces the complexity . But it's similar LC-IBDFE How to improve , It is based on the assumption that the bit error rate of each iteration is the same and very small , In reality, this situation is difficult to meet the conditions . The other is in IBDFE in , When there is serious channel fading , It will lead to overestimation of correlation factors , This leads to the spread of errors . In response to this question , The existing achievements mainly include the joint equalization algorithm of joint channel estimation and channel equalization . But the complexity of this algorithm is further increased .
3. Part of the source code
clc;
clear all;
close all;
warning off;
addpath 'func\'
rng('default');
rng(1);
Blk_size = 512; % Block size 512
Chu_size = 64; %chu Sequence , size 64
NFrame = 1000;
SNR = [0:1:14]; % Signal-to-noise ratio dB
Modsel = 2; %QPSK
Fs = 10*10^3; % Sampling rate
Ts = 1/Fs;
Fc = 5*10^3; % Carrier frequency
Fd = 10; % Doppler shift
tau = [0 0.5 0.5 1.2 1.2 2.1 2.1 3.3 3.3 4.8 4.8 6.5 6.5 8.5 10.8]*10^-4;
pdb = [0 -0.967 -0.967 -0.967 -1.933 -1.933 -1.933 -1.933 -2.900 -2.900 -2.900 -2.900 -2.86 -3.86 -3.84];
% Channel model
Channel = rayleighchan(Ts,Fd,tau,pdb);
%FFT Transformation
H_channel0 = fft(Channel.PathGains./sqrt(sum((abs(Channel.PathGains)).^2)),Blk_size+Chu_size+Chu_size);
%CHU Sequence
Chuseq = zeros(1,Chu_size);
for k = 0:Chu_size-1
tmps(k+1) = pi*k^2./Chu_size;
end
I = cos(tmps);
Q = sin(tmps);
Chuseq = I+sqrt(-1)*Q;
% Bit error rate
%turbo Parameters
Mss = 295;
for n = 1:length(SNR)
ErrMMSE = 0;
for k = 1:NFrame
[n,k]
rng(k);
% Random
Tdin = randint(1,Mss);
% utilize turbo Interleaver for , structure TB-DEF, Three way output
output = [func_turbo_code(Tdin)];
output = reshape(output, 1, []);
seridata1 = [output,0,0];
% modulation
Data = modulation(seridata1,Modsel);
Tx = [Chuseq,Data,Chuseq];
Channel0 = Channel.PathGains./sqrt(sum((abs(Channel.PathGains)).^2));
Rx1 = filter(Channel0,1,Tx);
Rx2 = awgn(Rx1,SNR(n),'measured');
Rx3 = Rx2;%(Chu_size+1:Chu_size+Blk_size);
H_channel = H_channel0;
% Frequency domain equalization
Y = fft(Rx3,Blk_size+Chu_size+Chu_size);
Wk = conj(H_channel)./(H_channel.*conj(H_channel)+10^(-SNR(n)/10));
Zk = Y.*Wk;
Qk = zeros(size(Zk));
Bk = (Blk_size-Chu_size)*(abs(H_channel).^2+10^(-SNR(n)/10))./(sum(abs(H_channel).^2+10^(-SNR(n)/10)))-1;
P = 5;
% call CNN Output weight of neural network
load CNNmodel.mat
Iter = 5;
for iter = 1:Iter
Wk = conj(H_channel)./(H_channel.*conj(H_channel)+10^(-SNR(n)/10)/P).*(1+Bk);
Zk = Y.*Wk;
Uk = Zk-Qk;
RxMMSE0 = ifft(Uk,Blk_size+Chu_size+Chu_size);
xn = sign(real(RxMMSE0))+sqrt(-1)*sign(imag(RxMMSE0));
% Go to UW
RxMMSE1 = xn(Chu_size+1:Blk_size);
% To adjudicate
RxMMSE = demodulation(RxMMSE1,Modsel);
Tdecode = round(func_turbo_decode(2*RxMMSE(1:end-2)-1));
tmps = Tdecode;
XK = fft([tmps,Chuseq],length(RxMMSE1));
% call CNN Deep learning neural networks , Calculation Bk value
Bk0 =([H_channel.*conj(H_channel)]+10^(-SNR(n)/10)/P)/(mean(([H_channel.*conj(H_channel)]+10^(-SNR(n)/10)/P)))/(Blk_size)-1;
Bk = func_CNN(H_channel,Bk0,cnn);
Qk = [XK,ones(1,192)].*Bk;
end
CrrMMSE = find((Tdin-Tdecode) == 0);
ErrMMSE = ErrMMSE+(Mss-length(CrrMMSE));
end
% Statistical bit error rate
errors(n) = ErrMMSE/(Mss*NFrame*Modsel);
end
figure
semilogy(SNR,errors,'b-o');
hold on;
grid on;
xlabel(' Signal-to-noise ratio SNR(dB)')
ylabel(' Bit error rate SBR')
save R1.mat SNR errors
4. Simulation results

A1-169
边栏推荐
- 一天上手Aurora 8B/10B IP核(5)----从Framing接口的官方例程学起
- "Analysis of 43 cases of MATLAB neural network": Chapter 41 implementation of customized neural network -- personalized modeling and Simulation of neural network
- Class design basis and advanced
- Introduction to Robotics II. Forward kinematics, MDH method
- u本位合约爆仓清算解决方案建议
- Fourier series
- Eight steps of agile development process
- Custom classloader that breaks parental delegation
- Kotlin基础学习 16
- How to establish its own NFT market platform in 2022
猜你喜欢

【力扣刷题】15.三数之和(双指针);17.电话号码的字母组合(递归回溯)

Visual slam Lecture 3 -- Lie groups and Lie Algebras
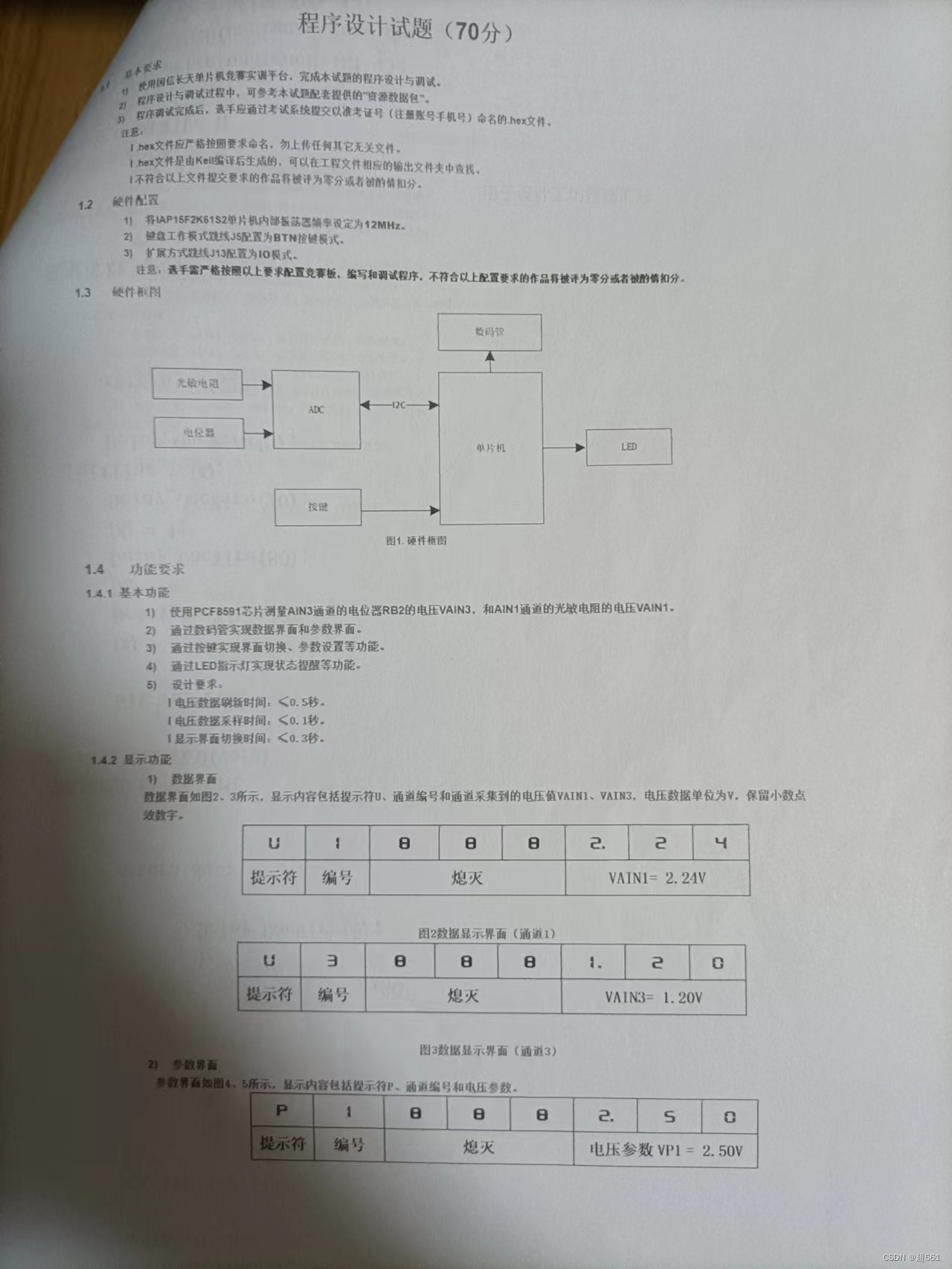
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十一届
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(RT-Thread)—— 实验1 LED 闪烁实验(学习笔记)
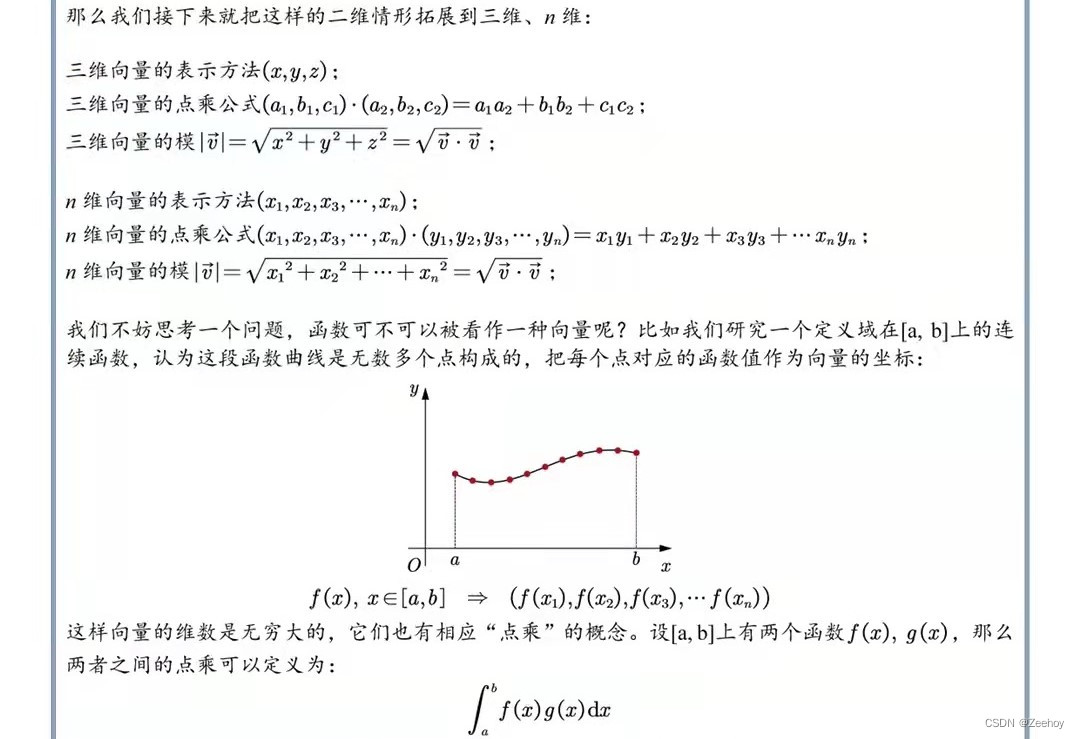
傅里叶级数

In the era of programmers' introspection, five-year-old programmers are afraid to go out for interviews
![[designmode] builder model](/img/e8/855934d57eb6868a4d188b2bb1d188.png)
[designmode] builder model
How to establish its own NFT market platform in 2022

《MATLAB 神經網絡43個案例分析》:第42章 並行運算與神經網絡——基於CPU/GPU的並行神經網絡運算
![[designmode] Prototype Pattern](/img/ee/c4e48c2ce8ff66f50f0bf13e5a0418.png)
[designmode] Prototype Pattern
随机推荐
Gradle foundation | customize the plug-in and upload it to jitpack
h5中的页面显示隐藏执行事件
Imageai installation
Kotlin basic learning 14
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十二届第二场
Haute performance et faible puissance Cortex - A53 Core Board | i.mx8m mini
Object oriented thinking
5G時代全面到來,淺談移動通信的前世今生
Lost a few hairs, and finally learned - graph traversal -dfs and BFS
Interface debugging tool simulates post upload file - apipost
What kind of interview is more effective?
What do you know about stock selling skills and principles
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十二届第一场
Exchange rate query interface
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(RT-Thread)—— 实验1 LED 闪烁实验(学习笔记)
Visual slam Lecture 3 -- Lie groups and Lie Algebras
焱融看 | 混合雲時代下,如何制定多雲策略
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十一届第一场
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第九届
毕设-基于SSM电影院购票系统