LyScriptThere are three basic stack manipulation methods available in the plugin,其中push_stack用于入栈,pop_stack用于出栈,And the most useful ispeek_stack函数,This function can be used to check the memory parameter at the specified stack location,This feature can be used to achieve,Detection of stack addresses,or a scan of the stack, etc.
LyScript项目地址:https://github.com/lyshark/LyScript
peek_stackThe command passed in is the stack subscript position by default0开始,并输出一个十进制有符号长整数,First realize the conversion between signed and unsigned numbers,Prepare for subsequent stack scans.
from LyScript32 import MyDebug
# Convert signed integer to unsigned number
def long_to_ulong(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return inter & ((1 << 32) - 1)
else:
return inter & ((1 << 64) - 1)
# Convert unsigned integer to signed number
def ulong_to_long(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return (inter & ((1 << 31) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 31))
else:
return (inter & ((1 << 63) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 63))
if __name__ == "__main__":
dbg = MyDebug()
connect_flag = dbg.connect()
print("连接状态: {}".format(connect_flag))
for index in range(0,10):
# Returns a signed number by default
stack_address = dbg.peek_stack(index)
# 使用转换
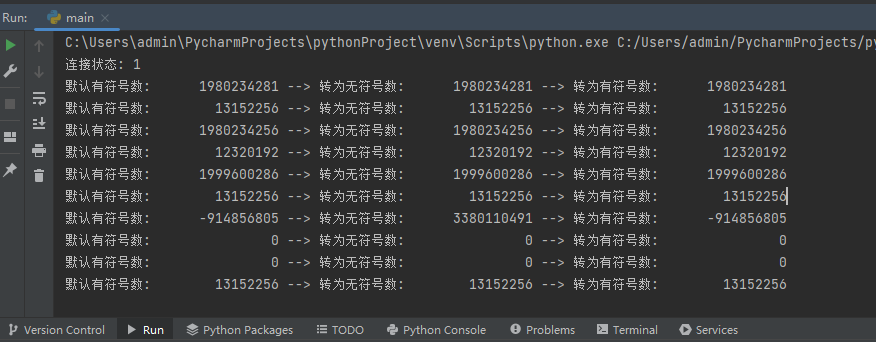
print("Default signed number: {:15} --> 转为无符号数: {:15} --> 转为有符号数: {:15}".
format(stack_address, long_to_ulong(stack_address),ulong_to_long(long_to_ulong(stack_address))))
dbg.close()
Through the above wrapper function,You can convert signed and unsigned numbers.
Continue to improve this feature,我们使用get_disasm_one_code()函数,Scan the stack address and get the disassembled code at that address.
from LyScript32 import MyDebug
# Convert signed integer to unsigned number
def long_to_ulong(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return inter & ((1 << 32) - 1)
else:
return inter & ((1 << 64) - 1)
# Convert unsigned integer to signed number
def ulong_to_long(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return (inter & ((1 << 31) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 31))
else:
return (inter & ((1 << 63) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 63))
if __name__ == "__main__":
dbg = MyDebug()
connect_flag = dbg.connect()
print("连接状态: {}".format(connect_flag))
for index in range(0,10):
# Returns a signed number by default
stack_address = dbg.peek_stack(index)
# Disassemble a line
dasm = dbg.get_disasm_one_code(stack_address)
# Get the module base address according to the address
if stack_address <= 0:
mod_base = 0
else:
mod_base = dbg.get_base_from_address(long_to_ulong(stack_address))
print("stack => [{}] addr = {:10} base = {:10} dasm = {}".format(index, hex(long_to_ulong(stack_address)),hex(mod_base), dasm))
dbg.close()
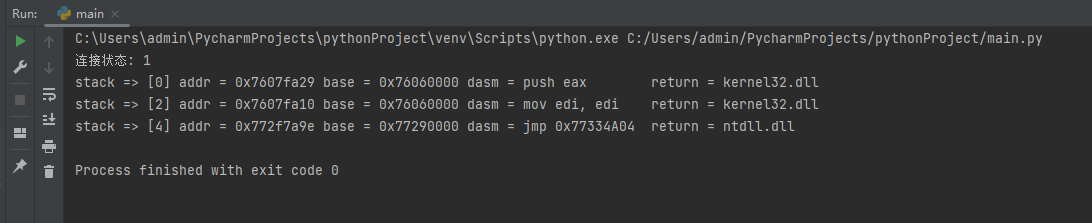
The resulting stack parameters are as follows:
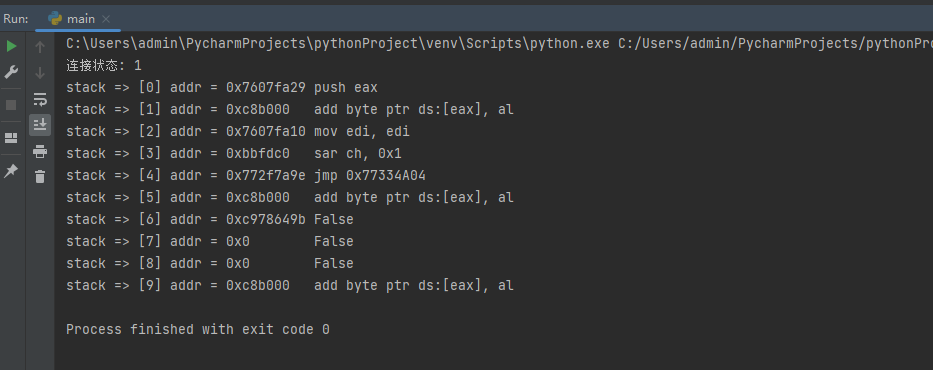
From this we can get the disassembly parameters at the stack,But if we need to retrieve if there is an address back to the module in a specific area of the stack,该如何实现呢?
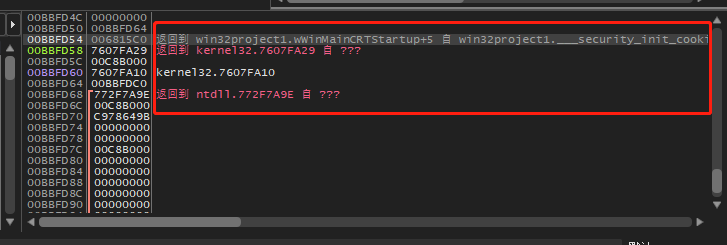
其实很简单,First we need to get the base addresses of all loaded modules in the global state of the program,Then get the actual address within the current stack memory address,And get the module base address through the actual memory address,Compare the global table to get where the current module is returned.
from LyScript32 import MyDebug
# Convert signed integer to unsigned number
def long_to_ulong(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return inter & ((1 << 32) - 1)
else:
return inter & ((1 << 64) - 1)
# Convert unsigned integer to signed number
def ulong_to_long(inter,is_64 = False):
if is_64 == False:
return (inter & ((1 << 31) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 31))
else:
return (inter & ((1 << 63) - 1)) - (inter & (1 << 63))
if __name__ == "__main__":
dbg = MyDebug()
connect_flag = dbg.connect()
print("连接状态: {}".format(connect_flag))
# Get all module information loaded by the program
module_list = dbg.get_all_module()
# Scan down the stack
for index in range(0,10):
# Returns a signed number by default
stack_address = dbg.peek_stack(index)
# Disassemble a line
dasm = dbg.get_disasm_one_code(stack_address)
# Get the module base address according to the address
if stack_address <= 0:
mod_base = 0
else:
mod_base = dbg.get_base_from_address(long_to_ulong(stack_address))
# print("stack => [{}] addr = {:10} base = {:10} dasm = {}".format(index, hex(long_to_ulong(stack_address)),hex(mod_base), dasm))
if mod_base > 0:
for x in module_list:
if mod_base == x.get("base"):
print("stack => [{}] addr = {:10} base = {:10} dasm = {:15} return = {:10}"
.format(index,hex(long_to_ulong(stack_address)),hex(mod_base), dasm,
x.get("name")))
dbg.close()
运行后,The position of all returned modules in the stack can be scanned.