当前位置:网站首页>Mysql database (I)
Mysql database (I)
2022-07-06 15:10:00 【Hand pluckable Xinchen】
1, The role of database
(1) Data storage : A large number of data generated by the program are saved when the program runs and after the program ends .
(2) Data integrity : Connect data and the structure between data , Connect dependencies between data and programs .
(3) Data reading : In order to make the written data more convenient to read .
(4) Data security : Prevent data loss caused by external factors .
(5) structured : The storage of data in the database can rely on the logic of two-dimensional table structure to store data , You can refer to the original dependency and institutional relationship of data to store data .
(6) independence : The data stored in the database and the application are independent of each other , They don't influence each other .
(7) participatory : Multiple users can jointly analyze the data resources in the computer database , The same data can be used by multiple people at the same time , So as to achieve efficient database sharing .
(8) Security : Password of the user when accessing the database , Restrict the user's permission , Or limit the storage of data .
2, The concept of databases
Keep it in a computer for a long time , Organized 、 A collection of large amounts of data that can be shared , It's a number “ Warehouse ”.
effect : Deposit 、 Management data .
classification : Relational database 、NoSQL database
3,MySQL The characteristics of database
(1) Easy to operate
(2) small , The function is all ready
(3) free , Open source databases
(4) Operable and windows or linux System
4, database structure
| database (Database) | Stored on disk as a file , That is, it corresponds to one or more physical files . |
| Field (Field) | Also called domain . Each column in the table is called a field . Each field has a corresponding description . |
| Indexes (Index) | An index is actually a special type of table , It contains the value of the keyword and the pointer to the actual record position , It can improve the efficiency of accessing the database . |
| Data sheet (Table) | Abbreviation table , It consists of a set of data records , The data in the database is organized in tables . A table is a set of related data arranged in rows ; Each table contains the same type of information . |
| Record (Record) | Each row in the table is called a record , It consists of several fields . |
| SQL sentence | Structured query statement commands , Used to get a set of specified records from one or more tables , Or perform the specified operation on a table . |
5,SQL Sentence classification
| name | explain | command | |
DDL ( Data definition language ) | Define and manage data objects , Such as a database , Data sheets, etc . | CREATE | establish |
| DROP | Delete | ||
| ALTER | modify | ||
DML ( Data operation language ) | Operate the data contained in the database object . | INSERT | insert data |
| UPDATE | Update data | ||
| DELETE | Delete data | ||
DQL ( Data query language ) | Used to query database data | SELECT | Inquire about |
DCL ( Data control language ) | The language used to manage the database , Including management authority and data change | GRANT | to grant authorization |
| COMMIT | Submit | ||
| ROLLBACK | Roll back | ||
6,DDL Statement operation database
(1) Create database CREATE DATABASE Database name ;
(2) Delete database DROP DATABASE Database name ;
(3) view the database SHOW DATABASES;
(4) Select database USE Database name ;
-- Create database
CREATE DATABASE day001;
-- Delete database
DROP DATABASE day001;
-- view the database
SHOW DATABASES;
-- Select database
USE day001;7,DDL Create database tables
grammar :
8, Field type of database table
Type at character
| type | explain | Value range | Storage requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| char[(M)] | Fixed long string , Retrieval is fast, but it takes space , 0 <= M <= 255 | M character | char[(M)] |
varchar[(M)] | Variable string ,0 <= M <= 65535 | Variable length | varchar[(M)] |
| tinytext | Micro text string | 16777215 length +3 Bytes | tinytext |
| text | Text string (4 individual G Size left and right ) | 4294967295 length +4 Bytes | text |
char and varchar Compare
| type | characteristic | In space | On the time | Use scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| char(M) | Fixed length | Waste storage space | Efficient | Not much storage , High speed requirement |
| varchar(M) | Variable length | Save storage space | Low efficiency | Not CHAR The situation of |
value type
tinyint | Very small data | There is a signed value : -2 ^7 ~ 2^7-1, Unsigned value :0 ~ 28-1 | 1 byte |
smallint | Smaller data | There is a signed value : -2 15 ~ 215 -1 , Unsigned value : 0 ~ 216 -1 | 2 byte |
mediumin | Medium data | There is a signed value : -2 23 ~ 223 -1 , Unsigned value : 0 ~ 224 -1 | |
int | Integers | There is a signed value : -2^31 ~ 2^31-1, Unsigned value :0 ~ 2^32-1 | 4 byte |
bigint | A large integer | There is a signed value : -2^63 ~2^63-1, Unsigned value :0 ~2^64-1 | 8 byte |
float | Single-precision floating-point | ±1.1754351e -38 | 4 byte |
double | Double precision floating point | ±2.2250738585072014e -308 | 8 byte |
Decimal | Floating point numbers in string form | decimal(m, d) | m Bytes |
Date and time type
| type | explain | Value range | Storage requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| DATE | YYYY-MM-DD, Date format | 1000-01-01~ 9999-12-31 | DATE |
TIME | Hh:mm:ss , Time format | -838:59:59~838:59:59 | TIME |
DATETIME | YY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss | 1000-01-01 00:00:00 to 9999-12-31 23:59:59 | DATETIM |
TIMESTAMP | YYYYMMDDhhmmss Time in format | 197010101000000 ~2037 Some time in the year | TIMESTAMP |
YEAR | YYYY The year value of the format | 1901~2155 | YEAR |
9, Database field comments
10, Query the database table structure created
DESCRIBE teacher;
DESC teacher;Mode two :show create table Table name
SHOW CREATE TABLE teacher;11, Modify and delete database tables
(1) Modify the name of the table ALTER TABLE The old name of the table RENAME AS The new name of the table ;
(2) Add fields ALTER TABLE Table name ADD Field name Column type [ attribute ];
(3) Delete field ALTER TABLE Table name DROP Field name ;
(4) Modify fields
Mode one :ALTER TABLE Table name MODIFY Field name Column type [ attribute ];
Mode two :ALTER TABLE Table name CHANGE Old field name new field name data type attribute ;
(5) Delete table DROP TABLE Table name ;
-- Modify the name of the table
ALTER TABLE teacher RENAME AS laoshi;
-- Add fields
ALTER TABLE teacher ADD t_phone CHAR(11) COMMENT ' Teacher's phone number ';
-- Delete field ( Dangerous operation )
ALTER TABLE teacher DROP tea_name;
-- Modify fields Substitution , If you don't write, the default value will be used
-- Data can be converted to modified data types , The length meets the modified length .
-- The way 1:modify
ALTER TABLE teacher MODIFY t_phone CHAR(20);
-- The way 2:change
-- alter table teacher change Old field name new field name data type attribute ;
ALTER TABLE teacher CHANGE t_phone dianhua CHAR(11) COMMENT ' Telephone ';
-- Delete table ( Dangerous operation )
DROP TABLE teacher;12, constraint
Concept : Constraints are actually constraints on the data in the table
effect : The purpose of adding constraints in the table design is to ensure that the records in the table are complete and effective
species :
Non empty constraint (not null)
Uniqueness constraint (unique)
Primary key constraint (primary key) PK
Foreign key constraints (foreign key) FK
Check constraint ( at present MySQL I won't support it 、Oracle Support )
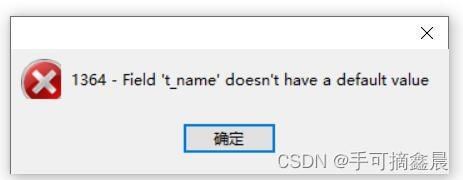
13, Non empty constraint
Concept : use not null Constraint field cannot be null value , Specific data must be given
-- Non empty constraint
CREATE TABLE teacher2(
t_name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT ' A passer-by ',
t_age TINYINT
);If the field is empty, an error will be reported
14, Unique constraint
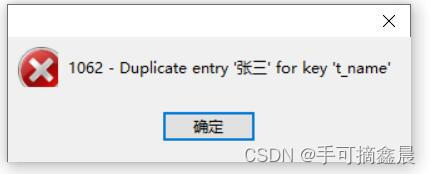
Concept :unique Constrained fields , Have uniqueness , Do not repeat , But it can be null
-- Unique constraint
-- Mode one : Row level unique constraint
CREATE TABLE teacher3(
t_name VARCHAR(10) UNIQUE,
t_age TINYINT
);
-- Mode two : Table level unique constraint
CREATE TABLE teacher4(
t_name VARCHAR(10),
t_age TINYINT,
-- Table level constraints name constraints
CONSTRAINT uniqu_tname_tage UNIQUE(t_name,t_age) -- Union sole constraint ( As like as two peas , It is a violation of the only constraint )
);If the fields are the same, an error will be reported
15, Primary key constraint
Concept : Primary key (primary key) Is one or more fields in a table , Its value is used to uniquely identify a record in the table
-- Primary key constraint
-- 1, All tables must have a primary key
-- 2, Only one primary key is allowed for each table
-- 3, The columns of the set primary key cannot be duplicated ( Uniqueness )
-- 4, Not allowed to be empty ( Not for null)
-- 5, Generally, it is the type of primary key INT,BIGINT, In turn, increasing (auto_increment)
CREATE TABLE teacher5(
t_name VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY,
t_age TINYINT
);
CREATE TABLE teacher6(
t_no INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
t_name VARCHAR(10),
t_age TINYINT
);
-- Table level primary key
CREATE TABLE teacher7(
t_email VARCHAR(20),
t_passwd VARCHAR(10),
t_name VARCHAR(10),
PRIMARY KEY(t_email,t_name), -- There can only be one
UNIQUE(t_email),
UNIQUE(t_passwd),
UNIQUE(t_email,t_name)
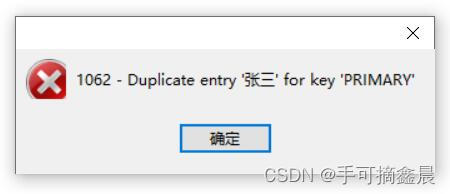
);16, Foreign key constraints
Foreign keys : Foreign keys are used to associate with another table . It's a field that can determine another table record , Used to keep data consistent . If there are two tables A、B,id yes A Primary key of , and B There are also id Field , be id It's a watch B The foreign key .
A Is the basic table or parent table , Main table ,B For information sheet , Sub table , Side table
Definition :foreign key( The field name of the table ) references Parent table name ( Field name of parent table )
-- Foreign key constraints
-- First create the parent table , Create a sub table
-- Foreign key data can be empty
-- When adding data , First, add the data of the parent table , Add sub table
-- When deleting data , First, delete the data of the sub table , Then delete the data of the parent table
-- Like what? ( Parent table ) It can be used as ( Sub table ) The foreign key ( Or primary key , Or the only )
CREATE TABLE A(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
a_name VARCHAR(10)
);
CREATE TABLE B(
bid INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
b_name VARCHAR(10),
id INT,
FOREIGN KEY(id) REFERENCES A(id)
);
If the value primary key of the added foreign key data does not exist
17, Add constraints
| Add non empty constraints | alter table Table name modify Field name not null |
| Add unique constraints | alter table Table name add unique( Field name ) |
| Add primary key constraint | alter table Table name add primary key( Field name ) |
| Add a foreign key constraint | alter table Table name add constraint N1 foreign key( Field name ) references Parent table ( Parent table field name ) |
SHOW CREATE TABLE teacher;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`dianhua` char(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' Telephone '
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
-- to tea_age Add non empty constraints
ALTER TABLE teacher MODIFY tea_age INT(11) NOT NULL;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
-- to tea_name Add unique constraints
ALTER TABLE teacher MODIFY tea_name VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name` (`tea_name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
-- to tea_name Add primary key constraint
ALTER TABLE teacher MODIFY tea_name VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_age` (`tea_age`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
18, Deletion of constraints
Delete not null constraint | alter table Table name modify Name type ; |
Delete unique constraint | alter table Table name drop index Unique constraint name ; |
Delete primary key constraint | alter table Table name drop primary key; |
Delete foreign key constraint | alter table Table name drop foreign key Foreign key name ; |
-- Delete tea_age Non empty constraint of
ALTER TABLE teacher MODIFY tea_age INT(11);
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name` (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name_2` (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_age` (`tea_age`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
-- Delete tea_age The only constraint
ALTER TABLE teacher DROP INDEX tea_age;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name` (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name_2` (`tea_name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
-- Delete the primary key of the table
ALTER TABLE teacher DROP PRIMARY KEY;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tea_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`tea_age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name` (`tea_name`),
UNIQUE KEY `tea_name_2` (`tea_name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci边栏推荐
- Keil5 MDK's formatting code tool and adding shortcuts
- Which version of MySQL does php7 work best with?
- Video scrolling subtitle addition, easy to make with this technique
- 如何成为一个好的软件测试员?绝大多数人都不知道的秘密
- [oiclass] maximum formula
- 软件测试方法有哪些?带你看点不一样的东西
- Global and Chinese markets of PIM analyzers 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- UCORE lab2 physical memory management experiment report
- DVWA exercise 05 file upload file upload
- Global and Chinese market of maleic acid modified rosin esters 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
猜你喜欢
Wang Shuang's detailed learning notes of assembly language II: registers
想跳槽?面试软件测试需要掌握的7个技能你知道吗
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (I)

Rearrange spaces between words in leetcode simple questions
自动化测试你必须要弄懂的问题,精品总结
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (II)
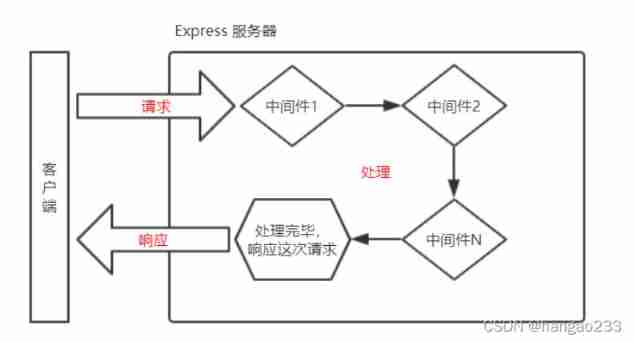
Express
The latest query tracks the express logistics and analyzes the method of delivery timeliness
基于485总线的评分系统双机实验报告
Stc-b learning board buzzer plays music 2.0
随机推荐
软件测试需求分析之什么是“试纸测试”
Login the system in the background, connect the database with JDBC, and do small case exercises
Database monitoring SQL execution
Leetcode simple question: check whether two strings are almost equal
Video scrolling subtitle addition, easy to make with this technique
STC-B学习板蜂鸣器播放音乐2.0
Global and Chinese market of maleic acid modified rosin esters 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
[pointer] delete all spaces in the string s
Oracle foundation and system table
Global and Chinese market of RF shielding room 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 1 after class exercises and answers summary
Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 2 after class exercises and answer summary
Global and Chinese market for antiviral coatings 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Report on the double computer experiment of scoring system based on 485 bus
What level do 18K test engineers want? Take a look at the interview experience of a 26 year old test engineer
[Ogg III] daily operation and maintenance: clean up archive logs, register Ogg process services, and regularly back up databases
What is the transaction of MySQL? What is dirty reading and what is unreal reading? Not repeatable?
Global and Chinese markets of PIM analyzers 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Logstack introduction and deployment -- elasticstack (elk) work notes 019
Soft exam information system project manager_ Project set project portfolio management --- Senior Information System Project Manager of soft exam 025
