当前位置:网站首页>image enhancement
image enhancement
2022-07-08 02:10:00 【Strawberry sauce toast】
Catalog
One 、 Spatial image enhancement algorithm
( One ) Direct gray transformation algorithm
( 3、 ... and ) Grayscale adjustment
( Four ) Spatial filtering enhancement
(1) Linear smoothing filtering
(2) Nonlinear smoothing filtering
(2) Nonlinear sharpening filter
Two 、 Frequency domain enhancement
1. Fourier transform low-pass filtering
The introduction
- Image enhancement is to highlight some information in an image according to specific needs , At the same time, weaken or remove some unnecessary information , Subjective ;
- Image enhancement makes the processed image more suitable for human visual characteristics or machine analysis , In order to achieve more advanced image processing and analysis ;
- Image enhancement hopes to remove noise and enhance edges , But the two contradict , Therefore, image enhancement often compromises the two , Find a good cost function to achieve the purpose of enhancement
- It is divided into Airspace enhancement and Frequency domain enhancement Two categories: .
One 、 Spatial image enhancement algorithm
airspace : Refers to the space composed of pixels , The spatial enhancement algorithm acts directly on the pixel value .
( One ) Direct gray transformation algorithm
1. Logarithmic transformation
characteristic : Compress the contrast of high gray areas in the input image , Expand the contrast of low gray value areas , It can make the details of the low gray value area easier to see .
2. Grayscale cut
(1) characteristic : Enhance the contrast of a specific range , Highlight the brightness of a specific gray range in the image .
(2) Method :(a) Display the gray level of interest with a larger value , Other gray levels are displayed with smaller gray values ;
(b) Display the gray level of interest with a larger value , Other gray levels remain unchanged .
( Two ) Histogram enhancement
1. Histogram properties
- The histogram reflects the overall gray distribution of the image , Intuitively , If the pixels of an image occupy all possible gray levels and are evenly distributed , Then the image has high contrast ( Highest gray level / Minimum gray level ) And changeable gray tones ;
- Histogram does not contain location information , Just reflect the amount of gray , It has nothing to do with the position of gray , Different images may have similar or identical histogram distribution ;
- Histogram can be superimposed , The gray histogram of an image is equal to the sum of the histograms of its various parts ;
- Histogram has statistical characteristics .
2. Histogram equalization
(1) advantage
The probability density function of the processed image can be approximately uniformly distributed , As a result, the dynamic range of pixel values is expanded ;
(2) shortcoming
Unable to suppress noise
( 3、 ... and ) Grayscale adjustment
J=imadjust(I,[low_in high_in],[low_out high_out],gamma);among ,[low_in,high_in] Specifies the grayscale range that the input image needs to be mapped ,[low_out,high_out] Specifies the grayscale range of the output image .
adopt gamma Parameters can choose the mapping method ,gamma=1 Time is linear mapping ,gamma<1, Brighter ;gamma>1, Darker .

( Four ) Spatial filtering enhancement
1. Smooth filtering
Smooth filtering can be achieved by low-pass filtering , The purpose is to blur the image or eliminate image noise .
It is divided into linear smoothing filtering and nonlinear smoothing filtering .
(1) Linear smoothing filtering
a. Mean filtering
b. Gauss filtering : In essence, it belongs to weighted mean filtering , The weight of a pixel is obtained by Gaussian weighting from the distance from the point to the central pixel .
MATLAB Use fspecial Function to generate filter template
h=fspecial(type)
h=fspecial(type, parameters)among ,type Used to specify filter type ,parameters Is a specific function related to the filter .
| type | parameters | explain |
| average | hsize | Rectangular mean filter ,hsize The format is [m,n], Used to specify the size of the rectangle |
| disk | radius | The generation radius is radius Circular filter |
| gaussian | hsize,sigma | The standard deviation is sigma、 The size is hize Gaussian low pass filter |
| laplacian | alpha | The coefficient is alpha Two dimensional Laplace operation |
| log | hsize,sigma | The standard deviation is sigma、 The size is hsize Gaussian filter rotationally symmetric Laplace operator |
| motion | len,theta | By angle theta Move len Pixel motion filter |
| prewitt | nothing | Approximate computing gradient operator |
| sobel | nothing | The approximate calculation gradient operator of the spatial position between pixels is considered |
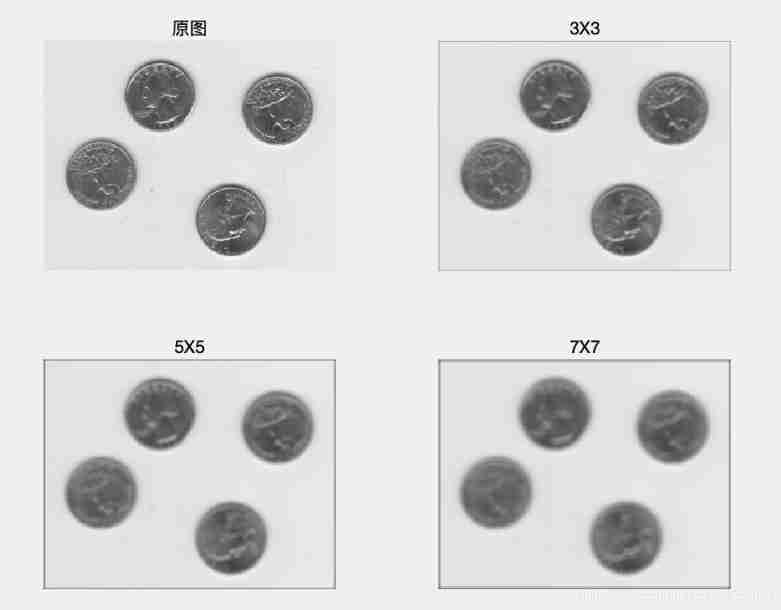
e.g. Use mean filters of different sizes for the same image , Check the filtering effect .
I=imread('eight.tif');
subplot(221)
imshow(I);title(' Original picture ')
subplot(222)
J1=filter2(fspecial('average',3),I);
imshow(uint8(J1));title('3X3');
subplot(223)
J2=filter2(fspecial('average',5),I);
imshow(uint8(J2));title('5X5');
subplot(224)
J3=filter2(fspecial('average',7),I);
imshow(uint8(J3));title('7X7');Although the mean filter considers the role of neighborhood points , But the influence of spatial location is not considered . actually , The point closer to a point in the neighborhood , The greater the impact on this point , The weighted mean filtering template can be used , For example, the weighting coefficient of the template is obtained by sampling the two-dimensional Gaussian function , The corresponding filter is called Gaussian filter .
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
(2) Nonlinear smoothing filtering
The most commonly used nonlinear smoothing filter is median filter , That is, the pixels of the image in the neighborhood are sorted by gray level , Then choose the intermediate value as the filtering result .
B=medfilt2(A)
B=medfilt2(A,[m n])
B=medfilt2(A,[m n],padopt)
among ,[m n] Specify the size of the filter template , The default size is 3*3;padopt Used to specify the image matrix A The continuation form of the edge of .
Median filter is better than mean filter in detail retention .
2. Sharpening filter
(1) Linear sharpening filter
Linear high pass filter template :
| -1 | -1 | -1 |
| -1 | 8 | -1 |
| -1 | 8 | -1 |
Laplace operator : The center coefficient is greater than 0, Other coefficients are less than 0, The sum of all coefficients is 0. When the Laplace template slides in the image , For areas with little or no change in grayscale , Its filter output is small or 0.
e.g. High pass filtering of an image using Laplace operator .
I=imread('blobs.png');
h=fspecial('laplacian');
J=filter2(h,I);
subplot(121)
imshow(I);title(' Original picture ');
subplot(122)
imshow(J);title(' Laplace filtering ') 
(2) Nonlinear sharpening filter
- The mean filter can blur the image , It is summed in the calculation process , Mathematically corresponding to integral ;
- The nonlinear sharpening filter is mathematically realized by differentiation , among Gradient operator Is the most commonly used differential operator , Describes the gray change rate of the image along a certain direction .
- The commonly used spatial nonlinear sharpening filter operators are sobel operator 、prewitt operator 、log operator ( Laplace Gauss operator ), The definition of these operators is mainly based on the basic concept of differentiation .
e.g. Different nonlinear sharpening filters are used to filter the image
I=imread('blobs.png');
h1=fspecial('sobel');
J1=filter2(h1,I);
h2=fspecial('prewitt');
J2=filter2(h2,I);
h3=fspecial('log');
J3=filter2(h3,I);
subplot(221)
imshow(I);title(' Original picture ');
subplot(222)
imshow(J1);title('sobel operator ')
subplot(223)
imshow(J2);title('prewitt operator ')
subplot(224)
imshow(J3);title('log operator '); 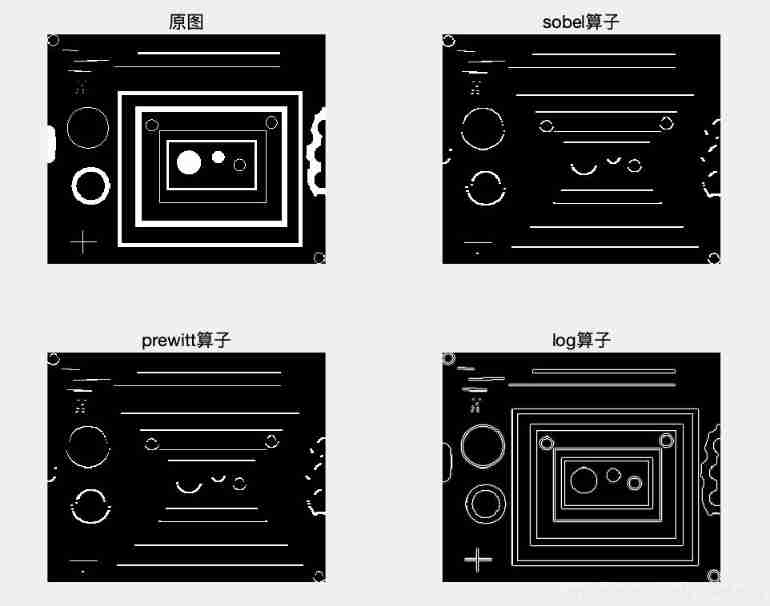
default sobel Operator and prewitt Operators are solving horizontal details , That is, differential calculation in the vertical direction , The vertical details can be extracted by transposing the templates of these two operators .
h2_2=h2';
J2_2=filter2(h2_2,I);
figure
subplot(131)
imshow(J2);title(' Level of detail ')
subplot(132);
imshow(J2_2);title(' Vertical details ')
subplot(133);
imshow(or(J2,J2_2),[]);title(' Full details ') 
Two 、 Frequency domain enhancement
Frequency domain enhancement is to transform the image to other space first , Then we use the characteristics of this space to process the data in the transform domain , Finally, it is transformed into the original image space .
Frequency domain enhancement is mainly divided into 3 Step :
- Choose the appropriate transformation method , Transform the image into frequency domain space ;
- According to the processing objectives , The transform coefficients are processed in the frequency domain space ;
- Inverse transform the processed result , Get the enhanced image .
( One ) Low pass filtering
The energy of signal or image is mainly concentrated in low frequency and intermediate frequency , And noise often appears in high frequency , therefore , Using low-pass filter can achieve the purpose of denoising .
1. Fourier transform low-pass filtering
......
边栏推荐
- Usage of hydraulic rotary joint
- Cross modal semantic association alignment retrieval - image text matching
- Alo who likes TestMan
- How mysql/mariadb generates core files
- Give some suggestions to friends who are just getting started or preparing to change careers as network engineers
- Key points of data link layer and network layer protocol
- 科普 | 什么是灵魂绑定代币SBT?有何价值?
- Flutter 3.0框架下的小程序运行
- COMSOL --- construction of micro resistance beam model --- final temperature distribution and deformation --- addition of materials
- VIM use
猜你喜欢

Master go game through deep neural network and tree search
metasploit

Many friends don't know the underlying principle of ORM framework very well. No, glacier will take you 10 minutes to hand roll a minimalist ORM framework (collect it quickly)
Neural network and deep learning-5-perceptron-pytorch
PB9.0 insert OLE control error repair tool
静态路由配置全面详解,静态路由快速入门指南
![[knowledge map paper] Devine: a generative anti imitation learning framework for knowledge map reasoning](/img/c1/4c147a613ba46d81c6805cdfd13901.jpg)
[knowledge map paper] Devine: a generative anti imitation learning framework for knowledge map reasoning
软件测试笔试题你会吗?
![[target tracking] |atom](/img/33/529b483a0a848e0e4263ba24462d5c.png)
[target tracking] |atom

2022国内十大工业级三维视觉引导企业一览
随机推荐
微软 AD 超基础入门
电路如图,R1=2kΩ,R2=2kΩ,R3=4kΩ,Rf=4kΩ。求输出与输入关系表达式。
COMSOL --- construction of micro resistance beam model --- final temperature distribution and deformation --- addition of materials
#797div3 A---C
Get familiar with XML parsing quickly
ArrayList源码深度剖析,从最基本的扩容原理,到魔幻的迭代器和fast-fail机制,你想要的这都有!!!
metasploit
From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
Why did MySQL query not go to the index? This article will give you a comprehensive analysis
2022国内十大工业级三维视觉引导企业一览
Vim 字符串替换
WPF 自定义 写实风 雷达图控件
Remote sensing contribution experience sharing
Keras' deep learning practice -- gender classification based on inception V3
PHP calculates personal income tax
Is NPDP recognized in China? Look at it and you'll see!
《ClickHouse原理解析与应用实践》读书笔记(7)
Node JS maintains a long connection
谈谈 SAP iRPA Studio 创建的本地项目的云端部署问题
JVM memory and garbage collection-3-runtime data area / method area