当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode (417) -- Pacific Atlantic current problem
Leetcode (417) -- Pacific Atlantic current problem
2022-07-07 05:16:00 【SmileGuy17】
Leetcode(417)—— The Pacific Atlantic current problem
subject
There is one m × n m \times n m×n Rectangular Island , And The Pacific Ocean and The Atlantic ocean adjacent . “ The Pacific Ocean ” On the left and upper boundary of the continent , and “ The Atlantic ocean ” On the right and lower boundaries of the continent .
The island is divided into a grid of square cells . Given a m × n m \times n m×n The integer matrix of heights , heights[r][c] Representation coordinates (r, c) Upper cell Height above sea level .
There is more rain on the island , If the height of adjacent cells Less than or equal to The height of the current cell , The rain can go straight north 、 south 、 In the east 、 West flow to adjacent cells . Water can flow into the ocean from any cell near the ocean .
Return grid coordinates result Of 2D list , among result[i] = [ri, ci] Indicates that rainwater flows from the cell (ri, ci) flow It can flow to the Pacific Ocean or the Atlantic Ocean .
Example 1:
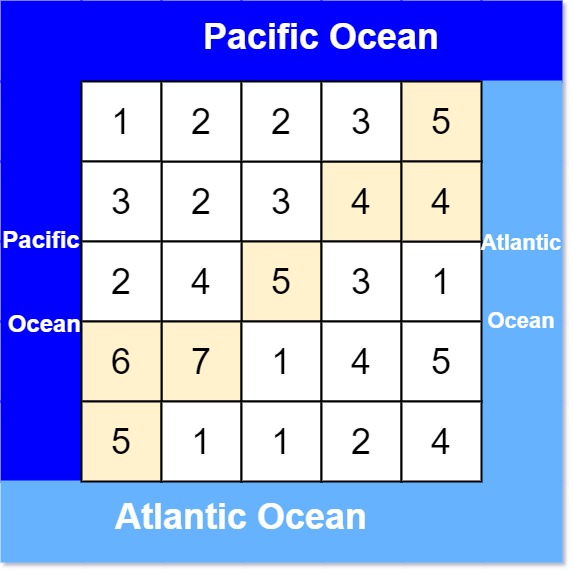
Input : heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
Output : [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
Example 2:
Input : heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
Output : [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
Tips :
- m == heights.length
- n == heights[r].length
- 1 1 1 <= m, n <= 200 200 200
- 0 0 0 <= heights[r][c] <= 1 0 5 10^5 105
Answer key
Search backward from the boundary , To reduce time complexity
Method 1 :DFS
Ideas
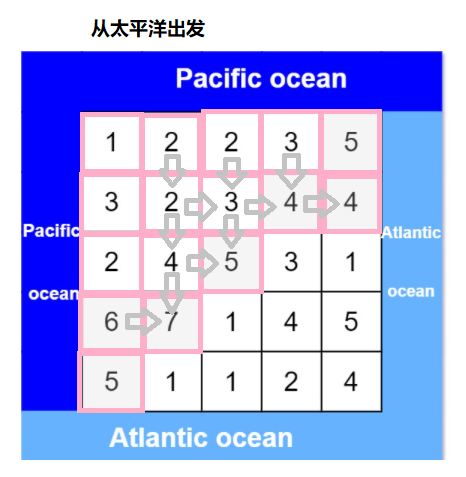
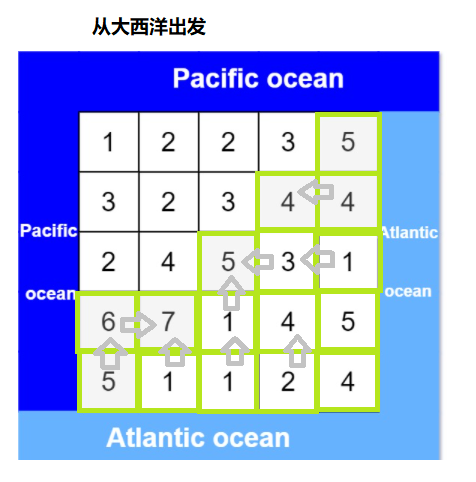
The direction of rainwater flow is from high to low , The rainwater on each cell can only flow to adjacent cells with a height less than or equal to the current cell . Start with a cell , The flow of rainwater is simulated by search method , Then you can judge whether rainwater can flow from this cell to the ocean .
If Start directly with each cell Simulate the flow of rainwater , be Will repeatedly traverse each cell , Lead to high time complexity . To reduce time complexity , You can reverse search from the boundary of the matrix to find the cells where the rainwater flows to the boundary , During reverse search , You can only move to cells with the same height or larger at a time .
Because the boundary of the Pacific Ocean is on the left , The right and lower boundaries of the matrix are the Atlantic Ocean , Therefore, starting from the left and upper boundaries of the matrix, we can find the cells where the rain flows to the Pacific Ocean , Reverse search from the right and lower boundaries of the matrix to find the cells where rainwater flows to the Atlantic Ocean .
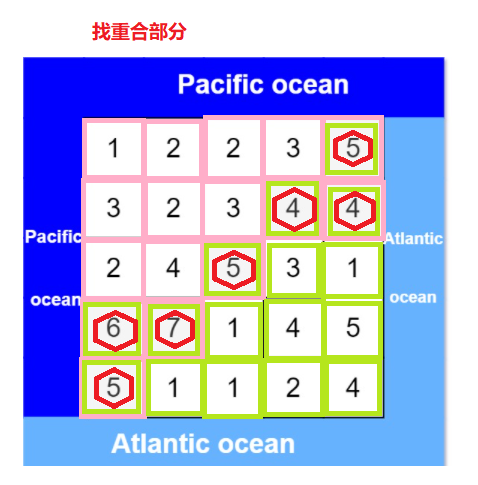
You can use depth first search to achieve reverse search , During the search process, you need to record whether each cell can reach from the Pacific in the opposite direction and from the Atlantic in the opposite direction . After the reverse search , Traverse each grid , If a grid can reach both the Pacific and the Atlantic in the opposite direction , Then the grid can reach both the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean , Add the grid to the answer .
Code implementation
Leetcode Official explanation :
static const int dirs[4][2] = {
{
-1, 0}, {
1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> heights;
void dfs(int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>> & ocean) {
int m = ocean.size();
int n = ocean[0].size();
if (ocean[row][col]) {
return;
}
ocean[row][col] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newCol = col + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < m && newCol >= 0 && newCol < n && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col]) {
dfs(newRow, newCol, ocean);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
this->heights = heights;
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, 0, pacific);
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dfs(0, j, pacific);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(i, n - 1, atlantic);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
dfs(m - 1, j, atlantic);
}
vector<vector<int>> result;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
vector<int> cell;
cell.emplace_back(i);
cell.emplace_back(j);
result.emplace_back(cell);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
My own :( recursive )
class Solution {
vector<int> direction{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; // Used to traverse four directions
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& ocean, int a, int b){
ocean[a][b] = true;
int p1, p2;
for(int n = 0; n < 4; n++){
p1 = a + direction[n];
p2 = b + direction[n+1];
if(0 > p1 || p1 >= heights.size() || 0 > p2 || p2 >= heights[0].size())
continue;
if(heights[p1][p2] >= heights[a][b] && ocean[p1][p2] == false)
DFS(heights, ocean, p1, p2);
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
// From the outside to the inside
int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<bool>> Pacific_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
vector<vector<bool>> Atlantic_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// Up and down
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
DFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, 0, i);
DFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, n -1, i);
}
// about
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
DFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, i, 0);
DFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, i, m - 1);
}
for(int a = 0; a < n; a++){
for(int b = 0; b < m; b++){
if(Pacific_Ocean[a][b] && Atlantic_Ocean[a][b])
ans.push_back(vector<int>{
a, b});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns . Depth first search can traverse each cell up to twice , Finding cells that can be reached in both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans requires traversing the entire matrix , So the time complexity is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
- Spatial complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns . The number of recursive call layers of depth first search is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), Record whether each cell can reach the Pacific and Atlantic O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) Space , So the complexity of space is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
Method 2 :BFS
Ideas
Reverse search can also be achieved using breadth first search . During the search process, it is also necessary to record whether each cell can reach in the opposite direction from the Pacific Ocean and from the Atlantic Ocean . After the reverse search , Traverse each grid , If a grid can reach both the Pacific and the Atlantic in the opposite direction , Then the grid can reach both the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean , Add the grid to the answer .
Code implementation
Leetcode Official explanation :
static const int dirs[4][2] = {
{
-1, 0}, {
1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> heights;
void bfs(int row, int col, vector<vector<bool>> & ocean) {
if (ocean[row][col]) {
return;
}
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
ocean[row][col] = true;
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
qu.emplace(row, col);
while (!qu.empty()) {
auto [row, col] = qu.front();
qu.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newCol = col + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < m && newCol >= 0 && newCol < n && heights[newRow][newCol] >= heights[row][col] && !ocean[newRow][newCol]) {
ocean[newRow][newCol] = true;
qu.emplace(newRow, newCol);
}
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
this->heights = heights;
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
bfs(i, 0, pacific);
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
bfs(0, j, pacific);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
bfs(i, n - 1, atlantic);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
bfs(m - 1, j, atlantic);
}
vector<vector<int>> result;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
vector<int> cell;
cell.emplace_back(i);
cell.emplace_back(j);
result.emplace_back(cell);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
My own :
class Solution {
vector<int> direction{
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; // Used to traverse four directions
void BFS(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& ocean, int a, int b){
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
ocean[a][b] = true;
qu.push(make_pair(a, b));
int n, m, nextn, nextm;
while(!qu.empty()){
n = qu.front().first;
m = qu.front().second;
qu.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
nextn = n + direction[i];
nextm = m + direction[i+1];
if(0 > nextn || nextn >= heights.size() || 0 > nextm || nextm >= heights[0].size())
continue;
if(heights[nextn][nextm] >= heights[n][m] && ocean[nextn][nextm] == false){
ocean[nextn][nextm] = true;
qu.push(make_pair(nextn, nextm));
}
}
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
// From the outside to the inside
int n = heights.size(), m = heights[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<bool>> Pacific_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
vector<vector<bool>> Atlantic_Ocean(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
// Up and down
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
BFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, 0, i);
BFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, n - 1, i);
}
// about
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
BFS(heights, Pacific_Ocean, i, 0);
BFS(heights, Atlantic_Ocean, i, m - 1);
}
for(int a = 0; a < n; a++){
for(int b = 0; b < m; b++){
if(Pacific_Ocean[a][b] && Atlantic_Ocean[a][b])
ans.push_back(vector<int>{
a, b});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns . Breadth first search can traverse each cell up to twice , Finding cells that can be reached in both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans requires traversing the entire matrix , So the time complexity is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
- Spatial complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns . The queue space for breadth first search is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), Record whether each cell can reach the Pacific and Atlantic O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) Space , So the complexity of space is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
Method 3 : Union checking set
Ideas
The part of maintaining connectivity can use 「 Union checking set 」 To do it : Start with the edge grid adjacent to the Pacific Ocean and Pacific_Ocean connected , Connect the edge grid adjacent to the Atlantic Ocean with Atlantic_Ocean connected , Then run method 1 or method 2 DFS/BFS, Finally, it will be both Pacific_Ocean Connected and connected Atlantic_Ocean The connected lattice adds the answer .
Code implementation
My own :
nothing , Forget to write
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns .DFS and BFS Traverse each cell at most twice , Finding cells that can be reached in both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans requires traversing the entire matrix , So the time complexity is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
- Spatial complexity : O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), among m m m and n n n These are matrices heights \textit{heights} heights The number of rows and columns .BFS The queue space of is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn), and DFS The recursive stack space or auxiliary stack space of is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn). Record whether each cell can reach the Pacific and Atlantic O ( 2 × m n ) O(2 \times mn) O(2×mn) Space , So the complexity of space is O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn).
边栏推荐
- 接口间调用为什么要用json、fastjson怎么赋值的、fastjson [email protected]映射关系问题
- U++ 元数据说明符 学习笔记
- Leetcode minimum difference in student scores
- Leetcode longest public prefix
- Ansible reports an error: "MSG": "invalid/incorrect password: permission denied, please try again“
- How to choose an offer and what factors should be considered
- 【问道】编译原理
- PLC Analog output analog output FB analog2nda (Mitsubishi FX3U)
- y58.第三章 Kubernetes从入门到精通 -- 持续集成与部署(三一)
- Error: No named parameter with the name ‘foregroundColor‘
猜你喜欢
U++4 interface learning notes
Error: No named parameter with the name ‘foregroundColor‘
![[opencv] image morphological operation opencv marks the positions of different connected domains](/img/c3/f437bad9432dedbbb14c8a62ba5180.png)
[opencv] image morphological operation opencv marks the positions of different connected domains
Operand of null-aware operation ‘!‘ has type ‘SchedulerBinding‘ which excludes null.

How to choose an offer and what factors should be considered
Complete code of C language neural network and its meaning

Mysql database (basic)
QT simple layout box model with spring

The sooner you understand the four rules of life, the more blessed you will be
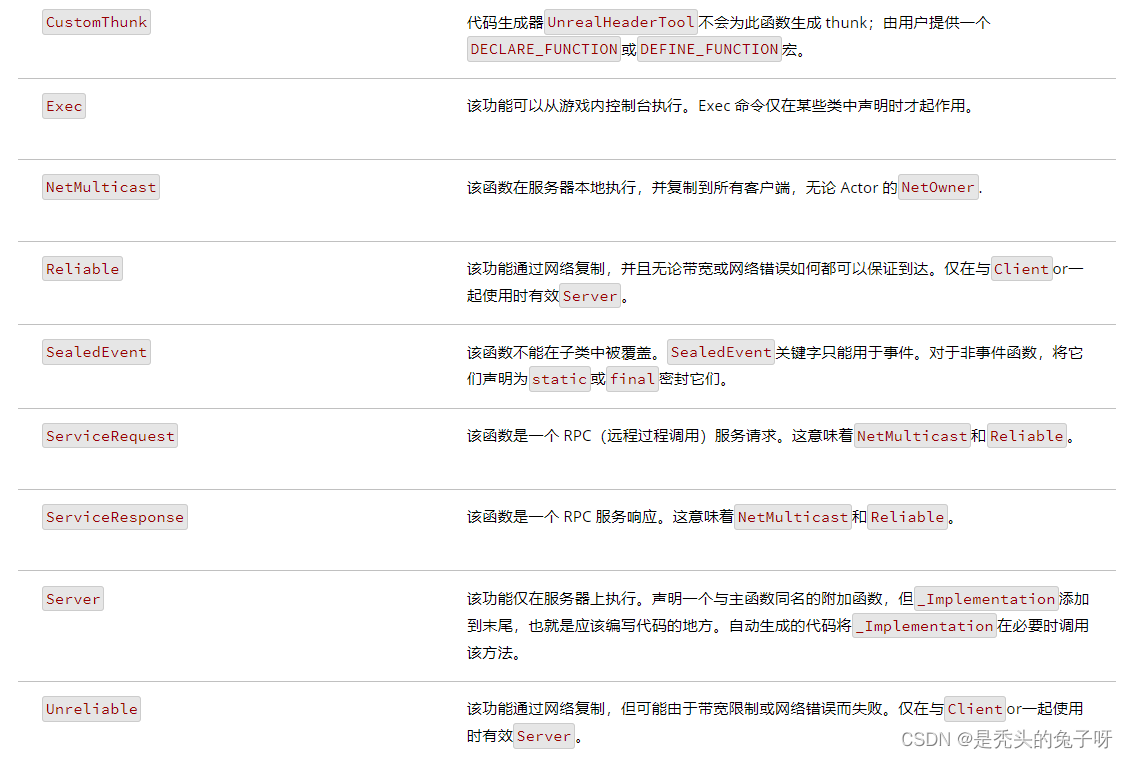
U++ game learning notes
随机推荐
Operand of null-aware operation ‘!‘ has type ‘SchedulerBinding‘ which excludes null.
一个酷酷的“幽灵”控制台工具
IMS data channel concept of 5g vonr+
Simulate thread communication
Is PMP really useful?
最全常用高数公式
If you‘re running pod install manually, make sure flutter pub get is executed first.
Liste des hôtes d'inventaire dans ansible (je vous souhaite des fleurs et de la romance sans fin)
Weebly mobile website editor mobile browsing New Era
U++ 元数据说明符 学习笔记
SQL injection cookie injection
DFS,BFS以及图的遍历搜索
拿到PMP认证带来什么改变?
The sooner you understand the four rules of life, the more blessed you will be
Dbsync adds support for mongodb and ES
Full link voltage test: the dispute between shadow database and shadow table
最长公共子序列(LCS)(动态规划,递归)
Analysis -- MySQL statement execution process & MySQL architecture
在米家、欧瑞博、苹果HomeKit趋势下,智汀如何从中脱颖而出?
Leetcode(46)——全排列