当前位置:网站首页>[gym 102832h] [template] combination lock (bipartite game)
[gym 102832h] [template] combination lock (bipartite game)
2022-07-05 23:49:00 【SSL_ TJH】
Combination Lock
Topic link :GYM 102832H
The main idea of the topic
Give you a password lock ( Up to five ), Tell you how it started , Then two people take turns to choose a position and screw it up or down one space .
Then make sure that the number obtained each time has not appeared before and is not the given number .
It's up to you to decide whether to win first .
Ideas
I've been writing for a day .
This is a bipartite graph game, which can be said to be a template , After all, every operation of this password lock must have odd and even changes, which should be able to be seen ( Except me ).
Then there is the bipartite graph game :
A bipartite graph , Then, starting from a point, everyone takes turns to move it by the side , Move to a new location every time , Unable to move failure .
Then there is the conclusion : If all the maximum matching schemes of this graph contain starting points , The first hand will win , Otherwise, the backhand will win .
Then there is the proof :
adequacy : If the starting point is included S S S, If you follow the matching edge with each step first , The backhand can only follow . Because if you don't follow , That forms a set S → p 1 → p 2 → p n S\rightarrow p_1\rightarrow p_2\rightarrow p_n S→p1→p2→pn, The matching side is S − p 1 , p 2 − p 3 , . . . , p n − 2 − p n − 1 S-p_1,p_2-p_3,...,p_{n-2}-p_{n-1} S−p1,p2−p3,...,pn−2−pn−1.
Then we can move right collectively : p 1 − p 2 , p 3 − p 4 , . . . , p n − 1 − p n p_1-p_2,p_3-p_4,...,p_{n-1}-p_{n} p1−p2,p3−p4,...,pn−1−pn, In this way, the same length is also the largest match , But it doesn't include S S S.
The need for : If the starting point is not included S S S, That doesn't include S S S The maximum match of . The first step must be to walk on the matching point ( Otherwise, this edge can be put into the maximum match ), Then walk along the matching side with your hand , You can't get out first .
Because if the last one is a non matching point S → p 1 → p 2 → p n S\rightarrow p_1\rightarrow p_2\rightarrow p_n S→p1→p2→pn, The match is p 1 − p 2 , . . . p n − 2 − p n − 1 p_1-p_2,...p_{n-2}-p_{n-1} p1−p2,...pn−2−pn−1, You can expand it on the left and right to get S − p 1 , p 2 − p 3 , . . . , p n − 1 − p n S-p_1,p_2-p_3,...,p_{n-1}-p_n S−p1,p2−p3,...,pn−1−pn, That's not the biggest match .
Then consider how to judge whether a point must be in the maximum match .
In fact, there is a most intuitive way ( That's what I use here ), Just remove this point and run it again , Add this point and run again , See whether the maximum matches of the two times are the same .( Here you can not duplicate the previous edge traffic , Then you only need to judge whether there is traffic for the second time )
Then there is another way that you can run a maximum match first , Then see if there is a substitute edge ( That is, a point of a matching edge and a non matching point have connected edges , Then another point can be replaced ).
Then the new one can replace others , Then try every one that is not matched , You can get which points can be replaced and which cannot be inside .
Code
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3)
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fgcse")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fgcse-lm")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fipa-sra")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-pre")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-vrp")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fpeephole2")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ffast-math")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fsched-spec")
#pragma GCC optimize("unroll-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-labels")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fdevirtualize")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcaller-saves")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcrossjumping")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fthread-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-funroll-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fwhole-program")
#pragma GCC optimize("-freorder-blocks")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fschedule-insns")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-tail-merge")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fschedule-insns2")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fstrict-aliasing")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fstrict-overflow")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcse-skip-blocks")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcse-follow-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fsched-interblock")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fpartial-inlining")
#pragma GCC optimize("no-stack-protector")
#pragma GCC optimize("-freorder-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-findirect-inlining")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fhoist-adjacent-loads")
#pragma GCC optimize("-frerun-cse-after-loop")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-small-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-finline-small-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-switch-conversion")
#pragma GCC optimize("-foptimize-sibling-calls")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fexpensive-optimizations")
#pragma GCC optimize("-funsafe-loop-optimizations")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-functions-called-once")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fdelete-null-pointer-checks")
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int m, n, ST, M, a[] = {
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000}, le[N], KK;
int tot, S, T, deg[N], lee[N];
bool sp[N], odd[N];
queue <int> q;
struct node {
int x, to, nxt, op;
}e[N * 20];
int read() {
int re = 0; char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
re = (re << 3) + (re << 1) + c - '0';
c = getchar();
}
return re;
}
void Init() {
KK = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) le[i] = -1;
memset(sp, 0, sizeof(sp));
}
void link(int x, int y, int z) {
e[++KK] = (node){
z, y, le[x], KK + 1}; le[x] = KK; e[++KK] = (node){
0, x, le[y], KK - 1}; le[y] = KK;
}
void calc(int i) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int bit = i / a[j] % 10, x;
if(bit != 9) x = i + a[j];
else x = i - 9 * a[j];
if (!sp[x]) link(i, x, 1);
if (bit) x = i - a[j];
else x = i + 9 * a[j];
if (!sp[x]) link(i, x, 1);
}
}
bool bfs() {
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++) lee[i] = le[i], deg[i] = 0;
q.push(S); deg[S] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int i = le[now]; ~i; i = e[i].nxt)
if (!deg[e[i].to] && e[i].x) {
deg[e[i].to] = deg[now] + 1;
q.push(e[i].to);
}
}
return deg[T];
}
int dfs(int now, int sum) {
if (now == T) return sum;
int go = 0;
for (int &i = lee[now]; ~i; i = e[i].nxt)
if (deg[e[i].to] == deg[now] + 1 && e[i].x) {
int this_go = dfs(e[i].to, min(e[i].x, sum - go));
if (this_go) {
e[i].x -= this_go; e[e[i].op].x += this_go;
go += this_go; if (go == sum) return go;
}
}
if (go == 0) deg[now] = 0;
return go;
}
int dinic() {
int re = 0; while (bfs()) re += dfs(S, INF); return re;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int id = 0, x = i; while (x) {
id += x % 10; x /= 10;} odd[i] = id & 1;
}
int TT = read();
while (TT--) {
Init();
m = read(); n = read(); ST = read();
M = a[m]; tot = M; S = ++tot; T = ++tot;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x = read(); sp[x] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
if(sp[i]) continue;
if(odd[i] == odd[ST]) {
calc(i);
if (i != ST) link(S, i, 1);
}
else {
link(i, T, 1);
}
}
dinic();
link(S, ST, 1);
if (dinic()) printf("Alice\n");
else printf("Bob\n");
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Opencvsharp (C openCV) shape detection and recognition (with source code)
- C# 文件与文件夹操作
- Dynamic planning: robbing families and houses
- 保研笔记四 软件工程与计算卷二(8-12章)
- What if the C disk is not enough? Let's see how I can clean up 25g of temp disk space after I haven't redone the system for 4 years?
- Open source CRM customer relationship system management system source code, free sharing
- 20220703 week race: number of people who know the secret - dynamic rules (problem solution)
- CloudCompare&PCL 点云随机添加噪声
- Online yaml to CSV tool
- C reflection and type
猜你喜欢

Rasa 3. X learning series -rasa x Community Edition (Free Edition) changes
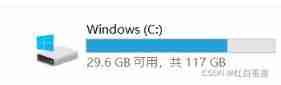
What if the C disk is not enough? Let's see how I can clean up 25g of temp disk space after I haven't redone the system for 4 years?
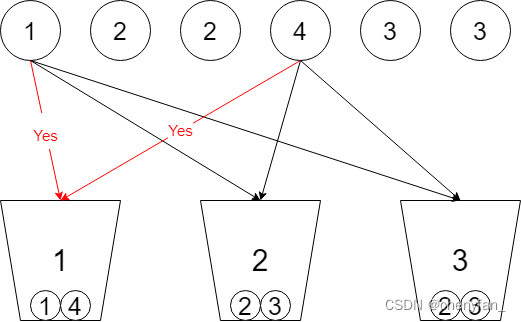
698. 划分为k个相等的子集 ●●

PADS ROUTER 使用技巧小记
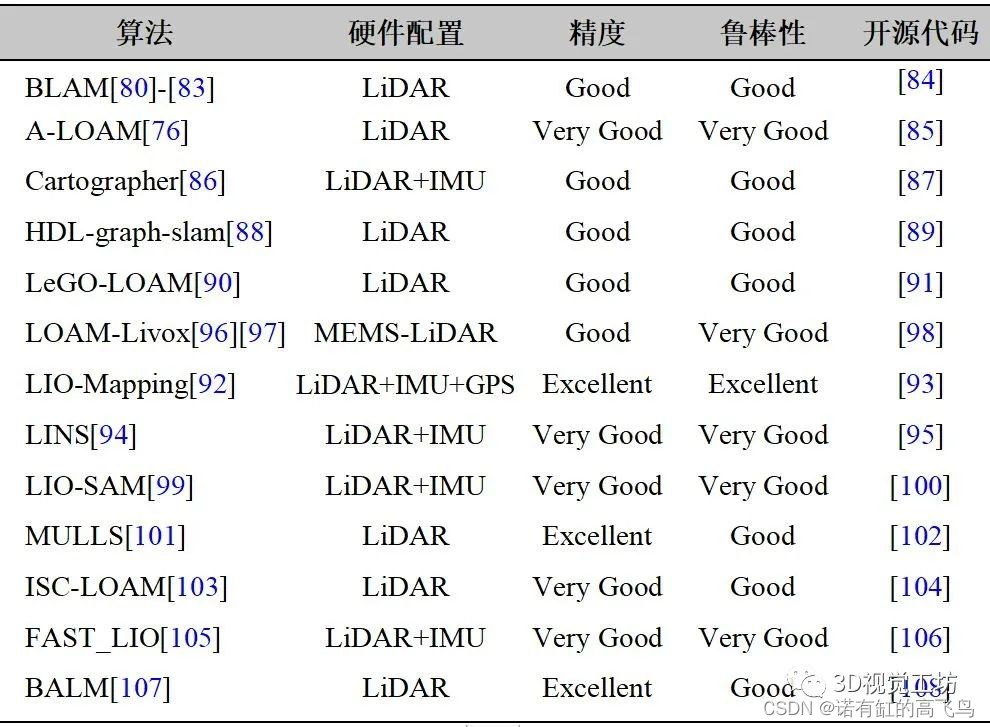
激光slam学习记录
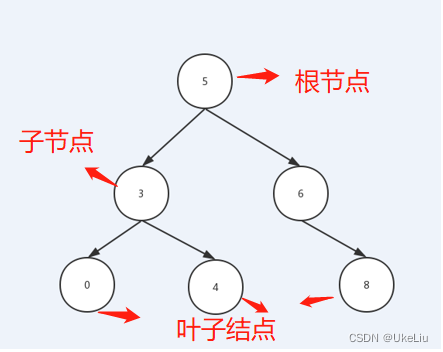
【二叉搜索树】增删改查功能代码实现

5. Logistic regression

How to rotate the synchronized / refreshed icon (EL icon refresh)
如何获取localStorage中存储的所有值
Brushless drive design -- on MOS drive circuit
随机推荐
Breadth first search open turntable lock
shardingsphere源码解析
【SQL】各主流数据库sql拓展语言(T-SQL 、 PL/SQL、PL/PGSQL)
妙才周刊 - 8
Redis high availability - master-slave replication, sentinel mode, cluster
Part III Verilog enterprise real topic of "Niuke brush Verilog"
698. 划分为k个相等的子集 ●●
Initialiser votre vecteur & initialisateur avec une liste Introduction à la Liste
【luogu P3295】萌萌哒(并查集)(倍增)
14 MySQL-视图
Zhongjun group launched electronic contracts to accelerate the digital development of real estate enterprises
Xinyuan & Lichuang EDA training camp - brushless motor drive
GFS分布式文件系統
成为程序员的你,后悔了吗?
Why use weak pointers for delegation- Why use weak pointer for delegation?
5. Logistic regression
UVA11294-Wedding(2-SAT)
Open3D 点云随机添加噪声
Rasa 3. X learning series -rasa x Community Edition (Free Edition) changes
CloudCompare&PCL 点云随机添加噪声