当前位置:网站首页>C miscellaneous two-way circular linked list
C miscellaneous two-way circular linked list
2022-07-06 09:59:00 【Bright-SKY】
Catalog
Knowledge point 1【 Bidirectional circular linked list 】
Knowledge point 2【 Tail insertion of bidirectional linked list 】
Knowledge point 3【 Traversal of double linked list 】
Knowledge point 3【 Two way linked list queries a node 】
Knowledge point 4【 Delete the specified node from the bidirectional linked list 】
Knowledge point 4【 Two way linked list release linked list node 】
Knowledge point 5【Linux Kernel list 】
Knowledge point 1【 Bidirectional circular linked list 】
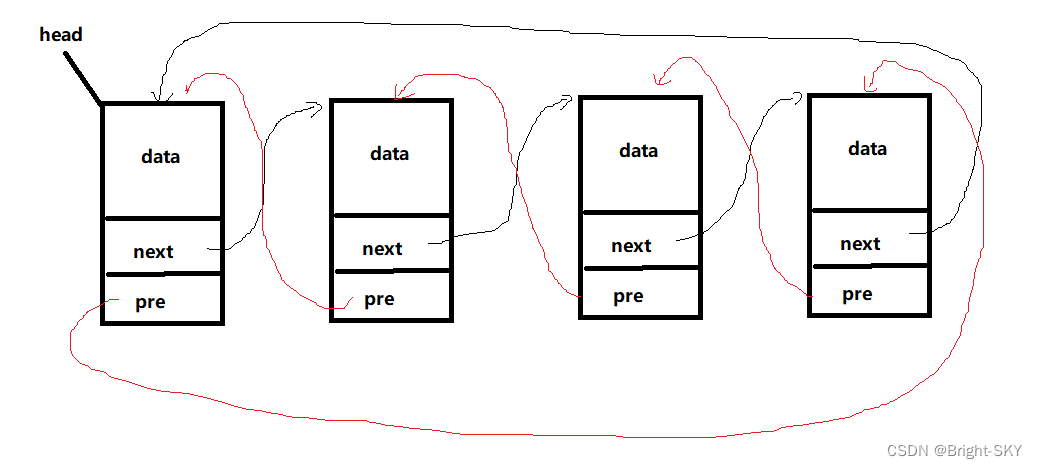
Knowledge point 2【 Two way linked list Tail insertion 】
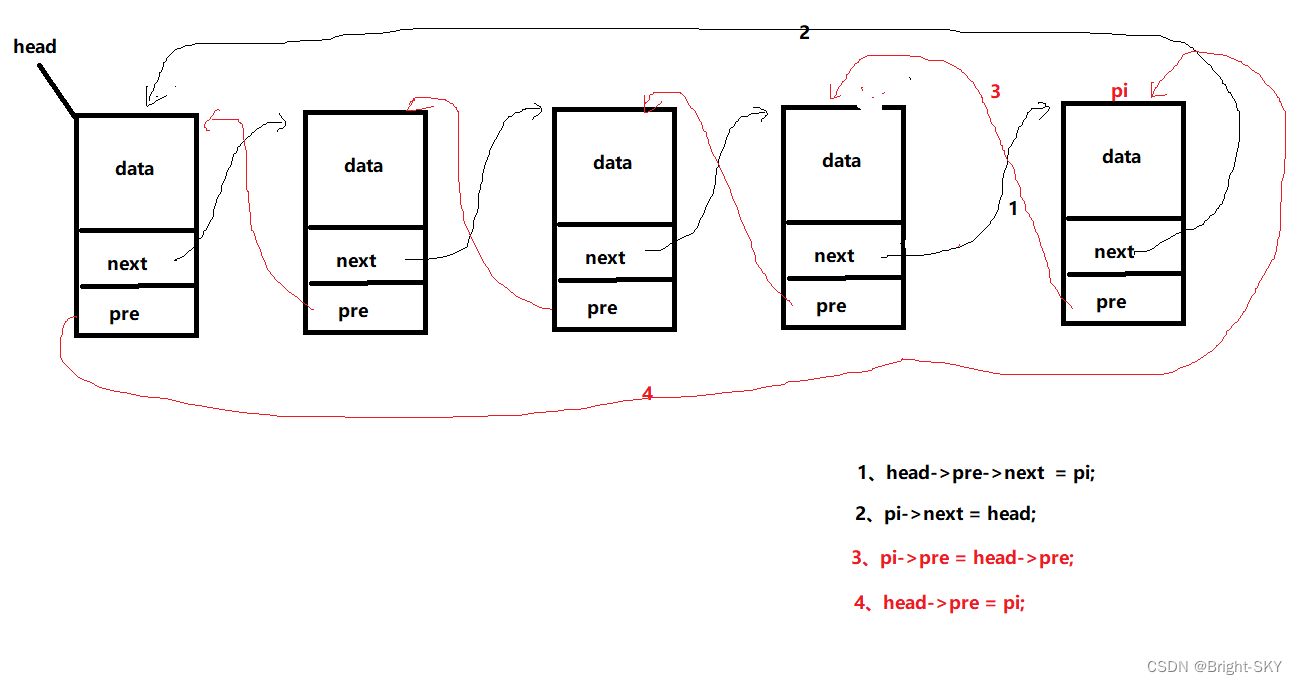
STU* insert_link(STU *head, STU tmp)
{
// Apply for space for the inserted node
STU *pi = (STU *)calloc(1,sizeof(STU));
if(pi == NULL)
{
perror("calloc");
return head;
}
*pi = tmp;
// Tail insertion
if(NULL == head)
{
pi->next = pi;
pi->pre = pi;
head = pi;
return head;
}
else
{
head->pre->next = pi;
pi->next = head;
pi->pre = head->pre;
head->pre = pi;
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 3【 Two way linked list Traverse 】
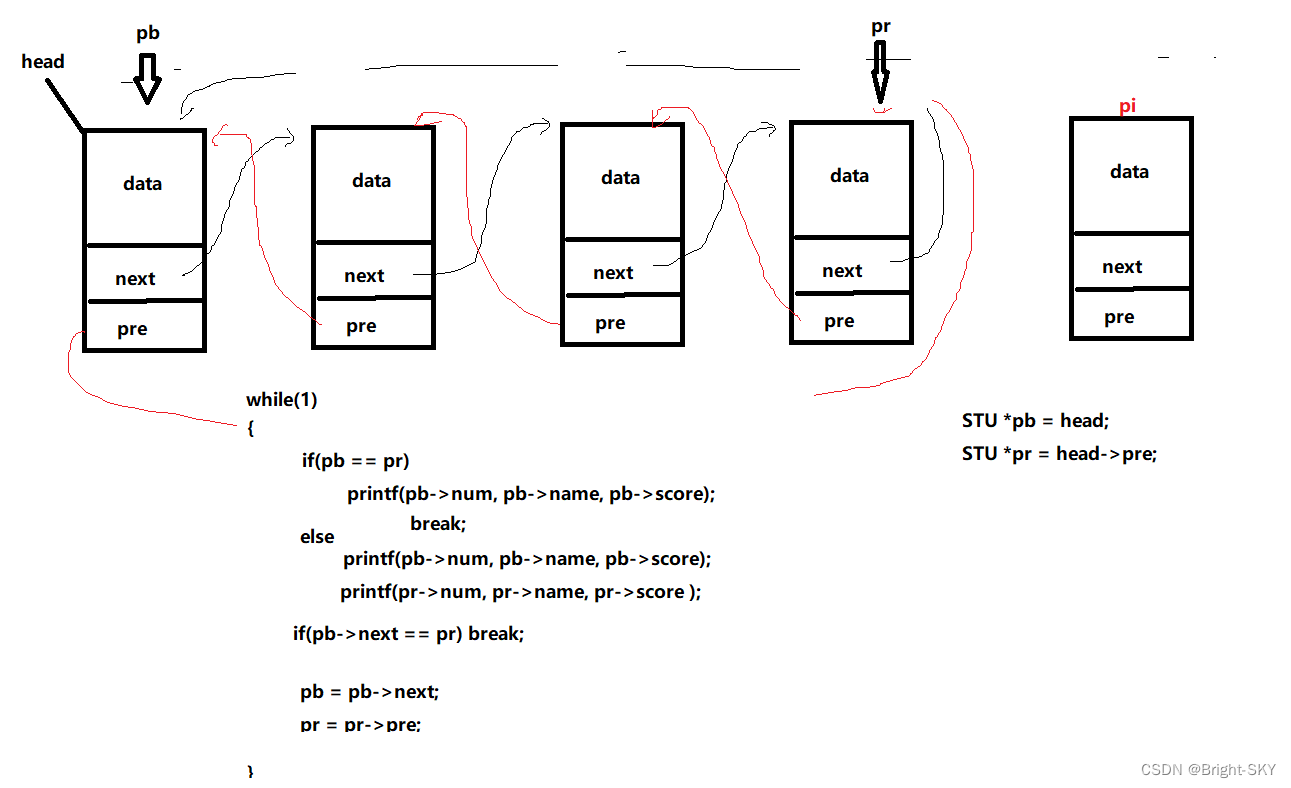
void printf_link(STU *head)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(NULL == head)
{
printf(" The list does not exist \n");
return;
}
else
{
STU *pb = head;
STU *pr = head->pre;
while(1)
{
if(pb == pr)
{
printf("%d %s %f\n", pb->num, pb->name, pb->score);
break;
}
else
{
printf("%d %s %f\n", pb->num, pb->name, pb->score);
printf("%d %s %f\n", pr->num, pr->name, pr->score);
}
if(pb->next == pr)
break;
pb=pb->next;
pr = pr->pre;
}
}
return;
}Knowledge point 3【 Double linked list Inquire about A node 】
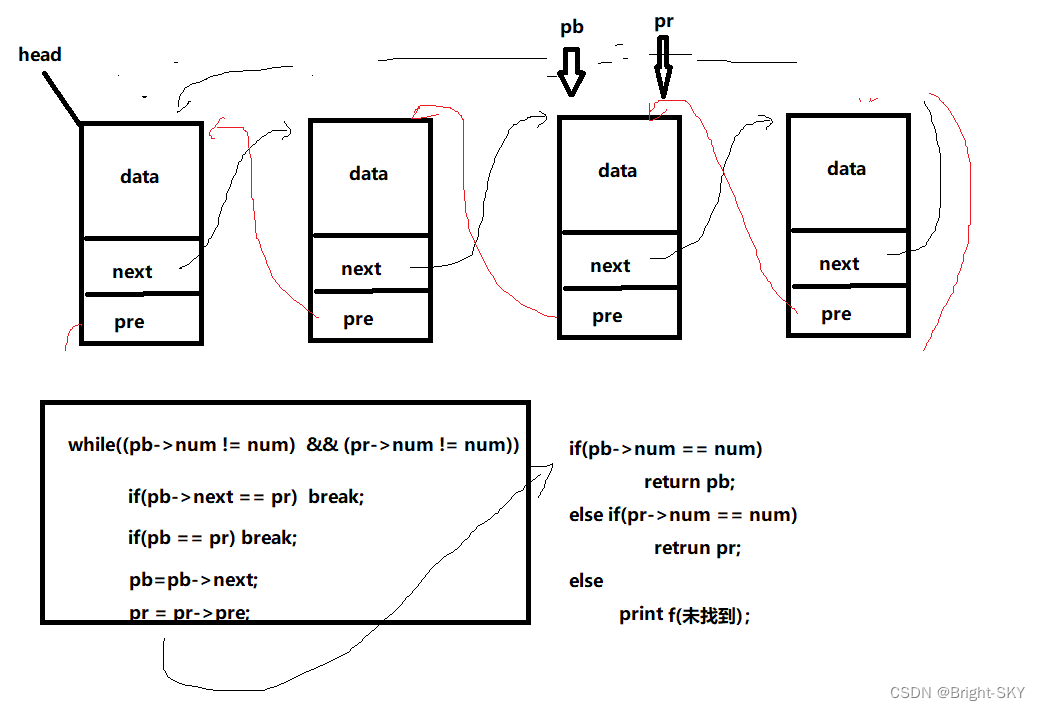
STU *search_link(STU *head, int num)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(NULL == head)
{
printf(" The list does not exist \n");
return head;
}
else
{
STU *pb = head;
STU *pr = head->pre;
while((pb->num != num) && (pr->num != num))
{
if(pb->next == pr) break;
if(pb == pr) break;
pb = pb->next;
pr = pr->pre;
}
if(pb->num == num)
return pb;
else if(pr->num == num)
return pr;
else
{
printf(" No related nodes found \n");
return NULL;
}
}
return NULL;
}Knowledge point 4【 Double linked list Delete Specify nodes 】
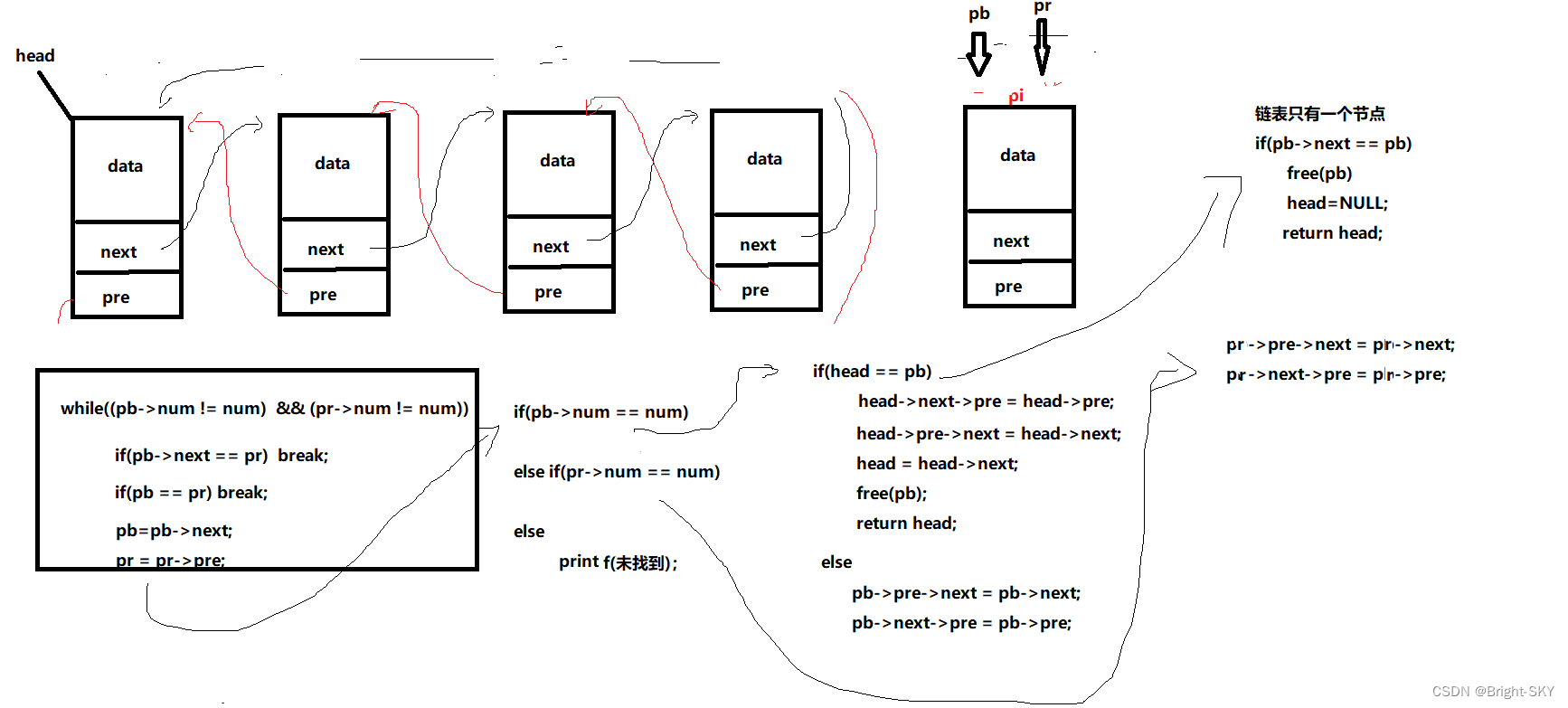
STU* delete_link(STU *head, int num)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(NULL == head)
{
printf(" The list does not exist \n");
return head;
}
else
{
STU *pb = head;
STU *pr = head->pre;
while((pb->num != num) && (pr->num != num))
{
if(pb->next == pr) break;
if(pb == pr) break;
pb = pb->next;
pr = pr->pre;
}
if(pb->num == num)
{
if(head == pb)// Delete header node
{
if(pb->next == pb)// A linked list has only one node
{
head = NULL;
}
else// The linked list has more than one node
{
head->pre->next = head->next;
head->next->pre = head->pre;
head = head->next;
}
free(pb);
return head;
}
else// Delete 、 Middle tail node
{
pb->pre->next = pb->next;
pb->next->pre = pb->pre;
}
}
else if(pr->num == num)
{
pr->pre->next = pr->next;
pr->next->pre = pr->pre;
}
else
{
printf(" No related nodes found \n");
return NULL;
}
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 4【 Double linked list Release List nodes 】
STU* free_link(STU *head)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(NULL == head)
{
printf(" The list does not exist \n");
return head;
}
else
{
STU *pb = head;
head->pre->next = NULL;
while(pb != NULL)
{
head = head->next;
free(pb);
pb = head;
}
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 5【Linux kernel Linked list 】
list.h
/**
* Simple version of two-way circular linked list ( Reference resources Linux Kernel linked list implementation )
* @auther: BrightSKY
* @function: No data end specified , You can mount various types of data , It realizes the insertion and deletion of any node position in the linked list , Replacement of any node , Provide forward and reverse traversal
* @extend: Welcome according to the existing API Expand the function , It can realize the operation of extended multi linked list , Linked list retrieval and arrangement algorithms
*/
#ifndef __LIST_H__
#define __LIST_H__
/**
* New node initializes macro definitions
* @name: Nodes that need to be initialized
*/
#define LIST_NODE_INIT(name) {&(name), &(name)}
/**
* Calculate the offset of the pointer field in the host structure
* @type: Host structure type
* @member: Pointer domain member name
*/
#define offsetof(type, member) ((char *) &((type *)0)->member)
/**
* Known host structure type 、 Pointer domain member name 、 The pointer field address reverses the host structure address
* @ptr: Pointer field address
* @type: Host structure type
* @member: Pointer domain member name
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
/**
* Forward traversal of linked list , Does not contain the head node
* @pos: Pointer to the linked list node , Be similar to c++ iterator
* @head: Chain header node
* @member: Pointer domain member name
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&(pos->member) != &((head)->member); \
pos = list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* Reverse traversal of linked list , Does not contain the head node
* @pos: Pointer to the linked list node , Be similar to c++ iterator
* @head: Chain header node
* @member: Pointer domain member name
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \
&(pos->member) != &((head)->member); \
pos = list_entry((pos)->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* Linked list pointer field data structure
*/
typedef struct list_node{
struct list_node *next, *prev;
}list_node;
/**
* API Method
*/
void list_push_node_back(list_node *new, list_node *node);
void list_push_node_front(list_node *new, list_node *node);
void list_del_node(list_node *node);
void list_replace(list_node *new, list_node *old);
#endiflist.c
/**
* Simple version of two-way circular linked list ( Reference resources Linux Kernel linked list implementation )
* @auther: BrightSKY
* @function: No data end specified , You can mount various types of data , It realizes the insertion and deletion of any node position in the linked list , Replacement of any node , Provide forward and reverse traversal
* @extend: Welcome according to the existing API Expand the function , It can realize the operation of extended multi linked list , Linked list retrieval and arrangement algorithms
*/
#include "list.h"
/**
* The bottom implementation of inserting anywhere in the linked list
* @new: New linked list node address
* @prev: The address of the previous node where the new node is inserted
* @next: The address of the next node where the new node is inserted
*/
static inline void __list_push(list_node *new, list_node *prev, list_node *next){
next->prev = new;
prev->next = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
}
/**
* Insert node : The new node is inserted behind the specified node
* @new: New linked list node address
* @node: Specify the node address , The new node will be inserted after this node
*/
void list_push_node_back(list_node *new, list_node *node){
__list_push(new, node, node->next);
}
/**
* Insert node : The new node is inserted in front of the specified node
* @new: New linked list node address
* @node: Specify the node address , The new node will be inserted in front of this node
*/
void list_push_node_front(list_node *new, list_node *node){
__list_push(new, node->prev, node);
}
/**
* Delete node : Specify the node to remove the linked list
* @node: Specify the node address , Node to be deleted
*/
void list_del_node(list_node *node){
node->next->prev = node->prev;
node->prev->next = node->next;
}
/**
* Replacement node : Replace the old node with the new node
* @new: New node address
* @old: Old node address
*/
void list_replace(list_node *new, list_node *old){
list_del_node(old);
list_push_node_back(new, old->prev);
}main.c
/**
* Simple version of two-way circular linked list Using routines (Demo)
* @auther: BrightSKY
* @function: No data end specified , You can mount various types of data , It realizes the insertion and deletion of any node position in the linked list , Replacement of any node , Provide forward and reverse traversal
* @extend: Welcome according to the existing API Expand the function , It can realize the operation of extended multi linked list , Linked list retrieval and arrangement algorithms
*/
#include "list.h"
#include "stdio.h"
/**
* Custom linked list structure ( Including pointer field and data field , Pointer fields need to use list_node)
* @data: Custom data fields , It can be any number of data and types
* @list_node: Pointer to the domain , The operation core of bidirectional circular linked list
*/
typedef struct my_list{
int data;
list_node list;
}my_list;
/**
* Create a chain header , Pointer field initialization can use LIST_NODE_INIT Macro initialization
*/
my_list head = {0, LIST_NODE_INIT(head.list)};
/**
* The main function , This routine directly inserts and traverses the linked list in the simplest way , It is convenient for everyone to learn
*/
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
/* Create nodes */
my_list node1 = {1, LIST_NODE_INIT(node1.list)};
my_list node2 = {2, LIST_NODE_INIT(node2.list)};
my_list node3 = {3, LIST_NODE_INIT(node3.list)};
/* Insert the node by head insertion */
list_push_node_back(&node1.list, &head.list);
list_push_node_back(&node2.list, &head.list);
/* The tail insertion method inserts the node */
list_push_node_front(&node3.list, &head.list);
/* Create a linked list iterator */
my_list *n = NULL;
/* Call the forward convenience of the linked list , Use iterators to access and output */
list_for_each_entry(n, &head, list)
{
printf("n = %d\n", n->data);
}
printf("-------------------------\n");
/* Delete the node pointed to by the header node */
list_del_node(head.list.next);
/* Call the reverse convenience of the linked list , Use iterators to access and output */
list_for_each_entry_reverse(n, &head, list)
{
printf("n = %d\n", n->data);
}
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- 五月刷题02——字符串
- MapReduce instance (VIII): Map end join
- How can I take a shortcut to learn C language in college
- Installation de la pagode et déploiement du projet flask
- Single chip microcomputer realizes modular programming: Thinking + example + system tutorial (the degree of practicality is appalling)
- Pointer learning
- 手把手教您怎么编写第一个单片机程序
- A wave of open source notebooks is coming
- May brush question 02 - string
- Mexican SQL manual injection vulnerability test (mongodb database) problem solution
猜你喜欢
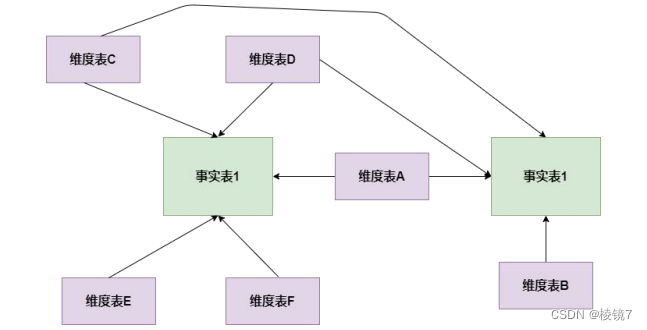
What are the models of data modeling
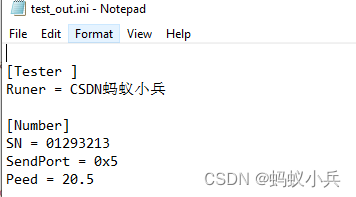
CAPL script pair High level operation of INI configuration file
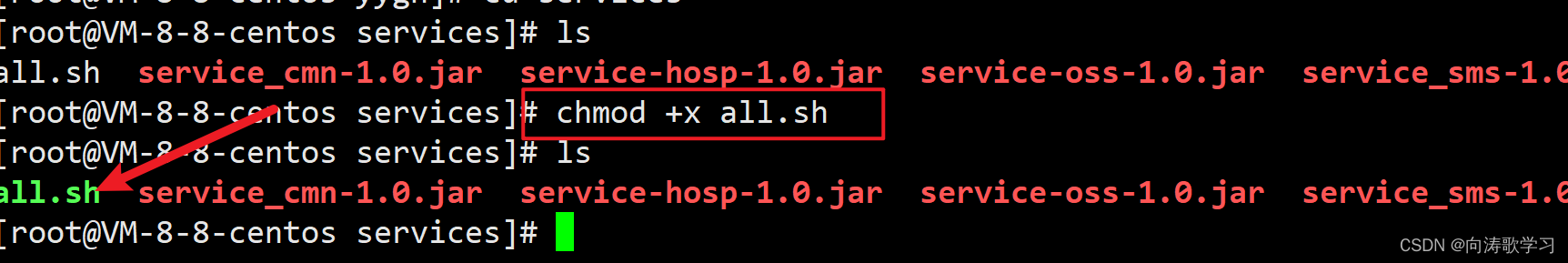
如何让shell脚本变成可执行文件
宝塔的安装和flask项目部署
13 医疗挂号系统_【 微信登录】
![《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]](/img/4f/5688c391dd19129d912a3557732047.jpg)
《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]
Contrôle de l'exécution du module d'essai par panneau dans Canoe (primaire)
CAPL script printing functions write, writeex, writelineex, writetolog, writetologex, writedbglevel do you really know which one to use under what circumstances?

Une grande vague d'attaques à la source ouverte
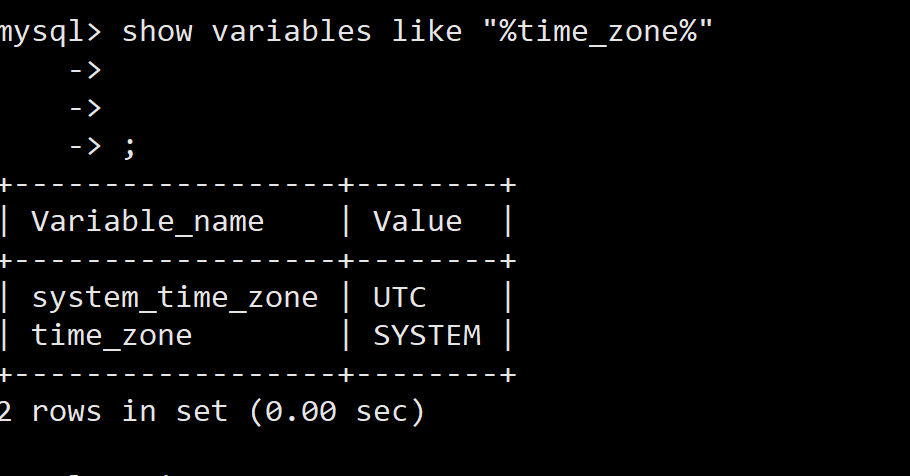
Docker MySQL solves time zone problems
随机推荐
Bugku web guide
AI的路线和资源
单片机实现模块化编程:思维+实例+系统教程(实用程度令人发指)
Competition vscode Configuration Guide
面试突击62:group by 有哪些注意事项?
五月刷题02——字符串
May brush question 01 - array
Cmooc Internet + education
Keep these four requirements in mind when learning single chip microcomputer with zero foundation and avoid detours
17 medical registration system_ [wechat Payment]
History of object recognition
Control the operation of the test module through the panel in canoe (primary)
学习单片机对社会的帮助是很大的
C杂讲 动态链表操作 再讲
May brush question 02 - string
Regular expressions are actually very simple
Defensive C language programming in embedded development
C杂讲 文件 续讲
Nc29 search in two-dimensional array
A wave of open source notebooks is coming