当前位置:网站首页>[HBZ sharing] how to locate slow queries in cloud database
[HBZ sharing] how to locate slow queries in cloud database
2022-07-06 04:21:00 【hbz-】
How to configure Mysql The slow query
1. Query slow log related information :SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%query%'
2. Open slow logging file :set global slow_query_log = 'ON'
3. The file name of the slow log :slow_query_log_file
4. Configure the slow query time :set global long_query_time = 1 // Modify slow query time 1s, That is, the query exceeds 1s It is recorded in the slow query log
5. Be careful : After modifying the slow query time , Remember to reconnect to take effect
How to locate slow queries
- adopt EXPLAIN Query whether the statement is indexed , If you don't leave the index, it means you have left the full table scan
- Be careful : The production environment generally does not allow this , The production environment usually passes through the automation platform , From the visual interface
EXPLAIN How to use ?
- Usage mode :EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM test WHERE age = 10
EXPLAIN Medium Type Field meaning
- type = all: Direct full table scanning data , Extremely inefficient
- type = index: Need to optimize , Although it is also the index , But express Full table scanning 【 Indexes 】 file , Not scanning data
- type = range:sql The minimum satisfaction condition is range, Query only rows in a given range , Use an index to select rows
- type = ref: Generally, this level is required , When the field is added with a general index , And the condition happens to be this field , That was ref type , For example, use name = ‘hbz’ This condition , and name Created a normal index , At this point ref
- type = eq_ref: Through primary key or Unique index Association table The query is eq_ref, Except for const The best result
- type = const: High performance level , Index according to the primary key id look for , It's usually const, No need to optimize
Mysql Why should the best left prefix rule be followed in joint indexing ?
- The union index will take precedence over the prefix
- If the order of association is name, age, position
- give an example :
// The order :name, age, postion --> Because the condition is in the order of joint index , So it triggers ref Index level
SQL: SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE name = 'hbz' and age = 21 and positon = 'tetst'
// Only name --> Because the condition is prefixed name, So it triggers ref Index level
SQL: SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE name = 'hbz'
// Only name, position --> Because the condition is prefixed name, So it triggers ref Index level
SQL: SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE name = 'hbz' and positon = 'tetst'
// Only position, No, name --> Because there is no prefix name, So the index will not be triggered
SQL: SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE positon = 'tetst'
// Yes name, But it is inconsistent with the joint index order --> There are conditions name Field , So the index will be triggered , Although not in order , however mysql The bottom layer will put name Put optimization ahead
SQL: SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE positon = 'tetst' and name = 'hbz'
- in summary , The so-called leftmost prefix rule , Namely , If where With name, Then the index must be taken ,name It doesn't matter where the order of , because mysql The bottom layer will be optimized , hold name Put it at the front . But if not name, Other field order pairs of the joint index cannot be indexed . This is called the best prefix rule , The beginning field of the union index must exist .
边栏推荐
- Lora gateway Ethernet transmission
- Global and Chinese markets for otolaryngology devices 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- P3033 [usaco11nov]cow steelchase g (similar to minimum path coverage)
- 满足多元需求:捷码打造3大一站式开发套餐,助力高效开发
- The value of two date types is subtracted and converted to seconds
- Comprehensive ability evaluation system
- Cross domain and jsonp details
- Data processing methods - smote series and adasyn
- 颠覆你的认知?get和post请求的本质
- VNCTF2022 WriteUp
猜你喜欢

颠覆你的认知?get和post请求的本质

Web components series (VII) -- life cycle of custom components
Sorting out the latest Android interview points in 2022 to help you easily win the offer - attached is the summary of Android intermediate and advanced interview questions in 2022
![Mlapi series - 04 - network variables and network serialization [network synchronization]](/img/fc/aebbad5295481788de5c1fdb432a77.jpg)
Mlapi series - 04 - network variables and network serialization [network synchronization]
When debugging after pycharm remote server is connected, trying to add breakpoint to file that does not exist: /data appears_ sda/d:/segmentation
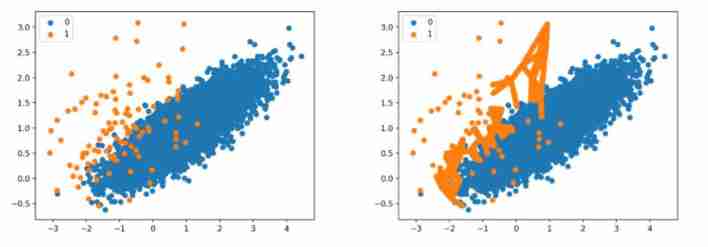
Data processing methods - smote series and adasyn
Tips for using dm8huge table
捷码赋能案例:专业培训、技术支撑,多措并举推动毕业生搭建智慧校园毕设系统
CADD course learning (8) -- virtual screening of Compound Library
电脑钉钉怎么调整声音
随机推荐
Python book learning notes - Chapter 09 section 01 create and use classes
[leetcode question brushing day 33] 1189 The maximum number of "balloons", 201. The number range is bitwise AND
C. The Third Problem(找规律)
DM8 archive log file manual switching
MySQL transaction isolation level
P3500 [POI2010]TES-Intelligence Test(二分&离线)
Mixed development of QML and QWidget (preliminary exploration)
P2648 make money
2/13 qaq~~ greed + binary prefix sum + number theory (find the greatest common factor of multiple numbers)
Execution order of scripts bound to game objects
coreldraw2022新版本新功能介绍cdr2022
Overturn your cognition? The nature of get and post requests
Python book learning notes - Chapter 09 section 01 create and use classes
Query the number and size of records in each table in MySQL database
CertBot 更新证书失败解决
Fedora/rehl installation semanage
lora网关以太网传输
Figure application details
Stable Huawei micro certification, stable Huawei cloud database service practice
The value of two date types is subtracted and converted to seconds